When Should I See A Doctor
If you experience any of the symptoms of heart disease or heart attack, don’t hesitate to contact a doctor and get help. “For some heart problems, every minute counts,” says Dr. Lowenstein. “Blocked blood flow to the heart or an abnormal heartbeat need attention right away. A heart attack can result in permanent damage to the heart muscle within 30 minutes. Delaying help could mean you end up with a more serious problem that could result in a hospital stay or even death. Even if you’re not sure you’re having a heart issue, it’s better to be safe than sorry. Call 911 or get to a hospital, where doctors can examine and treat you promptly.”
Why Have I Been Offered Statins
Having a high level of LDL cholesterol is potentially dangerous, as it can lead to a hardening and narrowing of the arteries and cardiovascular disease .
CVD is a general term that describes a disease of the heart or blood vessels. It’s the most common cause of death in the UK.
The main types of CVD are:
- coronary heart disease when the blood supply to the heart becomes restricted
- angina chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscles
- heart attacks when the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked
- stroke when the supply of blood to the brain becomes blocked
A doctor may recommend taking statins if either:
- you have been diagnosed with a form of CVD
- your personal and family medical history suggests you’re likely to develop CVD at some point over the next 10 years and lifestyle measures have not reduced this risk
Find out more about when statins may be recommended.
Data Source And Search Strategy
We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure , Wanfang Database, and Chinese Scientific Journal Database from the inception dates to October 31, 2017. The search strategy used the following general terms individually or combined: âstatinâ, âHMG-CoAâ, âsimvastatinâ, âfluvastatinâ, âlovastatinâ, âpravastatinâ, âatorvastatinâ, ârosuvastatinâ, âcoronaryâ, âheartâ, âanginaâ, âCADâ, âCHDâ, âmyocardial infarctââ, âMIâ. The detailed search strategy is shown in Supplementary Material 2. We also checked the reference lists of existing reviews to identify the included studies.
Read Also: Why Is My Resting Heart Rate Increasing
How Common Are The Side Effects Of Statins
As with all drugs, statins carry a risk of side effects. The most common is muscle ache or pain. About 10 percent of people on a statin will develop this, although it is usually fairly mild, and it is entirely reversible without causing damage to the muscle when the drug is discontinued. In 1 out of 10,000 cases, a patient on a statin will develop serious pain and muscle damage. This is so rare that Ive never seen it in a patient.
Typically, we can eliminate the muscle aches by changing the dose of the statin or switching to a different statin, as the molecular structures of statin medications can be quite different. We usually can find one a patient can tolerate well without side effects.
Other side effects can include increased risk for diabetes and liver damage, but these are also quite rare.
The West Of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study

The paper is published today in the journal Circulation. It follows on from a five-year 1995 study in which researchers observed the long-term effects of statins on patients involved in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study trial. The researchers took into account the original five-year study and followed the patients for a further 15 years.
This is the strongest evidence yet that statins reduce the risk of heart disease and death in men with high LDL.
Professor Kausik Ray
School of Public Health
The WOSCOPS study provided the first conclusive evidence that treating high LDL in men with pravastatin for five years significantly reduces the risk of heart attack or death from heart disease compared with placebo. Statins were subsequently established as the standard treatment for primary prevention in people with elevated cholesterol levels.
Now, researchers have completed analyses of the 15-year follow up of 5,529 men, including 2,560 with LDL cholesterol above 190 mg/dL of the original 6,595, chosen because they had no evidence of heart disease at the beginning of the present study.
Participants were aged 45-64 years. During the five-year initial trial they were given pravastatin or placebo. Once the trial ended the participants returned to their primary care physicians, and an additional 15-year period of follow-up ensued.
Professor Kausik Ray
School of Public Health
Don’t Miss: Cough After Open Heart Surgery
Cholesterol Lowering Drug Can Help Prevent Heart Attacks Strokes
High cholesterol is a familiar warning sign for cardiovascular disease. While some people can control their cholesterol through diet and exercise, others also may need medication. Thats where statins come in.
Statins are commonly used to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. Millions of people who have heart disease or are at high risk take them and help protect their hearts that way.
Who needs statins?
Treatment for high cholesterol is based on overall risk for cardiovascular disease.
Your doctor will consider all your risk factors, including cholesterol levels and medical conditions, says Todd Hitchcock, MD, a cardiologist at Scripps Clinic Carmel Valley. If you doctor recommends statins, its because you are at risk for heart disease or stroke.
Other risk factors include smoking, lack of exercise, high blood pressure, diabetes, high blood sugar levels, excess weight or obesity, family history of heart disease and older age.
Statins are also recommended for people whove had a heart attack or stroke even if they dont have high cholesterol.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance made by the liver that travels through the blood. There are two types of cholesterol. One is good. The other is bad.
HDL cholesterol is the good cholesterol. It helps remove the bad cholesterol and protect the arteries.
Why is high cholesterol bad?
How do statins work?
What are the risks and benefits of statins?
- Heart & Vascular
Related tags:
Medicines To Prevent Heart Attack And Stroke: Questions For The Doctor
Statins are medicines that reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke by helping to lower the amount of cholesterol and other fats in the blood.
