Causes Of Heart Failure
The heart is a double pump made up of four chambers. Deoxygenated blood from the veins enters the right upper chamber , is passed to the right lower chamber , and then pumped to the lungs.
Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left upper chamber and then enters the left lower chamber . The blood is then pumped around the body, under pressure, via arteries.
In a person with heart failure, one or both ventricles dont empty properly. This leads to increased pressure in the atria and the nearby veins. This backlog of blood can affect the kidneys and lungs interfering with their function and leading to a build-up of fluid in the lungs, abdominal organs and legs.
In some people with heart failure, rather than failed pumping of the blood from the ventricle, there is failed relaxation of the ventricle.
If the heart is not pumping and becomes stiff and unable to relax, it can cause the blood to pool in the hearts ventricles. This can cause pressure build up and can put strain on the heart.
Heart failure can be caused by several conditions, including:
Types Of Heart Failure
Systolic heart failure happens when your heart muscle doesn’t squeeze with enough force. When that’s the case, it pumps less oxygen-rich blood through your body.
With diastolic heart failure, your heart squeezes normally, but the ventricle — the main pumping chamber — doesn’t relax properly. Less blood can enter your heart, and the blood pressure in your lungs goes up. When that happens, you get fluid in your lungs, legs, and belly.
The Four Stages Of Heart Failure
- Reactions 0 reactions
There are four stages of heart failure. The stages range from being at risk of heart failure to having advanced heart failure. These stages were created by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology and were given letter titles A, B, C, and D. Each stage has different recommended treatments depending on a multitude of factors.1
Recommended Reading: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are The Causes Of Congestive Heart Failure
There are many reasons why you might develop congestive heart failure.
The most common reason people develop heart failure in America is blockages in the arteries that surround and feed the heart . With this condition, the blockages prevent blood from feeding the heart muscle, making it weak.
Some of the common conditions which can either increase your risk for or directly cause congestive heart failure include:
The symptoms of congestive heart failure are not the same for everyone.
However, very often heart failure causes patients to gain fluid around their bodies.
Fluid can accumulate in and around the lungs causing difficulty breathing. Fluid can accumulate in the legs and abdomen causing swelling. When heart failure causes these severe symptoms, patients may require the assistance of an experienced cardiologist to help figure out and treat their condition.
