What Is The Pathway Of Oxygenated And Deoxygenated Blood
Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle, through the arteries, to the capillaries in the tissues of the body. From the tissue capillaries, the deoxygenated blood returns through a system of veins to the right atrium of the heart.
You may ask, How does blood flow through the heart Simple?
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs where it is oxygenated.
How Can You Prevent Heart Attacks And Strokes
According to the American Heart Association, no matter what age you are, your heart can benefit from a healthy diet and adequate physical activity. Tthere are numerous specific suggestions about how you can decrease your risk for heart disease. For example:
- Lower cholesterol .
- Lower tryglicerides.
What Does The Circulatory System Do
The circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart.
The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, and to cells, and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide. These roadways travel in one direction only, to keep things going where they should.
You May Like: List The Steps Of How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart To The Lungs
- Once blood travels through the pulmonic valve, it enters your lungs. This is called the pulmonary circulation.
- From your pulmonic valve, blood travels to the pulmonary artery to tiny capillary vessels in the lungs.
- Here, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood.
- At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, passes from the blood into the air sacs.
- Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale.
- Once the blood is purified and oxygenated, it travels back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Each Heart Beat Is A Squeeze Of Two Chambers Called Ventricles
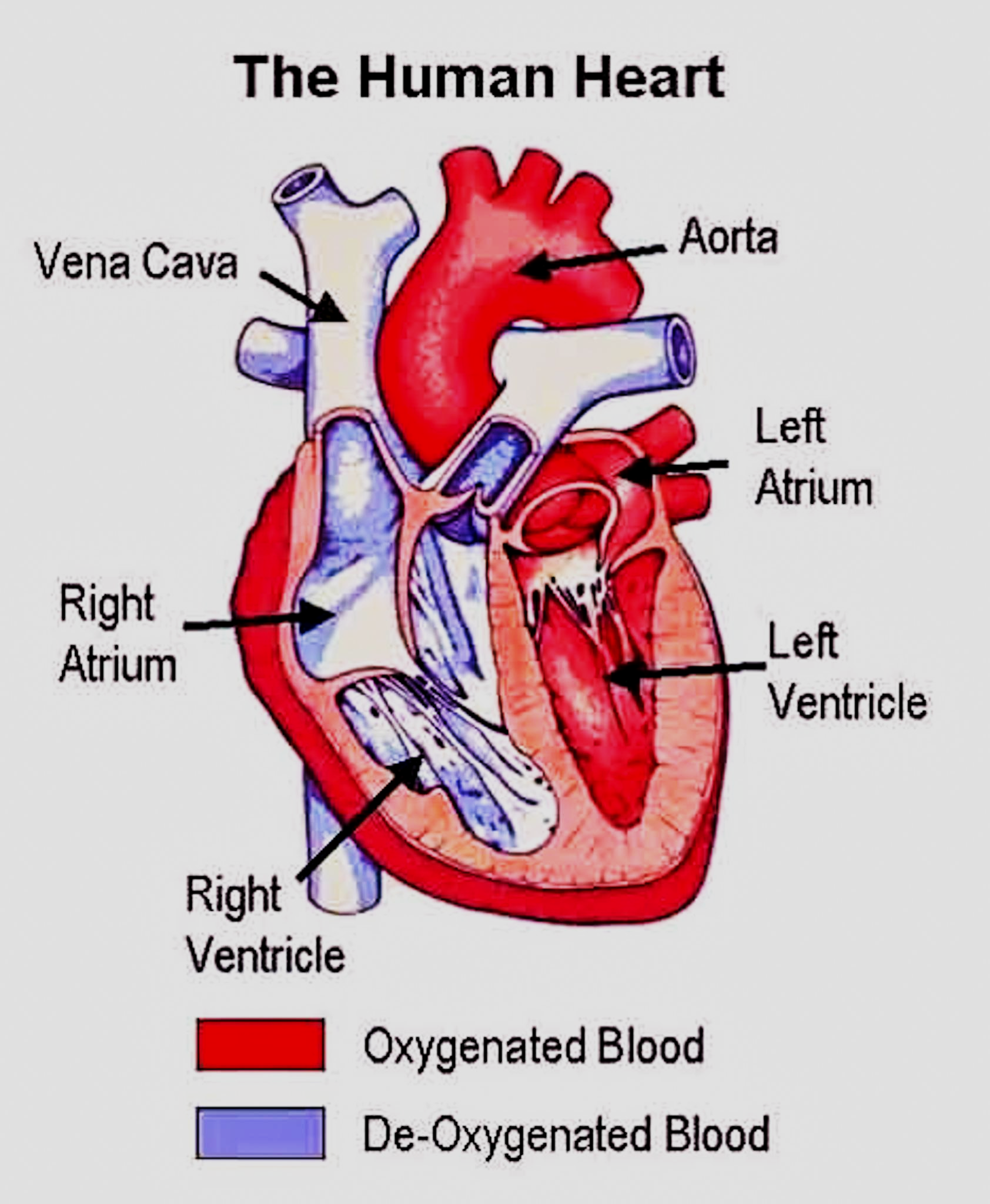
The ventricles are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood empties into each ventricle from the atrium above, and then shoots out to where it needs to go. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, then pumps the blood along to the lungs to get oxygen. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium, then sends it on to the aorta. The aorta branches into the systemic arterial network that supplies all of the body.
