What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure
Untreated heart failure can eventually lead to congestive heart failure , a condition in which blood builds up in other areas of your body. In this potentially life threatening condition, you may experience fluid retention in your limbs as well as in your organs, such as the liver and lungs.
Additional complications of heart failure can include:
- stroke
- arrhythmias, like atrial fibrillation
Walk Barefoot On The Earth
Yet again, this seems like advice coming from hippie mumbo-jumbo. Only, the hard science is now saying that earthing or simply having bare skin contact with the earth, is one of the most potent anti-oxidants there is. The electromagnetic field of our planet has the ability to donate free ions to us, helping to reduce the viscosity of our blood and counter damage to arteries. Vigorous barefoot walking helps improve blood circulation everywhere in the body.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B
ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
You May Like: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
What Do Symptoms Of End Stage Congestive Heart Failure Look Like
Dyspnea
Dyspnea or shortness of breath can occur both during activity and rest. This is the symptom that often sends patients racing to the hospital late at night. Work with your hospice or palliative care team to manage symptoms at home and avoid these stressful hospital trips.
Chronic Cough
When the heart cannot keep up with the supply of blood moving between it and the lungs, fluid can build up in the lungs. This results in a chronic cough or wheezing that can produce white or pink mucus.
Edema
As the hearts ability to pump slows down, fluid can build up in the body. This creates swelling in the extremities particularly the feet, ankles, legs, or abdomen.
Lack of Appetite
As the digestive system receives less blood, patients may feel full or nauseous. Not wanting to eat is a natural part of the body shutting down, but families often find this distressing. Learn more about why it is okay for your loved one to stop eating and drinking at end of life.
High Heart Rate
In response to a loss in pumping capacity, the heart begins to beat faster. The patient experiences this as a racing or throbbing heartbeat.
Confusion
When the heart stops working effectively, it can change sodium levels in the blood. This leads to memory loss, confusion, and a general feeling of disorientation.
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
Recommended Reading: Ibs And Heart Palpitations
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to heart failure include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- cardiomyopathy conditions affecting the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems , such as atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
Signs Symptoms And Complications
Symptoms of heart failure depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. If you have mild heart failure, you may not notice any symptoms except during hard physical work. Symptoms can depend on whether you have left-sided or right-sided heart failure. However, you can have symptoms of both types. Symptoms usually get worse as your heart grows weaker.
Heart failure can lead to serious and life-threatening complications.
You May Like: Is Congestive Heart Failure Genetic
How Is Heart Failure Treated/managed
Treatment of heart failure depends on the underlying cause and this will direct the main treatment to prevent further deterioration. Heart failure can be cured if it has a treatable cause.
If the causes are due to coronary heart disease then the patient may require coronary stents or . If there is a heart valve cause, then the defective valve will need surgery to repair or replace the valve.
All heart failure patients will need:
- Lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking and watching fluid intake and reduce alcohol consumption.
- Medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take three to four different types which have evidence to show they strengthen the heart and improve prognosis. This includes beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARNI and SGLT2 inhibitors. Other medicines, such as diuretics, may be used to help with the symptoms.
In cases where patients are seen to be experiencing continued deteriorating heart function despite the best and optimal medication, the following may be considered:
- Cardiac resynchronising therapy In very severe heart failure conditions, a specialised type of pacemaker has shown to benefit and improve symptoms as well as prolonging life by resynchronising the contractility of the two main pumping chambers of the heart.
- Cardiac transplant If there is no scope for recovery and the condition deteriorates then in suitable patients, a heart transplant may be considered.
What Are The Different Types Of Chf
Heart failure can occur on the left side of the heart, the right side, or both. Most commonly, it begins in the heart’s primary pumping chamber – the left ventricle. Each specific type of CHF is accompanied by its own distinct characteristics:
- Right-sided CHF – Right-sided CHF develops when the right ventricle struggles to deliver blood to the lungs. As blood backs up into the blood vessels, the body begins to retain fluid in the abdomen and lower body.
- Left-sided CHF – Left-sided CHF is the most common form of CHF and begins when the left ventricle cannot effectively deliver blood throughout the body. Eventually, this can lead to fluid retention throughout the body, particularly around the lungs.
Cases of left-sided CHF can be further classified into one of two sub-types, characterized by the manner in which the ventricle is affected:
- Systolic CHF – Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly.
- Diastolic CHF – Diastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff. Because the chamber must relax in order to fill with blood between contractions, this stiffness means that an inadequate amount of blood is available to pump out to the rest of the body.
