What Are The Parts Of The Heart
Your heart is a bit like a house. It has:
- outer walls
- electrics .
Heart walls
The walls of your heart are made of powerful muscle tissue, which squeezes and relaxes to pump blood around your body. This muscle tissue is divided into three layers.
- The endocardium .
- The myocardium .
- The epicardium .
Heart chambers
Your heart is made up of four chambers, two on the right and two on the left. These are like the rooms of your house.
The top two chambers are called the left and right atrium and the bottom two are called the left and right ventricles.
They are divided by a thin wall called the .
Heart valves
There are four heart valves, which act like doors between the chambers of the heart. They open and close as your heart pumps.
The valves only open one way. This stops blood flowing in the wrong direction between the chambers of your heart.
The two valves that sit between the upper and lower chambers of the heart are called the atrioventricular, or AV valves.
The tricuspid valve is the door between the right atrium and ventricle.
The mitral valve is the door between the left atrium and ventricle.
The other two valves are the doors out of the ventricles. They are called semilunar, or SL valves.
The aortic valve is the door out of the left ventricle into the aorta.
The pulmonary valve is the door out of the right ventrical into the pulmonary artery.
The blood vessels
How the heart pumps
The heart’s conduction system
How the heart pumps
The coronary arteries
Why Does Our Heart Go Lub
Our heart beats approximately 60-80 beats/min ; each time it beats it makes a sound similar to LUB-DUB and between each LUB and DUB of the heart, the heart pumps blood through our circulatory system. Ever wondered where those sounds come from?? Well, the valves;that;we spoke about earlier namely the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary and aortic valves are the ones responsible for these sounds. When the tricuspid and mitral valve close between their respective atriums and ventricle, the sound LUB is produced; each time the pulmonary and aortic valves shut to prevent backflow to the ventricles, the sound DUB is produced. Now, sure enough, these valves dont shut as loudly as you slam;your bedroom door, but the LUB-DUB sounds can definitely be heard when you hear the recorded sound of a heartbeat, or press your ear to someone elses chest!
About The Heart And Blood Vessels
The heart is the hardest working muscle in the human body. Located almost in the center of the chest, a healthy adult heart is the size of a clenched adult fist.;By;age;70, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times. The heart is always working. It pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood;daily.
A child’s heart works just as hard as an adult’s heart. In fact, at rest, a baby’s heart may beat up to 130 to 150;times a minute. An adult’s heart often beats between 60 and 100 times a minute. The rate at which the heart pumps gradually slows down from birth to teen years.
The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart and blood vessels. It circulates blood throughout the body. A healthy cardiovascular system is vital to supplying the body with oxygen and nutrients.
You May Like: Why Does Your Heart Rate Go Up When You Exercise
There Are Three Main Types Of Blood Vessels
Arteries
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues.The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart.
- They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
- They branch several times, becoming smaller and smaller as they carry blood further from the heart.
Capillaries
- Capillaries are small, thin blood vessels that connect the arteries and the veins.
- Their thin walls allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and waste products to pass to and from the tissue cells.
Veins
- These are blood vessels that take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Veins become larger and larger as they get closer to the heart.
- The superior vena cava is the large vein that brings blood from the head and arms to the heart, and the inferior vena cava brings blood from the abdomen and legs into the heart.
This vast system of blood vessels – arteries, veins, and capillaries – is over 60,000 miles long. That’s long enough to go around the world more than twice!
Blood flows continuously through your body’s blood vessels. Your heart is the pump that makes it all possible.
Improving Health With Current Research
Learn about the following ways the NHLBI continues to translate current research and science into improved health for people who have heart conditions. Research on this topic is part of the NHLBI’s broader commitment to advancing heart and vascular disease scientific discovery.
Learn about some of the pioneering research contributions we have made over the years that have improved clinical care.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Average Heart Rate Per Minute
How Does The Heart Beat
The atria and ventricles work together, alternately contracting and relaxing to pump blood through your heart. This is your heartbeat. The electrical system of your heart is the power source that makes this possible.
Your heartbeat is triggered by electrical impulses that travel down a special pathway through your heart.
- The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells called the SA node , located in the right atrium. This node is known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The electrical activity spreads through the walls of the atria and causes them to contract.
