What Do The Numbers Mean
Ejection Fraction 55% to 70%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Heart function may be normal or you may have heart failure with preserved EF .
Ejection Fraction 40% to 54%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Slightly below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Less blood is available so less blood is ejected from the ventricles. There is a lower-than-normal amount of oxygen-rich blood available to the rest of the body. You may not have symptoms.
Ejection Fraction 35% to 39%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Moderately below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Mild heart failure with reduced EF .
Ejection Fraction Less than 35%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Severely below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Moderate-to-severe HF-rEF. Severe HF-rEF increases risk of life-threatening heartbeats and cardiac dyssynchrony/desynchronization .
Normal Heart. A normal left ventricular ejection fraction ranges from 55% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example means that 65% of total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
HF-pEF. If you have HF-pEF, your EF is in the normal range because your left ventricle is still pumping properly. Your doctor will measure your EF and may check your heart valves and muscle stiffness to see how severe your heart failure is.
What Causes Congestive Heart Failure
Several factors can cause congestive heart failure. They include:
- Presence of other diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure
- Addictions like smoking and alcohol
Although heart failure is a serious condition, it does not mean that the heart stops functioning altogether. With proper management, persons who have congestive heart failure can lead nearly normal lives, depending on its severity. Besides the required medical and surgical interventions, it is important to eat healthy, stay active as possible, and refrain from alcohol, smoking, and drug abuse. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , almost half of the patients with congestive heart failure live beyond five years.
Treatment Of Severe Congestive Heart Failure
Severe congestive heart failure with acute pulmonary edema is often diagnosed and initially treated in an emergency room setting. Treatment includes:
- Intensive monitoring and stabilization of heart rhythm and vital signs. In some cases, this may require cardiopulmonary resuscitation , and advanced life-support measures, such as and mechanical ventilation to support breathing.
- Intravenous medications to rapidly draw fluid out of the lungs and reduce on the heart
- Monitoring your heart rate and rhythm with an electrocardiogram and blood tests to determine the extent of heart damage
- Supplemental oxygen to ease breathing and increase the amount of oxygen that is delivered to the heart tissue and the rest of the body
- Treatment of abnormal heart rhythms with medications and possibly electrical or
Don’t Miss: Acetaminophen Heart Rate
Medications Used To Treat Congestive Heart Failure
Treatment of congestive heart failure also includes medications. Doctors prescribe medicine to manage symptoms and to make it easier for the heart to function, which will improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Medications include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors , which lower blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart
- Angiotensin-II receptor blockers , which are an alternative to lower blood pressure for those who can’t tolerate ACE inhibitors. Examples include losartan and valsartan .
- Combination valsartan-sacubitril , which is used in place of an ARB or ACE inhibitor
- Aldosterone blockers , which may be used for severe congestive heart failure
- Anticoagulants , which prevent the formation of blood clots that can lead to and stroke
- Beta-blockers , which lower blood pressure, control heart rate, and reduce strain on the heart
- Cholesterol-lowering medications , which can reduce the risk of heart attack and . Cholesterol-lowering medications also reduce the risk of recurrent heart attack and stroke.
