Your Blood Pressure Is Impressive: Always Low But Dang Your Baseline Heart Rate Is Always Fast Like In The 90s
Every body is different however, higher resting heart rates can be an indication of underlying conditions such as hyperthyroidism, dehydration, the effects of drugs/medications , stress and high levels of stress hormones, or even deconditioning , explains Stacy Mitchell Doyle, MD, resident physician of FoodTherapyMD and long-time advocate of plant-based nutritional protocols.
Additional Causes of Baseline Fast Pulse
Overtraining in athletes or fitness enthusiasts
Menopausal/postmenopausal hormonal fluctuations
Though these aforementioned causes can be treated, the issue is the effect that a chronically fast pulse has on the heart.
Low blood pressure does not cancel out this effect.
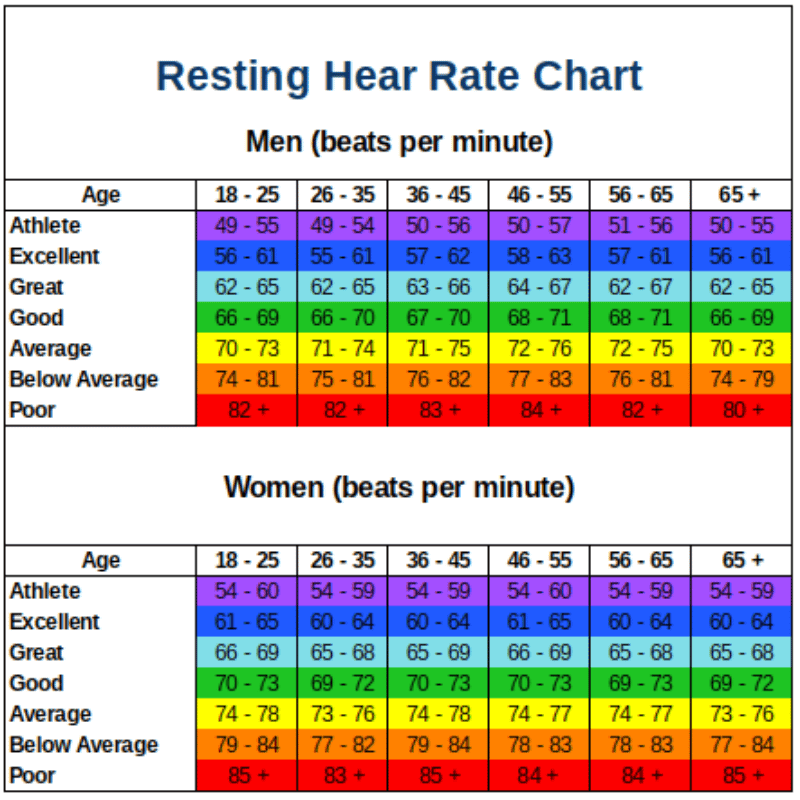
Though historically, a normal pulse was defined as between 60 and 100 beats per minute, that was before the studies began coming out that linked a rapid resting heart rate with several serious conditions.
Higher heart rates mean your heart is working harder to pump blood, and over time, higher resting heart rates have been associated with higher incidence of heart disease, stroke and all-cause mortality, says Dr. Doyle.
Yesterdays Normal Is Todays Fast90s
A study that came out in 2010 found that heart rates exceeding 83 beats per minute were associated with a 55 percent greater risk of cardiovascular death and a 79 percent higher risk of all-cause mortality.
And high blood pressure, plus other cardiovascular risk factors, were adjusted for.
Low Blood Pressure And Rapid Heart Rate
- Medical Author: Dan Brennan, MD
Last Editorial Review: 6/15/2020
Your symptoms are present in a wide variety of medical conditions, including dehydration, low blood pressure, and panic attacks. Keep track of how you are feeling. If you suspect dehydration, start with drinking some more fluids. If you are concerned about your symptoms, then you should contact your doctor.
While the list below can be considered as a guide to educate yourself about these conditions, this is not a substitute for a diagnosis from a health care provider. There are many other medical conditions that also can be associated with your symptoms and signs. Here are a number of those from MedicineNet:
Treatment Of Heart Block
Heart block normally only needs to be treated if it’s causing symptoms.
Depending on the cause of heart block and your symptoms, you may need to have a small device called a pacemaker fitted in your chest. A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device inserted under the skin of your chest. It sends frequent electrical pulses to keep your heart beating regularly.
Treatment for heart block usually works well. Most people live a normal active life with a pacemaker.
