Here’s A Rundown Of The Likely Chain Of Events After You Call 911
For a suspected heart attack, paramedics can often perform initial testing in the ambulance while the patient is en route to the hospital. Image: Thinkstock
Every 43 seconds, someone in the United States has a heart attack. If one day that someone is you or a loved one, it may be helpful to know what’s likely to happen, both en route to the hospital and after you arrive.
For starters, always call 911 to be transported via ambulance rather than going by car. Contrary to what you might assume, speed isn’t the only rationale. “If you’re having a heart attack, there are two reasons why you want to be in an ambulance,” says Dr. Joshua Kosowsky, assistant professor of emergency medicine at Harvard Medical School. One is that in the unlikely event of cardiac arrest, the ambulance has the equipment and trained personnel to restart your heart. Cardiac arrest, which results from an electrical malfunction that stops the heart’s pumping ability, is fatal without prompt treatment. However, most heart attacks do not cause cardiac arrest, Dr. Kosowsky stresses. “It’s rare, but it’s certainly not a risk you want to take while you’re driving or riding in a car.”
Whats The Worst Meat To Eat
Avoid processed meats
Finally, health experts say to stay away from processed meats, which are generally considered to be unhealthy. These include any meat that has been smoked, salted, cured, dried, or canned. Compared to fresh meat, processed meats are high in sodium and can have double the amount of nitrates.
Understanding A Woman’s Heart Means Knowing What To Look For
01.12.2012
Reyna Robles was always the first one up and the last one to bed, the kind of person whose warmth and energy seemed effortless, possessed of more than enough steam to come home from her full-time job, to select recipes from her large collection of cookbooks to prepare a meal for her husband and children, and then to take her dogs for walk and help her kids with homework. Before bedtime, she’d fit in a good work out.
She wasn’t one to complain, either, except the spring day when she suddenly felt a pain in her chest as she exercised. It was a cramp-like pain, not anything like the normal muscle aches Robles expected from her body after vigorous activity. “I didn’t think I should be feeling chest pains,” she said. She wasn’t even 40.
She saw her doctor, who ordered an EKG. Everything was fine, Robles was told. Nothing was wrong with her heart. But the pain kept coming back, and that worried her. “Exercise should feel good,” she said. “It shouldn’t hurt.” She went back to her doctor, who ordered more tests. Still nothing, she was told. Soon, she started feeling the pain even when she wasn’t exercising. “I intuitively knew something wasn’t right,” she said. Still, none of the doctors she saw could discern a problem. And she began to doubt herself, “although I knew I wasnt imagining it. It was real.”
I intuitively knew something wasn’t right. I knew I wasn’t imagining it.
- blood test
Don’t Miss: Where Does Oxygenated Blood Enter The Heart
Blood Test And Ecg May Safely Rule Out Heart Attack
A high sensitivity troponin test accurately ruled out a heart attack amongst a third of patients presenting to the emergency department with chest pain. A patient with no detectable troponin and normal electrocardiogram was almost certain not to have had a heart attack.
Many people come to hospital with chest pain, but more than 75% of them have not had a heart attack. The two tests accurately ruled out heart attack in 30% of all chest pain presentations, but more than a third of people who didnt have a heart attack also tested positive. Only around a quarter of people with raised troponin have had a heart attack. The tests were less reliable in people who had chest pain for less than three hours.
The findings support existing NICE guidelines to use high sensitivity troponin testing in people with a suspected heart attack but without the classic features on an electrocardiogram. The test should not be used indiscriminately for all chest pain presentations.
Caution is needed due to the variability in individual study results, patient populations and testing protocols.
