The Venous Return Curve
If right atrial pressure were changed in steps over the entire range of possible atrial pressures and venous return were measured at each point, plotting the data set would yield a complete venous return curve, which is presented in . As mentioned earlier, such measurements would have to be made during total blockade of the autonomic nervous system so that circulatory reflexes would be normal. Notice that, at the normal right atrial pressure value , venous return is 100%, which is 5 L/min in man. Venous return falls progressively as right atrial pressure increases, until right atrial pressure reaches 7 mm Hg, the normal value for mean systemic pressure. At that point, venous return is 0 because the pressure gradient for venous return is 0. As right atrial pressure falls below 0, the venous return curve increases at a progressively declining rate until flow reaches a plateau at approximately 4 mm Hg. As discussed above, the reason for the curvilinear nature in this portion of the relationship, termed the transition zone, is the progressive increase in vascular resistance due to the collapse of increasing numbers of veins as right atrial pressure becomes more negative.
The complete venous return curve over the range of right atrial pressure from 8 to 8 mm Hg. Venous return values are for humans.
How Can I Protect My Heart And Pulmonary Arteries
Many of the conditions that affect the pulmonary arteries are present at birth. While you cant prevent these problems, these actions can promote better heart health:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Get at least 150 minutes of cardiovascular physical activity every week.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
What Is The Name Of The Blood Vessels That Carry Blood To And From The Lungs
pulmonary arterypulmonary
Refering to the common carotid artery supplies blood to the head and face. The blood vessel that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. It is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood.
Also, what is the blood vessel that carries blood to the heart called? blood vessels: Blood moves through many tubes called arteries and veins, which together are called blood vessels. The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries. The ones that carry blood back to the heart are called veins.
People also ask, what carries blood away from the lungs?
Key terms
Also Check: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
When Should I Talk To A Doctor
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Bluish lips or skin color.
- Swollen ankles, feet or abdomen.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your pulmonary arteries play an important role getting carbon dioxide out of your blood and oxygen back into it. Many conditions that affect the pulmonary arteries and pulmonary blood circulation are congenital or present at birth. But coronary artery disease and other heart disease can damage the pulmonary arteries. Depending on the heart problem, you may need surgery or other treatments to improve blood flow and oxygenation. Your healthcare provider can offer suggestions on ways to improve your heart health.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/10/2021.
References
- Adult Congenital Heart Association. . Accessed 3/10/2021.Pulmonary Hypertension
- American Heart Association. Problem: . Accessed 3/10/2021.Pulmonary Valve Regurgitation
- Castaner E, Gallardo X, Rimola J, et al. Radiologic overview. RadioGraphics. Accessed 3/10/2021.Congenital and acquired pulmonary artery anomalies in the adult:
- Kreibich M, Siepe M, Kroll J, et al. Circulation. 2015 131:310-16. Accessed 3/10/2021.Aneurysms of the pulmonary artery.
- Tucker WB, Weber C, Burns B. . StatPearls . 2020. Accessed 3/10/2021.Anatomy, thorax, heart pulmonary arteries
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
Each Heart Beat Is A Squeeze Of Two Chambers Called Ventricles
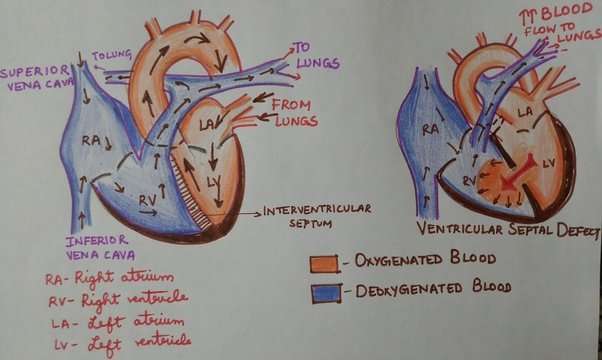
The ventricles are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood empties into each ventricle from the atrium above, and then shoots out to where it needs to go. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, then pumps the blood along to the lungs to get oxygen. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium, then sends it on to the aorta. The aorta branches into the systemic arterial network that supplies all of the body.
Read Also: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are The Different Types Of Arteries
There are three types of arteries. Each type is composed of three coats: outer, middle, and inner.
