How Your Heart Works
Your heart
The human heart is one of the hardest-working organs in the body.
On average, it beats around 75 times a minute. As the heart beats, it provides pressure so blood can flow to deliver oxygen and important nutrients to tissue all over your body through an extensive network of arteries, and it has return blood flow through a network of veins.
In fact, the heart steadily pumps an average of 2,000 gallons of blood through the body each day.
Your heart is located underneath your sternum and ribcage, and between your two lungs.
The hearts four chambers function as a double-sided pump, with an upper and continuous lower chamber on each side of the heart.
The hearts four chambers are:
- Right atrium. This chamber receives venous oxygen-depleted blood that has already circulated around through the body, not including the lungs, and pumps it into the right ventricle.
- Right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood from the right atrium to the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery sends the deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen in exchange for carbon dioxide.
- Left atrium. This chamber receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins of the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
- Left ventricle. With the thickest muscle mass of all the chambers, the left ventricle is the hardest pumping part of the heart, as it pumps blood that flows to the heart and rest of the body other than the lungs.
The Four Chambers Of The Heart
Your heart has a right and left side separated by a wall called the septum. Each side has a small collecting chamber called an atrium, which leads into a large pumping chamber called a ventricle. There are four chambers: the left atrium and right atrium , and the left ventricle and right ventricle .The right side of your heart collects blood on its return from the rest of our body. The blood entering the right side of your heart is low in oxygen. Your heart pumps the blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs so it can receive more oxygen. Once it has received oxygen, the blood returns directly to the left side of your heart, which then pumps it out again to all parts of your body through an artery called the aorta. Blood pressure refers to the amount of force the pumping blood exerts on arterial walls.
Which Part Of The Heart Pumps Blood To The Lungs
heart pumps blood to the lungsheartbloodlungspumps
In this regard, which chamber of the heart pumps blood to the lungs?
right ventricle
Similarly, which part of the heart pumps blood into the ventricles? Function. During systole, the ventricles contract, pumping blood through the body. During diastole, the ventricles relax and fill with blood again. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium via the mitral valve and pumps it through the aorta via the aortic valve, into the systemic circulation.
Herein, how does blood flow through the heart to the lungs?
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs where it is oxygenated.
What prevents backflow of blood in the heart?
The pulmonary valve sits between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. Its role is to prevent the backflow of blood into the right ventricle after it contracts. The aortic valve sits between the left ventricle and the aorta and prevents backflow of blood into the left ventricle after it contracts.
Also Check: Dangers Of Exceeding Maximum Heart Rate
How Does The Heart Beat
The atria and ventricles work together, alternately contracting and relaxing to pump blood through your heart. The electrical system of the heart is the power source that makes this possible.
Your heartbeat is triggered by electrical impulses that travel down a special pathway through the heart.
- The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells called the SA node , located in the right atrium. This node is known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The electrical activity spreads through the walls of the atria and causes them to contract.
- A cluster of cells in the center of the heart between the atria and ventricles, the AV node is like a gate that slows the electrical signal before it enters the ventricles. This delay gives the atria time to contract before the ventricles do.
- The His-Purkinje network is a pathway of fibers that sends the impulse to the muscular walls of the ventricles, causing them to contract.
At rest, a normal heart beats around 50 to 90Ã times a minute. Exercise, emotions, fever, and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster, sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute.
How Can I Protect My Heart And Pulmonary Arteries
Many of the conditions that affect the pulmonary arteries are present at birth. While you cant prevent these problems, these actions can promote better heart health:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Get at least 150 minutes of cardiovascular physical activity every week.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Read Also: What Are The Early Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
The Cardiac Cycle Includes All Blood Flow Events The Heart Accomplishes In One Complete Heartbeat
The muscular wall of the heart powers contraction and dilation. Each contraction and relaxation is a heartbeat. Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out of the heart through the pulmonary and aortic valves. Diastole occurs when blood flows from the atria to fill the ventricles.
