How Can Organophosphate Poisoning Be Prevented
Protective gear should include covering the head and neck, wearing a mask or respirator, and using eye protection. Any exposure to organophosphates should be washed off immediately with water and a mild alkaline soap. Avoid the use of detergents, as they may increase absorption by removing the skins protective oil.
Atropine For Mobitz Ii And Complete Heart Block
In your AHA provider manual, you will see it stated in the bradycardia section that atropine is not effective for Mobitz II and complete heart block. I have had a number of people ask why it is not effective. Read below for the explanation.
First, lets look at atropine and how it works. Atropine increases the firing of the sinoatrial node and conduction through the atrioventricular node of the heart by blocking the action of the vagus nerve.
With 3rd-degree block, there is a complete block and disassociation of the electrical activity that is occurring in the atria and ventricles. Since atropines effect is primarily on the SA node in the atria, a 3rd-degree block would prevent its effect on the SA node from influencing the rate of ventricular contraction which is needed to improve perfusion.
With Mobitz-II, aka, second-degree AV block type II, the situation is similar. There is a partial block in the electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, and thus the effects of atropine would not significantly change the status of the ventricles. This block can also rapidly progress to 3rd-degree block.
To summarize, atropine may speed the firing rate of the SA node , but the ventricles are not responding to anything the atria puts out. Thus, the heart rates will not increase.
Caution with Atropine
Now back to the bradycardia drugs
Epinephrine and Dopamine
Dosing:
IV infusion for bradycardia:
Precautions
We Need More Precise Terminology Than Symptomatic Bradycardia
The AHA has a single algorithm for symptomatic bradycardia. ;However, symptomatic bradycardia is a very broad entity. ;For example, both of the following patients have symptomatic bradycardia:
- A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with gradually worsening dyspnea for the past month. ;He is found to have a third-degree heart block with a ventricular escape rhythm at 45 beats per minute. ;He looks fine.
- The woman in the case above.
It may be useful to split symptomatic bradycardia into two conditions:
- Stable symptomatic bradycardia: ;These patients have reached an equilibrium with stable vital signs and symptoms. ;They have achieved a compensated state . ;They require monitoring and urgent therapy, but they are not actively dying.
- Bradycardic periarrest: ;These patients have deteriorating vital signs and worsening symptoms. ;They are in a decompensated state, with progressive instability as they slip into a death spiral . ;These patients require emergent therapy to avert progression to full arrest .
In some ways, the therapeutic approach to a patient with stable symptomatic bradycardia is opposite to the approach to a patient with bradycardic periarrest:
Recommended Reading: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Side Effects And Contraindications
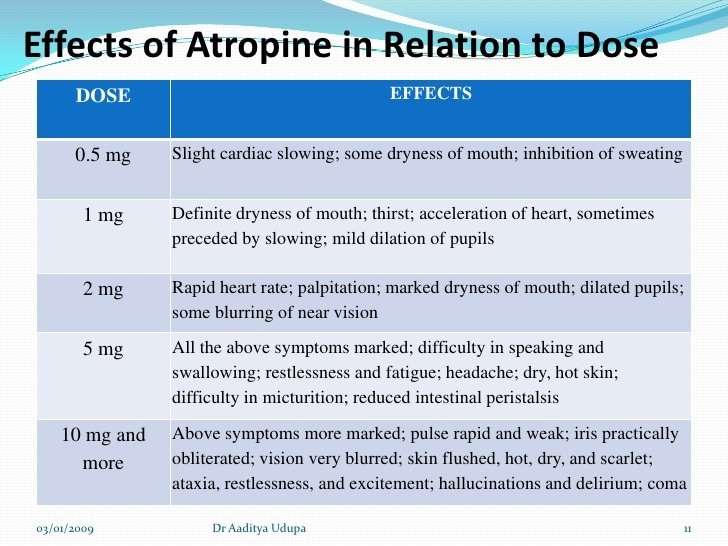
The anticholinergic effects of atropine can produce tachycardia, pupil dilation, dry mouth, urinary retention, inhibition of sweating , blurred vision and constipation. However, most of these side effects are only manifested with excessive dosing or with repeated dosing. Atropine is contraindicated in patients with glaucoma.