Don’t Miss: What Causes High Blood Pressure And Low Heart Rate
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
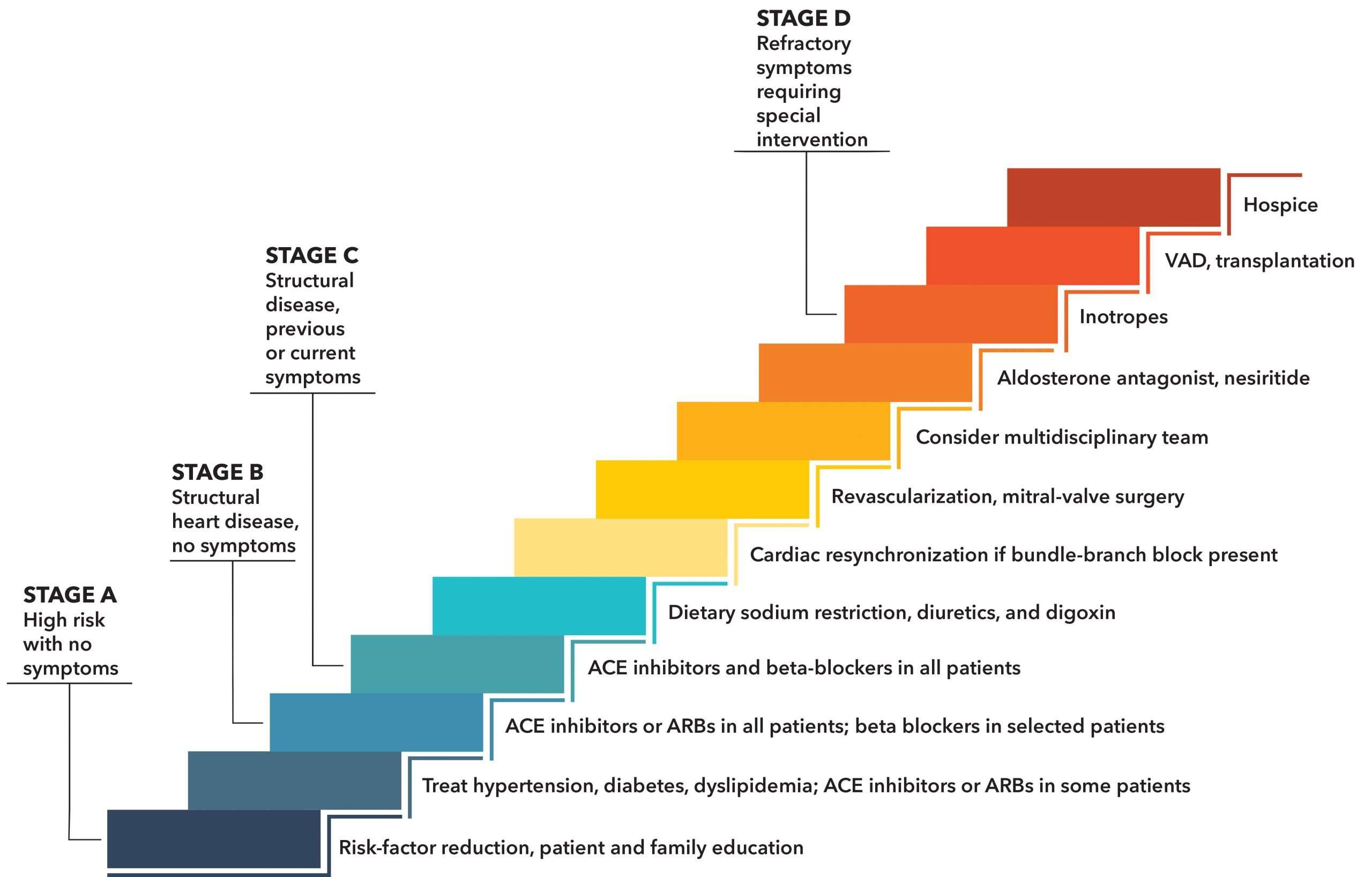
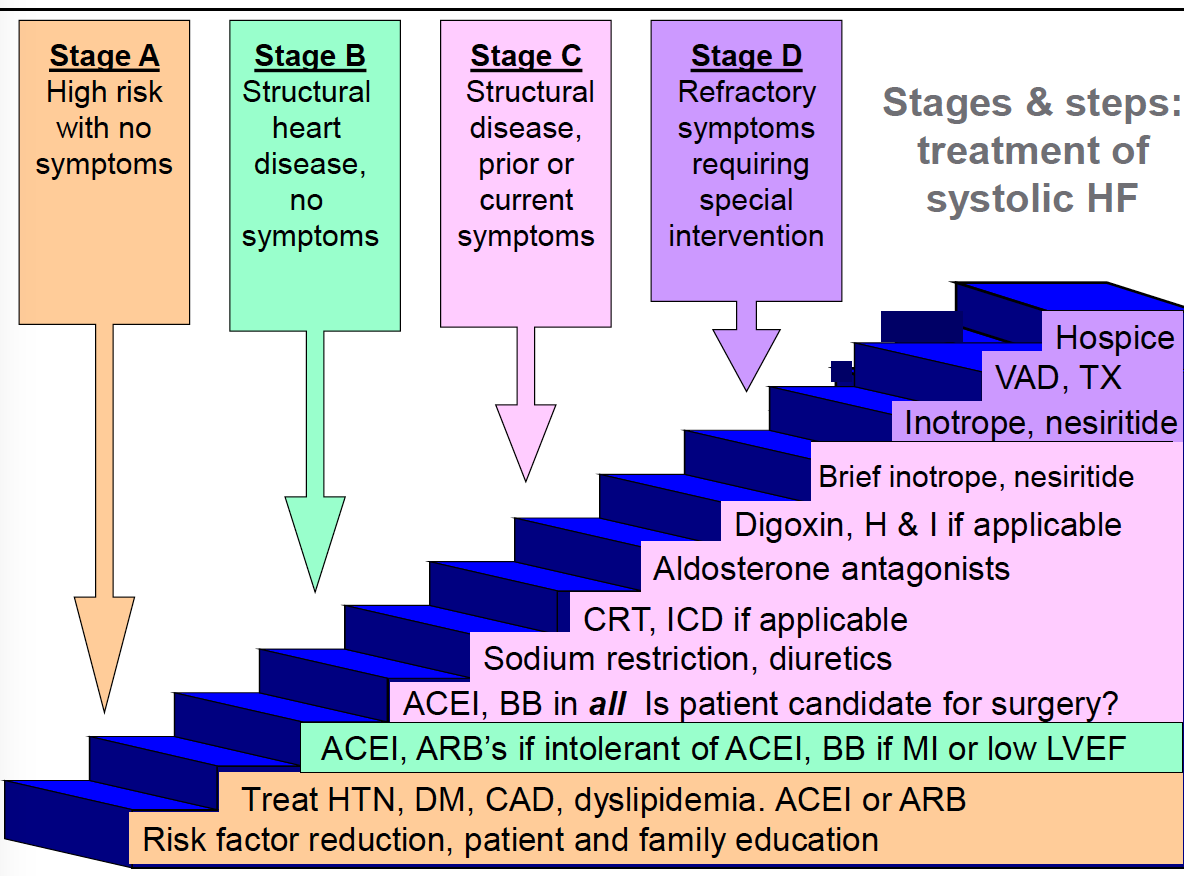
What Are The Stages Of Chf
Congestive heart failure is a progressive condition that can worsen over time. Depending on the severity of CHF and its associated symptoms, cases are classified into one of four potential categories:
|
Stage |
||
|
Stage I CHF can typically be managed through lifestyle modifications and medicaiton. |
||
|
Physical activity may lead to symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. |
Management of Stage II CHF is very similar to Stage I but may require more careful monitoring. |
|
|
Any physical activity is likely to result in notable symptoms, more severe than Stage II. |
Treatment of Stage III CHF is far more complicated than lower stages. Consult with a cardiologist to learn more. |
|
|
Symptoms are always present, even while at rest. Physical activity is likely not possible. |
Stage IV CHF has no cure, but there are options available to increase patient comfort. Speak with a cardiologist to learn more. |
Also Check: Does Tylenol Help With Chest Pain
What Is The Treatment For Stage B
The treatments for Stage B heart failure includes all the treatments for Stage A and, for patients with reduced heart muscle contraction, the use of important classes of drugs such as ACE-inhibitors, ARBs, and specific beta blockers. Some of these patients may also be appropriate candidates for implantable cardioverter-defibrillators .
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosed
Heart failure is diagnosed with a physical exam and tests that may include:
- Electrocardiogram to measure the electrical activity in the heart
- Brain natriuretic peptide or N-terminal pro-BNP blood tests
- BNP or NT-proBNP level is high in people with heart failure
Also Check: Enalapril Heart Rate
Can Surgery Be Used To Treat Heart Failure
In heart failure, surgery may sometimes prevent further damage to the heart and improve the heart’s function. Procedures used include:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. The most common surgery for heart failure caused by coronary artery disease is . Although surgery is more risky for people with heart failure, new strategies before, during, and after surgery have reduced the risks and improved outcomes.
- Heart valve surgery. Diseased heart valves can be treated both surgically and non-surgically .
- Implantable left ventricular assist device . The LVAD is known as the “bridge to transplantation” for patients who haven’t responded to other treatments and are hospitalized with severe systolic heart failure. This device helps your heart pump blood throughout your body. It allows you to be mobile, sometimes returning home to await a heart transplant. It may also be used as destination therapy for long-term support in patients who are not eligible for transplant.
