Results Compared To Stent Placement
CABG or stent placement is indicated when medical management â anti-angina medications, , , , and/or tight control in â do not satisfactorily relieve ischemic symptoms.
A 2018 meta-analysis with over 4000 patient cases found to have significant advantages compared with conventional CABG. Reduced incidence of , reduced hospital stay duration and reduced duration were all reported. In contrast, HCR was found to be compared to CABG.
What Causes Coronary Artery Disease
CAD is caused by plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the heart and other parts of the body.
Plaque is made up of deposits of cholesterol and other substances in the artery. Plaque buildup causes the inside of the arteries to narrow over time, which can partially or totally block the blood flow. This process is called atherosclerosis.
Surgery And Other Procedures
Your doctor may also recommend surgery or other procedures involving your coronary arteries or other parts of your heart. For example, they may recommend:
- implantation of a pacemaker, defibrillator, or both to improve your hearts electrical function
- atherectomy to remove plaque from your arteries
- balloon angioplasty to help improve blood flow in narrowed arteries
- insertion of a stent, a device designed to hold arteries open
- radiation therapy after the lumen in a prior placed arterial stent repeatedly narrows, to try to keep your artery lumen from narrowing again
In very serious cases, your doctor may recommend a coronary artery bypass graft . During this open chest surgery, your surgeon will remove a portion of a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body and reattach it to your heart to restore arterial blood supply. This allows blood to bypass the segment of blocked artery, flowing through the new blood vessel and connecting to the coronary artery downstream from the segment of blockage.
If the damage to your heart is too great to repair, you may need a heart transplant.
If left untreated, IC can lead to blood clots, heart failure, and even death. Its critical to treat the underlying cause of your IC to prevent complications.
Your long-term outlook will depend on several factors, including:
- how much damage your heart has sustained
- the effectiveness of your treatment
- your lifestyle choices
Youre more likely to develop complications if you:
Also Check: Blood Pressure Versus Heart Rate
Can Coronary Heart Disease Be Prevented
You can prevent coronary heart disease by reducing or eliminating your risk factors. A Heart Health Check with your doctor or nurse will help you to identify your risk factors, and to build a plan to change them.
If your doctor thinks you may already have coronary heart disease, they will ask you to take some tests to confirm their diagnosis. These may include:
- a blood test to check your cholesterol levels
- a blood pressure check
- an electrocardiogram or an echocardiogram
- an angiogram
If you have coronary heart disease, your doctor will help you build a personalised plan for improving your symptoms and preventing heart attacks.
If you have had a heart attack, it is even more important you manage your risk factors and follow your treatment plan. Make sure you check in frequently with your healthcare team.
What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Ischemic Heart Disease
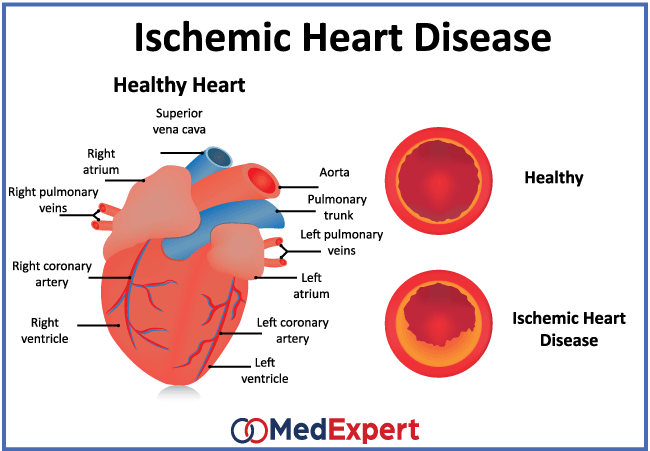
At age 50, the average woman can expect to live 7.9 years with heart disease, while the figure for the average man is 6.7 years. At each age, women are more likely to spend time diagnosed with disease and without a heart attack. Men at every age can expect to spend more years after a heart attack than women.
Don’t Miss: Low Heart Function Symptoms
How To Prevent Coronary Heart Disease
Studies show that heart-healthy livingnever smoking, eating healthy, and being physically activethroughout life can prevent coronary heart disease and its complications.
Work with your doctor to set up a plan that works for you based on your lifestyle, your home and neighborhood environments, and your culture. Working with a team of healthcare providers may help with making changes in your diet, being physically active, managing other medical conditions, and helping you quit smoking.
Prevent Complications Over Your Lifetime
Your doctor will work with you to manage medical conditions that can raise your risk of heart problems and complications.