- A cluster of cells in the center of the heart between the atria and ventricles, the AV node is like a gate that slows the electrical signal before it enters the ventricles. This delay gives the atria time to contract before the ventricles do.
- The His-Purkinje network is a pathway of fibers that sends the electrical impulse from the AV node to the muscular walls of the ventricles, causing them to contract.
At rest, a normal heart beats around 50 to 90 times a minute. Exercise, emotions, anemia, an overactive thyroid, fever, and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster, sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute.
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, as well as the side and back of the left ventricle. The left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
You May Like: How High Should Your Heart Rate Be
Right Ventricle Sends Blood Needing Oxygen To The Lungs
The blood needing oxygen is pumped out of the right ventricle, through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery then divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries, carrying blood to the right and left lungs. In the lungs the blood gives up its carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen.
Heart Trivia: How Much Blood Does Your Heart Pump Each Day
By Adam Pick on March 18, 2009
Any guesses as to how much blood your heart pumps each day?
Need a hint? Its more than 10 gallons.
Need another hint? Its more than 100 gallons.
To find out how much blood your heart pumps each-and-every day of your life Scroll down below the beating heart animation.
According to The Texas Heart Institute, most healthy hearts can pump up to 2,000 gallons of blood during each twenty-four hour period. Isnt that incredible?
I just did the math. During the time you just read this blog , your heart pumped 1.38 gallons of blood through your body!!!
Why am I writing about this? Well This is exactly why our heart valves need to function properly. If our valves do not open-and-close tightly, the heart needs to pump even more blood which puts additional strain on the heart. If the heart works overtime for long periods of time, the cardiac muscle can thicken, dilate and, ultimately, fail.
Keep on tickin!
Recommended Reading: What Is Your Heart Rate
Continue Learning About Heart And Circulatory System
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Pretty Cool It’s My Pulse
Even though your heart is inside you, there is a cool way to know it’s working from the outside. It’s your pulse. You can find your pulse by lightly pressing on the skin anywhere there’s a large artery running just beneath your skin. Two good places to find it are on the side of your neck and the inside of your wrist, just below the thumb.