The Valves Are Like Doors To The Chambers Of The Heart
Four valves regulate and support the flow of blood through and out of the heart. The blood can only flow one waylike a car that must always be kept in drive. Each valve is formed by a group of folds, or cusps, that open and close as the heart contracts and dilates. There are two atrioventricular valves, located between the atrium and the ventricle on either side of the heart: The tricuspid valve on the right has three cusps, the mitral valve on the left has two. The other two valves regulate blood flow out of the heart. The aortic valve manages blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta. The pulmonary valve manages blood flow out of the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk into the pulmonary arteries.
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Which Heart Chamber Sends Deoxygenated Blood To The Lungs
4.4/5right ventricleright atriumleft ventricleleft atrium
Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs, and then re-enters the heart Deoxygenated blood leaves through the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery. From the right atrium, the blood is pumped through the tricuspid valve , into the right ventricle.
One may also ask, which heart chamber receives blood from the pulmonary veins quizlet? left atrium
Also asked, which part of the heart pumps blood to the lungs?
The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The left side of the heart receives the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the body.
How does oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flow through the heart?
Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body. From the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart.
What Are The Parts Of The Heart
Your heart is a bit like a house. It has:
- outer walls
- electrics .
Heart walls
The walls of your heart are made of powerful muscle tissue, which squeezes and relaxes to pump blood around your body. This muscle tissue is divided into three layers.
- The endocardium .
- The myocardium .
- The epicardium .
Heart chambers
Your heart is made up of four chambers, two on the right and two on the left. These are like the rooms of your house.
The top two chambers are called the left and right atrium and the bottom two are called the left and right ventricles.
They are divided by a thin wall called the .
Heart valves
There are four heart valves, which act like doors between the chambers of the heart. They open and close as your heart pumps.
The valves only open one way. This stops blood flowing in the wrong direction between the chambers of your heart.
The two valves that sit between the upper and lower chambers of the heart are called the atrioventricular, or AV valves.
The tricuspid valve is the door between the right atrium and ventricle.
The mitral valve is the door between the left atrium and ventricle.
The other two valves are the doors out of the ventricles. They are called semilunar, or SL valves.
The aortic valve is the door out of the left ventricle into the aorta.
The pulmonary valve is the door out of the right ventrical into the pulmonary artery.
The blood vessels
How the heart pumps
The heart’s conduction system
How the heart pumps
The coronary arteries
Recommended Reading: Claritin Heart Racing
What Are The Symptoms Of Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Often, there are no symptoms associated with these defects. The defects are usually found during routine physical examinations. In cases where there are symptoms, they may include:
- Trouble breathing.
- Bluish tones to the skin .
- Poor eating habits.
- Swelling in the abdomen or around the eyes.
- Rapid heartbeat.
How Does My Heart Pump Blood
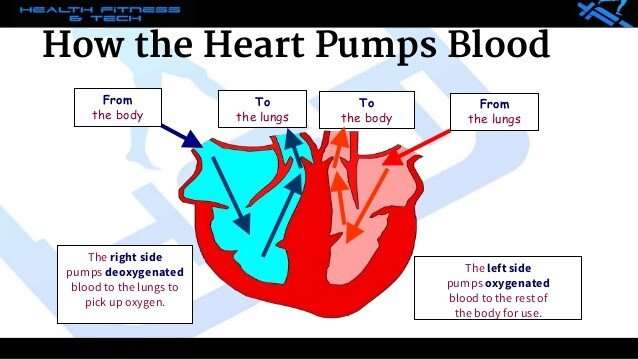
Your heart is divided into two separate pumping systems, the right side and the left side.
- The right side of your heart receives oxygen-poor blood from your veins and pumps it to your lungs, where it picks up oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
- The left side of your heart receives oxygen-rich blood from your lungs and pumps it through your arteries to the rest of your body.
Your heart has four separate chambers that pump blood, two on the right side and two on the left.
Don’t Miss: Does Acetaminophen Raise Your Blood Pressure
What Are The Parts Of The Circulatory System
Two pathways come from the heart:
- The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again.
