There’s No Such Thing As Overreacting
Because of all the reasons you just learned about, it’s obvious why it’s critical to get to the hospital as fast as possible. As Dr. Ruthmann says, Time is tissue. Seek help at the first sign of chest pain or other symptoms and you may limit the damage to your heart . STEMI heart attackswhen an artery is completely blocked, and no blood or oxygen can reach your heartare particularly dangerous. Its the type of heart attack that can be rapidly fatal if not quickly treated. Nearly two out of five heart attacks fall into this category. You won’t know what type you’re having, which is why it’s important to get help ASAP.
What Is A Cardiac Rehabilitation Program
Before you leave the hospital, your doctor may talk to you about a cardiac rehabilitation program. These programs provide information that will help you understand your risk factors. It will help you live a healthy lifestyle that can prevent future heart problems. You will learn about exercise and diet, and how to reach and maintain a healthy weight. You will also learn ways to control your stress level, your blood pressure, and your cholesterol levels.
Your cardiac rehabilitation program will probably start while you are still in the hospital. After you leave the hospital, your rehabilitation will continue in a rehab center. The rehab center may be at the hospital or in another location.
Most cardiac rehabilitation programs last 3 to 6 months. Your doctor will talk to you about how often you need to attend the program. Once you enroll in a cardiac rehabilitation program, regular attendance is important. The more lifestyle changes you make, the better your chances of preventing future heart problems.
The sooner you get medical help, the greater your chances of surviving a heart attack. Do not delay getting immediate medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of heart attack.
Life After A Heart Attack
A heart attack is often a devastating event that severely disrupts your life. Still, many people find ways to live a full, enjoyable life after having one.
Some people experience their heart attack as a wake-up call that they need to make certain lifestyle changes.
Eating habits may need to be changed after a heart attack, along with lifestyle factors like stress and physical activity.
Recovering from a heart attack can be physically and emotionally taxing, with some people experiencing depression stemming from their limitations.
Its important to reach out for any help you need to deal with recovery-related challenges.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Affect Blood Pressure
What To Do If You Recognize A Heart Attack
If you think theres any chance you or someone else may be having a heart attack, you need to get medical help as quickly as possible. Even if it turns out to be something else, it is better to act quickly than risk putting your life on the line.
If you recognize the signs of a heart attack, call 9-1-1 immediately. The sooner that treatment begins, the greater likelihood that you can minimize damage to the heart.
The person having the symptoms should not drive. Always have someone else drive you to the hospital if you are not being transported by ambulance.
If the person goes unconscious, you can start cardiopulmonary resuscitation while you wait for emergency medical services . If you are in a public place, ask if there is an AED on site. An AED is a portable device that can check someone’s heart rhythm and, if necessary, deliver an electric shock to help someone who is in cardiac arrest.
Find trainings in CPR and AED use through the American Red Cross, so you are prepared if you are ever in an emergency situation.
Q How Can I Test My Heart At Home
- Check pulse and heart rate: Feel your pulse to check your heart rate and rhythm. A pulse matches up with a heartbeat that pumps blood through your arteries and heart rate is the number of times your heart beats in one minute. The stronger the pulse, the better is the strength of your blood flow and blood pressure.
- Check Blood Pressure: When at rest, the normal blood pressure is less than 120 over less than 80. The reading of 130/80 or higher is high blood pressure. If you have a consistent high BP then there’s a probability of your heart being blocked.
- Blood Test: Check the sodium, potassium, albumin, and creatinine levels in your blood. Abnormal levels could suggest possible signs of heart failure, or kidney or liver problems.
Also Check: List The Steps Of How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Having A Heart Attack
Although there are several risk factors that you cant control, there are many ways you can help yourself and reduce your risk of a heart attack. These include:
- Schedule a checkup: Find a primary care provider and see them at least once a year for a checkup or wellness visit. An annual checkup can catch many of the early warning signs of heart disease, including signs that you can’t feel. These include your blood pressure, blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels and more.
- Quit tobacco products: This includes smokeless tobacco and all vaping products.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for 20 to 30 minutes of moderately intense physical activity a week.
- Eat a healthy diet: Examples include the Mediterranean or Dash diets. A plant-based diet approach is an excellent alternative.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Your primary care provider can advise you on a healthy goal weight and provide you resources and guidance to help you reach that goal.
