Seattle Heart Failure Model
2 days agoNYHA Class 1. BiV Pacer/ICD. Same as BiV pacer. LVAD. NYHA Class 4 and. EF 25% and. Mean 2 year survival 50%. If you want to see the effect in the model anyway, make the patient characteristics match the criteria, then click on the device you want, then set the patient criteria back to the original values.
Read Also: How To Make Your Heart Stop Beating Fast
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
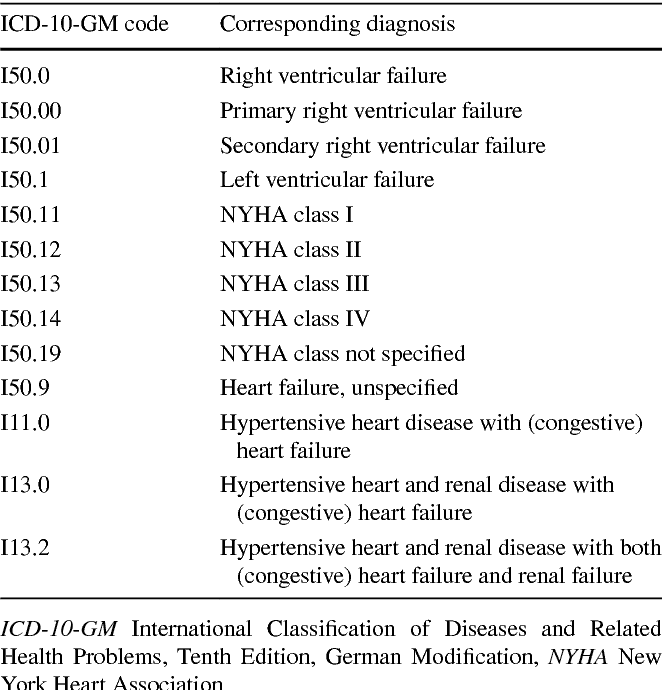
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized head to toe into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I50.9:
Inclusion Terms
Donât Miss: How To Prevent Congestive Heart Failure
Acute Exacerbation Of Diastolic Chf Icd 10
The Acute Exacerbation Of Diastolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.30. Exacerbation does not have a specific code entry either in the diastolic subcategory, for this reason, the code only for acute diastolic CHF is used to describe the condition unless there is the description of acute on chronic heart failure. The code of choice under this category is I50.31.
Recommended Reading: Best Chest Heart Rate Monitor
Also Check: Heart Rate Of 140
Coding For Secondary Hypertension: I15
Although the main focus of this article has been essential hypertension, including comorbidities of heart failure and chronic kidney disease, there may be some patients in the primary care setting who have hypertension secondary to other disease states. In these cases, providers cannot use the hypertension ICD-10 codes discussed above. Instead, use the following codes:
-
I15.0, Renovascular hypertension,
-
I15.1, Hypertension secondary to other renal disorders,
-
I15.2, Hypertension secondary to endocrine disorders,
-
I15.8, Other secondary hypertension,
-
I15.9, Secondary hypertension, unspecified.
The five secondary hypertension codes require that you also code the underlying condition. ICD-10 typically permits either the underlying condition or the secondary hypertension code to be listed first depending on the reason for the patient encounter. The exception to this is I15.8, Other secondary hypertension. Because this is an âotherâ code, the âotherâ condition must be coded first.
Chronic Combined Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- I50.42 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Chronic combined systolic and diastolic hrt fail
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.42 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.42 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.42 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Heart Rate Stays Elevated After Exercise
Acute On Chronic Diastolic Chf Icd 10
The Acute On Chronic Diastolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.33.
When looking at diastolic under failure/heart in the alphabetic index, the ICD 10 system provides subcategory I50.3 for diastolic heart failure. Under this category, several codes according to different specified descriptions are provided I50.33 at the bottom of this subcategory is the code of choice to fully describe the condition acute on chronic diastolic heart failure.
