What Are The 4 Chambers And 4 Valves Of The Heart
The 4 heart valves are:
- Tricuspid valve. This valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
- Pulmonary valve. The pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
- Mitral valve. This valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
- Aortic valve.
What Is The 4 7 8 Sleep Trick
The 4-7-8 breathing technique, also known as relaxing breath, involves breathing in for 4 seconds, holding the breath for 7 seconds, and exhaling for 8 seconds. This breathing pattern aims to reduce anxiety or help people get to sleep. Some proponents claim that the method helps people get to sleep in 1 minute.
How The Heart Works
The human heart pumps blood to every part of your body. Learn about the different parts of the heart and watch our video about how a healthy heart works.
Your heart is the pump which powers your body. It supplies blood carrying oxygen and nutrients to every cell, nerve, muscle and vital organ in your body.
It sits in your chest between your lungs, slightly to the left of centre, and is protected by your rib cage.
Your heart is about the size of your clenched fist and weighs about 300 grams .
Watch our step-by-step video of how the heart works
Recommended Reading: Does A Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
The Heart Wall Is Composed Of Three Layers
The muscular wall of the heart has three layers. The outermost layer is the epicardium . The epicardium covers the heart, wraps around the roots of the great blood vessels, and adheres the heart wall to a protective sac. The middle layer is the myocardium. This strong muscle tissue powers the hearts pumping action. The innermost layer, the endocardium, lines the interior structures of the heart.
The Four Chambers Of The Heart
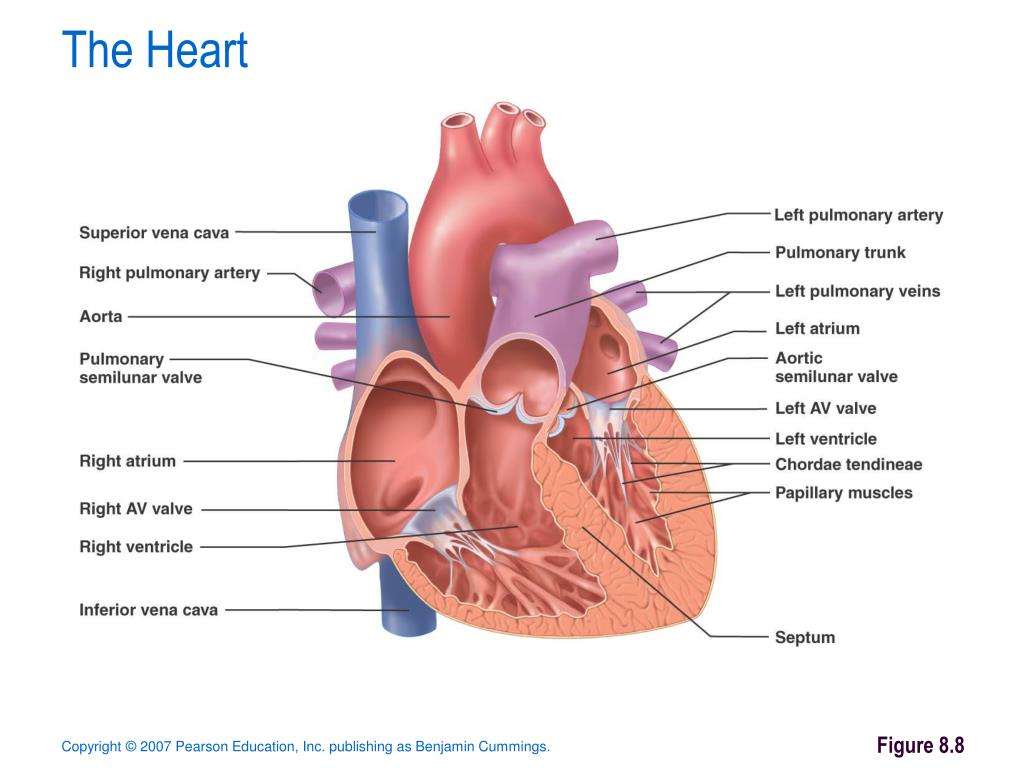
Your heart has a right and left side separated by a wall called the septum. Each side has a small collecting chamber called an atrium, which leads into a large pumping chamber called a ventricle. There are four chambers: the left atrium and right atrium , and the left ventricle and right ventricle .The right side of your heart collects blood on its return from the rest of our body. The blood entering the right side of your heart is low in oxygen. Your heart pumps the blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs so it can receive more oxygen. Once it has received oxygen, the blood returns directly to the left side of your heart, which then pumps it out again to all parts of your body through an artery called the aorta. Blood pressure refers to the amount of force the pumping blood exerts on arterial walls.