- Manage your existing health conditions: This includes high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Reduce your stress: Consider techniques such as yoga, deep breathing and meditation.
- Take your medications: Dont just take medications when you remember to or when you have a doctors appointment coming up.
- Keep all your medical appointments: Seeing your healthcare providers regularly can help uncover heart-related issues or other medical problems you didn’t know you had. This can also help treat problems sooner rather than later.
What Are The Different Medical Terms For A Heart Attack
Acute coronary syndrome : An umbrella term for situations where the blood supplied to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked. Learn more about ACS.
STEMI: A common name for ST-elevation myocardial infarction, a type of heart attack caused by a complete blockage in a coronary artery.
NSTEMI: A non-ST-elevated myocardial infarction, a type of heart attack in which an artery is partially blocked and severely reduces blood flow.
Myocardial infarction : The damaging or death of an area of the heart muscle resulting from a blocked blood supply to that area. Its also the medical term for a heart attack.
Coronary thrombosis: Formation of a clot in one of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. Also called coronary occlusion.
Coronary occlusion: An obstruction of a coronary artery that hinders blood flow to some part of the heart muscle. Coronary occlusion is a cause of heart attack.
Recommended Reading: Is Congestive Heart Disease Hereditary
Changing Your Lifestyle Can Reduce Your Risk Of Heart Attack
Dealing with the lifestyle factors that contribute to CVD, which you can change, can help reduce your risk of heart attack. Things you can do include:
- take medicines as prescribed
- eat plenty of vegetables, fruits and wholegrains
- eat a variety of healthy protein sources especially fish and seafood, legumes , nuts and seeds. Smaller amounts of eggs and lean poultry can also be included in a heart healthy diet. If choosing red meat, make sure the meat is lean and limit to 1 to 3 times a week
- unflavoured milk, yoghurt and cheese if you have high blood cholesterol you should choose reduced fat varieties
- healthy fat choices with nuts, seeds, avocados, olives and their oils for cooking
- herbs and spices to flavour foods, instead of adding salt
- drink mainly water
Q Are There Any Female
Read Also: Heart Size Upper Limits Of Normal
Will I Have To Take Medicine For The Rest Of My Life
If you have had a heart attack, your doctor will probably want you to take certain medicines for a long time. This can help reduce your risk of more heart problems. Your doctor can answer your questions about these medicines. He or she can tell you the benefits and risks of taking them.
- Aspirin can reduce the risk of a heart attack. A low dose of aspirin each day can keep your blood from forming clots that can eventually block the arteries. Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of aspirin therapy.
- Antiplatelet medicines also help stop blood clots from forming. These drugs are especially important to take for at least a year if you have had a stent placed in your heart.
- Beta blockers are a group of drugs that lower the heart rate and blood pressure. They help improve blood flow to the heart.
- ACE inhibitors are a group of drugs that can help if your heart is not pumping blood well. This medicine helps open your arteries and lower your blood pressure. This improves blood flow.
- Statins are a group of drugs that are used to control cholesterol. They lower bad cholesterol levels and may help increase good cholesterol .
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Your doctor is likely to ask you questions, including:
- How severe are your symptoms?
- Are they constant or do they come and go?
- What, if anything, seems to improve your symptoms? If you have chest pain, does it improve with rest?
- What, if anything, worsens your symptoms? If you have chest pain, does strenuous activity make it worse?
- Have you been diagnosed with high blood pressure, diabetes or high cholesterol?
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Lower Heart Rate
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Is there a test I can take to see if my arteries or blocked so I know if Im at risk of a having a heart attack?
- What is the likely cause of my heart attack?
- How serious was my heart attack?
- What course of treatment do you recommend? Do I need medicine? Surgery?
- Do I need to participate in a cardiac rehabilitation program?
- When can I return to normal physical and sexual activity?
- What is my risk of having another heart attack?
- Are my family members at an increased risk of heart attack?
- Do I need to take medicine to prevent another heart attack?
- Will the medicine interact with any of the medicine I already take?
- What lifestyle changes should I make at home to prevent another heart attack?
- Can sexual activity cause a heart attack?