Don’t Miss: Low Heart Rate Chest Pain
Q What Can I Do To Prevent Low Blood Pressure
Treatment Of Fast Heart Rate
Treat the Underlying Cause: Most important is to ensure there is no underlying systemic problem that is causing the fast heart rate. If there is anemia, for example, that will need to be treated. Infection and dehydration would need to be treated. Hormonal imbalances would require treating. Medications will be reviewed and any potential offending agents will need to be stopped if possible.
Medications: It is important not just to treat a number the reason underlying must be sought out. If the fast heart rate is thought to be from a cardiac cause then the appropriate treatment should be given. If there is significant muscle dysfunction then treatment aimed at strengthening the heart is given. If there are problems with the electrical system of the heart then medicines to slow the rate may be given such a beta blockers or calcium channel blockers. In some cases stronger medicines that prevent the occurrence of the arrhythmia in the first place may be prescribed, known as anti-arrhythmic medications. Specialists known as electrophysiologists typically prescribe anti-arrhythmic medications.
Also Check: Survival Rate Of Heart Attack By Age
Treatment For Low Blood Pressure Depends On The Cause
If a cause can be found, a GP will be able to recommend treatment to ease your symptoms.
For example, they may suggest:
- changing medicines or altering your dose, if this is the cause
- wearing support stockings this can improve circulation and increase blood pressure
Medicine to increase blood pressure is rarely needed because simple lifestyle measures or treating the underlying cause is usually effective.
Read Also: A1c 5.7 Average Blood Sugar
What Are The Types Of Tachycardia
There are 3 types of tachycardia.
- Supraventricular where problems with the electrical signals in the upper chambers of the heart cause the heart to beat faster. This reduces blood flow to the rest of your body because your heart can’t pump blood as effectively. Two common types of supraventricular tachycardia are atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation.
- Ventricular where problems with the electrical signals in the lower chambers of the heart cause the heart to beat faster. This affects its ability to pump blood to the rest of your body.
- Sinus tachycardia where the natural pacemaker in your heart sends electrical signals faster than normal. This can be in response to a stressor described below, or it can be a sign of anaemia, problems with the thyroid gland or general ill health.
Read Also: Does Exercise Lower Heart Rate
Heart Rate Blood Pressure And Hypertensionlocation Location Location
However, the relationship between heart rate and blood pressure is more complicated when both central and peripheral blood pressures are considered. The studies mentioned above measured blood pressure peripherally. Recent investigations have revealed the importance of central blood pressures and the conduction properties of the vasculature in relation to adverse outcomes. Typical office blood pressure measurement is obtained peripherally, usually from the brachial artery. Unfortunately, this measurement does not account for marked variability in vascular compliance, leading to differences between central pressure measurements and pressure measurements peripherally of up to 20 mmHg . These marked differences have led to increased interest in detection of the central blood pressure profile as an important clinical marker for increased cardiovascular risk.
Causes And Risk Factors Of A Low Pulse Rate
Here are some conditions that can cause a low pulse rate:
Sick sinus syndrome
This syndrome is also known as sinus node dysfunction and primarily affects the sinoatrial node, which is the area in the top of the heart where the heartbeat impulse originates. The condition is more common in older people.
With this condition, your pulse rate will abnormally slow down and cause lightheadedness and dizziness because there is not enough blood and oxygen circulating to meet your bodys needs.
Atrioventricular blockage
Low heart pulse rate can be caused if the hearts signals dont move correctly from the atria to the ventricles . If this happens, the condition is called an atrioventricular block.
There are different versions of this condition, which can be detected by an EKG tracing or further cardiac testing to help pinpoint the area of dysfunction.
In some cases, a permanent pacemaker may be needed if no reversible cause is found.
Metabolic problems
Some metabolic issues can result in a lower heart pulse rate. The most common is hypothyroidism, which occurs when the thyroid gland fails to release enough hormones. The condition can affect the health of blood vessels and the metabolism level, consequently slowing down the heart pulse rate.
About 5% of Americans have hypothyroidism,¹ making it very common among otherwise healthy individuals.
Other metabolic conditions that can lead to low heart rate include:
Heart medication
Don’t Miss: Do Heart Palpitations Go Away
What Causes Low Blood Pressure And High Pulse Rate
Low blood pressure can cause high pulse rate. Also, in certain types of arrhythmias high pulse rate can result in fall in the blood pressure. High pulse rate refers to pulse greater than 100 per minute, and is also referred to as tachycardia.