Read Also: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Does The Heart Look Like And How Does It Work
- The heart is an amazing organ. It starts beating about 22 days after conception and continuously pumps oxygenated red blood cells and nutrient-rich blood and other compounds like platelets throughout your body to sustain the life of your organs.
- Its pumping power also pushes blood through organs like the lungs to remove waste products like CO2.
- This fist-sized powerhouse beats about 100,000 times per day, pumping five or six quarts of blood each minute, or about 2,000 gallons per day.
- In general, if the heart stops beating, in about 4-6 minutes of no blood flow, brain cells begin to die and after 10 minutes of no blood flow, the brain cells will cease to function and effectively be dead. There are few exceptions to the above.
- The heart works by a regulated series of events that cause this muscular organ to contract and then relax .
- The normal heart has 4 chambers that undergo the squeeze and relax cycle at specific time intervals that are regulated by a normal sequence of electrical signals that arise from specialized tissue.
- In addition, the normal sequence of electrical signals can be sped up or slowed down depending on the needs of the individual, for example, the heart will automatically speed up electrical signals to respond to a person running and will automatically slow down when a person takes a nap.
What Are The Most Important Parts Of The Heart
What Are the Parts of the Heart?
- The two bottom chambers are the right ventricle and the left ventricle. These pump blood out of the heart. A wall called the interventricular septum is between the two ventricles.
- The two top chambers are the right atrium and the left atrium. They receive the blood entering the heart.
Also Check: Can This 10 Second Trick Prevent Your Heart Attack
How Does Your Heart Work
Your heart is made up of 2 pumps. The pump on the right hand side receives blood that has already delivered its oxygen round the body and sends this blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen .
The pump on the left hand side receives oxygen-rich blood and then pumps it out into the arteries to deliver its oxygen around the body.
What Are The 3 Main Functions Of The Heart
What are the four main functions of the heart?
- Pumping oxygenated blood to the other body parts.
- Pumping hormones and other vital substances to different parts of the body.
- Receiving deoxygenated blood and carrying metabolic waste products from the body and pumping it to the lungs for oxygenation.
- Maintaining blood pressure.
Recommended Reading: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
Left Side Of The Heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
What Controls The Unidirectional Flow Of The Blood From One Chamber To Another
After you have got an answer to the main question, What are the four chambers of the human heart? it is pertinent to discuss how different chambers of the heart ensure the unidirectional flow of the blood. It is due to the presence of the heart valves that the pumping organ prevents the backflow of the blood.
There are four heart valves in total, namely, the bicuspid valve, the tricuspid valve, the aortic valve, and the pulmonary valve. The bicuspid and the tricuspid valves lie between the atria and the ventricles. The aortic valve lies between the left ventricle and the aorta, and the pulmonary valve is present between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Right Ventricle Sends Blood Needing Oxygen To The Lungs