Heart failure can also cause patient to feel a palpitation, which an uncomfortable recognition of the forceful, rapid, or irregular beating of the heart. As heart failure places a strain on the heart, that strain can cause palpitations.
If you experience any of these symptoms, its important to speak with a medical professional.
Pharmacological Management Of End Stage Heart Failure
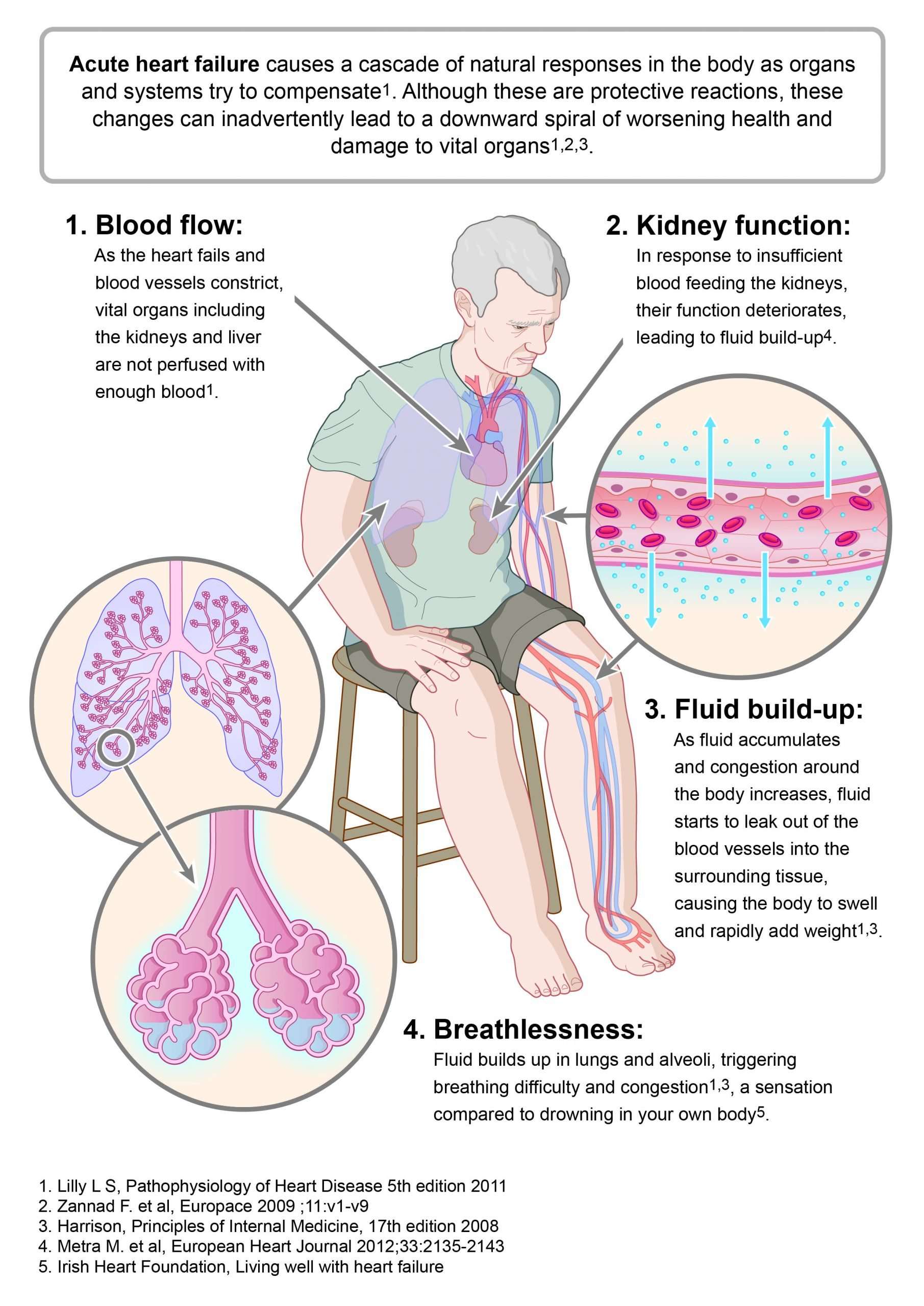
Table 1Pharmacological management of end stage heart failure,,,,
| Goal 1: Improvement of morbidity and mortality |
| ACE inhibitors |
| ARBs |
| Selected blockers |
| Goal 2: Control of symptoms |
| Diuretics |
| Digitalis |
ACE, angiotensinconverting enzyme ARBs, angiotensin II type I receptor blockers.
Table 2Overview of the drugs used for the pharmacological management of end stage heart failure,,,,
| Drug class | |
|---|---|
| Cough, hyperkalaemia, renal insufficiency, angioedema | |
| Enalapril | |
| Blockade of theangiotensin II type Ireceptor | Losartan |
| Blockade of the 1adrenergic receptor | Metoprolol succinate |
| Blockade of the aldosterone receptor | Spironolactone |
| Blockade of the Na+/Cl cotransporter | Hydrochlorothiazide |
| Blockade of the Na+/2Cl/K+ cotransporter | Furosemide |
| Blockade of theNa+/K+ ATPase | Digoxin |
As patients with end stage heart failure frequently show signs of fluid retention or have a history of such, inhibitors of the reninangiotensin system should be coadministered with diuretics, which usually leads to rapid symptomatic improvement of dyspnoea and exercise tolerance while lacking significant effects on survival. End stage heart failure usually requires the use of loop diuretics, which may be effectively used in combination with thiazides in case of treatment refractory fluid overload due to a synergistic mechanism of action .
Recommended Reading: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
Congestive Heart Failure Treatment Options
Middle Georgia Heart takes a comprehensive approach, beginning with the necessary tests to make an accurate diagnosis. These tests include electrocardiogram , echocardiogram, stress tests, heart monitors, and more. Depending on the stage of heart failure, we will take the necessary approach to treatment. Treatment plans can range from small lifestyle changes to procedures performed by our experts.
How Is Copd Treated In Patients With Hf
Moreover, caution is advised with use of inhaled 2-agonists for the treatment of COPD in patients with HF. Finally, noninvasive ventilation, added to conventional therapy, improves the outcome of patients with acute respiratory failure due to hypercapnic exacerbation of COPD or HF in situations of acute pulmonary edema.