Living With A Heart Attack

After youve had a heart attack, you are at higher risk of having another one. Your doctor will likely recommend heart-healthy lifestyle changes to help reduce your risk. They include:
- Maintaining a heart-healthy diet.
- Being physically active.
- Quitting smoking.
Symptoms during a second heart attack may be different than the first one. If you have any new symptoms of heart attack or are in any doubt, call 911. Early treatment is the key to surviving a heart attack.
Recommended Reading: Mayo Clinic Heart Rate
What Causes Heart Attacks
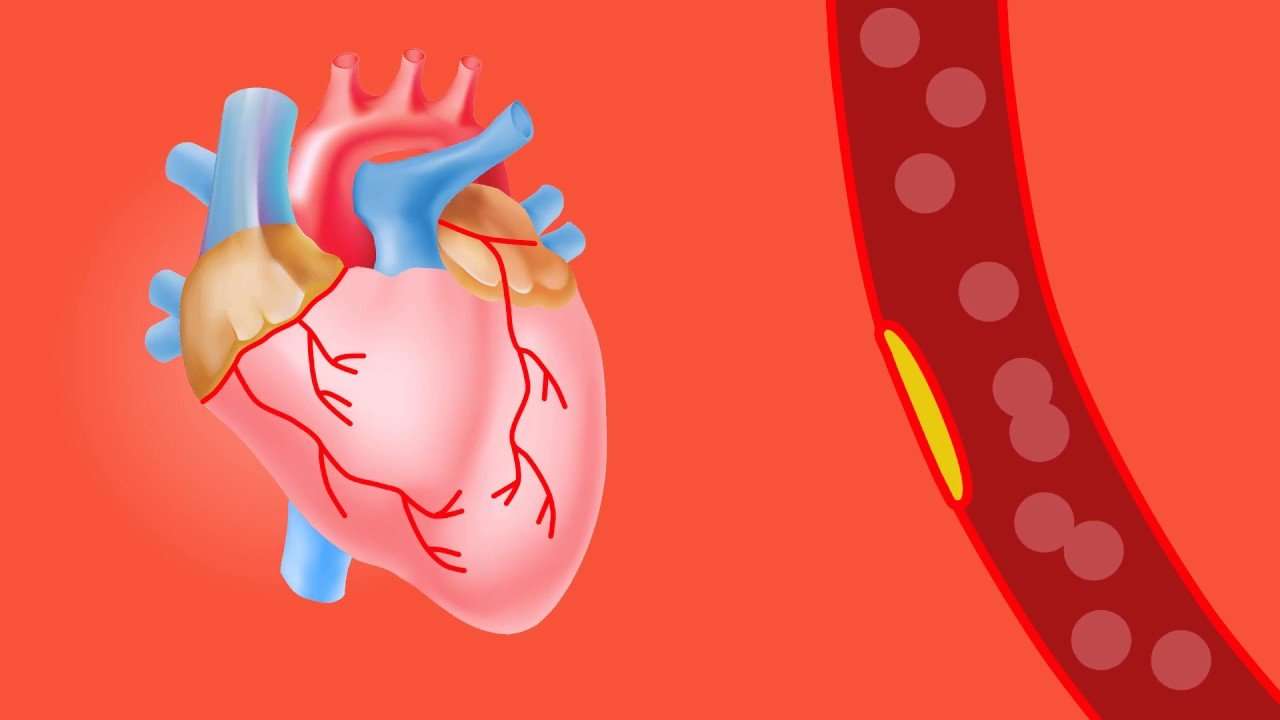
The most common cause of a heart attack is coronary heart disease. This is where fatty deposits, cholesterol and other substances build up in the walls of the coronary arteries that supply oxygen to the heart. Over time, this build-up hardens into plaque that can break off at any time and cause a blood clot which blocks the artery.
In some cases, heart attacks have another cause:
- Coronary artery spasm is an unusual narrowing of blood vessels that can stop blood flow to the heart.
- Spontaneous coronary artery dissection is a sudden tear in the wall of a coronary artery, which can also affect people who have few risk factors for heart disease.
Certain lifestyle factors are shown to increase your chances of heart disease and having a heart attack.