Revised 03/15/07
Specific Drugs And Therapeutic Indications
Atropine is a muscarinic receptor antagonist that is used to inhibit the effects of excessive vagal activation on the heart, which is manifested as sinus bradycardia and AV nodal block. Therefore, atropine can temporarily revert sinus bradycardia to normal sinus rhythm and reverse AV nodal blocks by removing vagal influences.
Read Also: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Safe Prescribing And Management
One way of reducing potential side effects is by instilling the drops in a way that reduces risk of atropine passing through the puncta with eventual systemic absorption. Ensure clean hands and that the bottle top does not touch the eye. Instruct parents to retract the lower lid of the child and place the drop in the pouch formed while the child looks up. Place a single drop and instruct the patient to close their eye immediately. Place a finger gently but firmly on the nasal corner of the closed eye and hold for about two minutes. By doing this technique or the very similar DOT technique , systemic absorption is reduced.15
If your childhood myopic patient does not have any of the potential contraindications listed above, the use of low dose atropine should be safe for the majority.8,9,14,16 As with all medications, careful monitoring of the patient for tolerance, compliance and side effects and ongoing follow up is a must.
Unstable Or Stable Symptomatic Bradycardia
These symptoms can be split into two categories: hemodynamically unstable versus;hemodynamically stable. Hemodynamically unstable bradycardias refer to those that lead to a loss of perfusion and are accompanied by hypotension or symptoms that show a lack of brain perfusion . Usually, these symptoms are a result of the bradycardia, so fixing the bradycardia might resolve the symptoms.
Chest pain and shortness of breath can accompany either hemodynamically stable or unstable bradycardia. In unstable bradycardia, the lack of perfusion could be the cause of chest pain or dyspnea. In stable bradycardia, other cardiac conditions could be leading to both the symptoms and the bradycardia. Some emergency medical service systems consider bradycardia stable if the only accompanying symptoms are chest pain or shortness of breath. Other systems consider it unstable. Paramedics should always follow their local protocols.
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How Long Do The Effects Of Organophosphates Last And How Long To They Persist In The Body
The acute effects of exposure to organophosphorus pesticides are well known, but the chronic effects are unclear. Recent studies suggest that abnormalities of the central and peripheral nervous systems persisted for up to 5 years after acute poison- ing due to a single large dose of organophosphates .
Approaches Of Different Guidelines To Symptomatic Bradycardia
Let’s consider the strategies recommended by three guidelines for management of bradycardia.
Above is the AHA guideline for adult bradycardia. ;This is a good approach to a patient with stable symptomatic bradycardia. ;The algorithm starts with atropine , and escalates to more aggressive therapies. ;Even the most aggressive therapy recommended is fairly tame.
Above is the AHA guideline for pediatric bradycardia algorithm. ;Unlike the adult algorithm, this seems designed for bradycardic peri-arrest. ;The first drug on the algorithm is an epinephrine bolus of 10 mcg/kg. ;This is far more aggressive than the adult algorithm. ;For example, Harry Potter would receive about 100 times more epinephrine than Vin Diesel would:
Finally, a bradycardia algorithm designed for anesthesia is shown below . ;This algorithm strikes a middle-ground between the two guidelines above: its options include atropine or bolusing with 10-100 micrograms of epinephrine.