Combined Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- end stage heart failure, if applicable
- Chronic combined systolic and diastolic heart failure
- Combined systolic and diastolic heart failure, chronic
- 222 Cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami, hf or shock with mcc
- 223 Cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami, hf or shock without mcc
- 291 Heart failure and shock with mcc
- 292 Heart failure and shock with cc
- 293 Heart failure and shock without cc/mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
- heart I50.9ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.9
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- Cardiac, heart or myocardial failure NOS
- Congestive heart disease
Also Check: Symptoms Heart Failure Women
Hypertension And Chronic Kidney Disease: I12
Unlike hypertension and heart disease, where the provider must determine whether a causal relationship exists, if the patient has hypertension and develops chronic kidney disease, ICD-10 presumes a cause and effect relationship and classifies the condition as hypertensive chronic kidney disease. Note, however, that if the chronic kidney disease came first, then the combination falls into the secondary hypertension codes discussed later in this article.
Both ICD-9 and ICD-10 require specifying the stage of the chronic kidney disease to properly code the condition. Very few patients have a true glomerular filtration rate measured and most staging relies on the estimated glomerular filtration rate . Most laboratory reports provide a race-based reference range. It is not uncommon for these estimates to have slight variability and for the patient’s staging to vary between stage 2 and 3. Note that ICD-10 differentiates stage 5 from end-stage renal disease by the need for chronic dialysis.
ICD-10 requires first using an I12 code for the combined diagnosis of hypertension and chronic kidney disease:
-
I12.0, Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 5 chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease,
-
I12.9, Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 1 through 4 chronic kidney disease or unspecified chronic kidney disease.
These two codes require an additional N18 code to identify the stage of kidney disease, with documentation typically referencing the most recent eGFR:
Diastolic Chf Icd 11 Code
The Diastolic CHF ICD 11 Code is BD10. ICD 11 does not have category and subcategory but these terms are named as stem code and extensions respectively. The main stem code is the same just like the category in ICD-10 BD10 there is no code for exacerbation.
There are some extensions about types of heart failure that are divided based on code rules of ICD-11 like if there is an effect on physical activity or not and others. Currently, BD10 with an acute extension should be used to code this condition.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Heart Attack Symptoms Go On
Also Check: What Does It Feel Like To Have A Heart Attack
Acute Congestive Heart Failure With Diastolic Or Systolic Dysfunction
How should acutely decompensated congestive heart failure with diastolic or systolic dysfunction be coded in ICD-10-CM? There is no longer an index entry for diastolic/systolic dysfunction. For example, a patient is admitted for treatment of acute congestive heart failure. The provider documents, Acutely decompensated congestive heart failure with diastolic dysfunction. Can this be coded as acute diastolic congestive heart failure?
To read the full article, sign in and subscribe to AHA Coding Clinic® for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS .
Access to this feature is available in the following products:
|
Conquer All Your Heart Failure Icd
Hint: Report I50.21 for acute systolic heart failure.
Heart failure can be tricky to code because you may see numerous acronyms, and you need to decipher whether its chronic, acute, or acute on chronic. If you dont pay close attention to all of the details in the documentation, you run the risk of reporting the wrong code.
Learn which codes you will report for different types of heart failure to always report clean claims in your cardiology practice.
Differentiate Between Systolic, Diastolic Heart Failure
When a patient has heart failure, their heart does not adequately pump blood to meet their bodys need for blood and oxygen. This, in turn, can cause blood and fluids to back up in the patients body in their lungs, hands, or feet.
Heart failure can be categorized as systolic or diastolic, says Rebecca Sanzone, CPC, CPMA, quality assurance specialist at St. Vincent Medical Group/ Accension Health and coding consultant at the American College of Cardiology.
Systolic heart failure: HFrEF is the acronym for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, which is also known as systolic heart failure. When a patient has systolic heart failure, the left ventricle of their heart is not able to contract normally, so their heart cant pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation.
The clinical definition of systolic heart failure is an ejection fraction < 50%, Sanzone explains.
In diastolic heart failure, the ejection fraction > = 50%, Sanzone adds.
Don’t Miss: Target Heart Rate For Weight Loss Calculator
Is Diastolic Dysfunction Considered Heart Failure
Chagasic heart disease may represent an optimal academic model of diastolic heart failure that spares systolic function. A patient is said to have diastolic dysfunction if he has signs and symptoms of heart failure but the left ventricular ejection fraction is normal.
Also question is, is diastolic dysfunction congestive heart failure?