What Is Coronary Artery Disease
Most heart attacks are caused by coronary artery disease . This is when a gradual build-up of fatty streaks form in the coronary arteries. These are the arteries that deliver oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The build-up of fatty streaks makes the coronary arteries narrow and stiffen over time.
As the coronary arteries narrow, it becomes more difficult for oxygenated blood to reach the heart muscle, sometimes causing pain and discomfort known as angina.
If a piece of plaque cracks, it may cause a blood clot to form and block a coronary artery, cutting off the blood supply to a part of the heart muscle. This causes a heart attack.
The heart attack symptoms you feel during a heart attack are caused by your heart muscle being starved of oxygen. This prevents your heart from beating as normal.
Read Also: Lower Part Of Heart Not Working Properly
Other Common Signs And Symptoms
Pay attention to these other possible symptoms of a heart attack:
- Breaking out in a cold sweat
- Feeling unusually tired for no reason, sometimes for days
- Nausea and vomiting
- Light-headedness or sudden dizziness
- Any sudden, new symptoms or a change in the pattern of symptoms you already have
Not everyone having a heart attack has typical symptoms. If you’ve already had a heart attack, your symptoms may not be the same for another one. However, some people may have a pattern of symptoms that recur.
The more signs and symptoms you have, the more likely it is that you’re having a heart attack.
How Is Heart Attack Diagnosed
You may need several tests to determine the cause of your symptoms.
- Electrocardiogram. This test records the electrical activity of your heart. It can help diagnose heart rhythm problems. It can also find damage from a decrease in blood flow.
- Blood tests.When blood flow decreases, special proteins leak into the blood system. A blood test can detect these proteins. Your doctor will want to test your blood several times during the first 24 to 48 hours after yours symptoms start.
Other tests your doctor may want you to have include:
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to create pictures of your heart. The pictures show how well your heart is pumping. It can show if there are problems with your heart valves.
- Chest X-ray.This looks at the size and shape of your heart. It can show if there is any fluid in your lungs.
- Nuclear imaging.This test injects a tiny radioactive substance into your blood. This substance travels to your heart to create pictures of it. It shows how well your heart is pumping. The radioactive substance is safe and leaves your body after the test is finished.
- Coronary angiography. This test is sometimes called cardiac catheterization. It involves inserting a long tube into a blood vessel. The tube is guided to the heart or arteries that carry blood to the heart. A substance is injected into the tube that makes it visible by X-ray. It allows your doctor to see where the blockage that caused the decrease in blood flow to your heart is located.
Also Check: Does Tylenol Help With Heart Attacks
Causes Of Heart Attack
A heart attack, as previously described, occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. However, other conditions, traits or habits may also raise your risk for this condition. These are known as risk factors and include:
Non-modifiable risk factors: These factors are irreversible and cannot be changed. The more of these risk factors you have, the greater your chance of a heart attack.
- Male gender
- Occur at any age however, if youre over 40 or have multiple risk factors work closely with your doctor.
- Family history/Genetics
- Little to no physical activity
- Obesity or having a body mass index BMI of 30 or greater
- Long history of cigarette smoking and/or drug abuse
- Diabetes: when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high
- Extreme emotional stress
Q How Is Smoking Related To A Heart Attack
- Lack of oxygen supply to the heart
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate.
- Clotting of blood.
- Damage to cells that line coronary arteries and other blood vessels.
You May Like: Can Dehydration Cause Increased Heart Rate
Surgical And Other Procedures
In addition to medications, you might have one of these procedures to treat your heart attack:
-
Coronary angioplasty and stenting. In this procedure, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention , doctors guide a long, thin tube through an artery in your groin or wrist to a blocked artery in your heart. If you’ve had a heart attack, this procedure is often done immediately after a cardiac catheterization, a procedure used to find blockages.
The catheter has a special balloon that, once in position, is briefly inflated to open a blocked coronary artery. A metal mesh stent almost always is inserted into the artery to keep it open long term, restoring blood flow to the heart. Usually, you get a stent coated with a slow-releasing medication to help keep your artery open.
-
Coronary artery bypass surgery. In some cases, doctors perform emergency bypass surgery at the time of a heart attack. If possible, however, you might have bypass surgery after your heart has had time about three to seven days to recover from your heart attack.
You’ll likely remain in the hospital for several days after blood flow to your heart is restored and your condition is stable.
