The St Pauls Rehabilitation Experience
Located conveniently near you, St. Pauls Senior Community offers comprehensive senior rehabilitation services to provide support for you and your loved one through any upcoming medical procedures, injury recovery, or other health concerns. We know youre likely to have questions, and wed be happy to answer them for you. To get more information, please contact us. Our team is ready to help!
You May Like: How To Figure Out Your Heart Rate
How To Get The Data You Need
Shahian says that if the hospital youre considering doesnt share its data with Consumer Reports or STS, try to get that information on your own.
But calling the hospital directly isnt the best bet: When we tried that at several hospitals, the staff wasnt able to connect us with the right person to answer our questions.
Instead, Shahian recommends asking your surgeon these questions:
- Does the hospital where you perform surgery participate in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons database?
- If so, how does it perform in the STS ratings, and would you be willing to go over their most recent report with me?
If the surgeon wont have that discussion or says the hospital doesnt collect the data, Shahian says to consider another doctor and medical center.
Editors Note: This article also appeared in the May 2017 issue of Consumer Reports magazine.
Risk Adjustment And Benchmarking
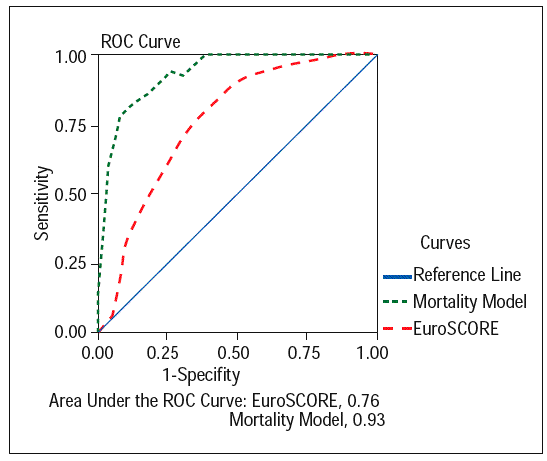
For the benchmarking procedure, risk adjustment was performed using the logistic EuroSCORE. This model is the most commonly used risk-adjustment method in Europe and its definitions are used in the NVT database. The logistic EuroSCORE was calculated for each patient. Subsequently, benchmarking was performed using each early mortality measure. A random effects model was fitted with one of the mortality measures as the outcome variable and including the logistic EuroSCORE as covariate. A random effects model accounts for within-hospital variability and between-hospital variability and is the preferred type of regression model used for comparison between centres . This regression model thus assumes that mortality is partly explained by patient characteristics and partly by a centre effect, which is specific to each centre and can be compared across centres .
Also Check: What Is Heart Stent Surgery
What Happens Before Heart Surgery
Preparation for your surgery can take weeks or months. Before your heart surgery is scheduled, your medical care team will evaluate your condition. Your care team will likely include your primary care doctor and cardiologist. Youll also consult with a cardiothoracic surgeon .
Your care team will give you a medical evaluation. This includes:
- Talking about your symptoms and how long theyve been going on.
- Talking about your medical history and your biological familys medical history.
- Blood tests to check your cholesterol and other important numbers.
Your team will also run some diagnostic tests. These tests provide a detailed picture of your heart function and any problems. They also help you and your care team decide if you need surgery and what type you need.
If you need surgery, your care team will tell you exactly how to prepare and what to expect. Its important to follow their recommendations about:
- When to stop taking any medications.
- When to begin fasting the day before your surgery.
- Quitting smoking or tobacco use and reducing alcohol consumption to lower your risk of complications.
Be sure to ask any questions you have, even if they seem small or you think you asked them already. Its better to double-check to make sure youre as prepared as possible for your surgery.
What to expect after youre admitted to the hospital
- Tests like an EKG or chest X-ray.
- Hair shaved from the spot where youll have your incision.
- Glasses and contact lenses.
Newborn Cardiac Surgery Survival
Performing heart surgery on newborn babies is more challenging due to the young age and small size of the patients. By comparing newborn survival rates along with STAT category, parents can get an idea of how well the surgeons perform in the most challenging cases.
What we measure:
We compare our survival rates for newborn patients with national averages by the complexity of the surgery.
What it means:
At Childrens Colorado, our surgeons have extensive experience correcting heart defects in even the youngest patients some just a few hours old. Our survival rates for STAT 1, STAT 2 and STAT 5 cases are higher than the national averages.