- The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
In pulmonary circulation:
- The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide. The blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
In systemic circulation:
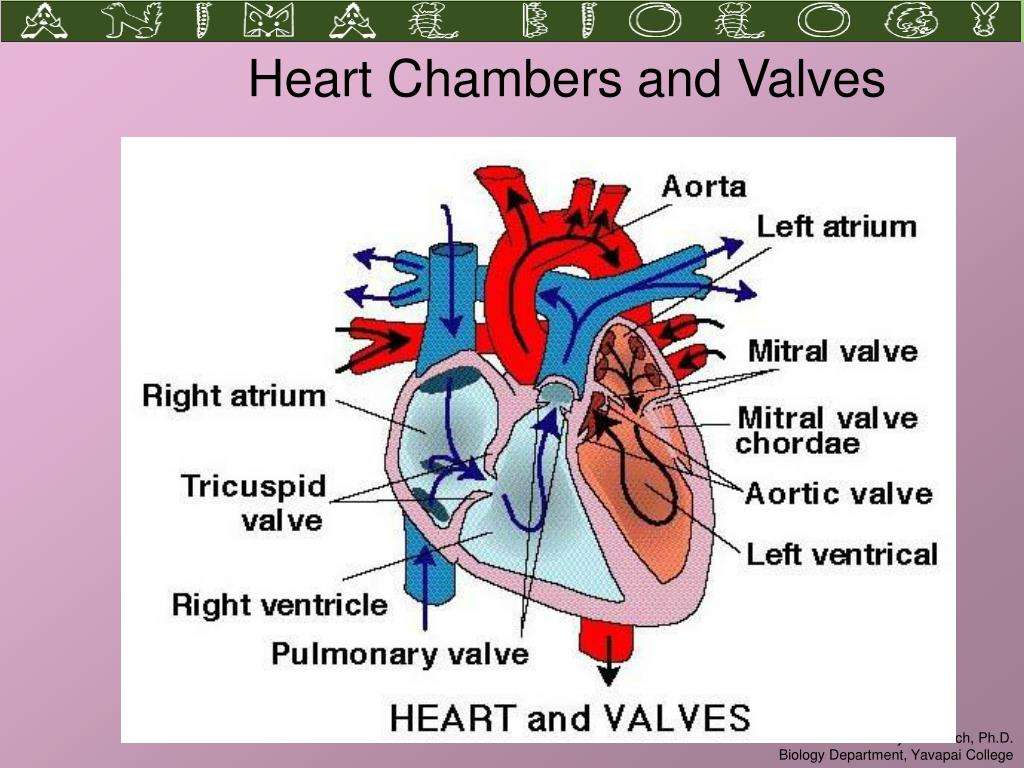
Hearts Chambers And Valves
The heart has two sides. The right side of the heart accepts used blood that is returning from the tissues of the body, and pumps that blood into the lungs, where it is replenished with oxygen. The left side of the heart accepts replenished blood from the lungs, and then pumps that blood out to all the bodys organs.
Each side of the heart has two chambers, for a total of four chambers. The two ventricles are muscular chambers capable of propelling the blood out of the heart. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood to all other organs.
The two atria accept the blood returning to the heart . At just the right moment, the right and left atria empty their accumulated blood into the right and left ventricles.
The four heart valves open and close at just the right moment to keep the blood moving in the proper direction through the heart.
It is helpful to visualize the heart functioning as two separate pumps, working in series the right heart pump, and the left heart pump.
Read Also: Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Symptoms
+ Diagram Of The Heart Oxygenated And Deoxygenated Blood
11+ Diagram Of The Heart Oxygenated And Deoxygenated Blood. Letâs examine the anatomy of the heart along with some diagrams that show how the heart operates. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools.
An online interactive study guide to tutorials and quizzes on the anatomy and physiology of the heart, using interactive animations and diagrams. The heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Excess interstitial fluid is then.
You May Like: How To Calculate Max Hr
How Can You Prevent Heart Attacks And Strokes
According to the American Heart Association, no matter what age you are, your heart can benefit from a healthy diet and adequate physical activity. Tthere are numerous specific suggestions about how you can decrease your risk for heart disease. For example:
- Lower cholesterol .
- Lower tryglicerides.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Right Ventricle Sends Blood Needing Oxygen To The Lungs
The blood needing oxygen is pumped out of the right ventricle, through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery then divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries, carrying blood to the right and left lungs. In the lungs the blood gives up its carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen.