Congestive heart failure occurs when the cardiac output is not adequate enough to meet the demands of the body. Heart failure can be due to the following: Systolic dysfunction Diastolic dysfunction
What are the signs and symptoms of diastolic heart failure?
Heart failure signs and symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath when you exert yourself or when you lie down.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Persistent cough or wheezing with white or pink blood-tinged phlegm.
How do you diagnose diastolic heart failure?
It is characterized by a stiff left ventricle with decreased compliance and impaired relaxation, which leads to increased end diastolic pressure. Signs and symptoms are similar to those of heart failure with systolic dysfunction. The diagnosis of diastolic heart failure is best made with Doppler echocardiography.
Unspecified Diastolic Heart Failure

- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- I50.30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.30 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.30 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.30 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Also Check: How To Cure Heart Palpitations
Blood Pressure Check By Clinical Staff
Code 99211 is appropriate for blood pressure checks performed by clinical staff on a date when no physician service takes place. The nonphysician service must be in compliance with incident-to policy, when applicable . Do not report 99211 when a patient requests a blood pressure check not included in the physician’s plan of care if the payer follows Medicare’s incident-to policy. Additionally, remember that diagnosis coding should be based only on the physician or other qualified health care professional’s documentation. That means if elevated blood pressure is the documented reason for the check by clinical staff and the reading is abnormal, a code for hypertension cannot be assigned without appropriate documentation by a physician or other qualified health care professional.
Scenario: Normal blood pressure check. A week after you have seen a patient who had a borderline high blood pressure reading, the patient returns to your office at your request for blood pressure measurement by your clinical staff . The patient’s blood pressure is within normal limits, so you advise the patient to schedule the next annual wellness visit.
| Diagnosis |
| 99211 Established patient E/M office visitIncident-to policy applies |
| Diagnosis |
| 99211 Established patient E/M office visit |
What Is Acute On Chronic Chf
When heart muscles are damaged chronically, the term Chronic is used to define such a condition but sometimes, a chronically damaged heart can get a viral infection, certain vessels blockage, or shortness of breath leading to acute heart failure of chronic CHF. Medical professionals call it acute on chronic heart failure. The simple definition could be Sudden onset of chronic heart condition.
Also Check: Post Open Heart Surgery
Q& A: Congestive Heart Failure Coding
Q: In the past few weeks, we noticed physicians are documenting acute congestive heart failure with preserved ejection fraction , instead of diastolic or systolic. In speaking with the physicians, they say the heart failure is not diastolic or systolic. What is the best way to approach this issue?
A: You are experiencing a very common frustration for both coders and CDI specialists. The term preserved EF in general equates to a diastolic heart failure. But, as you clearly understand, we cannot apply the code for the diastolic heart failure with the use of that verbiage.
The descriptions of diastolic and systolic in categorizing heart failure are older terms, and the code set has not yet caught up to the new wording. I encouraged my providers to state diastolic heart failure with preserved EF. This documentation gives coders what they need, and allows physicians to use clinically-accepted language.
AHAs Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM, First Quarter, 2014 speaks to this. It provides two examples. First, can heart failure with preserved EF or heart failure with preserved systolic function be coded as diastolic heart failure? Second, can heart failure with reduced EF, heart failure with low EF, or heart failure with reduced systolic function be coded as systolic heart failure?
Recommended Reading: Plant With Heart Shaped Leaf
Acute Diastolic Heart Failure
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- I50.31 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.31 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.31 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.31 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Recommended Reading: What Are Symptoms Of Heart Attack
The Icd Code I50 Is Used To Code Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Acute decompensated heart failure is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of decompensation can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, infection, or thyroid disease.
| Specialty: |
The types are based on which part of the heart is affected.
Left sided heart failure : This is the most common type of heart failure found in medical record. It is related to the pumping of blood by left ventricle. This can be either Systolic or Diastolic.
Systolic It is also called HFrEF which means heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Diastolic Another term for this is HFpEF which means heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Right sided heart failure : It is related to the pumping of blood by right ventricle.
Biventricular heart failure : This is a type of heart failure in which ventricles of both the sides are unable to pump enough blood.
Q& A: Documentation For Coding Heart Failure
Sharme Brodie,RN, CCDS
Q: If the documentation states, diastolic heart failure euvolemic or diastolic HF hypervolemic, can we code chronic diastolic HF and acute diastolic HF, respectively?