You May Like: What Are Heart Attack Symptoms
Data Analysis And Outcomes
The POCMA analysis was performed by a multidisciplinary and technical group composed of cardiologist, cardiac surgeon, intensive care physician, nurse and a perfusionist from the coordinating center. Using POCMA, the identified seminal event was then categorized according to the phase of the event during peri-operative care . A list of categories and subcategories capable of triggering mortality was developed based on POCMA for each perioperative phase. When multiple contributing factors were found, the first potential event was chosen, representing the best time for systematic correction of the course of mortality. Death of cardiac surgery patients was defined as avoidable if the chance of survival with better care or in the absence of contributing factors was> 50%. When there were no identifiable factors for a sudden death of a patient, it was defined as unavoidable death .
Recovering From An Aortic Valve Replacement
Youâll usually need to stay in hospital for about a week after an aortic valve replacement, although it may be 2 to 3 months before you fully recover.
You should take things easy when you first get home, but you can start to gradually return to your normal activities over the next few weeks.
Youâll be given specific advice about any side effects you can expect while you recover and any activities you should avoid.
You wonât usually be able to drive for around 6 weeks and youâll probably need 6 to 12 weeks off work, depending on your job.
Read Also: Heart Of Vegas Fan Page Bonus 2021
Also Check: Steps In Dying From Congestive Heart Failure
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement
Aortic Stenosis is a heart disease affecting the aortic valve. This valve is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. With AS, the aortic valve is too narrow, causing a very high internal pressure due to the heart working extra hard to pump blood through it. This pressure triggers the cardiac muscle to thicken to increase its strength, and eventually tires out and results in a life-threatening condition.
The majority of patients with AS, with or without symptoms present, need to have minimally invasive aortic valve replacement to replace the defective valve with a new mechanical or biological heart valve prosthesis. If there has been a diagnosis of severe AS, even if symptoms are not present, patients should be evaluated as soon as possible for surgical intervention. Clinical evidence shows that delaying surgery is dangerous.
Severe symptomatic aortic valve stenosis is a lethal condition that requires effective aortic valve replacement. No other medical treatment exists for this condition and, without surgery, 75% of patients will die within 3 years of being symptomatic.
Read Also: What Does A Heart Attack Look Like On An Ecg
Australian Heart Attack Survival Among Best In World But Could Be Better
Researchers have praised healthcare systems in Australia and New Zealand, after both nations recorded some of the worlds best long-term recovery rates for heart attack sufferers.
University of Queensland and Prince Charles Hospital cardiologist Associate Professor Isuru Ranasinghe and UQ Faculty of Medicines Dr Linh Ngo contributed to a study which found 62.3 per cent of heart attack sufferers in these nations lived a further seven years or more.
The survival rates we reported exceed those in the United States and England and are in the realm of Sweden, which had the best reported seven-year survival rate, Dr Ranasinghe said.From the 239,402 admissions with acute myocardial infarction , we found the survival rate in Australian and New Zealand hospitals was 76.2 per cent after three years, 68.6 per cent after five years, and 62.3 per cent at seven years.In particular, the prognosis for patients aged under 65 was excellent, with survival rates after seven years exceeding 85 per cent.Improved, evidence-based care is likely to explain these high survival rates, with secondary preventative measures such as targeted medicines increasing substantially since the year 2000.âIn the years 1999 and 2016, the frequency of urgent cardiac stenting rose from 43 to 71 per cent of cases for patients with segment elevation myocardial infarction with a similar increase observed in New Zealand.â
Recommended Reading: What Should Your Heart Rate Be When Walking
Also Check: What Is Healthy Resting Heart Rate
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy And Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator Device
If you have heart failure, you may need a special type of device called cardiac resynchronisation therapy device. As well as treating heart arrhythmias, this device also synchronises your hearts chambers to contract and relax in a regular way, which improves the pumping action of your heart.
There is also a type of CRT that can be used as above and in addition can deliver a shock to treat dangerous heart arrhythmias and then synchronise your hearts chambers to normal rhythm once more. This is CRT-D .
Recovery After Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is a serious procedure that necessitates constant monitoring and post-operative care. After the procedure, a person may need to stay in the intensive care unit for a few days to receive further treatment. A breathing tube will be left in place for a while after the operation to help with breathing. In addition, a line is left in the vein to provide pain treatment. A person could be connected up to a variety of various monitoring devices. A person will most likely stay in the hospital for roughly a week after exiting ICU. After leaving the hospital, it normally takes 4 to 6 weeks to recover at home. Take your time and be patient. Returning to normal levels of activity can take weeks or months. As part of a specific cardiac rehabilitation programme, some doctors may provide specialist support for daily activities and other aspects of recovery. Blood tests, heart scans, and stress testing may be part of the aftercare for each patient. During a treadmill activity, the heart is monitored as part of a stress test.
