What Is The Outlook For People With Heart Failure
With the right care, heart failure may not stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis or outlook for the future will depend on how well your heart muscle is functioning, your symptoms, and how well you respond to and follow your treatment plan.
Everyone with a long-term illness, such as heart failure, should discuss their desires for extended medical care with their doctor and family. An “advance directive” or “living will” is one way to let everyone know your wishes. A living will expresses your desires about the use of medical treatments to prolong your life. This document is prepared while you are fully competent in case you are unable to make these decisions at a later time.
Show Sources
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. Thereâs no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so youâll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, youâll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Donât Miss: 100 Resting Heart Rate
Seattle Heart Failure Model
2 days agoNYHA Class 1. BiV Pacer/ICD. Same as BiV pacer. LVAD. NYHA Class 4 and. EF 25% and. Mean 2 year survival 50%. If you want to see the effect in the model anyway, make the patient characteristics match the criteria, then click on the device you want, then set the patient criteria back to the original values.
Also Check: Can Hypothyroidism Cause Heart Palpitations
Read Also: Heart Rate Of 100
What Is Acute On Chronic Chf
When heart muscles are damaged chronically, the term Chronic is used to define such a condition but sometimes, a chronically damaged heart can get a viral infection, certain vessels blockage, or shortness of breath leading to acute heart failure of chronic CHF. Medical professionals call it acute on chronic heart failure. The simple definition could be Sudden onset of chronic heart condition.
Clinical Findings Of Acute Congestive Heart Failure
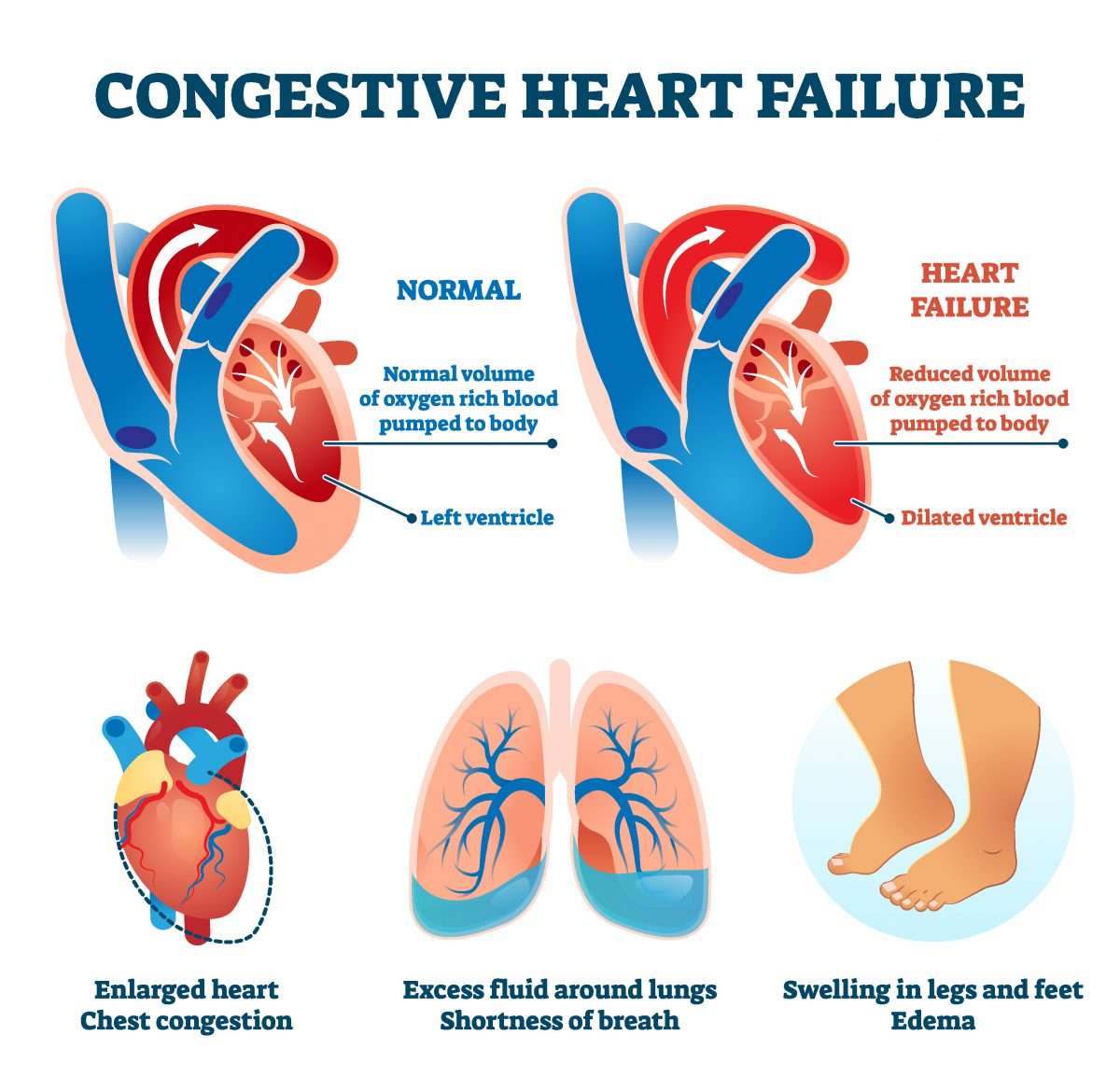
Heart failure is primarily a clinical syndrome. It is a constellation of findings and symptoms that point to a failing pump in which the heart functions. Common symptoms include dyspnea, lower extremity edema, rapid weight gain, and fatigue. A failing heart causes pulmonary edema and fluid third spacing. These are the primary reasons for symptoms. Physical exam findings that support such a syndrome include jugular venous distension, pitting edema of the lower extremities, crackles or rales on pulmonary auscultation, and S3 gallop if there is systolic heart failure. Despite the delineation of diastolic versus systolic heart failure, in the ED, the treatment for acute heart failure is the same. Common interchangeable terms include decompensated or symptomatic heart failure.