- Digitalis drugs , which slow and strengthen the beating of the heart to make the heart muscle more effective in pumping blood
- Diuretics , which pull excess fluid out of the lungs and tissues of the body by increasing urine production
Difference Between Pneumonia And Congestive Heart Failure
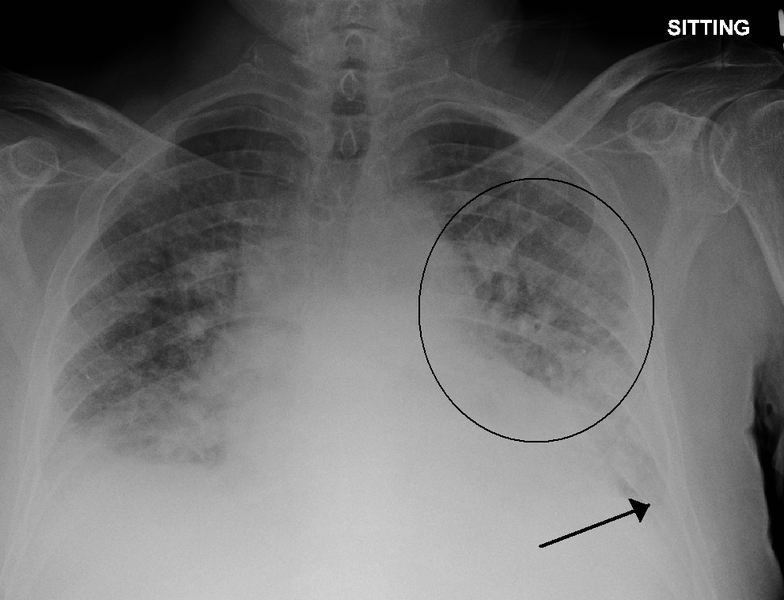
Categorized under Disease | Difference between Pneumonia and Congestive heart failure
Pneumonia vs congestive heart failure
Coughing is one of the commonest symptoms of any condition affecting the respiratory system, right from the nose to the lungs. Occasionally, it may be a symptom of a medical condition of the cardio-vascular system too. Few signs and accompanying symptoms will give the diagnosis to a qualified doctor. Pneumonia and a congestive heart failure are two very different medical conditions that might present just with a cough. Heres how the two differ.
Pneumonia is an infection of the lung tissue. It affects the air sacs called alveoli that form the lung tissue. It is most commonly caused by bacteria and viruses. Rarely is it caused by a fungus or due to an autoimmune disorder. Congestive heart failure is a serious medical condition where there is failure of the pumping action of the heart, leading to accumulation of blood within the heart and deficiency of it everywhere else in the body. Both of these have cough as a leading symptom and often the only one.
The cause of pneumonia commonly is an infectious agent like a virus, bacteria or a fungus. Causes of congestive heart failure are plenty. The leading cause of heart failures is ischaemic heart disease followed by smoking, diabetes, obesity, hypertension and congenital heart diseases.
Read Also: Fluticasone Heart Palpitations
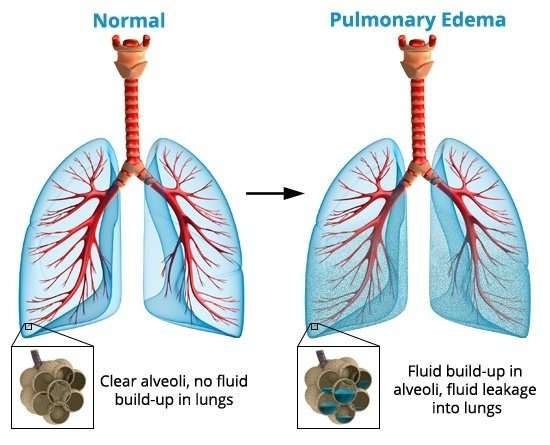
How Pulmonary Edema Happens In Case Of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart failure gives rise to pulmonary edema. The initial stage of congestive heart failure may not be that problematic for lungs, but when the heart is unable to pump blood properly and insufficiently to the whole part of the body for a long term, the blood starts backing up in the veins which carry blood through the lungs. With the increase in the pressure, the blood in these vessels leak and the fluid is pushed in the alveoli or the air sacs of the lungs. As the heart failure worsens and slowly fluid starts accumulating in lungs. The fluid accumulates in the other parts of the body and produces edema especially in the legs, ankles and feet.
To prevent pulmonary edema, it is important to check, diagnose and correct the congestive heart failure diseases, if it is present. Below are few symptoms which are indicative of a Congestive Heart Failure:
- Impaired thinking, delirium and confusion.
- Appetite loss.
- Tiredness, fatigue.
If these occur, it is important to get it diagnosed and treated on proper time or else it can be fatal in the near future. Fortunately there are improvements and advancements in the treatment of congestive heart failure, but only 50% of the patients will have an average expectancy of about five years or less. Those who have serious CHF have more risk of life and 90% of patients may die within one year.
What Are The Stages Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic long-term condition that gets worse with time. There are four stages of heart failure . The stages range from “high risk of developing heart failure” to “advanced heart failure,” and provide treatment plans. Ask your healthcare provider what stage of heart failure you are in. These stages are different from the New York Heart Association clinical classifications of heart failure that reflect the severity of symptoms or functional limits due to heart failure.