You’ll know that you’ve found your pulse when you can feel a small beat under your skin. Each beat is caused by the contraction of your heart. If you want to find out what your heart rate is, use a watch with a second hand and count how many beats you feel in 1 minute. When you are resting, you will probably feel between 70 and 100 beats per minute.
When you run around a lot, your body needs a lot more oxygen-filled blood. Your heart pumps faster to supply the oxygen-filled blood that your body needs. You may even feel your heart pounding in your chest. Try running in place or jumping rope for a few minutes and taking your pulse again now how many beats do you count in 1 minute?
Also Check: How To Slow Your Heart Rate
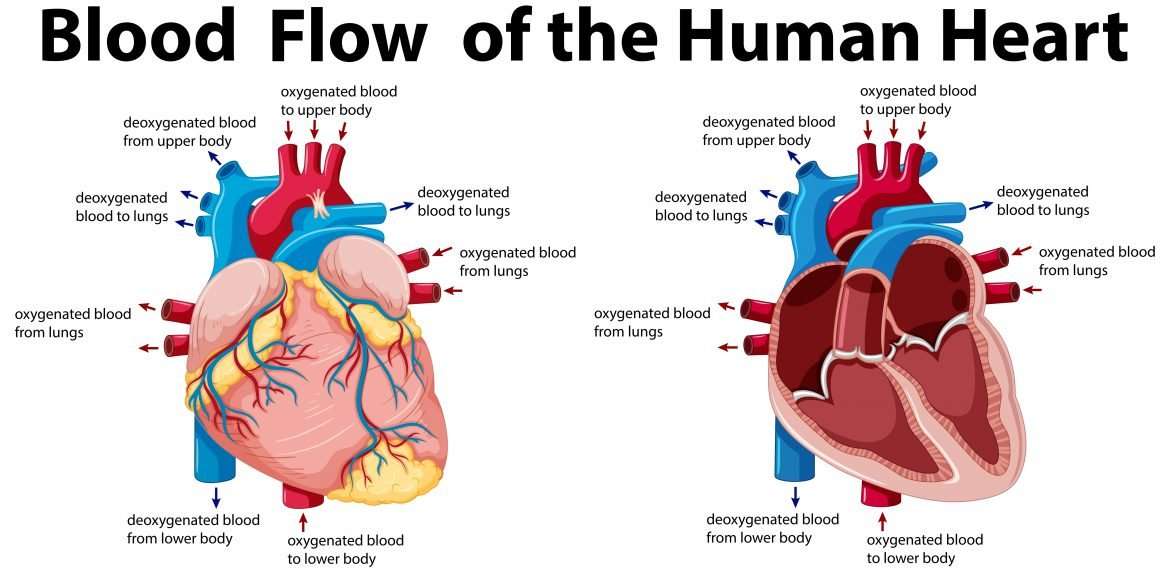
Right Side Of The Heart
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atria while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated and then returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
How The Heart Beats
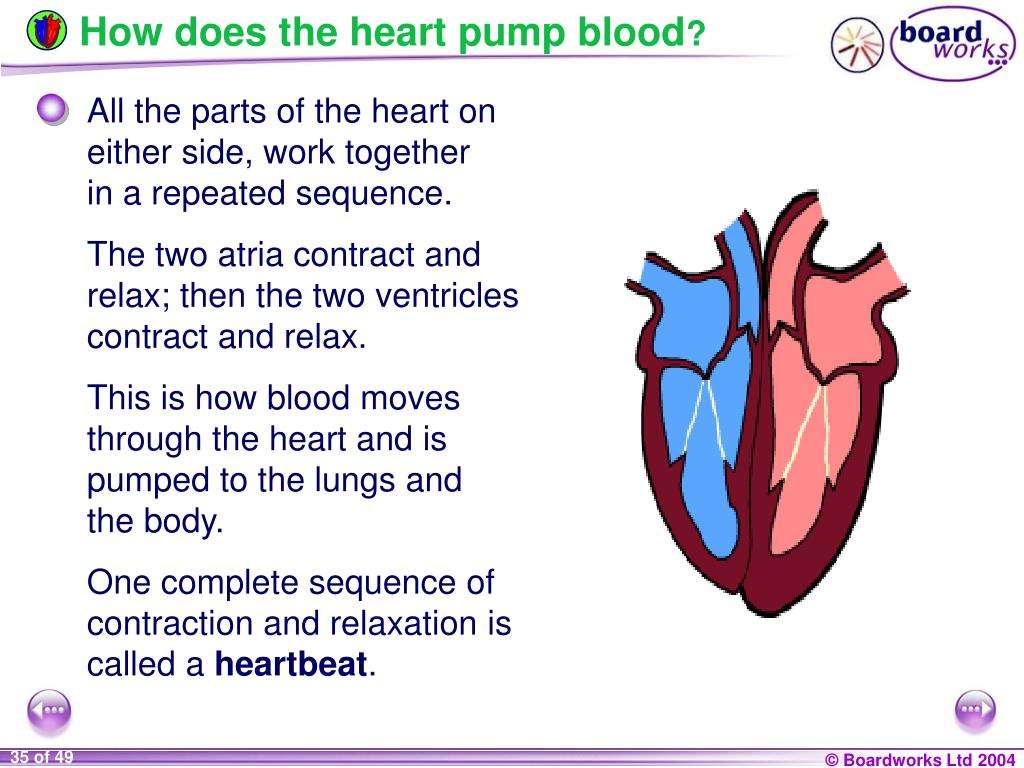
How does the heart beat? Before each beat, your heart fills with blood. Then its muscle contracts to squirt the blood along. When the heart contracts, it squeezes try squeezing your hand into a fist. That’s sort of like what your heart does so it can squirt out the blood. Your heart does this all day and all night, all the time. The heart is one hard worker!
Page 1
Don’t Miss: Elevated Heart Rate When Sick
The Heart Is A Muscle
Your heart is really a muscle. It’s located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it’s about the size of your fist. There are lots of muscles all over your body in your arms, in your legs, in your back, even in your behind.
But the heart muscle is special because of what it does. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste.
Your heart is sort of like a pump, or two pumps in one. The right side of your heart receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. The left side of the heart does the exact opposite: It receives blood from the lungs and pumps it out to the body.
Adding Oxygen To Blood
Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood enters the heart’s right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs.
The pulmonary artery then carries the oxygen-poor blood from your heart to the lungs. Your lungs add oxygen to your blood. The oxygen-rich blood returns to your heart through the pulmonary veins. Visit our How the Lungs Work Health Topic to learn more about what happens to the blood in the lungs.