The differential diagnosis for dyspnea with pulmonary adventitious lung sounds is broad. Brain natriuretic peptide can be helpful to make the diagnosis. However, some clinical conditions can falsely elevate the BNP. The pathophysiology of heart failure is complex and involves neurohormonal activation as well as sodium and water retention. Increased systemic vascular resistance worsens fluid retention. The cardiovascular system often promotes perfusion for a short period but unless addressed, can lead to increasing work for the heart. Likewise, this may lead to further complications like further decompensation, heart remodeling, and/or ischemia.
You May Like: High Reating Heart Rate
Causes Of Acute Heart Failure
Many conditions can weaken or damage the heart over time. This can lead to heart failure.
With chronic heart failure, your heart tries to adapt to the additional strain over time until it just cant adapt anymore. Thats when acute heart failure happens.
Its also possible for acute heart failure to happen even in people who otherwise seem healthy. There are a number of conditions that can put a sudden strain on your heart.
Causes of acute heart failure include:
- coronary artery disease, which can cause a narrowing of the arteries
- heart attack, which causes damage to the heart muscle and is often caused by coronary artery disease
- use of certain illegal drugs, such as cocaine
- chemotherapy and radiation treatments
In the United States, Black and Hispanic people receive heart failure diagnoses more often than people from other racial or ethnic groups. And Black people in the United States are also at the highest risk of dying from heart failure.
These trends are related to racism and inequities in healthcare, according to the American College of Cardiology.
To diagnose acute heart failure, your doctor will run certain tests. Your doctor can then identify your stage of heart failure, to help find the right treatment for you.
Acute On Chronic Systolic Chf Icd 10
The Acute On Chronic Systolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.23.
ICD 10 has a different subcategory of codes for both systolic and diastolic heart failures, I50.2 for systolic, and I50.3 for diastolic heart failure. If the diagnosis is described as only systolic but acute and chronic, the code, under this subcategory I50.23, is complete code for this condition. If the provider has not mentioned systolic or diastolic, never use code from the I50.3 or I50.2 category.
You May Like: Foods To Avoid With Congestive Heart Failure
Ecg Interpretation In Chf
- JAMA Rational Clinical Exam article lists these ECG features as the most important in AHF: atrial fibrillation , new T-wave changes or any abnormal ECG findings increase the likelihood of AHF, whereas a completely normal ECG decreases the likelihood of AHF
- Others to keep in mind: any other arrhythmia , left bundle branch block signifying possible poor LV function, and evidence of ventricular hypertrophy, which may signify untreated chronic hypertension or valvular disease
- Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema has been associated with giant, diffuse, symmetrical inverted T waves with QT prolongation
Education Counselling And Support
- A role is emerging for heart failure liaison nurses in educating and supporting patients and their families, promoting long term compliance, and supervising treatment changes in the community
- Depression is common, underdiagnosed, and often undertreated counselling is therefore important for patients and families, and the newer antidepressants seem to be well tolerated and are useful in selected patients
Short term bed rest is valuable until signs and symptoms improve: rest reduces the metabolic demand and increases renal perfusion, thus improving diuresis. Although bed rest potentiates the action of diuretics, it increases the risk of venous thromboembolism, and prophylactic subcutaneous heparin should be considered in immobile inpatients. Full anticoagulation is not advocated routinely unless concurrent atrial fibrillation is present, although it may be considered in patients with very severe impairment of left ventricular systolic function, associated with significant ventricular dilatation. Intravenous loop diuretics may be administered to overcome the short term problem of gut oedema and reduced absorption of tablets, and these may be used in conjunction with an oral thiazide or thiazide-like diuretic . Low dose spironolactone improves morbidity and mortality in severe heart failure, when combined with conventional treatment . Potassium concentrations should be closely monitored after the addition of spironolactone.
