The Atria Are The Hearts Entryways For Blood
The left atrium and right atrium are the two upper chambers of the heart. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood returning from other parts of the body. Valves connect the atria to the ventricles, the lower chambers. Each atrium empties into the corresponding ventricle below.
Blood In Need Of Oxygen Enters Heart
Blood in need of oxygen from around the body travels in the veins to the heart. This blood in need of oxygen is usually shown as blue or purple on diagrams.
This deoxygenated blood enters the top right hand side chamber of the heart, which is called the right atrium, via two large veins. Blood from the upper body, e.g. the head and arms, comes in via the superior vena cava. Blood from the lower body, that is the trunk and legs, comes in via the inferior vena cava.
What Is The Correct Order Of The Flow Of Blood
BloodbloodbloodBloodThe heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
- The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
- The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
Read Also: Can Dehydration Cause Increased Heart Rate
How The Heart Beats
How does the heart beat? Before each beat, your heart fills with blood. Then its muscle contracts to squirt the blood along. When the heart contracts, it squeezes try squeezing your hand into a fist. That’s sort of like what your heart does so it can squirt out the blood. Your heart does this all day and all night, all the time. The heart is one hard worker!
Page 1
Why Does Our Heart Go Lub
Our heart beats approximately 60-80 beats/min each time it beats it makes a sound similar to LUB-DUB and between each LUB and DUB of the heart, the heart pumps blood through our circulatory system. Ever wondered where those sounds come from?? Well, the valves that we spoke about earlier namely the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary and aortic valves are the ones responsible for these sounds. When the tricuspid and mitral valve close between their respective atriums and ventricle, the sound LUB is produced each time the pulmonary and aortic valves shut to prevent backflow to the ventricles, the sound DUB is produced. Now, sure enough, these valves dont shut as loudly as you slam your bedroom door, but the LUB-DUB sounds can definitely be heard when you hear the recorded sound of a heartbeat, or press your ear to someone elses chest!
You May Like: Can Antihistamines Cause Heart Palpitations
Regulation Of The Heart
The contraction of the muscle fibers in the heart is very organized and highly controlled. Rhythmic electrical impulses flow through the heart in a precise manner along distinct pathways and at a controlled speed. The impulses originate in the heart’s natural pacemaker , which generates a tiny electrical current.
The Heart Wall Is Composed Of Three Layers
The muscular wall of the heart has three layers. The outermost layer is the epicardium . The epicardium covers the heart, wraps around the roots of the great blood vessels, and adheres the heart wall to a protective sac. The middle layer is the myocardium. This strong muscle tissue powers the hearts pumping action. The innermost layer, the endocardium, lines the interior structures of the heart.
Also Check: How Does Atropine Increase Heart Rate
What Are The Parts Of The Circulatory System
Two pathways come from the heart:
- The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again.
- The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
In pulmonary circulation:
- The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide. The blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
In systemic circulation:
The Four Chambers Of The Heart
Your heart has a right and left side separated by a wall called the septum. Each side has a small collecting chamber called an atrium, which leads into a large pumping chamber called a ventricle. There are four chambers: the left atrium and right atrium , and the left ventricle and right ventricle .The right side of your heart collects blood on its return from the rest of our body. The blood entering the right side of your heart is low in oxygen. Your heart pumps the blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs so it can receive more oxygen. Once it has received oxygen, the blood returns directly to the left side of your heart, which then pumps it out again to all parts of your body through an artery called the aorta. Blood pressure refers to the amount of force the pumping blood exerts on arterial walls.
Don’t Miss: Fluticasone Heart Palpitations
Blood Supply Of The Heart
Like all organs, the heart needs a constant supply of oxygen-rich blood.
The coronary circulation, a system of arteries and veins, supplies the heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood and then returns oxygen-depleted blood to the right atrium.
The right coronary artery and the left coronary artery branch off the aorta to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. These two arteries branch into other arteries that also supply blood to the heart. The cardiac veins collect blood from the heart muscle and empty it into a large vein on the back surface of the heart called the coronary sinus, which returns the blood to the right atrium. Because of the great pressure exerted in the heart as it contracts, most blood flows through the coronary circulation only while the ventricles are relaxing between beats .
Right Ventricle Sends Blood Needing Oxygen To The Lungs
The blood needing oxygen is pumped out of the right ventricle, through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery then divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries, carrying blood to the right and left lungs. In the lungs the blood gives up its carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen.
Read Also: Can Antihistamines Cause Heart Palpitations
Blood Passes From Right Atrium To Right Ventricle
When the right atrium fills, the blood then passes through a one-way door called the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The valve stops blood from flowing backwards into the right atrium once its in the right ventricle. The right ventricle relaxes and venous blood in need of oxygen flows in.
How Can I Protect My Heart And Pulmonary Arteries
Many of the conditions that affect the pulmonary arteries are present at birth. While you cant prevent these problems, these actions can promote better heart health:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Get at least 150 minutes of cardiovascular physical activity every week.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Read Also: Flonase Chest Pain
Improving Health With Current Research
Learn about the following ways the NHLBI continues to translate current research and science into improved health for people who have heart conditions. Research on this topic is part of the NHLBI’s broader commitment to advancing heart and vascular disease scientific discovery.
