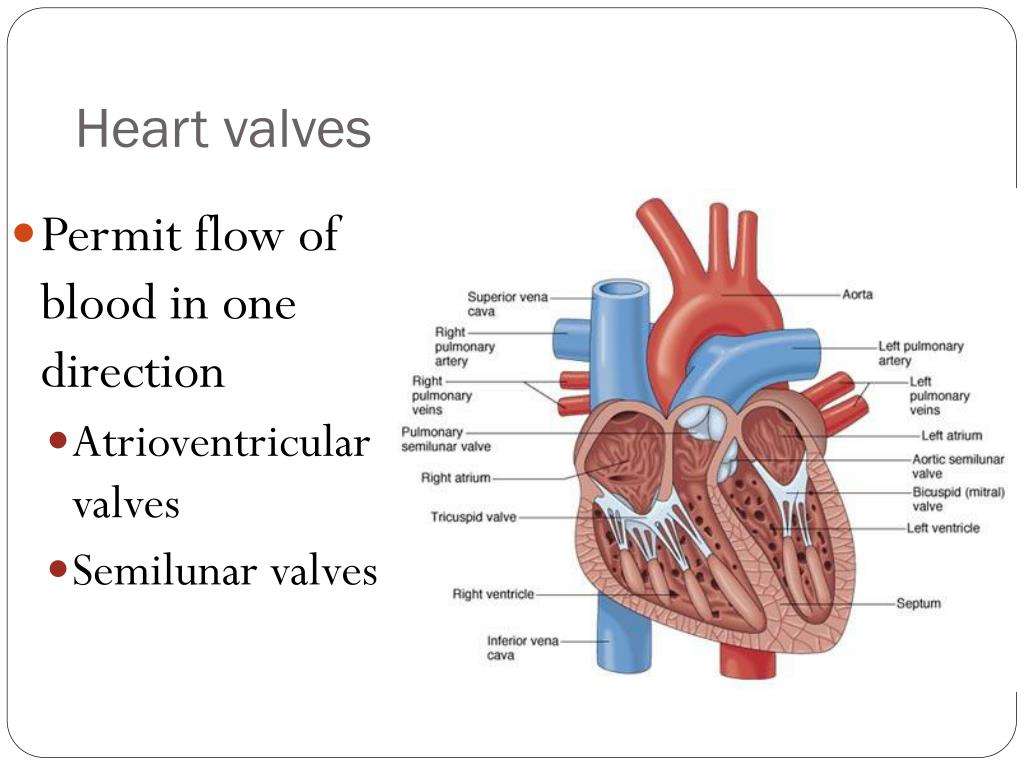
The Valves Are Like Doors To The Chambers Of The Heart
Four valves regulate and support the flow of blood through and out of the heart. The blood can only flow one waylike a car that must always be kept in drive. Each valve is formed by a group of folds, or cusps, that open and close as the heart contracts and dilates. There are two atrioventricular valves, located between the atrium and the ventricle on either side of the heart: The tricuspid valve on the right has three cusps, the mitral valve on the left has two. The other two valves regulate blood flow out of the heart. The aortic valve manages blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta. The pulmonary valve manages blood flow out of the right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk into the pulmonary arteries.
What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
left ventricleleft ventricle
The semilunar valves open when the ventricular muscle contracts and generates blood pressure within the ventricle higher than within the arterial tree. When the heart muscle relaxes the diastole phase begins again.
Similarly, what causes the closing of the aortic Semilunar valve? The Aortic ValveWhen ventricular systole ends, pressure in the left ventricle drops rapidly, and the valve closes due to a lack of pressure imposed on them from the left ventricle. Blood pressure within the aorta following systole also causes the closing of the valve.
Additionally, what is a Semilunar valve heart?
cardiovascular system. In human cardiovascular system: Valves of the heart. The semilunar valves are pocketlike structures attached at the point at which the pulmonary artery and the aorta leave the ventricles. The pulmonary valve guards the orifice between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
What is the function of the aortic Semilunar valve?
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in your body and carries blood with oxygen from the heart to the body. The semilunar valve prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle and keeps it moving towards the body. Here is a diagram of blood flow through the heart.
Atrial Systole And Diastole
Contraction of the atria follows depolarization, represented by the P wave of the ECG. As the atrial muscles contract from the superior portion of the atria toward the atrioventricular septum, pressure rises within the atria and blood is pumped into the ventricles through the open atrioventricular valves. At the start of atrial systole, the ventricles are normally filled with approximately 7080 percent of their capacity due to inflow during diastole. Atrial contraction, also referred to as the atrial kick, contributes the remaining 2030 percent of filling . Atrial systole lasts approximately 100 ms and ends prior to ventricular systole, as the atrial muscle returns to diastole.
Don’t Miss: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
How Your Heart Works
Your heart
The human heart is one of the hardest-working organs in the body.