You May Like: Types Of Open-heart Surgery
Read Also: Mayo Clinic Congestive Heart Failure
What Happens After Open
Two or three tubes will be in your chest when you wake up after surgery. These are to help drain fluid from the area around your heart. Intravenous lines may be inserted into your arm to deliver fluids, and a catheter may be inserted into your bladder to evacuate urine. Youll also be connected to equipment that tracks your heart rate. Nurses are available to support you if the need arises.Your first night is usually spent in the intensive care unit . For the next three to seven days, you will be relocated to a standard care room.
You May Like: Recovery From Heart Bypass Surgery Time
Selection Of The Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Sample
All patients over 75years of age who underwent SAVR due to SAS with or without concomitant revascularization at our institution, between January 2006 and January 2015, were included in the study. Exclusion criteria were other concomitant valve procedures, ascending aortic surgery, emergency, critical preoperative status, previous cardiac surgery, endocarditis and emergency.
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee. Informed consent was waived for this retrospective study.
Recommended Reading: Back Pain After Open Heart Surgery
Ecmo Secondary Outcomes And Adverse Events
19 of 37 non-survivors had a bleeding event while on ECMO. 5 of these 19 patients needed re-operation of their chest. 8 of 23 survivors had a bleeding event on ECMO. 2 of these 8 patients needed re-operation of their chest for bleeding. This was not significantly different between survivors and non-survivors, but trending towards increased bleeding events in non-survivors . Survivors needed a mean 13 units of blood, while non-survivors needed a mean of 25 units of blood, this was found to be significantly different .
14 of 37 non-survivors required re-operation, which was significantly more than survivors . 3 of 23 survivors required re-operation, 2 for bleeding and 1 for sternal wound dehiscence. 20 non-survivors and 5 survivors developed renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy without significant difference between these groups . 18 non-survivors and 13 survivors developed sepsis, again, not statistically different . 8 non-survivors and 1 survivor developed intracerebral hemorrhage/anoxic brain injury which was not significantly different . 1 non-survivor and 2 survivors developed DVT/PE, which was not significantly different . 4 Patients , had clotting in their ECMO circuit, of these 2 patients were not anticoagulated with heparin and occurred at a mean of 10 days. Of note, one patient had thrombosis of the circuit in the OR and did not survive.
How Often Is Sts Data Updated
Childrens Colorado and other centers submit data to the STS twice per year. The STS then verifies the data and generates reports that allow us to compare our results with our peers.
We publish our outcomes data on this website as soon as possible following the STS data release, also twice per year.
Also Check: Can Gas Cause Heart Palpitations
What Is The Mortality Rate For Open Heart Surgery
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: How Much Does Open Heart Surgery Cost
Good Survival Rates Found In Heart Surgery For Aged
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this article
NEW ORLEANS Eighty-year-olds with clogged arteries or leaky heart valves used to be sent home with a pat on the arm from their doctors and pills to try to ease their symptoms. Now more are getting open-heart surgery, with remarkable survival rates rivaling those of much younger people, two new studies show.
Years ago, physicians were told we were pushing the envelope to operate on a 70-year-old, said Dr. Vincent J. Bufalino, a cardiologist at Loyola University Chicago. But today we have elderly folks who are extremely viable, mentally quite sharp, who want to decide for themselves whether to take the risk, said Dr. Bufalino, one of those who reviewed the studies for the American Heart Association.
Even 90-year-olds are having open-heart surgery, said Dr. Harlan M. Krumholz, a Yale cardiologist who has done other research on older heart patients. Age itself shouldnt be an automatic exclusion, Dr. Krumholz said.
Not every older person can undergo such a challenging operation, but the results seen in the new studies show that doctors have become good at figuring out who can.
Read Also: Congestive Heart Failure Feeling Cold
Cardiac Symptoms And Lvef
58.8% of patients had repeated admissions for cardiac-related events at 10 years. There was a non-significant trend towards improved symptoms post CABG with 32.3% patients remaining in NYHA class 34 symptoms post CABG compared to 50% before CABG . Post CABG mean LVEF improved from 24.9% to 32.2% . Sixty-six percent of patients post operation remained with LVEF < 35% and 53.3% patients had LVEF improvement by 5% or more. 16.6% of patients required cardiac resynchronization therapy or implantation of implantable cardioverter defibrillator . The GDMT rate was more than 90%.