Recommended Reading: Can Acid Reflux Cause Palpitations
The Valves Are Like Doors To The Chambers Of The Heart
Four valves regulate and support the flow of blood through and out of the heart. The blood can only flow one waylike a car that must always be kept in drive. Each valve is formed by a group of folds, or cusps, that open and close as the heart contracts and dilates. There are two atrioventricular valves, located between the atrium and the ventricle on either side of the heart: The tricuspid valve on the right has three cusps, the mitral valve on the left has two. The other two valves regulate blood flow out of the heart. The aortic valve manages blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta. The pulmonary valve manages blood flow out of the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk into the pulmonary arteries.
Electrical Impulses Keep The Beat
The heart’s four chambers pump in an organized manner with the help of electrical impulses that originate in the sinoatrial node . Situated on the wall of the right atrium, this small cluster of specialized cells is the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses at a normal rate.
The impulse spreads through the walls of the right and left atria, causing them to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node, which acts as an electrical bridge for impulses to travel from the atria to the ventricles. From there, a pathway of fibers carries the impulse into the ventricles, which contract and force blood out of the heart.
Recommended Reading: Acid Reflux Heart Fluttering
How Does Oxygenated And Deoxygenated Blood Flow Through The Heart
heartoxygenated bloodof thecirculationdeoxygenated bloodheartof thecirculation
People Also Asked, How does oxygenated blood flow through the heart?
Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is brought back to the heart by the pulmonary veins which enter the left atrium. From the left atrium blood flows into the left ventricle.
Also know, what parts of the heart are oxygenated and deoxygenated? The left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary vein and pumps it into the aorta, while the right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava and pumps it into the pulmonary vein.
Contents
Why Is It Much Easier To Stop Blood Flowing From A Vein Than An Artery
Have thinner walls and lower pressure on the inside. The lower pressure can make it more difficult for the blood to return to the heart, so veins have one-way valves in them to prevent blood from pooling or flowing backward because of gravity or other forces. Have a wider diameter than arteries and can hold more blood.
Also Check: How Does Heart Disease Affect The Skeletal System
How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart
The right and left sides of the heart work together. The pattern described below is repeated over and over, causing blood to flow continuously to the heart, lungs, and body.
Right side of the heart
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the right atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
Left side of the heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
Which Blood Vessels Permit The Exchange Of Oxygen Carbon Dioxide
Exchange of Gases, Nutrients, and Waste Between Blood and Tissue Occurs in the Capillaries. Capillaries are tiny vessels that branch out from arterioles to form networks around body cells. In the lungs, capillaries absorb oxygen from inhaled air into the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide for exhalation.
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
The Interior Of The Heart
Below is a picture of the inside of a normal, healthy, human heart.
The illustration shows a cross-section of a healthy heart and its inside structures. The blue arrow shows the direction in which low-oxygen blood flows from the body to the lungs. The red arrow shows the direction in which oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs to the rest of the body.
Heart Chambers And Circulation Through The Heart
The human heart consists of four chambers: The left side and the right side each have one atrium and one ventricle. Each of the upper chambers, the right atrium and the left atrium, acts as a receiving chamber and contracts to push blood into the lower chambers, the right ventricle and the left ventricle. The ventricles serve as the primary pumping chambers of the heart propelling blood to the lungs or to the rest of the body.