Left Side Of The Heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
Read Also: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Which Of The Following Heart Chambers Pump Oxygenated Blood To The Body
From the left atrium blood flows into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the blood to the aorta which will distribute the oxygenated blood to all parts of the body.
Also to know is, which chamber pumps blood to the body?
The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Secondly, which heart chamber contains oxygenated blood quizlet? The left atrium, pulmonary veins, and aorta all contain oxygenated blood.
Likewise, which chamber of heart is oxygenated and deoxygenated blood found?
The right and left atria are the top chambers of the heart and receive blood into the heart. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation and the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary circulation.
Where does the left ventricle pump blood to?
The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium via the mitral valve and pumps it through the aorta via the aortic valve, into the systemic circulation.
You May Like Also
Blood Vessels Of The Heart
The blood vessels of the heart include:
- venae cavae deoxygenated blood is delivered to the right atrium by these two veins. One carries blood from the head and upper torso, while the other carries blood from the lower body
- pulmonary arteries deoxygenated blood is pumped by the right ventricle into the pulmonary arteries that link to the lungs
- pulmonary veins the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
- aorta this is the largest artery of the body, and it runs the length of the trunk. Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta subdivides into various branches that deliver blood to the upper body, trunk and lower body
- coronary arteries like any other organ or tissue, the heart needs oxygen. The coronary arteries that supply the heart are connected directly to the aorta, which carries a rich supply of oxygenated blood
- coronary veins deoxygenated blood from heart muscle is ‘dumped’ by coronary veins directly into the right atrium.
Don’t Miss: Fitbit 2 Heart Rate
Structure Of The Heart
The heart has four chambers . There is a wall between the two atria and another wall between the two ventricles. Arteries and veins go into and out of the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood to the heart. The flow of blood through the vessels and chambers of the heart is controlled by valves.
Electrical Impulses Keep The Beat
The heart’s four chambers pump in an organized manner with the help of electrical impulses that originate in the sinoatrial node . Situated on the wall of the right atrium, this small cluster of specialized cells is the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses at a normal rate.
The impulse spreads through the walls of the right and left atria, causing them to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node, which acts as an electrical bridge for impulses to travel from the atria to the ventricles. From there, a pathway of fibers carries the impulse into the ventricles, which contract and force blood out of the heart.
Don’t Miss: What Is An Unsafe Heart Rate
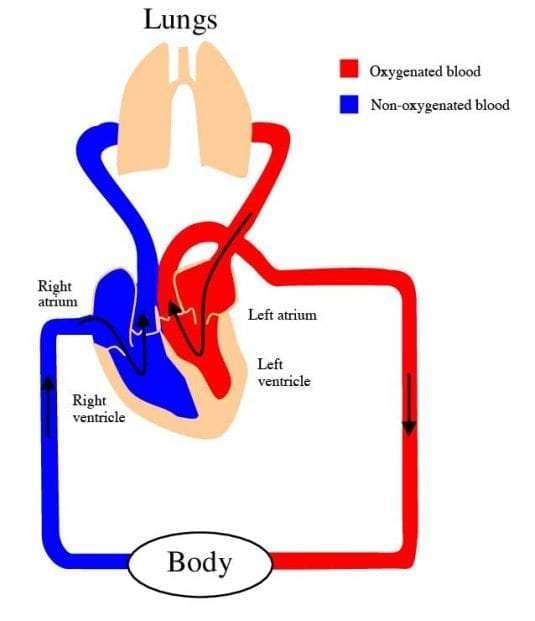
The Systemic Loop Goes All Over The Body
In the systemic loop, oxygenated blood is pumped from the left ventricle of the heart through the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The blood moves from the aorta through the systemic arteries, then to arterioles and capillary beds that supply body tissues. Here, oxygen and nutrients are released and carbon dioxide and other waste substances are absorbed. Deoxygenated blood then moves from the capillary beds through venules into the systemic veins. The systemic veins feed into the inferior and superior venae cavae, the largest veins in the body. The venae cavae flow deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart.
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