Your doctor will likely suggest heart-healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating heart-healthy foods, being physically active, and quitting smoking. Your doctor may refer you to other professionals, such as a registered dietitian or exercise physiologist. Your healthcare team can help you set up a personal plan to meet your health goals.
There are benefits to quitting smoking no matter how long or how much you have smoked. Coronary heart disease risk associated with smoking begins to decrease soon after you quit, and it generally continues to decrease over time. In addition:
You May Like: Damaged Left Ventricle
Learn The Warning Signs Of Serious Complications And Have A Plan
Coronary heart disease can lead to heart attack or stroke. If you think that you are or someone else is having the following symptoms, Every minute matters.
Heart attack
The signs and symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Prolonged or severe chest pain or discomfort not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin. This involves uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center or left side of the chest that can be mild or strong. This pain or discomfort often lasts more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back.
- Nausea, vomiting, light-headedness or fainting, or breaking out in a cold sweat. These symptoms of a heart attack are more common in women.
- Shortness of breath. This may accompany chest discomfort or happen before it.
- Upper body discomfort.This can be felt in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or upper part of the stomach.
Trends In Morbidity And Mortality
Data from the Framingham Heart Study showed the overall death rates from CHD decreased by 64 percent from 1950 to 1999. From 1996 to 2006, the annual death rate due to CHD declined by 36.4 percent, and the actual number of deaths declined by 21.9 percent . An analysis of NHANES CHD mortality data between 1980 and 2000 revealed that approximately 47 percent of the decline in mortality could be explained by the use of medical and surgical treatment , whereas approximately 44 percent of the mortality decline was attributed to changes in risk factors .
According to data from the National Registry of Myocardial Infarction, in-hospital mortality following acute MI declined from 11.2 percent in 1940 to 9.4 percent in 1999 . Moreover, a recent analysis of the Medicare fee-for-service population revealed that the adjusted hospitalization rate for acute MI declined by 5.8 percent per year from 2002 through 2007, although there was a slower rate of decline in African American patients compared with white patients .
You May Like: Does Tylenol Help With Heart Palpitations
Disability And Functional Limitation
Function with respect to cardiac disease is optimally assessed when the cardiovascular system is subjected to either physical or emotional stress testing hence, numerous well-known stress-testing methods have been developed, such as the step, bicycle ergometer, and exercise tolerance tests. More recently, the 6-minute walk test has evolved, either because the patient population was considered too frail to embark on a treadmill test or because of the unavailability of appropriate equipment. It is used most frequently in patients with heart failure .
Whether a graded exercise test correlates with the patients everyday activities such as walking and housework has been evaluated. Patients exercise performance was evaluated using a Naughton protocol, which provides a wide range of exercise durations to avoid submaximal exercise in patients with very low exercise tolerance. Exercise was stopped when the symptomatic endpointseither angina or inability to continue to exercise because of extreme fatiguewere reached. Ventricular tachycardia and hypotension were other endpoints, and each patient achieved maximal effort according to his or her own symptoms .
What Is Acute Coronary Syndrome
Acute coronary syndrome is the name given to types of coronary disease that are associated with a sudden blockage in the blood supply to your heart. Some people have symptoms before they have acute coronary syndrome, but you may not have symptoms until the condition occurs. Some people never have any symptoms. Changes caused by acute coronary syndrome can be seen on an electrocardiogram and in blood tests. Acute coronary syndrome is defined by the location of the blockage, length of time the artery is blocked and amount of damage and is defined as:
- Unstable angina: This may be a new symptom or can happen if you have stable angina that changes to unstable angina. You may start to have angina more often, when you are resting, or it may be worse or last longer. The condition can lead to a heart attack. If you have unstable angina, you will need medication, such as nitroglycerin or a procedure to correct the problem.
- Non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction : This is a type of heart attack that does not cause major changes on an ECG. But, a blood test will show that there is damage to your heart muscle.
- ST segment elevation myocardial infarction : This type of heart attack is caused by a sudden blockage of the blood supply to the heart.
These are life-threatening conditions that require emergency medical care.
Don’t Miss: Effects Of Exercise On Cardiac Output
Lack Of Regular Exercise
If you’re inactive, fatty deposits can build up in your arteries.
If the arteries that supply blood to your heart become blocked, it can lead to a heart attack. If the arteries that supply blood to your brain are affected it can cause a stroke.
Read about the physical activity guidelines for adults aged 19 to 64.