You May Like: What Caused Carrie Fisher’s Heart Attack
What Are The Different Types Of Chf
Heart failure can occur on the left side of the heart, the right side, or both. Most commonly, it begins in the heart’s primary pumping chamber – the left ventricle. Each specific type of CHF is accompanied by its own distinct characteristics:
- Right-sided CHF – Right-sided CHF develops when the right ventricle struggles to deliver blood to the lungs. As blood backs up into the blood vessels, the body begins to retain fluid in the abdomen and lower body.
- Left-sided CHF – Left-sided CHF is the most common form of CHF and begins when the left ventricle cannot effectively deliver blood throughout the body. Eventually, this can lead to fluid retention throughout the body, particularly around the lungs.
Cases of left-sided CHF can be further classified into one of two sub-types, characterized by the manner in which the ventricle is affected:
- Systolic CHF – Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly.
- Diastolic CHF – Diastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff. Because the chamber must relax in order to fill with blood between contractions, this stiffness means that an inadequate amount of blood is available to pump out to the rest of the body.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
You May Like: Slow Heart Condition Medical Term
What Do Symptoms Of End Stage Congestive Heart Failure Look Like
Dyspnea
Dyspnea or shortness of breath can occur both during activity and rest. This is the symptom that often sends patients racing to the hospital late at night. Work with your hospice or palliative care team to manage symptoms at home and avoid these stressful hospital trips.
Chronic Cough
When the heart cannot keep up with the supply of blood moving between it and the lungs, fluid can build up in the lungs. This results in a chronic cough or wheezing that can produce white or pink mucus.
Edema
As the hearts ability to pump slows down, fluid can build up in the body. This creates swelling in the extremities particularly the feet, ankles, legs, or abdomen.
Lack of Appetite
As the digestive system receives less blood, patients may feel full or nauseous. Not wanting to eat is a natural part of the body shutting down, but families often find this distressing. Learn more about why it is okay for your loved one to stop eating and drinking at end of life.
High Heart Rate
In response to a loss in pumping capacity, the heart begins to beat faster. The patient experiences this as a racing or throbbing heartbeat.
Confusion
When the heart stops working effectively, it can change sodium levels in the blood. This leads to memory loss, confusion, and a general feeling of disorientation.
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
The name of this condition can be a little confusing. When you have heart failure, it doesn’t mean your ticker stopped beating. What’s really going on is that your heart can’t pump blood as well as a healthy one.
The chambers of your heart may respond by stretching to carry more blood to pump through your body. They may become stiffer and thicker. This helps keep blood moving for a while, but in time, your heart muscle walls may get weaker.
Your kidneys react by causing your body to hold on to water and salt. Fluid may start to build up in your arms, legs, ankles, feet, lungs, or other organs.
The American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology have defined four stages of heart failure to help people understand how the condition changes over time and the kinds of treatments that are used for each.
Also Check: Enalapril Heart Rate
Congestive Heart Failure In Elderly Life Expectancy
In a recent study, it was reported that patients hospitalized with moderate systolic heart failure faced a median expected survival time of 2.4 years if they were aged 71 to 80 years and 1.4 years if they were aged 80 years or more. In patients with more advanced systolic dysfunction, life expectancy was even shorter.Sep 17, 2008
Congestive heart failure life expectancy
- Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years. For those with advanced forms of heart failure, nearly 90% die within one year.
Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years. For those with advanced forms of heart failure, nearly 90 % die within one year.
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask you many questions about your symptoms and medical history. Youâll be asked about any conditions you have that may cause heart failure . Youâll be asked if you smoke, take drugs, drink alcohol , and about what drugs you take.
Youâll also get a complete physical exam. Your doctor will listen to your heart and look for signs of heart failure as well as other illnesses that may have caused your heart muscle to weaken or stiffen.
Your doctor may also order other tests to determine the cause and severity of your heart failure. These include:
Other tests may be ordered, depending on your condition.