The blood needing oxygen is pumped out of the right ventricle, through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery then divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries, carrying blood to the right and left lungs. In the lungs the blood gives up its carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen.
The Right Side Of The Heart
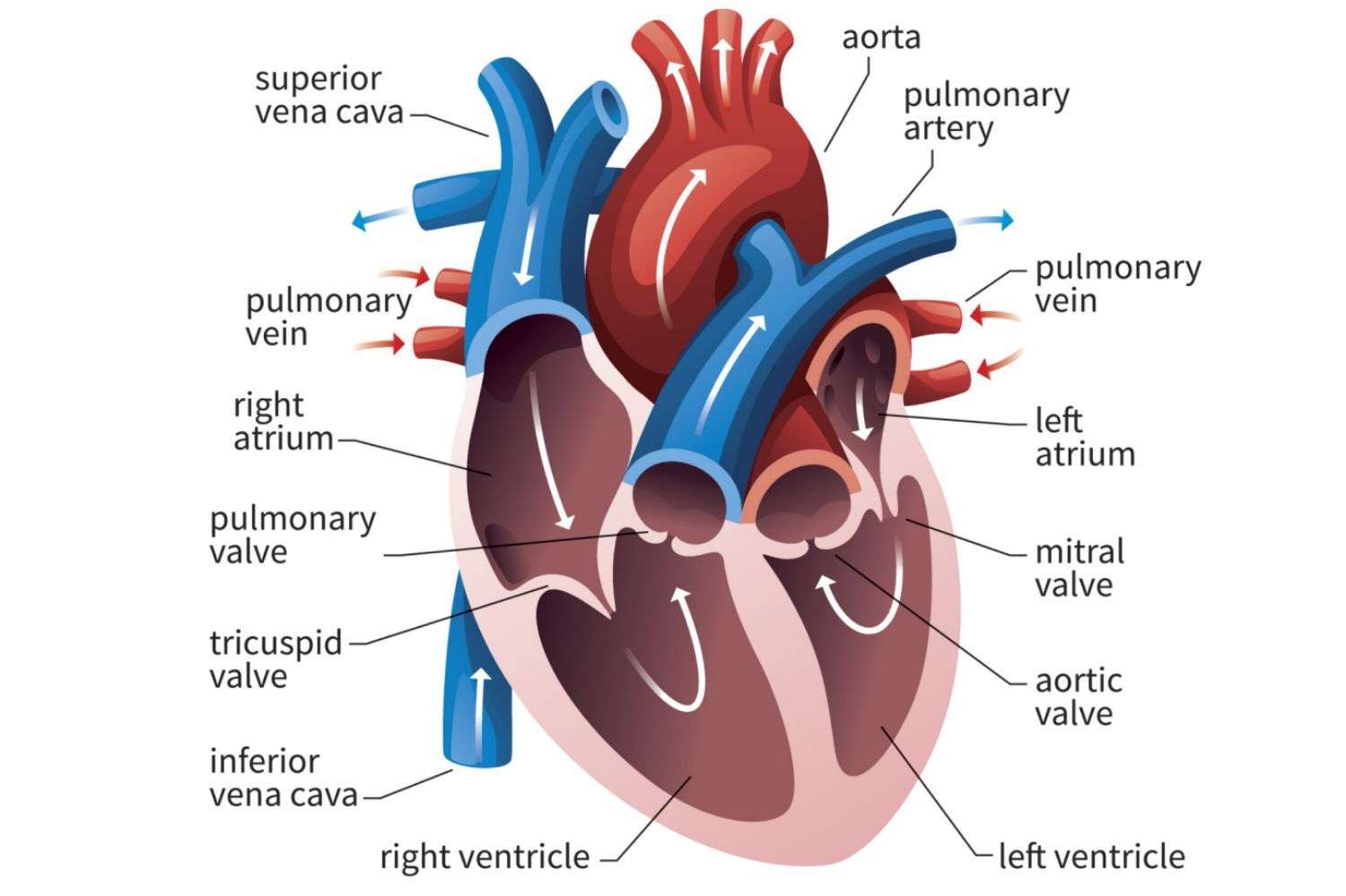
The superior and inferior vena cavae are in blue to the left of the muscle as you look at the picture. These veins are the largest veins in the body. They carry used blood to the right atrium of the heart.
Used blood has had its oxygen removed and used by the bodys organs and tissues. The superior vena cava carries used blood from the upper parts of the body, including the head, chest, arms, and neck. The inferior vena cava carries used blood from the lower parts of the body.
The used blood from the vena cavae flows into the hearts right atrium and then on to the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, the used blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. Here, through many small, thin blood vessels called capillaries, the blood picks up oxygen needed by all the areas of the body.
The oxygen-rich blood passes from the lungs back to the heart through the pulmonary veins .
Don’t Miss: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate When Exercising
What Are The Four Chambers Of Human Heart
A powerful natural pump in your body, the heart uses its chambers to manage the flow of blood in two distinct circuits, i.e. the systemic and pulmonary bloodstreams. Like the brain, the heart continues working tirelessly without stopping for a second and it makes the blood flow through all the blood vessels in your body in one minute! So, what are the four chambers of human heart? Read on to find useful information on the topic.
Heres youll get answers to the questions, like:
- How does the heart manage the flow of blood in two distinct circuits?
- What are the four chambers of the heart?
- What controls the unidirectional flow of the blood from one chamber to another?
Richard Klabunde, the author of Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts, contradicts the idea that the heart is solely responsible for pumping the blood through the organs of your body. According to the researcher, the heart as a pump only receives the blood from the venous blood vessels at low pressure, raises it to a higher pressure by contracting around it within the heart chambers, and then pushes it into the arterial blood vessels.
So, the flow of the blood is not driven by the output of the pumping organ by itself, but rather by the pressure that is generated within the arterial system as the heart pumps the blood into the vast network of vessels.
What Part Of The Heart Pumps Blood To The Body
4.2/5side of the heart pumps bloodside of the heartbloodpumpsbodyread here
The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Likewise, how does a heart pump blood? The right side of your heart gets blood from your body and pumps it into your lungs. Oxygen-poor blood flows in through the large veins to the right atrium. Then the blood moves into the right ventricle, which contracts and sends blood out of your heart to pick up oxygen from your lungs.
One may also ask, which part of the heart pumps blood to all parts of the body?
The left side of your heart receives oxygen-rich blood from your lungs and pumps it through your arteries to the rest of your body.