How Ekg/ecg/electrocardiogram Testing Helps In Regards To Heart Attacks
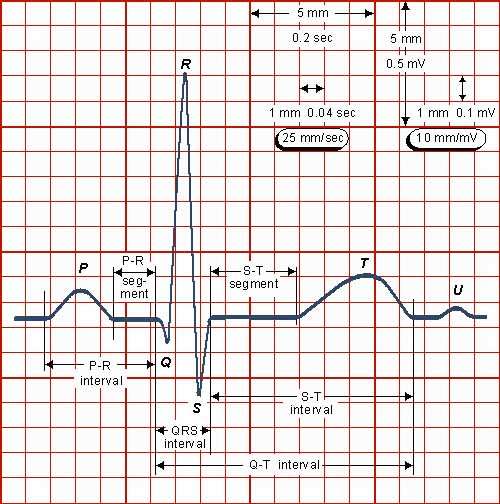
While EKG testing can be used to diagnosis a number of heart problems, it is most commonly used when there is a suspected heart attack. This testing can provide the information your cardiologist needs to determine whether you had a heart attack in the past or if you are currently experiencing one.
Even though this testing is valuable in detecting previous or current heart attacks, it does have one limitation predicting the future. These tests cannot predict how likely you will be to experience any future heart attacks.
Just because the test cannot predict future heart attacks, it doesnt mean there is no way to predict if one will happen. Cardiologists can use a number of things, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other information obtained from electrocardiography testing, to determine your risk level. If you are at a high risk for experiencing future heart attacks, your cardiologist can provide treatment recommendations and lifestyle changes that may help lower your risk.
You May Like: Dehydration And Arrhythmia
Will An Ekg Show A Past Heart Attack
EKG and a past heart attack: how far back can an EKG detect a heart attack? An EKG can reveal if you had a heart attack months or years ago. Heart attacks cause significant symptoms that need immediate medical attention. However, in 45% of cases, patients dont detect any abnormality with their hearts. These are silent heart attacks that dont cause any noticeable symptoms. You may wonder how an EKG shows a previous heart attack? Plausible by recording the inconsistent flow of blood.
A heart attack affects the consistent flow of blood in your heart. As a result, your heart tissue begins to lose oxygen and gradually dies. After months or years, this dead tissue will not conduct well with electricity while doing an EKG. So, your health provider will measure and print an abnormal electrical pattern. An expert health provider can assume that there is damage in your heart from a lack of oxygen. That means you may have a dangerous blockage in your coronary arteries. However, an abnormal EKG can be the reason for Ischemia or lack of blood flow. So, the doctors run multiple tests to determine the real reason. Combining with other diagnostic methods like blood tests and imaging, MRI, VT Scan, and Ultrasound, an EKG can easily detect a previous heart attack.
Blood Tests And Beyond
But not all heart attacks show up on the first ECG. So even if it looks normal, you’re still not out of the woods, says Dr. Kosowsky. The next step is an evaluation by a doctor or other clinician, who will ask about your medical history and details about the location, duration, and intensity of your symptoms. You’ll also have a blood test to measure troponin, a protein that rises in response to heart muscle damage. This blood test is very sensitive. But keep in mind that elevated levels don’t always show up right away. That’s why doctors sometimes have people stay for several hours to get a follow-up troponin measurement.
Other possible tests include a chest x-ray to look for alternative causes of chest discomfort, such as pneumonia or heart failure. A doctor also might give you a trial of medication to see whether it relieves your symptoms, and additional ECGs may be performed over time.
Often, if several troponin tests come back normal, the doctor may want to check your risk of a future heart attack with an exercise stress test. This test can reveal how your heart responds to the demands of increased blood flow needed during exercise. During a standard exercise test, you walk on a treadmill at progressively faster speeds, while trained staff monitors your heart’s electrical activity, your heart rate, and your blood pressure.
Read Also: Heart Bleeding Symptoms
Why Do You Need An Ekg
Can an EKG detect a heart attack? Not 100% correctly. However, it is the quickest way to monitor any heart-related problems.
The doctor may suggest you take an EKG if you have the following signs and symptoms.
- Chest discomfort
Your doctor usually requests you an electrocardiogram to check the following:
- To look for the cause of chest pain
- To evaluate heart-related problems, such as severe tiredness, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting.
- To identify irregular heartbeats.