- Elastic arteries are also called conducting arteries or conduit arteries. They have a thick middle layer so they can stretch in response to each pulse of the heart.
- Muscular arteries are medium-sized. They draw blood from elastic arteries and branch into resistance vessels. These vessels include small arteries and arterioles.
- Arterioles are the smallest division of arteries that transport blood away from the heart. They direct blood into the capillary networks.
There are four types of veins:
- Deep veins are located within muscle tissue. They have a corresponding artery nearby.
- Superficial veins are closer to the skins surface. They dont have corresponding arteries.
- Pulmonary veins transport blood thats been filled with oxygen by the lungs to the heart. Each lung has two sets of pulmonary veins, a right and left one.
- Systemic veins are located throughout the body from the legs up to the neck, including the arms and trunk. They transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore an artery.
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore a vein.
What Is The Vascular System
The vascular system, also called the circulatory system, is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph through the body. The arteries and veins carry blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues and taking away tissue waste matter. The lymph vessels carry lymphatic fluid . The lymphatic system helps protect and maintain the fluid environment of the body by filtering and draining lymph away from each region of the body.
The vessels of the blood circulatory system are:
-
Arteries. Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body.
-
Veins. Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back into the heart.
-
Capillaries. Tiny blood vessels between arteries and veins that distribute oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Blood moves through the circulatory system as a result of being pumped out by the heart. Blood leaving the heart through the arteries is saturated with oxygen. The arteries break down into smaller and smaller branches to bring oxygen and other nutrients to the cells of the bodys tissues and organs. As blood moves through the capillaries, the oxygen and other nutrients move out into the cells, and waste matter from the cells moves into the capillaries. As the blood leaves the capillaries, it moves through the veins, which become larger and larger to carry the blood back to the heart.
Also Check: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
The Exterior Of The Heart:
Below is a picture of the outside of a normal, healthy, human heart.
The illustration shows the front surface of the heart, including the coronary arteries and major blood vessels.
The heart is the muscle in the lower half of the picture. The heart has four chambers. The right and left atria are shown in purple. The right and left ventricles are shown in red.
Connected to the heart are some of the main blood vessels arteries and veins that make up the blood circulatory system.
The ventricle on the right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs.
When you breathe air in, oxygen passes from the lungs through blood vessels where its added to the blood. Carbon dioxide, a waste product, is passed from the blood through blood vessels to the lungs and is removed from the body when you breathe air out.
The atrium on the left side of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
The pumping action of the left ventricle sends this oxygen-rich blood through the aorta to the rest of the body.
What Are The Parts Of The Circulatory System
Two pathways come from the heart:
- The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again.
- The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
In pulmonary circulation:
- The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide. The blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
In systemic circulation:
Also Check: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Is Red Blood And Blue Blood
All blood is red. Hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein in red blood cells, mixes with oxygen to give blood its red color. Blood thats rich in oxygen is known as red blood.
Your veins carry oxygen-poor blood. This is sometimes called blue blood because your veins can look blue underneath the skin. The blood is actually red, but the low oxygen levels give veins a bluish hue.
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
- Real Learning Solutions Pty Ltd
53 pages
- Real Learning Solutions Pty Ltd
University of Melbourne INDIVIDUAL CHC33015
Aged Care 1.html
University of Melbourne INDIVIDUAL CHC33015
Aged Care 21.html
University of Melbourne INDIVIDUAL CHC33015
Aged Care 2.html
University of Melbourne INDIVIDUAL CHC33015
Aged care 15.html
University of Melbourne INDIVIDUAL CHC33015
Aged Care 24.html
University of Melbourne INDIVIDUAL CHC33015
Aged Care 6.html
Don’t Miss: Acetaminophen Heart Rate
How Does The Heart Beat
The heart gets messages from the body that tell it when to pump more or less blood depending on a person’s needs. For example, when you’re sleeping, it pumps just enough to provide for the lower amounts of oxygen needed by your body at rest. But when you’re exercising, the heart pumps faster so that your muscles get more oxygen and can work harder.
How the heart beats is controlled by a system of electrical signals in the heart. The sinus node is a small area of tissue in the wall of the right atrium. It sends out an electrical signal to start the contracting of the heart muscle. This node is called the pacemaker of the heart because it sets the rate of the heartbeat and causes the rest of the heart to contract in its rhythm.