On average, it beats around 75 times a minute. As the heart beats, it provides pressure so blood can flow to deliver oxygen and important nutrients to tissue all over your body through an extensive network of arteries, and it has return blood flow through a network of veins.
In fact, the heart steadily pumps an average of 2,000 gallons of blood through the body each day.
Your heart is located underneath your sternum and ribcage, and between your two lungs.
The hearts four chambers function as a double-sided pump, with an upper and continuous lower chamber on each side of the heart.
The hearts four chambers are:
- Right atrium. This chamber receives venous oxygen-depleted blood that has already circulated around through the body, not including the lungs, and pumps it into the right ventricle.
- Right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood from the right atrium to the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery sends the deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen in exchange for carbon dioxide.
- Left atrium. This chamber receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins of the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
- Left ventricle. With the thickest muscle mass of all the chambers, the left ventricle is the hardest pumping part of the heart, as it pumps blood that flows to the heart and rest of the body other than the lungs.
How The Heart Works
Your heart is a strong, muscular organ situated slightly to the left of your chest. It pumps blood to all parts of the body through a network of blood vessels by continuously expanding and contracting. On average, your heart will beat 100,000 times and pump about 2,000 gallons of blood each day.
The heart is divided into a right and left side, separated by a septum. Each side has an atrium and a ventricle . The heart has a total of four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle.
The right side of the heart collects oxygen-depleted blood and pumps it to the lungs, through the pulmonary arteries, so that the lungs can refresh the blood with a fresh supply of oxygen.
The left side of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs, then pumps blood out to the rest of the body’s tissues, through the aorta.
You May Like: Acetaminophen Heart Rate
Heart : Overview Function & Structure
A heart valve is a one-way valve that normally allows blood to flow in only one direction through the heart. The four valves are commonly represented in a mammalian heart that determines the pathway of blood flow through the heart.What heart chamber pushes blood through the aortic semilunar valve? Left ventricle Most blood flows passively into the ventricles through open AV valves. Yes, most of the ventricular filling is passive; atrial contraction adds just a little more blood.Circulatory system – order of blood flow through the heart; Step by step Pathway of Blood Flow Through the Heart Come also learn with us the heart’s anatomy, including where deoxygenated and oxygenated blood flow, in the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, atrium, ventricle, aorta…The aortic semilunar valves function is to close the left ventricle of the heart so the blood does not flow backwards into the heart. When the ventricles contract, the right ventricle pushes blood up through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary arteries via the pulmonary trunk, and the…Right atrium – Right tricuspid valve – Right ventricle – Pulmonary semilunar valve – Pulmonary arteries – Lungs the mitral valve to the left ventricle, big push through the aortic valve to the Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying…
CHAMBERS – VESSELS AND VALVES
QUESTION:;In part B, in the right atrium, what do the blue arrows represent?
How Does Blood Flow Through Your Lungs
Once blood travels through the pulmonic valve, it enters your lungs. This is called the pulmonary circulation. From your pulmonic valve, blood travels to the pulmonary artery to tiny capillary vessels in the lungs. Here, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, passes from the blood into the air sacs. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. Once the blood is purified and oxygenated, it travels back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Don’t Miss: Tylenol Heart Palpitations
The Four Main Valves Of The Heart Are As Follows:
Valves
| ;; Two of your heart valves are considered;atrioventricular valves. The atrioventricular valves include the;;tricuspid valve;and the;mitral;valve;. The atrioventricular valves, as you might expect, lie between the atria and the ventricles of the heart.;; | ;The other two heart valves are known as the the;semilunar valves.;The two semilunar valves include the;pulmonary semilunar valve;and the;aortic semilunar valve.; |
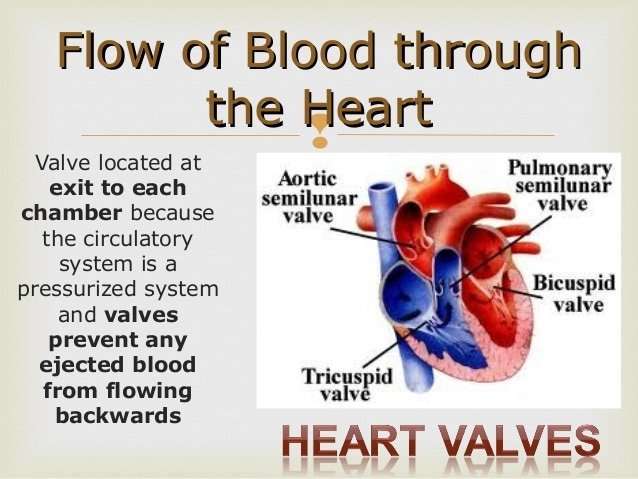
Blood Flow Through The Heart
The blood flow through the heart is quite logical. It happens with the heart cycle, which consists of the periodical contraction and relaxation of the atrial and ventricular myocardium . Systole is the period of contraction of the ventricular walls, while the period of ventricular relaxation is known as diastole. Note that whenever the atria contract, the ventricles are relaxed and vice versa. Lets put into words the heart blood flow diagram:
- The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior venae cavae and coronary sinus
- The right atrium contracts pushing blood through the right atrioventricular valve into the right ventricle. The right ventricle then contracts passing the blood into the pulmonary trunk via the pulmonary valve to reach the lungs;
- In the lungs, the blood gets oxygenated then moves back into the heart entering the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
- The left atrium contracts and pushes the blood into the left ventricle through the left atrioventricular valve.;
- The left ventricle pushes oxygenated blood through the aortic semilunar valve into the aorta, from which blood is distributed throughout the body.