- To monitor the overall heart health before a surgery
- After treatment for conditions such as a heart attack , endocarditis , to check your heart functions
- To examine the operation of an implanted pacemaker
- To monitor the work of certain heart medicines
- Whether you have had a previous heart attack
How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Quick treatment to get the blood flowing to your heart muscle again is important. This can reduce the amount of permanent damage to your heart and save your life.
Many people need to have emergency treatment to restore the blood flow:
- Coronary angioplasty re-opens the blocked coronary artery by inserting one or more stents. This helps keep the narrowed artery open.
- Thrombolysis involves giving you clot-busting medicine to dissolve the blood clot that’s blocking the coronary artery.
- Coronary bypass surgery helps to restore normal blood flow by using a blood vessel from your leg, arm or chest in your heart to bypass the blocked artery.
You might not have these treatments if your doctor decides it’s not safe or necessary.
Read Also: Reflux And Palpitations
What Are Silent Heart Attacks
A silent heart attack is a heart attack that has few or no symptoms. If youve had a silent heart attack, you may have an of developing another heart attack or heart failure. You may also have an elevated risk of mortality because the lack of symptoms often delays medical treatment.
When symptoms are present, theyre often so mild that they dont seem particularly concerning. Fatigue, mild chest pain that feels like indigestion, and flu-like symptoms are all possible signs.
Silent heart attacks are caused by a lack of blood flow to your heart like traditional heart attacks. Improving your overall cardiovascular health and regularly getting checkups can help minimize your risk.
Can You Detect Blocked Arteries From An Ecg
Cardiovascular problems are scary simply not knowing enough about the health of your heart can lead to major medical problems later in life. Electrocardiography, the practice of measuring electrical signals to diagnose potential problems with the heart, gives medical staff a non-invasive way of reviewing the hearts activity. An electrocardiogram refers to the actual test. While often used for many medical procedures, an ECG holds great potential for diagnosing cardiovascular problems.
Also Check: Tylenol And Blood Pressure
How Silent Heart Attacks Are Discovered
Some patients whose heart attacks go unrecognized learn about them weeks or months later when they visit the doctor, often for a yearly physical.
We can tell the size of the heart attack by how much heart muscle has been damaged, often on an electrocardiogram , or even more precisely on a cardiac ultrasound, or echocardiogram, says Dr. Rimmerman.
Other patients visit their doctors soon after a silent heart attack because they experience persistent symptoms, such as fatigue and shortness of breath.
Sometimes these symptoms are caused by a leaky mitral valve, caused by scarring of the heart muscle and associated valve dysfunction after a heart attack. Serious complications can follow, including decompensated heart failure, heart rhythm disorders and loss of consciousness.
What Can An Ekg Detect
The main purpose of an EKG is to determine the efficiency of blood pumping through the heart. By measuring the electrical pulses, an EKG can alert medical professionals of problems within the cardiovascular system. Some of the issues an EKG can show include:
- Blockages or narrowed arteries
- Evidence of a heart attack
- Problems in the hearts structure
With a quick EKG, doctors can determine if any issues are currently affecting the heart. However, an EKG can only monitor issues that are currently impacting the heart function some cardiovascular issues can come and go, making them difficult to detect on a random EKG. An EKG is often performed when a patient is experiencing symptoms of heart problems, like shortness of breath, chest pain or weakness.
One of the services we offer at Clinica Las Americas is EKG testing. Our experienced medical team can use the results of an EKG to identify possible heart problems and recommend further treatment to protect your health.
Don’t Miss: Can Benadryl Cause Arrhythmias
Nearly 80 Percent Of Heart Attacks In Us Are Never Diagnosed
Nearly 80 percent of heart attacks in the United States go undiagnosed, according to the first nationwide study of its kind.
These silent heart attacks, often mistaken for indigestion or muscle pain, might be too small to draw attention, but they are much more common than cardiologists had previously thought, the study, released Sunday, found. And since they put people at greater risk of additional heart attacks later on possibly big ones experts say patients who feel any chest pain should seek medical care, even if their symptoms only seem like heartburn.