- Heart transplant. A heart transplant is considered when heart failure is so severe that it doesn’t respond to all other therapies, but the person’s health is otherwise good.
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms
Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure are divided by doctors based on which side of the heart is affected the right or the left. However, since both sides of the heart eventually affect the functioning of the other side, it is simpler to look at all the symptoms that could occur with Congestive Heart Failure:
- Shortness of breath upon lying down or physical activity or even at rest, rapid, shallow breathing, cough that is persistent, excess phlegm formation
- Heaviness of heart, fast heart rate, missing beats or arrhythmias
- Swelling In the legs especially the ankles, in the chest, around the lungs, in the abdomen, around the liver and spleen
- Overall Tiredness, fatigue, muscle pain, loss of appetite, feeling restless, weight gain
- Brain fog, confusion, loss of memory
- Excess urination, especially at night
- Chest pain, abdomen pain and leg pain, with the swelling that puts pressure on these areas.
Congestive Heart Failure: Forgotten Ways To Improve Prognosis And Life Expectancy
What can you do? The very first thing is to improve the obvious lifestyle factors quit smoking, reduce alcohol consumption, get some exercise, eat healthier, etc. But that, you already know.
Could there be something fundamentally wrong with the way heart disease and its ultimate chronic result, Congestive Heart Failure is currently seen and treated?
According to an increasing band of M.D.s who are leading the charge to help people address the root cause, the answer is a resounding Yes!
Read Also: Is Tylenol Good For Heart Attack
Why Its Important To Know Your Ef
If you have a heart condition, it is important for you and your doctor to know your EF. Your EF can help your doctor determine the best course of treatment for you. Measuring your EF also helps your healthcare team check how well our treatment is working.
Ask your doctor how often you should have your EF checked. In general, you should have your EF measured when you are first diagnosed with a heart condition, and as needed when your condition changes.
Stage 2 Of Congestive Heart Failure
Stage two of congestive heart failure will produce symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, or heart palpitations after you participate in physical activity. As with stage one, lifestyle changes and certain medication can help improve your quality of life. Your doctor will discuss treatment with you and help you on your healthcare journey while living with CHF.
You May Like: Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure
Heart Failuresigns And Symptoms
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart fails to function properly. The terms “heart failure” and “congestive heart failure ” don’t mean that the heart has actually “failed” or stopped but mean one or more chambers of the heart “fail” to keep up with the volume of blood flowing through them.
Heart failure is brought on by a variety of underlying diseases and health problems.
Your condition may involve the left side, the right side or both sides of the heart. Each side has two chambers:
- An atrium or upper chamber
- A ventricle or lower chamber
Any one of these four chambers may not be able to keep up with the volume of blood flowing through it.
Two types of heart dysfunction can lead to heart failure, including:
- Systolic Heart Failure This is the most common cause of heart failure and occurs when the heart is weak and enlarged. The muscle of the left ventricle loses some of its ability to contract or shorten. In turn, it may not have the muscle power to pump the amount of oxygenated and nutrient-filled blood the body needs.
- Diastolic Failure The muscle becomes stiff and loses some of its ability to relax. As a result, the affected chamber has trouble filling with blood during the rest period that occurs between each heartbeat. Often the walls of the heart thicken, and the size of the left chamber may be normal or reduced.
What Do The Numbers Mean
Ejection Fraction 55% to 70%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Heart function may be normal or you may have heart failure with preserved EF .
Ejection Fraction 40% to 54%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Slightly below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Less blood is available so less blood is ejected from the ventricles. There is a lower-than-normal amount of oxygen-rich blood available to the rest of the body. You may not have symptoms.
Ejection Fraction 35% to 39%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Moderately below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Mild heart failure with reduced EF .
Ejection Fraction Less than 35%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Severely below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Moderate-to-severe HF-rEF. Severe HF-rEF increases risk of life-threatening heartbeats and cardiac dyssynchrony/desynchronization .
Normal Heart. A normal left ventricular ejection fraction ranges from 55% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example means that 65% of total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
HF-pEF. If you have HF-pEF, your EF is in the normal range because your left ventricle is still pumping properly. Your doctor will measure your EF and may check your heart valves and muscle stiffness to see how severe your heart failure is.
Also Check: Does Acetaminophen Increase Blood Pressure
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask you many questions about your symptoms and medical history. Youâll be asked about any conditions you have that may cause heart failure . Youâll be asked if you smoke, take drugs, drink alcohol , and about what drugs you take.
Youâll also get a complete physical exam. Your doctor will listen to your heart and look for signs of heart failure as well as other illnesses that may have caused your heart muscle to weaken or stiffen.
Your doctor may also order other tests to determine the cause and severity of your heart failure. These include:
Other tests may be ordered, depending on your condition.