A: Unfortunately, you may not like my answer, which is no, this documentation would not be acceptable to pick up either diagnoses of chronic or acute diastolic heart failure.
Code assignment is based on the physician documentation of the type and acuity of the HF. Euvolemic is a medical term that implies the patient appears to have normal circulatory or blood fluid volume. Hypervolemia or fluid overload is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood, because not every patient is in fluid overload or hypervolemia at the time of admission, many physicians are now use HF versus congestive heart failure in their documentation.
There are many types of HF, and CHF is just one type. There is a code in ICD-10-CM for fluid overload: E87.70, Fluid over, unspecified. This is also where hypervolemia would be coded.
Now, in AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2016, it did state that HFpEF could be referred to as diastolic heart failure and that HFrEF could be referred to as systolic heart failure. This advice supersedes information previously given in Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2014. This is why its very important to keep up with the advice given by Coding Clinic.
Recommended Reading: How Long After Open Heart Surgery Can You Travel
Don’t Miss: Is Heart Failure Curable
Referent Definitions Based On Echocardiogram
The referent definitions of HFrEF and HFpEF were based on echocardiograms conducted either 180 days before or 180 days after the ambulatory encounter for HF. There has been debate about the appropriate left ventricular ejection fraction cutoff to define HFrEF and HFpEF, with some experts suggesting that LVEF between 40 and 50 should be considered as a separate HF subtype. For this study, we examined the diagnostic performance of ICD-10 codes using 3 different LVEF cutoffs as the referent definitions for HFrEF and HFpEF. We defined HFrEF as LVEF < 50%, 45, and < 40% and we defined HFpEF as LVEF 50%, > 45, and 40%. The LVEF measurements were derived from echocardiogram reports using validated natural language processing algorithms developed by our team in prior work.
Because the LVEF can change over time, we conducted a sensitivity analysis where we examined diagnostic performance only for individuals who had an echocardiogram conducted within 30 days of the ambulatory encounter for HF. We also conducted a sensitivity analysis where we examined diagnostic performance of I50.2x to identify HFrEF and I50.3x to identify HFpEF based on only the first encounter of each unique patient.
Fransoo Et Al And Fransoo Et Al
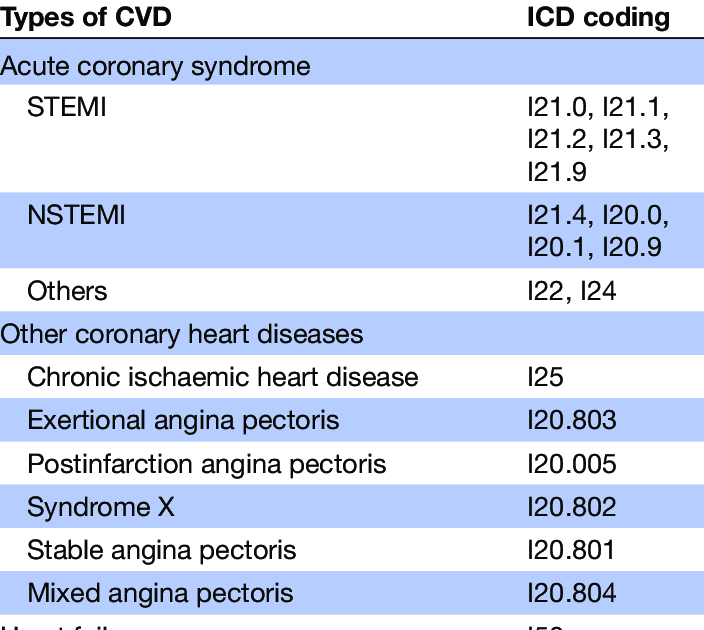
- In The 2013 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. and The 2019 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. residents were considered to have CHF if they met one of the following conditions:
- one or more inpatient hospitalizations in one year with a diagnosis for CHF: ICD-9-CM code 428 or ICD-10-CA code I50 OR
- two or more physician visits in one year with a diagnosis for CHF .
Only Manitoba residents aged 40 and older were included.For more information, please see:
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.20 â other international versions of ICD-10 I50.20 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
You May Like: What Does Heart Attack Feel Like
Recommended Reading: How To Measure Your Heart Rate