As the condition gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. You cannot go backwards through the stages. For example, if you are in Stage B, you cannot be in Stage A again. The goal of treatment is to keep you from progressing through the stages or to slow down the progression.
Treatment at each stage of heart failure may involve changes to medications, lifestyle behaviors and cardiac devices. You can compare your treatment plan with those listed for each stage of heart failure. The treatments listed are based on current treatment guidelines. The table outlines a basic plan of care that may apply to you. If you have any questions about any part of your treatment plan, ask a member of your healthcare team.
Read Also: Apple Watch Heart Rate Monitor Accuracy
Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment Of Pleural Effusion
The pleural effusion might show symptoms like dry cough, chest pain, fever, breathlessness, persistent hiccups etc. if one or more symptoms occur repeatedly, there should be an immediate diagnosis of the chest. The medical practitioner will perform a physical analysis and listen to the activity of lungs with the help of a stethoscope. A chest X-ray might also be done along with the following procedures:
- Ultrasound of the chest.
- Analysis of pleural fluid.
The pleural effusion can be complicated or uncomplicated type. The uncomplicated pleural effusions dont have any visible signs and symptoms and are not likely to cause permanent lung problem. The fluid in uncomplicated type may not be infective and may not cause inflammation. The complicated pleural type may contain fluid along with severe infection or inflammation. They require immediate attention and chest drainage. However, both the types require proper treatment. The fluid is removed carefully from the pleural membrane. A needle is inserted into the chest cavity and the fluid is sucked using a syringe. This procedure is known as Thoracocentesis.
Also Read:
Bacterial Pneumonia Far More Dangerous To The Heart Than Viral Pneumonia
- Date:
- Intermountain Medical Center
- Summary:
- Heart complications in patients diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia are more serious than in patients diagnosed with viral pneumonia, according to new research.
Heart complications in patients diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia are more serious than in patients diagnosed with viral pneumonia, according to new research from the Intermountain Heart Institute at Intermountain Medical Center in Salt Lake City.
In the study of nearly 5,000 patients, researchers found that patients diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia had a 60 percent greater risk of a heart attack, stroke, or death than patients who had been diagnosed with viral pneumonia.
“We’ve always known pneumonia was a risk factor for a major adverse cardiac event, like a heart attack, within the first 90 days of being diagnosed,” said J. Brent Muhlestein, MD, a cardiovascular researcher with the Intermountain Heart Institute at Intermountain Medical Center. “What we didn’t know was which type of pneumonia was more dangerous. The results of this study provided a clear answer, which will allow physicians to better monitor patients and focus on reducing their risk of a major adverse cardiac event.”
Results of the study will be presented during the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions in Chicago on Sunday, Nov. 11, at 10:30 a.m. CT.
The Intermountain Heart Institute at Intermountain Medical Center is part of the Intermountain Healthcare system based in Salt Lake City.
You May Like: What Causes Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction
Telling The Difference Between Dog Congestive Heart Failure And Pneumonia
My dog has an enlarged heart,a murmur and is coughing.An echo and an x-ray were taken in nov 2009 and the cardiologist said her heart is not in congestive failure so no medication was prescribed.She is still coughing but the cough now sounds like she has fluid in her lungs. how do i know if she is now in congestive heart failure or could it be something else like phnemonia? Thanks for your help.
-
By: Erin Broersma El Segundo, CA
Replied on 04/19/2011
If she has an enlarged heart and a murmur, there are medications that help the heart pump more efficiently. I would say if she saw a cardiologist, I would ask them about products such as Enalapril and Digoxin. If she is coughing due to her heart murmur, there are also medications that help open airways and pull fluid from the chest Theophylline, and Lasix . If she has pneumonia, she will be running a fever. She also will not feel well. If she is lethargic and not wanting to eat/drink, I would be concerned that she has pneumonia. It seems more likely, with her medical history, that she may be coughing due to the fact her heart is not working as well as it could be and fluid is forming around her heart and in her lungs. This is a normal side-effect of such a diagnosis and medications tend to alleviate the excess fluid and allow her to breathe much better, while reducing or eliminating the coughing.