High pulse rate or tachycardia is often associated with low blood pressure. Tachycardia is a reflex response to fall in blood pressure. When the blood pressure is low and the tissues of the body are not receiving adequate perfusion, the body raises heart rate in order to compensate for the low perfusion. Therefore, almost all causes of low blood pressure will result in low blood pressure with tachycardia.
Normal person with no symptoms and no primary disease condition will usually have normal pulse rate. In athletes and those who do regular exercise, both blood pressure and pulse rate might be low. This also is absolutely normal finding and requires no treatment.
Further evaluation is always necessary to ascertain the cause of low blood pressure and high pulse rate. Treatment is dependent upon the primary condition resulting in the hypotension and tachycardia.
Recommended Reading: What Can You Do To Raise Your Blood Pressure
Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure Levels
Eating a clean, balanced diet and being active can help you maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Consider adopting a DASH diet to create a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Lower your consumption of sodium, quit smoking, cut back on caffeine, and limit your alcohol intake to improve your health.
Consider the following lifestyle changes in conjunction with a balanced diet to help decrease symptoms associated with low blood pressure.
- Drink plenty of water
Also Check: High Heart Rate When Sick
What Are The Symptoms Of Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure often has no symptoms, but can sometimes mean that not enough blood is flowing to your brain or organs. This can cause symptoms such as:
- feeling dizzy, faint or light-headed
- feeling unsteady
- suddenly noticing your heartbeat
If you have these symptoms, stop what youre doing and sit down or lie down in case you fall, and drink some water.
Speak to your doctor or nurse if you experience these symptoms. As well as being unpleasant, they could mean youre at risk of having a fall. They could also be a sign of another health problem.
Can Low Blood Pressure And A High Heart Rate Be Normal
Yes, it can be normal, and this can happen if you stand up too fast. However, other factors can also cause it. Gravity pulls blood down into your legs and away from your brain when you stand up too quickly. This causes a drop in blood pressure, a condition known as orthostatic hypotension.
As a result, your heart rate increases to help the body maintain an adequate supply of oxygenated blood to the brain and other organs. This helps your body compensate for the drop in blood pressure. You may feel lightheaded or dizzy as a result.
Don’t Miss: How Accurate Is Heart Rate On Apple Watch
Does Heart Rate Affect Blood Pressure
Heart rate and blood pressure are controlled separately. However, they can impact each other. This is especially true at extremes, such as when heart rate is very high or blood pressure is very low.
In some cases, heart rate has a direct effect on blood pressure. For example, if the heart rate becomes dangerously high, such as during an arrhythmia, blood pressure often drops. This happens because the heart rate is too high for the heart to pump blood effectively.
On the other hand, blood pressure can also have an effect on heart rate. If you experience a condition called shock, in which the blood pressure is dangerously low, the heart rate typically rises. It does so to try to compensate and provide blood flow to the body. For example, this is seen in hypovolemic shock caused by low blood volume.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
If low blood pressure causes a person to pass out , seek treatment right away. Or call 911 or the local emergency number. If the person is not breathing or has no pulse, begin CPR.
- Black or maroon stools
Hypotension Blood pressure low Postprandial hypotension Orthostatic hypotension Neurally mediated hypotension NMH
Don’t Miss: What Is Considered A Low Heart Rate
Is There Such A Thing As Himalayan Pink Salt
Potential Risks of Himalayan Sea Salt Himalayan pink salt is a pink-hued variety of salt that is sourced near the Himalaya mountains of South Asia. Himalayan salt is believed by many to be a healthier alternative to common table salt, or sodium chloride. Though mined like rock salt, Himalayan pink salt is technically a sea salt.
Fast Heart Rate Overview And Conclusion
A fast heart rate although often defined as a heart rate over 90 is not necessarily abnormal and each case is different. History, physical exam and diagnostic testing are required in order to determine the significance of the heart rate and to see if any treatment is required. Treatment for non-cardiac causes of fast heart rate is to address the underlying cause. In the case of cardiac causes of fast heart rate, typically medication will be tried first or in some cases a procedure required particularly if the problem is with the electrical system of the heart.
Read Also: How Long After Shoveling Snow Can You Have A Heart Attack
The Difference Between Blood Pressure And Heart Rate
Blood pressure and heart rate are two different measurements. While they are frequently measured at the same time in the doctors office, they are distinctly different factors in heart health.