Heart attacks happen when arteries get blocked by plaques of cholesterol, making it impossible for oxygen-filled blood to nourish the heart. Without air, a part of the heart muscle dies, and scar tissue forms.
Even the smallest heart attack leaves behind a scar, which is more fibrous than living muscle and wont contract along with the rest of the organ. That makes the hearts job harder and increases the risk of heart failure.
In the past, researchers have looked for signs of silent heart attacks using a test known as an electrocardiogram, which detects the electrical current that keeps the heart pumping. When scar tissue forms after a heart attack, the electrical signal changes, and doctors can see that abnormality on the ECG. But sometimes, with smaller scars, this test just isnt precise enough to pick up on the difference.
Even the smallest heart attack leaves behind a scar.
What Did This Study Do
This review identified 11 cohorts including 9,241 adults presenting to the emergency department with chest pain. All received an ECG and high sensitivity troponin T test.
Researchers looked at whether a troponin level of less than 0.005 µg/L when combined with normal ECG, was accurate in ruling out a heart attack. Heart attack was confirmed, independently in most studies, according to the Universal Global Task Force definition. Other outcomes were death or major adverse cardiac event within 30 days.
Nine of the 11 studies had a high or unclear risk of bias. Individual studies varied in patient characteristics, timing and number of troponin tests, and their results. These factors may make meta-analysis inappropriate. All studies were from developed countries, but only one was from the UK.
Don’t Miss: Gerd And Heart Flutters
Ecg : When You Need It And When You Dont
An ECG records the electrical activity of your heart at rest. It provides information about your heart rate and rhythm, and shows if there is enlargement of the heart due to high blood pressure or evidence of a previous heart attack . However, it does not show whether you have asymptomatic blockages in your heart arteries or predict your risk of a future heart attack. The resting ECG is different from a stress or exercise ECG or cardiac imaging test. You may need an ECG test if you have risk factors for heart disease such as high blood pressure, or symptoms such as palpitations or chest pain. Or you may need it if you already have heart disease. But in other cases, you may think twice about having this test. Heres why:
Usually, you do not need an ECG if you dont have risk factors for heart disease or symptoms that suggest possible heart disease.
The test is not useful in routine checkups for people who do not have risk factors for heart disease such as high blood pressure or symptoms of heart disease, like chest pain. Yet, many people with no risk factors or symptoms have an ECG as part of their routine checkups. There are better ways to prevent heart disease than routine ECGs. The ECG will not harm you. However, it can sometimes show mild nonspecific abnormalities that are not due to underlying heart disease, but cause worry and lead to follow-up tests and treatments that you do not need.
When are ECGs needed?
How should you protect your heart?
How Does An Ekg Work
The beauty of an EKG test is that it is quick and painless for the patient. These medical devices use electrodes to measure and monitor the electrical pulses in the heart. Electrodes are placed on the skin around the heart on the torso, and sometimes on the limbs, to detect the electrical pulses that occur when the heart beats. This measures the electrical pulses as they move from the top of the heart down through the bottom chambers. The EKG procedure only takes a few minutes to begin and can quickly record the rhythm of the heart.
Don’t Miss: What Is An Unsafe Heart Rate
Can An Electrocardiogram Detect A Heart Attack
If it is believed you had a heart attack, your cardiologist may wish to have you undergo electrocardiography testing. This diagnostic testing, which involves running a test known as an electrocardiogram or EKG/ECG as it is sometimes called, can help provide your cardiologist with valuable information that shows the overall health of your heart.
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
Advanced treatment approaches are extending and improving quality-of-life for patients with congestive heart failure. Congestive heart failure is treated and managed through a combination of lifestyle modifications and a wide range of therapies, including medication and interventions, which help the heart to work more effectively and alleviate heart failure symptoms. Pacemakers and ventricular assist devices can make it easier for heart the heart to pump blood and remain in rhythm. For some patients with advanced heart failure, a heart transplant may be an option.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