Learn about some of the pioneering research contributions we have made over the years that have improved clinical care.
What Part Of The Heart Pumps Blood To The Body
4.2/5side of the heart pumps bloodside of the heartbloodpumpsbodyread here
The right ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Likewise, how does a heart pump blood? The right side of your heart gets blood from your body and pumps it into your lungs. Oxygen-poor blood flows in through the large veins to the right atrium. Then the blood moves into the right ventricle, which contracts and sends blood out of your heart to pick up oxygen from your lungs.
One may also ask, which part of the heart pumps blood to all parts of the body?
The left side of your heart receives oxygen-rich blood from your lungs and pumps it through your arteries to the rest of your body.
What pumps blood to the lungs?
The heart has a total of four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle. The right side of the heart collects oxygen-depleted blood and pumps it to the lungs, through the pulmonary arteries, so that the lungs can refresh the blood with a fresh supply of oxygen.
You May Like: How Does Blood Move Through The Heart
What Does The Heart Look Like And How Does It Work
- The heart is an amazing organ. It starts beating about 22 days after conception and continuously pumps oxygenated red blood cells and nutrient-rich blood and other compounds like platelets throughout your body to sustain the life of your organs.
- Its pumping power also pushes blood through organs like the lungs to remove waste products like CO2.
- This fist-sized powerhouse beats about 100,000 times per day, pumping five or six quarts of blood each minute, or about 2,000 gallons per day.
- In general, if the heart stops beating, in about 4-6 minutes of no blood flow, brain cells begin to die and after 10 minutes of no blood flow, the brain cells will cease to function and effectively be dead. There are few exceptions to the above.
- The heart works by a regulated series of events that cause this muscular organ to contract and then relax .
- The normal heart has 4 chambers that undergo the squeeze and relax cycle at specific time intervals that are regulated by a normal sequence of electrical signals that arise from specialized tissue.
- In addition, the normal sequence of electrical signals can be sped up or slowed down depending on the needs of the individual, for example, the heart will automatically speed up electrical signals to respond to a person running and will automatically slow down when a person takes a nap.
How Blood Flows Through The Heart And Lungs
The heart is a complex organ, using four chambers, four valves, and multiple blood vessels to provide blood to the body. Blood flow itself is equally complex, involving a cyclic series of steps that move blood trough the heart and to the lungs to be oxygenated, deliver it throughout the body, then bring blood back to the heart to re-start the process.
This is the key function of the cardiovascular system: consuming, transporting, and using oxygen throughout physical activity . Disruptions in blood flow through the heart and lungs can have serious effects.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Lower Blood Pressure
How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart
The cardiovascular or circulatory system is an important organ system of your body as it makes the blood flow through the heart, so it can transport oxygen, hormones, carbon dioxide, blood cells and nutrients to and from your body cells for nourishing the body, helping it fight diseases, stabilizing pH and temperature and maintaining homeostasis.For all these activities to take place, it is important the heart blood flow remains smooth and constant. Let us find out more about it.
What Does The Heart Look Like From The Inside
The heart is divided into two sidesthe right side and the left side. This is then further divided by a constriction into the upper and lower chambers, thereby resulting in 4 chambers of the heart. The 2 upper chambers are called the atria and the 2 lower chambers are called the ventricles. Thus, the 4 chambers of the heart are:
- Right atrium
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
The two atria are thin-walled structures separated into right and left halves by a septum running between them called the interatrial septum. The two ventricles are relatively thick-walled and separated by the interventricular septum running between them. One major circulatory vessel, either an artery or a vein, enters or leaves each chamber of the heart, thereby helping in the transport of blood. The flow of blood throughout the heart is controlled by a one-way valve system, which is extremely necessary to prevent the backflow of blood from the chambers. The valve present between the right atrium and the right ventricle is called the tricuspid valve a similar valve present on the left side is called the mitral valve.
Read Also: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
The Heart Is A Muscle
Your heart is really a muscle. It’s located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it’s about the size of your fist. There are lots of muscles all over your body in your arms, in your legs, in your back, even in your behind.
But the heart muscle is special because of what it does. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste.