Also Check: Have Statins Reduced Heart Attacks
Stage A Treatment Options
Treatment options in stage A mainly focus on promoting your overall health and disease prevention. If you meet the stage A criteria, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to slow or stop disease progression.
Heart Failure Doctor Discussion Guide
Can Heart Failure Be Prevented
You may be able to prevent or delay heart failure if you:
- Work with your provider to manage any health conditions that increase your risk of developing heart failure
- Make healthy changes in your eating, exercise, and other daily habits to help prevent heart disease
NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Don’t Miss: How High Can Heart Rate Go
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Congestive Heart Failure Unique
Yale Medicines team comprises heart failure cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, dedicated advanced-practice, registered nurses and nurse coordinators, dietitians, exercise physiologists, financial counselors, immunologists specializing in transplants, psychologists, and specialists in palliative care.
With a multidisciplinary approach, Yale Medicine physicians include the patients desires as well as input from the family to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that’s right for them.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
If you are experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, sudden swelling of the arms or legs, or fatigue on exertion, you may want to get checked by a healthcare professional.
Heart failure and CHF are chronic, progressive conditions that can often be managed with timely treatment, so do not wait to be seen by a healthcare professional if you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms.
Read Also: Congestive Heart Failure Survival Rate
Search Page 1/: Heart Failure Nyha Class Iii
3 days ago500 results found. Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M26.213 Malocclusion, Angles class III. Malocclusion, angle class iii Malocclusion, angles class iii Mesio-occlusion. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T86.32 Heart -lung transplant failure. Failure of heart-lung transplant.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Heart Attack In Women
Patient Discussion About Failure
Q. What Is the Treatment for Congestive Heart Failure? My mother is 76 years ols and has been suffering from a heart disease for many years. Lately she has developed congestive heart failure. How is this situation treated?
A.
Q. congestive heart failure how it works is it to do with fluid built up in your body
A.
Q. describe the symptoms of congestive heart failure
A.
Also Check: Stage 5 Congestive Heart Failure
Disposition For Ed Patients With Acute Congestive Heart Failure
- Multiple factors have been shown to predict worse prognosis and the need for admission: systolic BP < 120, low sodium, high BUN, elevated creatinine, elevated troponin, ECG changes, BNP > 500 and poor response to initial therapy other considerations for admission include patients with first-episode AHF
- Several prediction models for those who can be discharged from the ED have unacceptably high mortality rates at 30d , but may include patients with frequent visits to the ED for exact same presentations with good response and clear diagnosis, that have made inappropriate use of prescription medications, NSAIDs or salt intake these patients still need prompt follow-up with CHF clinic or their primary care provider
E Common Pitfalls And Side
Management of patients with AHF is complex and highly specific to the individual. However, there are some common pitfalls:
Hypotension: Most therapies for AHF can cause hypotension, and the development of hypotension in a number of studies has been related to poor clinical outcomes. Blood pressure , central venous pressure , body weight, urine output, and renal function should be carefully monitored to avoid hypotension. If hypotension ensues, rapidly remove inciting pharmacologic agents and position the patient as necessary to improve perfusion. In many patients, raising the legs will provide sufficient augmentation of venous return to improve symptoms.
Worsening renal function: This problem is the most vexing for clinicians, since worsening renal function can result from inadequate diuresis or be the result of excessive diuresis with volume depletion. In these situations, it is very helpful to have measurements of baseline BUN and creatinine as comparators. Ultimately, the treatment decision will be determined by the extent of volume overload as assessed by the JVP and other clinical factors, as well as the subsequent response to therapy. As noted above, transient decreases in renal function may not portend the poor prognosis, as previously believed, and may just reflect the response to therapy.
You May Like: What Heart Rate Should I Run At
Classification Of Acute Heart Failure
The definition of AHF presented here is broad and there have been many attempts to stratify this further . Although characterised by a distinctive set of signs and symptoms, a major challenge in classifying AHF as a single entity is that the patient population is not uniform. Patients admitted with HF exhibit a wide spectrum of disease and range from those with severe LV systolic dysfunction and low cardiac output to those with severe hypertension and normal or near-normal LV systolic function. The majority of patients with AHF lie between these extremes and therefore also demonstrate a distribution of underlying pathology and precipitants, leading to the common endpoint of fluid overload.