The heart cycle is regulated completely subconsciously by an autonomic nerve plexus called thecardiac plexus.
Do you find the anatomy of the heart confusing? Learn actively;all the features of this organ and cement them long term by testing yourself using Kenhub’s diagrams, quizzes and worksheets of the heart!;
Recommended Reading: Can Too Much Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
Structure Of The Heart
The heart has four chambers . There is a wall between the two atria and another wall between the two ventricles. Arteries and veins go into and out of the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood to the heart. The flow of blood through the vessels and chambers of the heart is controlled by valves.
Heart Anatomy: By The Numbers
1. Superior vena cava: Receives blood from the upper body; delivers blood into the right atrium.
2. Inferior vena cava: Receives blood from the lower extremities, pelvis and abdomen, and delivers blood into the right atrium.
3. Right atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior vena cava; transmits blood to the right ventricle, which pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
4. Tricuspid valve: Allows blood to pass from the right atrium to the right ventricle; prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium as the heart pumps .
5. Right ventricle: Receives blood from the right atrium; pumps blood into the pulmonary artery.
6. Pulmonary valve: Allows blood to pass into the pulmonary arteries; prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle.
7. Pulmonary arteries: Carry oxygen-depleted blood from the heart to the lungs.
8. Pulmonary veins: Deliver oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
9. Left atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary veins.
10. Mitral valve: Allows blood to flow into the left ventricle; prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium.
11. Left ventricle: Receives oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium and pumps blood into the aorta.
12. Aortic valve: Allows blood to pass from the left ventricle to the aorta; prevents backflow of blood into the left ventricle.
13. Aorta: Distributes blood throughout the body from the heart.
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
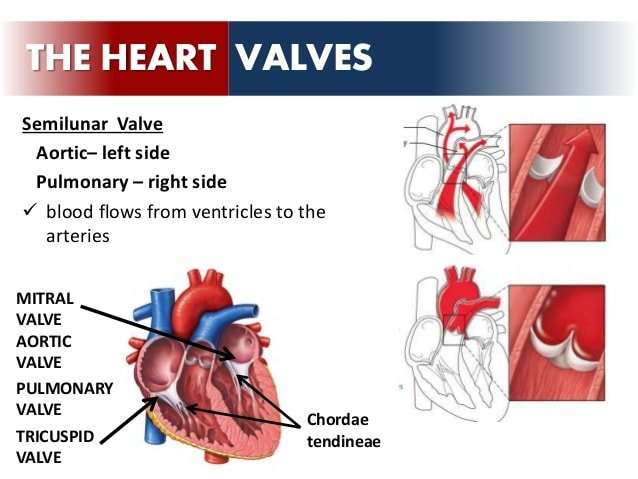
Valves Maintain Direction Of Blood Flow
As the heart pumps blood, a series of valves open and close tightly. These valves ensure that blood flows in only one direction, preventing backflow.
- The tricuspid valve is situated between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
- The mitral valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Each heart valve, except for the mitral valve, has three flaps that open and close like gates on a fence. The mitral valve has two valve leaflets.
The Atria Are The Hearts Entryways For Blood
The left atrium and right atrium are the two upper chambers of the heart. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood returning from other parts of the body. Valves connect the atria to the ventricles, the lower chambers. Each atrium empties into the corresponding ventricle below.