Read Also: How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
Systemic Side Effects And Allergies
If atropine passes through the puncta to the nasolacrimal duct and is absorbed through the nasal mucosa it has the potential to cause systemic side effects. These can include mouth and eye dryness,8 delirium or restlessness,4,8 tachycardia8 and flushed skin and face.8,9
A suggested mnemonic for remembering the systemic activity and side effects of atropine is hot as a hare, red as a beet, dry as a bone, blind as a bat, mad as a hatter.8 More significant cases of systemic atropine poisoning can cause drowsiness, central nervous depression, circulatory collapse with respiratory failure and death.8 Whilst atropine-related deaths are rare, due to the high metabolic excretion rate, a dose of as little 10mg can be fatal: or the oral ingestion of 20 drops of a 1% atropine solution.8 A case of this occurring in America8 highlights that whilst the safety profile of the eye drop is good, medication should be stored safely, properly and far out of the reach of children.
Anticholinergic medications have been associated with decreased cognitive function, but there is only a correlation between long term, high dose, systemic use,4 and further studies about the potential later life impacts of long term atropine dosing should be studied. It is presumed that with proper punctal occlusion and safe medicine storage, this would be unlikely in a child treated long term in the low concentrations prescribed for myopia control.
Side Effects Contraindications And Precautions
Atropine is contraindicated in patients with known atropine or other belladonna alkaloids hypersensitivity because they may develop an allergic or other adverse reaction, including anaphylaxis. Intense flushing of the face and trunk may occur 15 to 20 minutes following parenteral administration of atropine. This is called atropine flush and is not harmful when it occurs. Because of the potential for toxicity, atropine should not be administered in doses exceeding those recommended. Atropine may cause blurred vision, drowsiness, or dizziness. It should be used with caution in patients with known cardiac disease or a recent myocardial infarction. Because atropine can alter the heart rate , it should be used cautiously in patients with cardiac dysrhythmias, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, angina, or other cardiac instability where an increase in heart rate could be detrimental. Atropine should be used with caution during AMI because the drug can potentiate dysrhythmias. In addition, the increase in heart rate caused by atropine increases the oxygen demand on the heart and can exacerbate myocardial ischemia. Increased heart rate is undesirable in patients with hyperthyroidism or cardiovascular instability in acute hemorrhage .
Sandeep Gangadharan, … Charles L. Schleien, in, 2019
You May Like: Vitamin D3 And Heart Palpitations
What Effect Does Atropine Have On Heart Rate
4.7/5atropineAtropineheart rateheart
Injections of atropine are used in the treatment of bradycardia .
Also Know, does atropine work on heart block? In your AHA provider manual, you will see it stated in the bradycardia section that atropine is not effective for Mobitz II and complete heart block. Atropine increases the firing of the sinoatrial node and conduction through the atrioventricular node of the heart by blocking the action of the vagus nerve.
Similarly, you may ask, what is atropine for the heart?
Specific Drugs and Therapeutic IndicationsAtropine is a muscarinic receptor antagonist that is used to inhibit the effects of excessive vagal activation on the heart, which is manifested as sinus bradycardia and AV nodal block.
What are side effects of atropine?
Common side effects of atropine sulfate include:
- dry mouth,
Fret Analysis Of Pde Inhibition
To monitor inhibition of various PDE families by atropine, previously developed FRET-based sensors for human PDE3A, PDE4A1 and PDE5A were used. In addition, we developed a new Epac1-camps-PDE1A sensor to monitor the inhibition of PDE1A. To generate this construct, the mouse PDE1A sequence was fused in frame to the C-terminus of Epac1-camps via a BamHI restriction site and a helical linker MPLVDFFC.
Recommended Reading: List The Steps Of How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
What’s Atropine Used For
Atropine reduces excretion in the mouth, respiratory passages, relieves spasms and the constriction of the respiratory passages. Atropine can also diminish the paralysis of respiration resulting from the actions of toxic agents on the central nervous system prior to surgery. Atropine-induced parasympathetic is especially useful on the heart, where tachycardia develops due to paralysis of vagal control. Small doses of atropine slow down the heart rate before characteristic tachycardia develops. It is also used to treat spasms in the intestines, stomach, and other organs. It can also be used as an anticholinergicby blocking the effects of acetylcholinein the stomach, intestines, nervous system, urinary tract, certain glands, and other tissues.