Choice Of Source Of Grafts
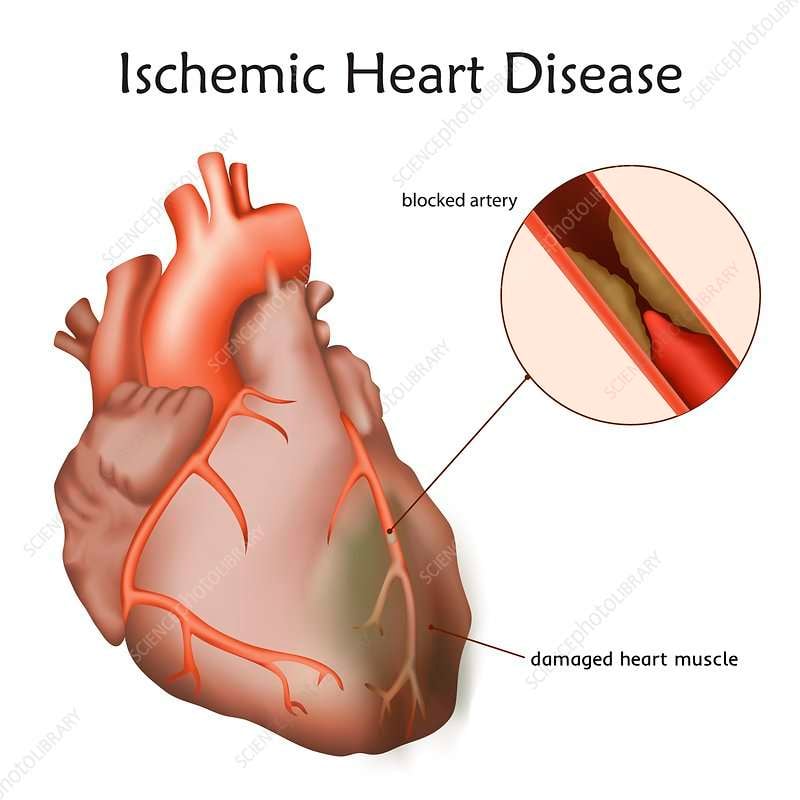
The choice of vessel is highly dependent upon the particular surgeon and institution. Typically, the left is grafted to the artery and a combination of other arteries and veins is used for other coronary arteries. The from the leg is used approximately in 80% of all grafts for CABG. The right internal thoracic artery and the from the forearm are frequently used as well in the U.S., radial artery and saphenous vein graft are usually harvested either endoscopically, using a technique known as , or with the open-bridging technique, employing two or three small incisions. The from the is infrequently used given the difficult mobilization from the .
You May Like: How To Find Thrz
Diagnosing Coronary Heart Disease
If a doctor feels you’re at risk of coronary heart disease, they may carry out a risk assessment.
They’ll ask you about your medical and family history and your lifestyle, and they’ll take a blood test.
Further tests may be needed to confirm coronary heart disease, including:
- a treadmill test
- giving up smoking
- controlling blood cholesterol and sugar levels
Keeping your heart healthy will also have other health benefits, such as helping reduce your risk of stroke and dementia.
What Is Coronary Heart Disease
Over time, a fatty material called atheroma can build up inside your coronary arteries. This process is called atherosclerosis. Eventually, your arteries may become so narrow that they can’t get enough oxygen rich blood to your heart. If a piece of atheroma breaks off, it can cause a blood clot form. This clot can block your coronary artery and cut off the supply of blood and oxygen to your heart muscle. This is known as a heart attack.
Read Also: Tylenol Effect On Blood Pressure
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
| This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to , without removing the technical details. |
| Coronary artery bypass surgery |
|---|
| Early in a coronary artery bypass operation, during vein harvesting from the legs and the establishment of by placement of an . The and are on the upper right. The patient’s head is at the bottom. |
| Other names |
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft surgery, and colloquially heart bypass or , is a surgical procedure to to an obstructed . A normal coronary artery transports to the itself, not through the main .
There are two main approaches. In one, the left , LITA is diverted to the of the . In this method, the artery is “” which means it is not detached from the origin. In the other, a is removed from a leg one end is attached to the or one of its major branches, and the other end is attached to the obstructed artery immediately after the obstruction to restore blood flow.
What Are The Risk Factors For Ischemic Heart Disease
The following are risk factors for ischemic heart disease:
- Smoking. Smoking as few as four cigarettes per day makes you seven times more likely to develop heart disease.
- High Blood Pressure.
Subsequently, one may also ask, what is the main cause of ischemic heart disease?