There are two distinct but linked circuits in the human circulation called the pulmonary and systemic circuits. The pulmonary circuit transports blood to and from the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and delivers carbon dioxide for exhalation. The systemic circuit transports oxygenated blood to virtually all of the tissues of the body and returns to the heart.
The blood that has traveled throughout the body is lower in oxygen concentration than when it entered. The superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava return blood to the right atrium. The blood in the superior and inferior venae cavae flows into the right atrium, which delivers blood into the right ventricle. This process of blood circulation continues as long as the individual remains alive. .
- Cardiovascular System Module 3: Heart Anatomy. : Donna Browne. Provided by: OpenStaxCollege. Located at: . License: CC BY: Attribution
You May Like: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, as well as the side and back of the left ventricle. The left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
The Four Chambers Of The Heart
Your heart has a right and left side separated by a wall called the septum. Each side has a small collecting chamber called an atrium, which leads into a large pumping chamber called a ventricle. There are four chambers: the left atrium and right atrium , and the left ventricle and right ventricle .The right side of your heart collects blood on its return from the rest of our body. The blood entering the right side of your heart is low in oxygen. Your heart pumps the blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs so it can receive more oxygen. Once it has received oxygen, the blood returns directly to the left side of your heart, which then pumps it out again to all parts of your body through an artery called the aorta. Blood pressure refers to the amount of force the pumping blood exerts on arterial walls.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Where Does Deoxygenated Blood Enter The Heart
Deoxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs, and then re-enters the heart Deoxygenated blood leaves through the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery. From the right atrium, the blood is pumped through the tricuspid valve , into the right ventricle.
Beside above, where does blood enter the heart? Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
Hereof, where does deoxygenated blood enter the heart quizlet?
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the superior vena cava. 2. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the inferior vena cava.
Where does blood become deoxygenated?
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the vena cava. Blood moves into right ventricle. Blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
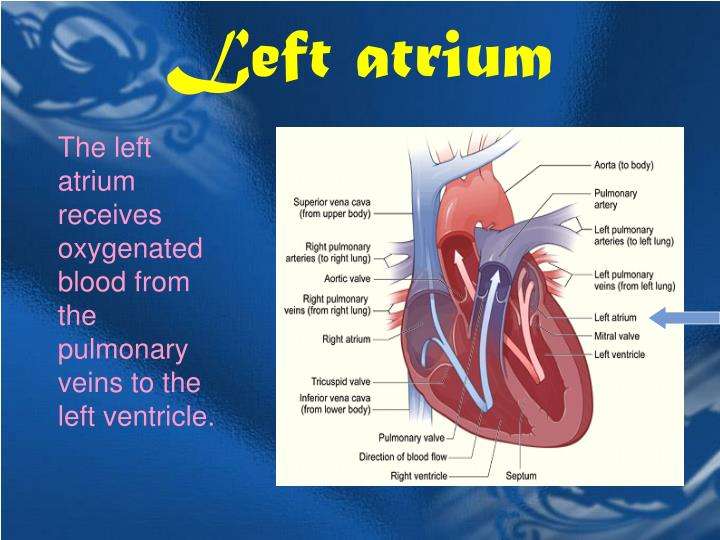
The Atria Are The Hearts Entryways For Blood
The left atrium and right atrium are the two upper chambers of the heart. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood returning from other parts of the body. Valves connect the atria to the ventricles, the lower chambers. Each atrium empties into the corresponding ventricle below.
Read Also: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
Oxygenation Of The Heart And Its Blood Circulation
The heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located at the centre of the thorax, between the two lungs. It is the engine of the circulatory system.
Its normal function is closely tied to its oxygenation.
The coronary arteries
Two arteries have the crucial task of supplying the heart with oxygen: these are the coronary arteries. Any reduction in the oxygen supply can have serious and sometimes irreversible consequences for the heart.
Lets take a closer look at the coronary arteries.
Left and Right coronary
The two coronary arteries, the left and the right, are located directly on the heart. They branch out through the entire cardiac muscle.
The coronary arteries are the first to leave the aorta. Their starting point is found immediately above the aortic valve.
For those interested in a more detailed look as to how the heart circulation works, we have provided the following information
Patients who have their coronary arteries repaired through the installation of a metal stent are often curious to know the name of the repaired artery. Here, then, are a few details on the anatomy of coronary arteries.