Effects Of Glycopyrrolate And Atropine On Heart Rate Variability
Corresponding Author
Departments of Anaesthesiology and Clinical Pharmacology, Turku University Central Hospital, and Cardiorespiratory Research Unit, University of Turku, Turku, Finland
Corresponding Author
Departments of Anaesthesiology and Clinical Pharmacology, Turku University Central Hospital, and Cardiorespiratory Research Unit, University of Turku, Turku, Finland
Don’t Miss: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Atropine Increases Camp Independently Of M1/2/3
To elucidate the exact molecular mechanisms of atropine action in the heart, we studied its effects in cardiomyocytes isolated from mice expressing the Förster resonance energy transfer -based cAMP-sensor Epac1-camps,. Stimulation of these cells with the -AR-agonist isoproterenol leads to an increase of intracellular cAMP which can be partially reversed by ACh. As expected, application of atropine after ACh fully blocked this ACh effect, while application of atropine alone, even at high concentrations , had no effect on cAMP levels . Unexpectedly, when applied after ISO and in the absence of ACh, atropine potentiated the -AR-induced cAMP response . The same atropine activity was observed in cells prestimulated with forskolin, a direct adenylyl cyclase activator . We next analyzed the concentration-response dependency of this atropine effect in cardiomyocytes and found that the maximal effect was achieved already at ~10nM , which is in the therapeutically relevant concentration range of this drug,.
How Do You Take Atropine Drops
Tilt your head back, look upward, and pull down the lower eyelid to make a pouch. Hold the dropper directly over your eye and place one drop into the pouch. Look downward and gently close your eyes for 1-2 minutes. Place one finger at the corner of your eye and apply gentle pressure for 2 to 3 minutes.
Read Also: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Can You Use Atropine In Complete Heart Block
4.5/5AtropineAtropinetotal dosageAtropinewillSecond-degree blockcomplete heart blockabout it here
However, if the block is in the His bundle, atropine may lead to an increased atrial rate, and a greater degree of block can occur with a slower ventricular rate. Atropine is unlikely to be successful in wide-complex bradyarrhythmias where the level of the block is below the level of the AVN.
Secondly, how long can you live with a complete heart block? An anterior wall MI with an infranodal complete heart block is a life-threatening condition. About 5 to 10% of patients with an inferior wall, MI will develop complete heart block, but this may resolve within 2 to 48 hours. In general, a complete heart block after an acute MI is rare.
Also Know, what medication is given for heart block?
Medication SummaryCommon drugs that induce atrioventricular block include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics, and digoxin. Withdrawal of the offending drugs is the first treatment for heart block.
What happens when you have a complete heart block?
Complete heart block occurs when the electrical signal can‘t pass normally from the atria, the heart’s upper chambers, to the ventricles, or lower chambers. If the atrioventricular node is damaged during surgery, complete heart block may result. Sometimes complete heart block occurs spontaneously without surgery.
Treatment Of Symptomatic Bradycardia
Stable bradycardia is addressed by treating the underlying cause of the bradycardia. If it is related to an acute myocardial infarction , treating the AMI should have a positive effect on the bradycardia. If its medication-related, removing or adjusting the medication should help.
Unstable bradycardia should be treated directly. Left untreated, hemodynamically unstable bradycardia can spiral out of control the lack of perfusion could further impact cardiac blood flow. Decreased perfusion in the brain can lead to strokes, dizziness, or confusion.
There are three ways to treat unstable symptomatic bradycardia: increase the blood pressure by increasing fluid volume in the cardiovascular system, constricting peripheral blood vessels to push blood toward vital organs, or increased heart rate. The most successful treatment uses a combination of all three.
A bolus of IV fluid infused can help increase blood pressure and improve perfusion. Sympathomimetic drugs, such as dopamine, can help shunt blood away from the periphery and focus the pressure on the core, especially the brain and heart. Sympathomimetic drugs may also help increase heart rate, which is the most direct treatment possible. In most cases, significant increases in heart rate will only come from either administering atropine sulfate or therapeutic pacing.