This is a neat classification system and focusses the treating physician towards the management of the underlying cause of AHF. However, given patients often present with a range of co-morbidities, the reasons for decompensation may not be apparent at initial presentation or indeed, there may be multiple contributing factors. Practically speaking, therefore, it may be more prudent to stratify patients with AHF based on their initial clinical presentation. This allows the attending physician to identify those most at risk in order to direct specific interventions such as instituting ionotropic agents and/or mechanical circulatory support.
Stage B Treatment Options
While stage A CHF is managed with lifestyle changes, the treatment plan for stage B typically includes taking medications regularly. People at this stage should still make the same lifestyle changes as those appropriate for stage A. However, your doctor may also prescribe additional treatments such as:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Beta blockers if youve had a heart attack and your EF is 40% or lower, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Possible surgery or intervention as a treatment for coronary artery blockage, heart attack, valve disease, or congenital heart disease
Recommended Reading: How Long Heart Attack Pain Last
Diseases Of The Circulatory Systemtype 2 Excludes
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Code First
B Physical Examination Tips To Guide Management

The physical exam may be used to assess the response to therapy and guide management.
Blood pressure should be carefully followed, though with the advent of improved noninvasive monitoring, invasive arterial lines are rarely necessary. Hypotension has been associated with poor outcomes in the setting of AHF, and iatrogenic hypotension should be assiduously avoided. Hypertension can be one of the major precipitants of AHF and should be treated.
Heart rate is often a reflection rather than a cause of the AHF episode, and the initial tachycardia often improves in conjunction with the improvement in dyspnea. However, atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response is a well-known precipitant of AHF.
Tachycardia may occur due to the positive chronotropic effects of some drugs , excessive volume depletion, or the onset/ worsening of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, especially atrial fibrillation. Bradycardia is less common and may be due to excess beta-blocker therapy.
Respiratory rate is often not as carefully assessed clinically, and may not be as reliably sensitive to therapy as other vital signs. Tachypnea may represent inadequate resolution of the initial episode of dyspnea or a new event, such as a pulmonary embolus. Fever is suggestive of underlying infectious process, particularly pneumonia or urinary tract infections, both of which can instigate AHF exacerbations.
You May Like: How Low Should Your Heart Rate Be
Iv Management With Co
The average age of the patient with AHF is in the 70s therefore, these patients tend to have multiple comorbidities in addition to the underlying cause of the heart failure. Many of these comorbidities can both cause and exacerbate AHF. Some of the most important comorbidities include:
Atrial fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation can be both a cause of and exacerbated by AHF. Many patients present in atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response with AHF, but generally, therapies are initially directed to the AHF, since the ventricular rate often decreases as the adrenergic drive resolves. However, in some patients, the AF assumes a more primary role, often with a very rapid ventricular response . In these patients, rate control is important and can be challenging.
In patients with preserved ejection fraction, beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are often effective. Calcium channel blockers active on the atrioventricular node, such as diltiazem and verapamil, should be avoided in patients with reduced ejection fraction, due to their acute negative inotropic properties. Digoxin, beta-blockers, and amiodarone are often used in the setting of AHF with reduced ejection fraction. Although one must always consider the risk of thromboembolic events, if the patient is truly hemodynamically unstable due to AF with rapid ventricular rate, electrical cardioversion remains an important option.
Chf Icd 10 Codes And Guidelines
Most of the heart failure codes include in chapter 9 of ICD-10 CM manual, diseases of circulatory system, code range I00-I99.
- Combination code If patient has any type of heart failure and hypertension, it should be combined and coded as I11.0 eventhough physician has not linked both. It should not be coded combined if the medical record states the conditions are unrelated.
- Heart failure should be coded additionally when coding I11.0
- Do not code I11.9 when coding I11.0 .
- When coding biventricular heart failure it is necessary to code the type of left heart failure also according to the code also note with I50.82
Go by Failure, Heart to find correct codes for heart failure in ICD-10 CM manual index.
Look at the below scenarios to clearly understand the coding concepts of CHF.
CHF ICD 10 Code Example 1
Elizabeth is a 65 year old female who comes to emergency department for shortness of breath and leg edema from past 2 days. She came to visit doctor as the symptoms are getting worse. She has hypertension and takes Lisinopril for the same. She does not have chest pain or palpitation. She is not a smoker. Her family history includes heart disease for her mother and brother. Vitals showed temperature 97.3 F, heart rate 72 bpm, respiratory rate 25, BP 150/96 mmHg. Physical exam showed pitting edema on both the extremities, shortness of breath and dry skin. Physician ordered for blood tests, EKG and chest X-ray. This case was diagnosed as acute diastolic heart failure.
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Have Heart Palpitations When I Lay Down