These electrical impulses make the atria contract first. Then the impulses travel down to the atrioventricular node, which acts as a kind of relay station. From here, the electrical signal travels through the right and left ventricles, making them contract.
One complete heartbeat is made up of two phases:
The Valves Are Like Doors To The Chambers Of The Heart
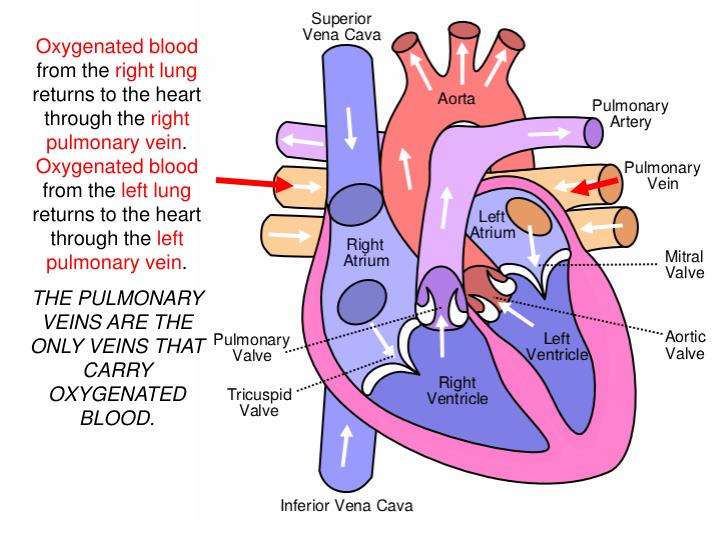
Four valves regulate and support the flow of blood through and out of the heart. The blood can only flow one waylike a car that must always be kept in drive. Each valve is formed by a group of folds, or cusps, that open and close as the heart contracts and dilates. There are two atrioventricular valves, located between the atrium and the ventricle on either side of the heart: The tricuspid valve on the right has three cusps, the mitral valve on the left has two. The other two valves regulate blood flow out of the heart. The aortic valve manages blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta. The pulmonary valve manages blood flow out of the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk into the pulmonary arteries.
Read Also: Flonase Heart Racing
The Four Chambers Of The Heart
Your heart has a right and left side separated by a wall called the septum. Each side has a small collecting chamber called an atrium, which leads into a large pumping chamber called a ventricle. There are four chambers: the left atrium and right atrium , and the left ventricle and right ventricle .The right side of your heart collects blood on its return from the rest of our body. The blood entering the right side of your heart is low in oxygen. Your heart pumps the blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs so it can receive more oxygen. Once it has received oxygen, the blood returns directly to the left side of your heart, which then pumps it out again to all parts of your body through an artery called the aorta. Blood pressure refers to the amount of force the pumping blood exerts on arterial walls.
How Do Blood Circulate In The Heart
Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the bodys tissues through the aorta.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate When Exercising
What Kind Of Blood Comes Back Into The Heart & Then Goes To The Lungs
The heart consists of four chambers in which blood flows. Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is brought back to the heart by the pulmonary veins which enter the left atrium.
What Carries Deoxygenated Blood
The pulmonary circulation is the portion of the circulatory system which carries deoxygenated blood away from the right ventricle, to the lungs, and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium and ventricle of the heart.
You may ask, Do arteries carry oxygenated blood?
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the tissues, except for pulmonary arteries, which carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation . There are two types of unique arteries.
Don’t Miss: Which Of The Following Signs Is Commonly Observed In Patients With Right-sided Heart Failure
Why Blood Pressure In Pulmonary Artery Is More Than That In Pulmonary Vein
The blood in the pulmonary arteries is pumped by the right ventricle of the heart. Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart and enter the left atrium. Since the blood in the pulmonary arteries is pumped by the heart, it flows under greater pressure than the blood in the pulmonary veins.