And now, the debate.
Also Check: What Branch Of Medicine Deals With Heart Disease
Can Levophed Cause Bradycardia
Can Levophed cause bradycardia? Overdosage with LEVOPHED may result in headache, severe hypertension, reflex bradycardia, marked increase in peripheral resistance, and decreased cardiac output.
Why does Levo cause bradycardia?;Via the vagus nerve, the parasympathetic nervous system stimulates neurons that release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at synapses with cardiac muscle cells. Acetylcholine then binds to M2 muscarinic receptors, causing the decrease in heart rate that is referred to as reflex bradycardia.
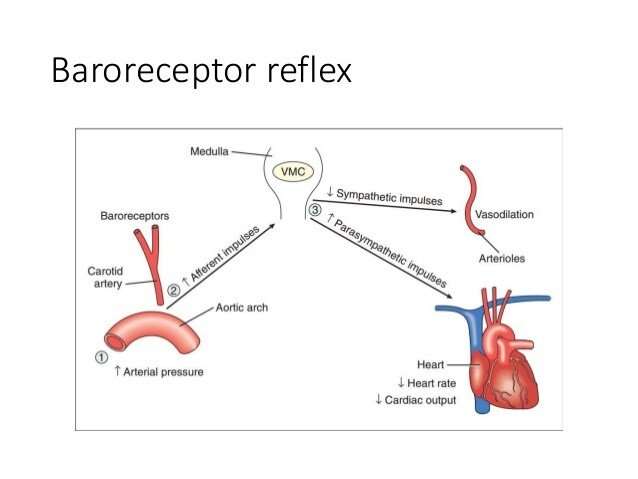
Why does norepinephrine cause reflex bradycardia?;A reflex bradycardia results from the infusion of low dose noradrenaline, as the vagal baroreceptor reflex forces a compensatory slowing of the sinus node. However, as the dose increases, the receptor selectivity decreases.
Can Levo cause tachycardia?;Hence, the use of Levophed during cyclopropane and halothane anesthesia is generally considered contraindicated because of the risk of producing ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. The same type of cardiac arrhythmias may result from the use of Levophed in patients with profound hypoxia or hypercarbia.
Can Pressors Cause Necrosis

Skin necrosis appears in different areas depending on the vasopressor agent used. While vasopressin induces skin necrosis at the extravasation sites or on the muscular parts of the limbs, noradrenaline skin necrosis typically appears on the tips of the fingers and toes, as in the case reported herein.
Read Also: What To Do When Someone Has A Heart Attack
Rationale For Using Epinephrine In Bradycardic Periarrest
There aren’t any prospective RCTs comparing atropine vs. epinephrine for bradycardia. ;In the absence of such evidence, the following is an argument for choosing epinephrine.
#1. Epinephrine is effective in a broader range of patients
Atropine works by poisoning the vagus nerve, thereby;removing parasympathetic inputs to the heart. ;This works beautifully for vagally-mediated bradycardia . ;However, it fails for bradycardias caused by other mechanisms . ;Overall, atropine is completely effective in only 28% of patients with symptomatic bradycardia .
Unlike atropine, epinephrine stimulates the entire myocardium . ;As such, epinephrine may be effective in a broaderrange of bradycardias compared to atropine:
- Atropine-responsive bradycardias due to excessive parasympathetic tone can generally still be overcome by epinephrine.
- Atropine-refractory bradycardias might be responsive to epinephrine.
Vavetsi 2008 evaluated outpatients with bradycardia for the effectiveness of atropine or isoproterenol . ;47 patients responded well to isoproterenol but not atropine, whereas none responded well to atropine but not isoproterenol. ;This supports the concept that beta-adrenergic stimulation is effective in a broader range of bradycardias compared to atropine .
#2. Epinephrine provides a greater amount of hemodynamic support
In periarrest, there isn’t time to start adding several drugs . ;A single agent is needed that will stabilize the patient. ;The one drug most likely to do that is epinephrine.