Figure 3Figure 4
The Number Of Procedures Per Surgeon Makes The Difference
An important factor in this is the number of procedures per surgeon. In our hospital, all specialist cardiac surgeons performed over 100 cardiac surgeries. The surgeon who performed the most operations performed 222 procedures, and I, as Director, performed 121 procedures, says Peter Svenarud, Consultant and Director of Karolinska’s Thoracic Surgery Department.
Over the past five years, the mortality rate for cardiac surgery at Karolinska University Hospital has dropped significantly. At the same time, the number of cardiac surgeries increased.
We work with continuous quality improvement in all parts of a well-functioning healthcare chain. We have well-developed surgical methods and optimised surgical planning. The waiting time for heart surgery is now only 13 days, says Peter Svenarud.
Don’t Miss: Why Has My Resting Heart Rate Suddenly Dropped
Survival Across Types Of Interventions And Across Centres
Figure shows the risk-adjusted survival and hazard functions, stratified in the following intervention groups: isolated CABG, isolated valve, CABG and valve and other cardiac surgery. The curves all correspond to a patient with the median logistic EuroSCORE value of 3.74%. Stabilization of hazards is seen after a varying period of time. The hazard in the isolated CABG subgroup appears to reach the constant phase much earlier than the other intervention groups, approximately after 60 days. For the isolated valve subgroup and for the CABG and valve group subgroup, this takes 90 and 120 days, respectively. The effect of the intervention group appeared to be time-dependent . This means that the effect of the type of intervention decreased with time.
Risk-adjusted survival functions for different types of interventions and accompanying hazard functions. Risk-adjusted survival curves are plotted, stratified by the following intervention groups: isolated CABG, isolated valve, CABG and valve and other cardiac surgery. The curves correspond to a patient with the median logistic EuroSCORE value of 3.74%. Even after risk adjustment, stabilization of hazards is seen after a varying period of time. The hazard in the isolated CABG subgroup appears to reach the constant phase much earlier than the other intervention groups.
Read Also: Which Carries Oxygenated Blood From The Lungs To The Heart
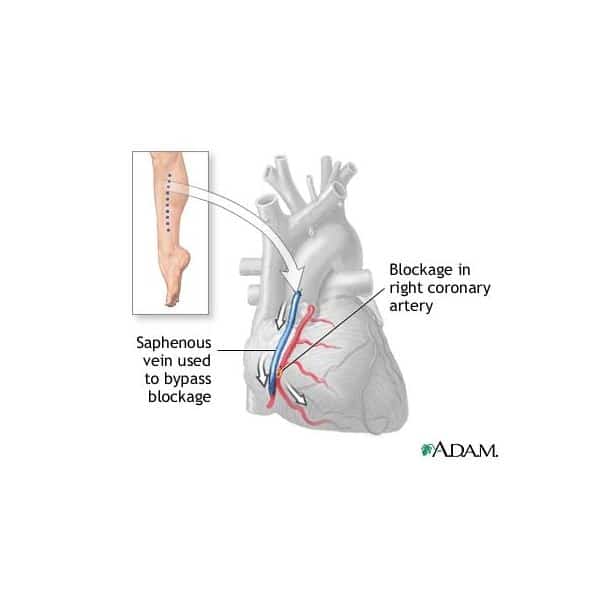
What Conditions Are Treated With Heart Surgery
Heart surgery treats a range of conditions that affect your heart and the blood vessels connected to your heart.
Aneurysms
An aneurysm is a bulge in your artery wall or heart muscle. One type of aneurysm is an aortic aneurysm. This occurs in your aorta, which is the large artery that carries blood out of your heart to the rest of your body. Aortic aneurysms may form in your belly . Less often, they form in your chest .
Aneurysms can also form in your heart muscle, usually in your left ventricle. This is the chamber of your heart responsible for pumping blood through your aorta.
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heartbeat. Your heart might beat too fast or too slow . Or, your heart may have an irregular rhythm. Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of irregular rhythm.
Over time, an arrhythmia can weaken your heart and lead to serious problems.
Congenital heart disease
Some congenital heart defects need to be repaired soon after birth. Other defects may not show symptoms right away. So, congenital heart disease can affect adults who never knew they had a problem. This often happens with atrial septal defects, which may not show symptoms until middle age.
Coronary artery disease
CAD may cause no symptoms. In some cases, it causes chest pain . If untreated, CAD can lead to a heart attack.
CAD is the most common form of heart disease, affecting about 18 million adults in the U.S.
Heart failure
Heart valve disease
- Stiff and narrow .
Don’t Miss: What Is A Dangerous Heart Rate For A Child