Components Of The Aorta
The aortic arch contains peripheral baroreceptors and chemoreceptors that relay information concerning blood pressure, blood pH, and carbon dioxide levels to the medulla oblongata of the brain. This information is processed by the brain and the autonomic nervous system mediates the homeostatic responses that involve feedback in the lungs and kidneys. The aorta extends around the heart and travels downward, diverging into the iliac arteries. The five components of the aorta are:
You May Like: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
How Does Blood Move Through The Heart
Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the bodys tissues through the aorta.
There are multiple functions going on in our bodies simultaneously. For smooth functioning and better coordination between organs, each work inside the body is differentiated so that the whole body works flawlessly.
One of the main functions of our body is the transportation of blood to and from the heart. There are two types of blood vessels arteries and veins in the circulatory system involved in carrying blood to the heart and away from the heart.
Arteries and veins, though they belong to the circulatory system, differs in their functionality and speciality. In this article, we will be looking at what exactly arteries and veins are and what are their significant differences.
Recommended Reading: Is Your Pulse And Heart Rate The Same Thing
How Does The Circulatory System Work
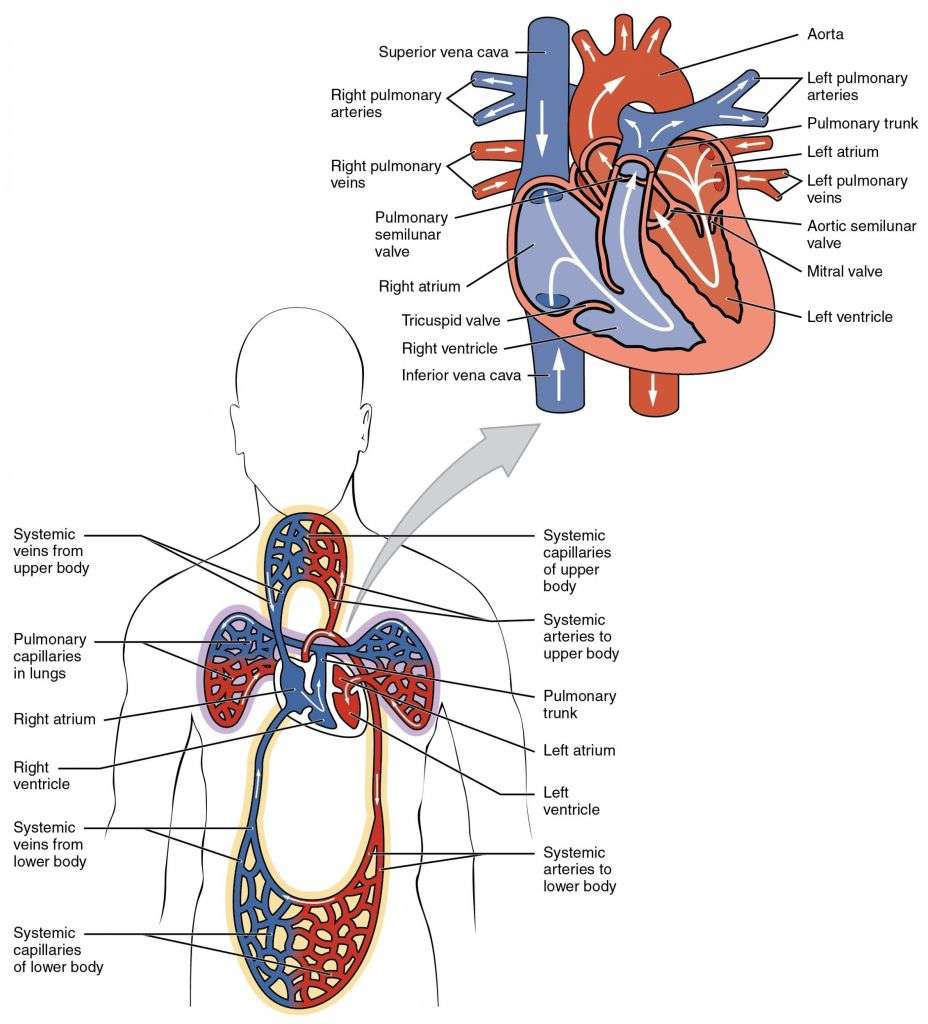
Your circulatory system functions with the help of blood vessels that include arteries, veins and capillaries. These blood vessels work with your heart and lungs to continuously circulate blood through your body. Heres how:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