The left coronary artery splits into two branches right after it leaves the heart. This first segment is called the left main coronary artery.
The arteries that branch out from it are called the diagonal branches.
In one person out of ten, the posterior interventricular artery is a branch of the circumflex coronary artery on the left side of the heart.
The Exterior Of The Heart:
Below is a picture of the outside of a normal, healthy, human heart.
The illustration shows the front surface of the heart, including the coronary arteries and major blood vessels.
The heart is the muscle in the lower half of the picture. The heart has four chambers. The right and left atria are shown in purple. The right and left ventricles are shown in red.
Connected to the heart are some of the main blood vessels arteries and veins that make up the blood circulatory system.
The ventricle on the right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs.
When you breathe air in, oxygen passes from the lungs through blood vessels where its added to the blood. Carbon dioxide, a waste product, is passed from the blood through blood vessels to the lungs and is removed from the body when you breathe air out.
The atrium on the left side of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
The pumping action of the left ventricle sends this oxygen-rich blood through the aorta to the rest of the body.
Recommended Reading: Tylenol Heart Palpitations
The Right Side Of The Heart
The superior and inferior vena cavae are in blue to the left of the muscle as you look at the picture. These veins are the largest veins in the body. They carry used blood to the right atrium of the heart.
Used blood has had its oxygen removed and used by the bodys organs and tissues. The superior vena cava carries used blood from the upper parts of the body, including the head, chest, arms, and neck. The inferior vena cava carries used blood from the lower parts of the body.
The used blood from the vena cavae flows into the hearts right atrium and then on to the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, the used blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. Here, through many small, thin blood vessels called capillaries, the blood picks up oxygen needed by all the areas of the body.
The oxygen-rich blood passes from the lungs back to the heart through the pulmonary veins .
Heart Contraction And Blood Flow
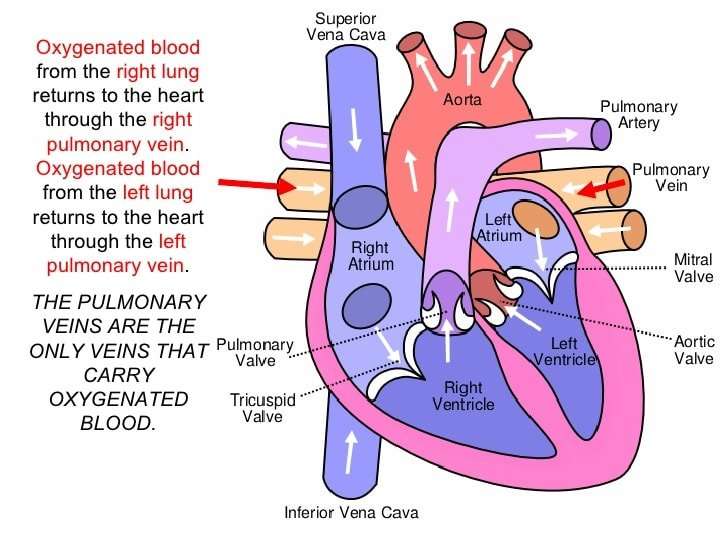
Almost everyone has heard the real or recorded sound of a heartbeat. When the heart beats, it makes a lub-DUB sound. Between the time you hear lub and DUB, blood is pumped through the heart and circulatory system.
A heartbeat may seem like a simple event repeated over and over. A heartbeat actually is a complicated series of very precise and coordinated events that take place inside and around the heart.
Each side of the heart uses an inlet valve to help move blood between the atrium and ventricle.
The tricuspid valve does this between the right atrium and ventricle. The mitral valve does this between the left atrium and ventricle. The lub is the sound of the mitral and tricuspid valves closing.
Each of the hearts ventricles has an outlet valve. The right ventricle uses the pulmonary valve to help move blood into the pulmonary arteries. The left ventricle uses the aortic valve to do the same for the aorta. The DUB is the sound of the aortic and pulmonary valves closing.
Each heartbeat has two basic parts: diastole and atrial and ventricular systole . During diastole, the atria and ventricles of the heart relax and begin to fill with blood.
At the end of diastole, the hearts atria contract and pump blood into the ventricles. The atria then begin to relax. Next, the hearts ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart.
Also Check: How Does Anemia Cause Heart Failure