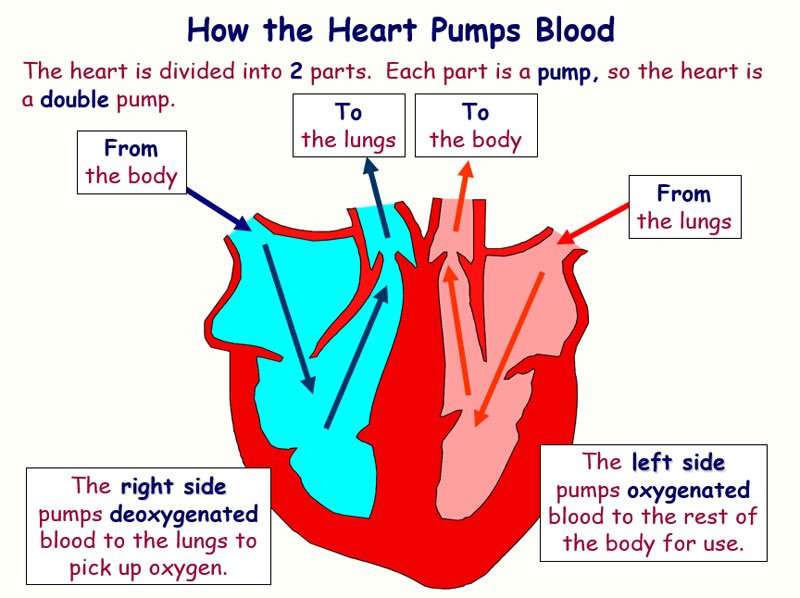
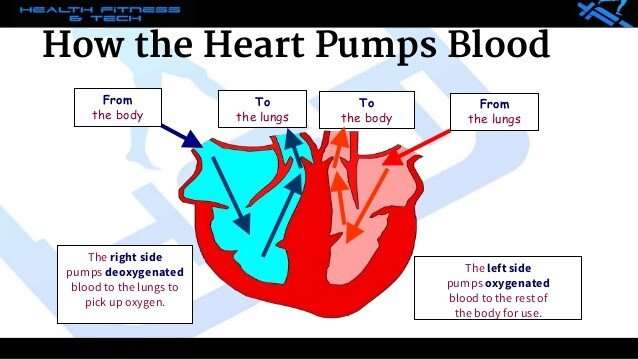
Your heart is sort of like a pump, or two pumps in one. The right side of your heart receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. The left side of the heart does the exact opposite: It receives blood from the lungs and pumps it out to the body.
Anatomy Of The Heart And Lungs
The heart and lungs are located in the thorax, or chest cavity. The heart pumps blood from the body to the lungs, where the blood is oxygenated. It then returns the blood to the heart, which pumps the freshly oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. The heart and lungs, together with the blood vessels, comprise the cardiovascular system. This system transports vital nutrients, gases, and hormones to the rest of the body.
The heart is a pear shaped organ, positioned centrally within the chest cavity, with the apex extending over to the left nipple. The heart is divided into a right and left side, each side having an atrium and ventricle. The contraction of the heart pumps blood throughout the body. The right side receives oxygen poor blood from the major veins of the body, and pumps this blood into the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The left side of the heart then receives oxygen rich blood from the lungs, and pumps this blood through the arteries, into the body.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
The Interior Of The Heart
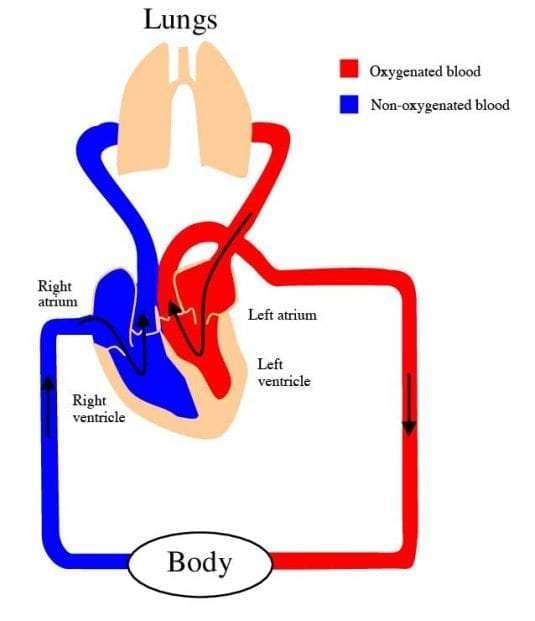
Below is a picture of the inside of a normal, healthy, human heart.
The illustration shows a cross-section of a healthy heart and its inside structures. The blue arrow shows the direction in which low-oxygen blood flows from the body to the lungs. The red arrow shows the direction in which oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs to the rest of the body.
Right Side Of The Heart
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atria while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated and then returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
Where Does The Right Side Of The Heart Receive Blood From
The right side of your heart receives oxygen-poor blood from your veins and pumps it to your lungs, where it picks up oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide. The left side of your heart receives oxygen-rich blood from your lungs and pumps it through your arteries to the rest of your body.
In this regard, where does blood go from the right side of the heart?
Right side of the heartBlood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into yourright ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
Secondly, where does the left side of the heart receive blood from? The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The left side of the heart receives the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the body.
Accordingly, where does the right atrium receive blood from?
The right atrium receives and holds deoxygenated blood from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, anterior cardiac veins and smallest cardiac veins and the coronary sinus, which it then sends down to the right ventricle , which in turn sends it to the pulmonary artery for pulmonary
What happens on the right side of the heart?
The right side of your heart receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. The left side of the heart does the exact opposite: It receives blood from the lungs and pumps it out to the body.
Research For Your Health
The NHLBI is part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health the Nations biomedical research agency that makes important scientific discoveries to improve health and save lives. We are committed to advancing science and translating discoveries into clinical practice to promote the prevention and treatment of heart, lung, blood, and sleep disorders, including heart conditions. Learn about current and future NHLBI efforts to improve health through research and scientific discovery.
Recommended Reading: Low Pulse High Blood Pressure Causes