Coronary artery disease develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart with blood, oxygen and nutrients become damaged or diseased. Cholesterol-containing deposits in your arteries and inflammation are usually to blame for coronary artery disease.
what is the greatest risk factor for heart disease? High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease. It is a medical condition that happens when the pressure of the blood in your arteries and other blood vessels is too high.
In this manner, what is coronary heart disease risk factors?
The traditional risk factors for coronary artery disease are high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, high blood pressure, family history, diabetes, smoking, being post-menopausal for women and being older than 45 for men, according to Fisher. Obesity may also be a risk factor.
How do risk factors increase CHD chances?
It’s essential for healthy cells, but too much in the blood can lead to CHD.
Your risk of developing atherosclerosis is significantly increased if you:
- smoke.
- have high blood pressure
- have a high blood cholesterol level.
- don’t take regular exercise.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate When Exercising
Living With Coronary Heart Disease
Finding coronary heart disease early can prevent it from getting worse. If left untreated, you could have a heart attack or get arrhythmias . CHD can lead to death. Proper diagnosis and treatment allows you to correct it with lifestyle changes and manage it with medicine or surgery. Surgery has various recovery timeframes.
Talk to your doctor about your specific outcomes and goals. You likely will need ongoing doctor visits and tests. CHD does increase your risk for a heart attack. Make sure you know the warning signs and when to call 911.
Ischemic Heart Disease Symptoms
If your coronary arteries narrow, they cant supply enough oxygen-rich blood to your heart especially when its beating hard, such as during exercise. At first, the decreased blood flow may not cause any coronary artery disease symptoms. As plaque continues to build up in your coronary arteries, however, you may develop coronary artery disease signs and symptoms, including:
- A common symptom of coronary heart disease is angina . You may feel pressure, squeezing or tightness in your chest, as if someone were standing on your chest. This pain, referred to as angina, usually occurs on the middle or left side of the chest. You also may feel it in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. Angina pain may even feel like indigestion. Angina tends to get worse with activity and go away with rest. Emotional stress also can trigger the pain.
The pain usually goes away within minutes after stopping the stressful activity. In some people, especially women, this pain may be fleeting or sharp and felt in the neck, arm or back.
- Shortness of breath. This symptom occurs if coronary heart disease causes heart failure. When you have heart failure, your heart cant pump enough blood to meet your bodys needs. Fluid builds up in your lungs, making it hard to breathe. If your heart cant pump enough blood to meet your bodys needs, you may develop shortness of breath or extreme fatigue with exertion.
Heart Attack
Don’t Miss: Heart Attack Frequency
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
Coronary artery bypass grafting is also known as bypass surgery, a heart bypass, or coronary artery bypass surgery.
It’s carried out in people whose arteries are narrowed or blocked.
A coronary angiogram will determine if you’re suitable for treatment.
Off-pump coronary artery bypass is a type of coronary artery bypass surgery. It’s performed while the heart continues to pump blood by itself without the need for a heart-lung machine.
A blood vessel is inserted between the main artery leaving the heart and a part of the coronary artery beyond the narrowed or blocked area.
Sometimes, an artery that supplies blood to the chest wall is used and diverted to one of the heart arteries. This allows the blood to bypass the narrowed sections of coronary arteries.
What Factors Affect Risk For Women Differently
Women are more likely than men to have medical conditions or life issues that raise their risk for coronary heart disease.
- Anemia,especially during pregnancy
- Low levels of HDL cholesterol
- Mild to moderate high blood pressure
- Smoking
Visit The Heart Truth® to learn more about coronary heart disease risk factors for women and how to lower them.
You May Like: Blood Pressure Vs Heart Rate
Why Does Coronary Heart Disease Affect Women Differently
Coronary heart disease is different for women than men because of hormonal and anatomical differences.
- Hormonal changes affect a womans risk for coronary heart disease. Before menopause, the hormone estrogen provides women with some protection against coronary artery disease. Estrogen raises levels of HDL cholesterol and helps keep the arteries flexible so they can widen to deliver more oxygen to the tissues of the heart in response to chemical and electrical signals. After menopause, estrogen levels drop, increasing a womans risk for coronary heart disease.
- The size and structure of the heart is different for women and men. A womans heart and blood vessels are smaller, and the muscular walls of womens hearts are thinner.
- Women are more likely to have nonobstructive coronary heart disease or coronary microvascular disease. These types are harder to diagnose than obstructive coronary artery disease, which can be harder to diagnose. This can cause delays in getting diagnosed and treated.