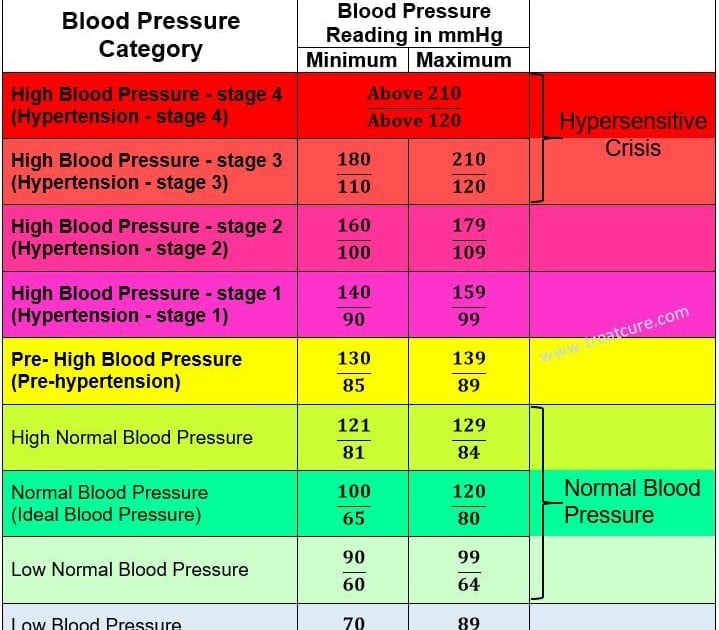
Blood pressure is the force exerted against the artery walls when blood pumps through the body, usually measured with two numbers. The top number measures the pressure as the heart beats and moves blood into the arteries. The bottom number measures the pressure as the heart relaxes between beats. A blood pressure reading of 120/80 is considered normal.
Heart rate, also called pulse, is the number of times your heart beats per minute. Heart rate can change based on activity level, age, medication, and other factors throughout life. For most adults, a resting heart rate of 50 to 100 beats per minute is considered normal. People who exercise regularly often have lower resting heart rates.
In some situations, such as periods of acute stress or danger, blood pressure and heart rate may both increase at the same time, but thats not always the case. Your heart rate can increase without any change occurring in your blood pressure. As your heart beats faster, healthy blood vessels will expand in size to allow increased blood flow, which helps your blood pressure remain relatively stable. This is often true during exercise, when your heart rate can increase substantially but your blood pressure may only change slightly.
Ask The Doctor: Does Heart Rate Affect Blood Pressure
Q. When doctors interpret a blood pressure reading, should they also consider the heart rate? I am a 78-year-old man and have had high blood pressure for more than 40 years. I frequently monitor my blood pressure at home, resting for five minutes before I take the reading. My blood pressure is often higher when my heart rate is close to its usual resting rate and lower when my heart is beating faster than that. Can the body’s demands that cause higher blood pressure be partially satisfied by a faster heart rate?
A. First, let me congratulate you on monitoring your blood pressure at home. This is a great way for you to take control of your high blood pressure, and a good step toward preventing a stroke. Knowing that your blood pressure at home is under consistent control is more important than getting isolated readings at the doctor’s office. You are also resting before taking the reading, and this is important to avoid spuriously high readings that happen when someone rushes around, and then sits down quickly to take a blood pressure reading.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctor’s visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
You May Like: How To Stop A Heart Attack Before It Happens
Solutionslow Blood Pressure 90s
If you find your heart rate is consistently high, but have a clean bill of health from your doctor, try more exercise and physical activity , urges Dr. Doyle.
Freepik.com/yahalya
Physical training will increase your hearts ejection fraction: the amount of blood pumped out with each beat.
One of the most effective, if not the most effective, types of exercise to accomplish this, especially in people under 65, is interval training.
Dr. Doyle also says to drink more water and stay hydrated, meditate and reduce stress, eliminate caffeine or any other stimulant, and eat those plant-based foods that supply you with phytonutrients and antioxidants that keep your heart and vessels healthy.
FoodTherapyMD is the brainchild of Dr. Mitchell Doyle and recognizes that phytonutrients, the substances that make plant food so amazing, can be tailored to fight specific disease states.
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. Shes also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
Other Types Of Abnormal Heart Rhythms

- Ectopic heartbeats occur when your heart misses a beat or adds an extra beat. They can arise from the atria or ventricles.
- Long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can cause fast and irregular heartbeats. These conditions are related to a specific abnormality in the hearts electrical system that can lead to fainting or even cardiac arrest.
- Paroxysmal arrhythmias are when the abnormal rhythm starts and stops suddenly. Episodes of paroxysmal arrhythmia can last for seconds, minutes, hours or up to a week.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Heart Rate Higher On Keto Diet