Also Check: Medical Name For Enlarged Heart
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms
Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure are divided by doctors based on which side of the heart is affected the right or the left. However, since both sides of the heart eventually affect the functioning of the other side, it is simpler to look at all the symptoms that could occur with Congestive Heart Failure:
- Shortness of breath upon lying down or physical activity or even at rest, rapid, shallow breathing, cough that is persistent, excess phlegm formation
- Heaviness of heart, fast heart rate, missing beats or arrhythmias
- Swelling In the legs especially the ankles, in the chest, around the lungs, in the abdomen, around the liver and spleen
- Overall Tiredness, fatigue, muscle pain, loss of appetite, feeling restless, weight gain
- Brain fog, confusion, loss of memory
- Excess urination, especially at night
- Chest pain, abdomen pain and leg pain, with the swelling that puts pressure on these areas.
Congestive Heart Failure: Forgotten Ways To Improve Prognosis And Life Expectancy
What can you do? The very first thing is to improve the obvious lifestyle factors quit smoking, reduce alcohol consumption, get some exercise, eat healthier, etc. But that, you already know.
Could there be something fundamentally wrong with the way heart disease and its ultimate chronic result, Congestive Heart Failure is currently seen and treated?
According to an increasing band of M.D.s who are leading the charge to help people address the root cause, the answer is a resounding Yes!
What Causes Heart Failure
Heart failure can be caused by many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle. Common conditions are:
- Coronary artery disease affects the arteries that carry blood and oxygen to the heart . The normal lining inside the arteries breaks down, the walls of the arteries become thick, and deposits of fat and plaque partially block the flow of blood. Over time, the arteries become very narrow or completely blocked, which causes a heart attack. The blockage keeps the heart from being able to pump enough blood to keep your organs and tissues healthy. When arteries are blocked, you may have chest pain and other symptoms of heart disease.
- Heart attack. A heart attack happens when a coronary artery suddenly becomes blocked and blood cannot flow to all areas of the heart muscle. The heart muscle becomes permanently damaged and muscle cells may die. Normal heart muscle cells may work harder. The heart may get bigger or stiff .
- Cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy is a term that describes damage to and enlargement of the heart muscle not caused by problems with the coronary arteries or blood flow. Cardiomyopathy can occur due to many causes, including viruses, alcohol or drug abuse, smoking, genetics and pregnancy .
- Tobacco and illicit drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Don’t Miss: Will Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure
How Long Can A 90 Year Old Live With Congestive Heart Failure
Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years . For those with advanced forms of heart failure , nearly 90 % die within one year .
What Are The Four Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
The New York Heart Association developed the four stages of congestive heart failure depending on the functional capabilities of the heart.
- Class I: Patients will have no problem while performing physical activity.
- Class II: Patients will have minor limitations of physical capacity due to a marked increase in physical activity. This leads to weakness, increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, and chest pain, but they may be comfortable at rest.
- Class III: Patients with marked limitation of physical activity in which minimal ordinary activity results in weakness, increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, and chest pain however they are comfortable at rest.
- Class IV: Patients cannot carry on any physical activity without discomfort and have symptoms of heart failure or chest pain, even at rest.
Recommended Reading: Can Acetaminophen Raise Blood Pressure
Can Surgery Be Used To Treat Heart Failure
In heart failure, surgery may sometimes prevent further damage to the heart and improve the heart’s function. Procedures used include:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. The most common surgery for heart failure caused by coronary artery disease is . Although surgery is more risky for people with heart failure, new strategies before, during, and after surgery have reduced the risks and improved outcomes.
- Heart valve surgery. Diseased heart valves can be treated both surgically and non-surgically .
- Implantable left ventricular assist device . The LVAD is known as the “bridge to transplantation” for patients who haven’t responded to other treatments and are hospitalized with severe systolic heart failure. This device helps your heart pump blood throughout your body. It allows you to be mobile, sometimes returning home to await a heart transplant. It may also be used as destination therapy for long-term support in patients who are not eligible for transplant.
- Heart transplant. A heart transplant is considered when heart failure is so severe that it doesn’t respond to all other therapies, but the person’s health is otherwise good.
Can You Recover From Congestive Heart Failure
Dr. Werden says full recovery depends on a variety of things, such as how well a patient responds to medication. A minority of people with congestive heart failure require surgery, and some will never enjoy the high quality of life they did before their hearts failed.
Read Also: Can Tylenol Help Heart Palpitations
How Long Can You Live With End
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition that worsens with each flare-up. Your outlook and prognosis are better if you are healthy overall, you have been following your treatment plan, and you are responding well to your treatments. Being willing to pursue invasive treatments like a heart transplant will also increase your life expectancy.
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Read Also: End Stage Coronary Artery Disease