What pumps blood to the lungs?
The heart has a total of four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle. The right side of the heart collects oxygen-depleted blood and pumps it to the lungs, through the pulmonary arteries, so that the lungs can refresh the blood with a fresh supply of oxygen.
Don’t Miss: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Supplying Oxygen To The Hearts Muscle
Like other muscles in the body, your heart needs blood to get oxygen and nutrients. Yourcoronary arteries supply blood to your heart. These arteries branch off from the aorta so that oxygen-rich blood is delivered to your heart as well as the rest of your body.
- The left coronary artery delivers blood to the left side of your heart, including your left atrium and ventricle and the septum between the ventricles.
- The circumflex artery branches off from the left coronary artery to supply blood to part of the left ventricle.
- The left anterior descending artery also branches from the left coronary artery and provides blood to parts of both the right and left ventricles.
- The right coronary artery provides blood to the right atrium and parts of both ventricles.
- The marginal arteries branch from the right coronary artery and provide blood to the surface of the right atrium.
- The posterior descending artery also branches from the right coronary artery and provides blood to the bottom of both ventricles.
Arteries supplying oxygen to the body. The coronary arteries branch off the aorta and supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. At the top of your aorta, arteries branch off to carry blood to your head and arms. Arteries branching from the middle and lower parts of your aorta supply blood to the rest of your body.
Some conditions can affect normal blood flow through these heart arteries. Examples include:
- The small cardiac vein.
What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
The left ventricle is the major muscular pump
What heart chamber pumps blood through the aortic semilunar valve?
From there, blood is forced through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. This is the muscular pump that sends blood out to the rest of the body. When the left ventricle contracts, it forces blood through the aortic semilunar valve and into the aorta.
What is the chamber that pushes blood through the aortic valve? The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs through the pulmonary valve. The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle through the mitral valve. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve out to the rest of the body.
What Chamber is the aortic semilunar valve?
The valve between the left ventricle and the aorta is the aortic semilunar valve. When the ventricles contract, atrioventricular valves close to prevent blood from flowing back into the atria.
Also Check: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Blood Supply To The Myocardium
The myocardium of the heart wall is a working muscle that needs a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients to function efficiently. For this reason, cardiac muscle has an extensive network of blood vessels to bring oxygen to the contracting cells and to remove waste products.
The right and left coronary arteries, branches of the ascending aorta, supply blood to the walls of the myocardium. After blood passes through the capillaries in the myocardium, it enters a system of cardiac veins. Most of the cardiac veins drain into the coronary sinus, which opens into the right atrium.
Electrical Impulses Keep The Beat
The heart’s four chambers pump in an organized manner with the help of electrical impulses that originate in the sinoatrial node . Situated on the wall of the right atrium, this small cluster of specialized cells is the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses at a normal rate.
The impulse spreads through the walls of the right and left atria, causing them to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node, which acts as an electrical bridge for impulses to travel from the atria to the ventricles. From there, a pathway of fibers carries the impulse into the ventricles, which contract and force blood out of the heart.
Don’t Miss: Flonase And Heart Palpitations
What Are The Coronary Arteries Of The Heart
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, side and back of the left ventricle, and the left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
Coronary artery disease occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries and prevents the heart from getting the enriched blood it needs. If this happens, a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open called collateral vessels may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
Structure Of The Heart
The human heart is a four-chambered muscular organ, shaped and sized roughly like a man’s closed fist with two-thirds of the mass to the left of midline.
The heart is enclosed in a pericardial sac that is lined with the parietal layers of a serous membrane. The visceral layer of the serous membrane forms the epicardium.
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
The Left Side Of The Heart
Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs passes through the pulmonary veins . It enters the left atrium and is pumped into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, the blood is pumped to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Like all of the organs, the heart needs blood rich with oxygen. This oxygen is supplied through the coronary arteries as its pumped out of the hearts left ventricle.
The coronary arteries are located on the hearts surface at the beginning of the aorta. The coronary arteries carry oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the heart.
How The Healthy Heart Works
The normal heart is a strong, hard-working pump made of muscle tissue. It’s about the size of a person’s fist.
The heart has four chambers. The upper two chambers are the atria, and the lower two are the ventricles . The chambers are separated by a wall of tissue called the septum. Blood is pumped through the chambers, aided by four heart valves. The valves open and close to let the blood flow in only one direction.
Congenital defects may involve a valve, a chamber, the septum, an artery or blood flow issues.
The four heart valves are:
Each valve has a set of “flaps” . The mitral valve normally has two flaps the others have three.
You May Like: How Do You Say Heart Attack In Spanish