The oxygen-rich blood from the lungs then enters the left atrium and is pumped to the left ventricle. The left ventricle generates the high pressure needed to pump the blood to your whole body through your blood vessels.
When blood leaves the heart to go to the rest of the body, it travels through a large artery called the aorta. A balloon-like bulge, called an aortic aneurysm, can sometimes occur in the aorta.
Read Also: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
What Does The Heart Look Like From The Inside
The heart is divided into two sidesthe right side and the left side. This is then further divided by a constriction into the upper and lower chambers, thereby resulting in 4 chambers of the heart. The 2 upper chambers are called the atria and the 2 lower chambers are called the ventricles. Thus, the 4 chambers of the heart are:
- Right atrium
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
The two atria are thin-walled structures separated into right and left halves by a septum running between them called the interatrial septum. The two ventricles are relatively thick-walled and separated by the interventricular septum running between them. One major circulatory vessel, either an artery or a vein, enters or leaves each chamber of the heart, thereby helping in the transport of blood. The flow of blood throughout the heart is controlled by a one-way valve system, which is extremely necessary to prevent the backflow of blood from the chambers. The valve present between the right atrium and the right ventricle is called the tricuspid valve; a similar valve present on the left side is called the mitral valve.
How Does The Heart Pump Blood
The heart is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium and the left ventricle. Each chamber has a one-way valve at the exit that prevents blood from flowing backwards. When each heart chamber contracts, the valve at its exit opens. When the heart chamber is finished contracting, the valve closes so blood does not flow backwards.
The valve in each chamber has a name. The tricuspid valve is in the right atrium. The pulmonary valve is in the right ventricle. The mitral valve is in the left atrium. The aortic valve is in the left ventricle.
When the heart muscle contracts , it is pumping blood out of the heart. The heart contraction comes in two stages. During the first stage, the right and left atria contract simultaneously, pumping blood to the right and left ventricles. Then, it is the ventricles turn to contract together so they can propel blood out of the heart. After this, the heart muscle relaxes before the next heartbeat. This way, blood can fill up the heart again.
The heart’s right side and left side have separate functions. The right side collects oxygen-poor blood from the body then pumps it to the lungs where it can pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The left side then collects oxygen-rich blood from the lungs so it can pump it to the body so cells have the oxygen they need to function properly.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When Someone Has A Heart Attack
How Does Your Heart Work
Your heart is made up of 2 pumps. The pump on the right hand side receives blood that has already delivered its oxygen round the body and sends this blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen .
The pump on the left hand side receives oxygen-rich blood and then pumps it out into the arteries to deliver its oxygen around the body.
How Does Blood Flow Through Your Lungs
Once blood travels through the pulmonic valve, it enters your lungs. This is called the pulmonary circulation. From your pulmonic valve, blood travels to the pulmonary arteries and eventually to tiny capillary vessels in the lungs.
Here, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, passes from the blood into the air sacs. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. Once the blood is oxygenated, it travels back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Read Also: What Does A Slow Heart Rate Mean
How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
Your heart works nonchalantly 24X7, 365 days throughout your life, ever since you evolved as an embryo in your mothers womb. In fact, heart is the very first organ to develop. You can monitor the beating heart as soon as 6 weeks of pregnancy. And, that could, perhaps be the reason why a good portion of the people tend to overlook at the heart and its arteries. They take it for granted and abuse it with stress, alcohol, smoking, and junk food.
Taking care of your heart is essential to ensure that it beats according to the specified rhythm and pumps the blood in the normal way. And that brings our attention to the topic how much blood does your heart pump?
Before you get into the details of the quantity of blood pumped, let us take a look at some interesting facts about human heart!
Human Heart Some Interesting Facts Revealed
If you have been thinking that the heart beats at the rate of 72 beats per minute, then you definitely got it wrong. The rate of heart beat varies in men and women.
In a healthy male, the heart weighs around 300 grams to 350 grams and beats at the rate of 70 beats per minute. In a healthy woman, the weight of the heart is somewhere between 240 grams to 300 grams, while the rate of heart beat is 78 beats per minute.
The Atria receives the blood while ventricles pumps out the blood. Blood always flows in a single direction in the heart. Any deviation in its standard flowing process is an indication of a major health condition.