Recommended Reading: Thrz Calculator
Chambers Of The Heart
Short video of blood flow through the heart. arteries Aortic arch Brachiocephalic artery Left common carotid artery Left subclavian artery Descending aorta.This preview shows page 7 – 10 out of 39 pages. Part DWhat heart chamber pushes blood through the aortic semilunar valve?Hint 1.Does oxygenated or deoxygenated blood 10/8/2016 Session 1 Heart 8/39 Correct Correct. The aortic valve is located between the left ventricle and the aorta.The heart is a muscular organ located in the middle mediastinum that pumps blood through the circulatory system. The heart is surrounded by the pericardium and is divided into four chambers: two at… Semilunar valves. Structure: : three crescent-shaped cusps without subvalvular apparatus.When blood leaves each chamber of the heart, it passes through a valve that is designed to prevent backflow of blood. There are four heart valves As the ventricle contracts, oxygen-enriched blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the arteries and eventually into veins…
The Flow Of Blood Through The Chambers Of The Heart
The blood vessels that transport blood to and from all the body make up the SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT.;So the 2 chambers of the heart that;receive;blood are the ATRIA;;and;the two chambers of the heart that;send;blood are the VENTRICLES.;The ventricles contract and relax rhythmically;to create the pumping action of the heart.;;;;;The right atrium receives the deoxygenated blood that has traveled through the body. This blood has a low level of oxygen and a high level of carbon dioxide. This blood also has low pressure since it has traveled a good distance since it got its last “push” from the heart.;;;This deoxygenated blood from the lower and upper body travels to the right atrium, and then travels to the right ventricle. When the right ventricle contracts, it pushes the deoxygenated blood out of the heart and sends it to the lungs. . ;As this blood passes by the lungs, it picks up oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide.;;; The;oxygenated blood from the lungs then travels back to the heart to get another “push” before it goes to the body . ;;; The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood coming from the lungs. This blood enters the left atrium and then travels to the left ventricle. The left ventricle contracts to push the oxygenated blood out of the heart and to the body in order to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the cells and to pick up unwanted substances like waste and carbon dioxide.;
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Each Heart Beat Is A Squeeze Of Two Chambers Called Ventricles
The ventricles are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood empties into each ventricle from the atrium above, and then shoots out to where it needs to go. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, then pumps the blood along to the lungs to get oxygen. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium, then sends it on to the aorta. The aorta branches into the systemic arterial network that supplies all of the body.
The Heart Wall Is Composed Of Three Layers
The muscular wall of the heart has three layers. The outermost layer is the epicardium . The epicardium covers the heart, wraps around the roots of the great blood vessels, and adheres the heart wall to a protective sac. The middle layer is the myocardium. This strong muscle tissue powers the hearts pumping action. The innermost layer, the endocardium, lines the interior structures of the heart.
You May Like: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
The Cardiac Cycle Includes All Blood Flow Events The Heart Accomplishes In One Complete Heartbeat
The muscular wall of the heart powers contraction and dilation. Each contraction and relaxation is a heartbeat. Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out of the heart through the pulmonary and aortic valves. Diastole occurs when blood flows from the atria to fill the ventricles.
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
LAB Session 2 – Blood Vessels.pdf
George Washington University
51 pages
University of Iowa INTEGRATIV 163
Homework 19A
George Washington University NURSING 3104
LAB Session 2 – Blood Vessels.pdf
Gaston College BIOLOGY W BIO 168
Lab18&19.pdf
George Washington University NURSING 3104
Session 8 – Urinary.pdf
Laney College BIOL 20A
Don’t Miss: How Much Blood Does An Adult Heart Pump Every Day
Electrical Impulses Keep The Beat
The heart’s four chambers pump in an organized manner with the help of electrical impulses that originate in the sinoatrial node . Situated on the wall of the right atrium, this small cluster of specialized cells is the heart’s natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses at a normal rate.
The impulse spreads through the walls of the right and left atria, causing them to contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node, which acts as an electrical bridge for impulses to travel from the atria to the ventricles. From there, a pathway of fibers carries the impulse into the ventricles, which contract and force blood out of the heart.
What Are The Parts Of The Heart
Your heart is a bit like a house. It has:
- outer walls
- electrics .
Heart walls
The walls of your heart are made of powerful muscle tissue, which squeezes and relaxes to pump blood around your body. This muscle tissue is divided into three layers.
- The endocardium .
- The myocardium .
- The epicardium .
Heart chambers
Your heart is made up of four chambers, two on the right and two on the left. These are like the rooms of your house.
The top two chambers are called the left and right atrium and the bottom two are called the left and right ventricles.
They are divided by a thin wall called the .
Heart valves
There are four heart valves, which act like doors between the chambers of the heart. They open and close as your heart pumps.
The valves only open one way. This stops blood flowing in the wrong direction between the chambers of your heart.
The two valves that sit between the upper and lower chambers of the heart are called the atrioventricular, or AV valves.
The tricuspid valve is the door between the right atrium and ventricle.
The mitral valve is the door between the left atrium and ventricle.
The other two valves are the doors out of the ventricles. They are called semilunar, or SL valves.
The aortic valve is the door out of the left ventricle into the aorta.
The pulmonary valve is the door out of the right ventrical into the pulmonary artery.
The blood vessels
How the heart pumps
The heart’s conduction system
How the heart pumps
The coronary arteries
Don’t Miss: Can Acid Reflux Cause Palpitations