What Procedures And Tests Diagnose Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure can be a medical emergency, especially if it acutely decompensates and the patient can present extremely ill with the inability to breathe adequately. In this situation, the ABCs of resuscitation need to be addressed while at the same time, the diagnosis of congestive heart failure is made.
Common tests that are done to help with the diagnosis of congestive heart failure include the following:
- Electrocardiogram to help assess heart rate, rhythm, and indirectly, the size of the ventricles and blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Blood tests may include a complete blood count , electrolytes, glucose, BUN, and creatinine .
- B-type natriuretic peptide may be helpful in deciding if a patient has shortness of breath from congestive heart failure or from a different cause. It is a chemical that is located in the heart ventricles and may be released when these muscles are overloaded.
- Echocardiography or ultrasound testing of the heart is often recommended to assess the anatomy and the function of the heart. In addition to being able to evaluate the heart valves and muscle, the test can look at blood flow within the heart, watch the chambers of the heart contract, and measure the ejection fraction .
Other tests may be considered to evaluate and monitor a patient with suspected congestive heart failure, depending upon the clinical situation.
You May Like: Tylenol And Heart Palpitations
Symptoms And Complications Of Heart Failure
If you have heart failure, it is important for you to know what kinds of symptoms you can experience. By paying close attention to your symptoms, you can help your healthcare provider optimize your therapy, both to keep your symptoms at bay and to reduce your chances of having some of the more serious complications of heart failure.
Most symptoms caused by heart failure can be divided into three general categories:
- Symptoms due to fluid overload and congestion
- Symptoms due to reduced cardiac pumping
- Symptoms due to cardiac arrhythmias
Symptoms Of Reduced Pumping Capability
The most prominent symptoms are:
- Extreme weakness and fatigue
- Muscle weakness and muscle wasting
- Lethargy and inanition
- Extreme weight loss
Obviously, symptoms like this are not compatible with a long life. Unless the cardiac function can be improved, or unless cardiac transplantation or a ventricular assist device can be used, once a person with heart failure develops these kinds of symptoms, death usually follows relatively soon.
Also Check: Is Congestive Heart Disease Hereditary
Prognosis Of Patients With Pre
A paper in the Journal of General Internal Medicine states: Thirty-day mortality from pneumonia was 24.4% among heart failure patients vs. 14.4% among other pneumonia patients.
The paper adds, We identified 33,736 patients with a first-time hospitalization for pneumonia, of whom 3,210 had a previous diagnosis of heart failure. The median age was 73 years
In addition: We were able to adjust for a wide range of prognostic factors assumed to be important for pneumonia, including cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disease, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease.
The paper also says that Our data indicated that pneumonia mortality increased with preadmission heart failure severity. treatment
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. Shes also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
General Prevention And Treatment Measures For Congestive Heart Failure
Treatment for congestive heart failure includes preventive care aimed at minimizing the risk factors for having a heart attack and other forms of heart disease. General preventive and treatment measures include:
- Lifestyle and dietary changes to achieve and maintain an ideal weight and fitness level. Doctors recommend a heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated fat, trans fats, and sodium. Excessive salt leads to and increases blood pressure.
- Periods of prescribed rest
- Regular medical care and treatment of risk factors, such as , hypertension, obesity, smoking, diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption
Read Also: Unsafe Heart Rate Resting
Hypertension Or High Blood Pressure
Another cause of congestive heart failure is high blood pressure or hypertension. If you have high blood pressure, your heart muscle works extra hard to pump blood through your body.
As time passes, because of the overexertion, the muscles in your heart can become too weak or too stiff to properly circulate blood to your body. If you have high blood pressure, your heart muscle workextra hard to pump blood through your body.
Outcomes Of Pneumonia In Patients With Heart Failure
- Shen L, Jhund PS, Anand IS, et al.
- Citation:
- Supriya Shore, MD
Quick Takes
- In post hoc analyses of two large, randomized cohorts with HFrEF and HFpEF patients, incidence of pneumonia was 29 and 39 per 1,000 patient-years, respectively.
- Patients with pneumonia in both cohorts were older with more comorbid conditions.
- Pneumonia was associated with an increased risk of two- to four-fold for HF hospitalization, all-cause mortality, and cardiovascular mortality in both HFrEF and HFpEF patients.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure And Heart Rate