Experts recommend that if youve never had a heart attack or stroke, you take a statin if all 3 of these statements are true:
- Youre age 40 to 75
- You have high cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure, or you smoke
- Your doctor has decided that you are at higher risk for heart attack and stroke
Statins arent right for everyone, and all medicines have pros and cons. When you talk with your doctor about taking a statin, its important to discuss your personal preferences as well as your risk for heart attack and stroke.
Also Check: Icd 10 Code Congestive Heart Failure
What Are The Side Effects Of Statins
Statins may cause mild side effects, including:
- Type 2 diabetes or high blood sugar.
Adults and teens can take statins. Most people dont have side effects from statins, but you shouldnt take them if youre pregnant, nursing or have certain types of liver disease. Let your provider know if you have diabetes. If youre already at risk for diabetes, statins can add to your risk of getting it.
Some people have an interaction with another medicine while taking statins. Whenever your provider considers prescribing medication for you, its important to tell them what else youre taking. That includes other prescription drugs, medicines you buy without a prescription, vitamins, herbs, supplements and recreational drugs.
If one type of statin gives you side effects, ask your provider if they can switch you to a different one. You may also want to ask your provider if you need to avoid grapefruit or pomegranate or their juices or if its ok to have a small amount. These foods can make it hard for your body to break some statins down, allowing too much of the drug to accumulate in your body and giving you more side effects.
Statins Lower Heart Attack Stroke Risk In People At Average Risk
Please note: This article was published more than two years ago, so some information may be outdated. If you have questions about your health, always contact a health care professional.
Editors note: This is one in a 10-part series of the top medical research advances of 2016 as determined by the American Heart Association.
Millions more people worldwide may benefit from cholesterol-lowering statins after a global study showed the drugs help reduce heart attacks and strokes in people at moderate risk. The risk fell slightly further when patients also took blood pressure drugs.
Medications to lower blood pressure have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease in people with elevated blood pressure and those at high risk, and statins have been shown to benefit those at high risk. But a group of researchers wanted to know if treating each condition alone or simultaneously might prevent heart attacks and strokes in an ethnically diverse group of average-risk people without cardiovascular disease.
HOPE-3s findings reinforce 2013 guidelines from the AHA and American College of Cardiology that recommend statins for more people.
Based on these latest findings, about 300 million people worldwide could be eligible for statin treatment, estimates Salim Yusuf, M.D., D.Phil., the studys lead investigator and professor of medicine at McMaster University in Canada.
You May Like: Congestive Heart Failure Stages Of Dying
Study Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
We included all randomized controlled trials , and the publication language was either English or Chinese. Participants without a clinical history of CHD were included, age and race were not limited. The treatment group was given statins alone or combined with usual care, and the control group was given nothing, placebo, or usual care. Usual care was generally determined based on the specific disease of the participants for example, patients with diabetes will be given hypoglycaemic agents such as metformin, and patients with hypertension will take captopril or other antihypertensive medicines. If we did not know whether the participants had CHD, these articles were excluded. In addition, we also excluded articles without full text. Moreover, the primary outcomes in this systematic review mainly included angina, nonfatal and/or fatal MI, any coronary heart events, coronary revascularization, and CHD deaths. The secondary outcomes involved any cardiovascular events, CVD deaths and all-cause mortality. We also reported the adverse events, which mainly comprised cancer, diabetes, gastrointestinal/hepatic/renal disorder, myalgia, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, alanine aminotransferase , aspartate aminotransferase , creatine kinase , and so forth. The results of the included studies must involve at least one of the primary outcomes.
Why Did My Doctor Prescribe Statins If My Cholesterol Is Normal
Even if your circulating cholesterol is normal according to the numbers onyour blood test results, there may already be plaque present in yourarteries that indicates youre at risk for cardiovascular disease, saysJohns Hopkins cardiologist Michael Blaha. Additional tests may show moreconclusively that plaque build-up is a problem.
Because many factors are involved, your cholesterol numbers may beconsidered normal and yet you may still be found to be at an elevated riskfor heart problems. As a result, statin medications are now used to lowerthe risk of heart disease and heart events in most anyone found to be athigh risk.
Recommended Reading: Can You Recover From Congestive Heart Failure
New Study Adds To Debate Over Statin Use To Prevent Cvd
The authors say while guidelines look at the benefits of statins to prevent cardiovascular disease , they do not adequately assess the harms. The new model takes this into account.
The 2013 recommendation from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association to use statins to prevent cardiovascular disease for some adults with long-term risk kicked off a debate that has not stopped.
Despite support from the US Preventive Services Task Force , some physicians say the harms of statins outweigh the benefits for many patients, and too many patients complain of side effects. Now, a new analysis in the Annals of Internal Medicine supports this viewfor too many patients, authors from the University of Zurich say, the benefits simply dont outweigh the harms.1
The researchers, led by Henock G. Yebyo, MSc, conducted an extensive analysis based on mathematical modeling and concluded the 2013 guidelines should be revised to use much higher 10-year risk thresholds when recommending statins for prevention, and guidelines should be customized based on age, gender, and statin type.
The ACC/AHA guideline called for use of statins for the primary prevention of CVD among adults with a 10-year risk of 7.5% of higher, based on the method of calculating risk contained in the guideline . As this calculator has made its way into practice, there have been adjustments for patient preference and most recently for coronary artery calcium scores to guide decision making.
Drilling Down On The Data:
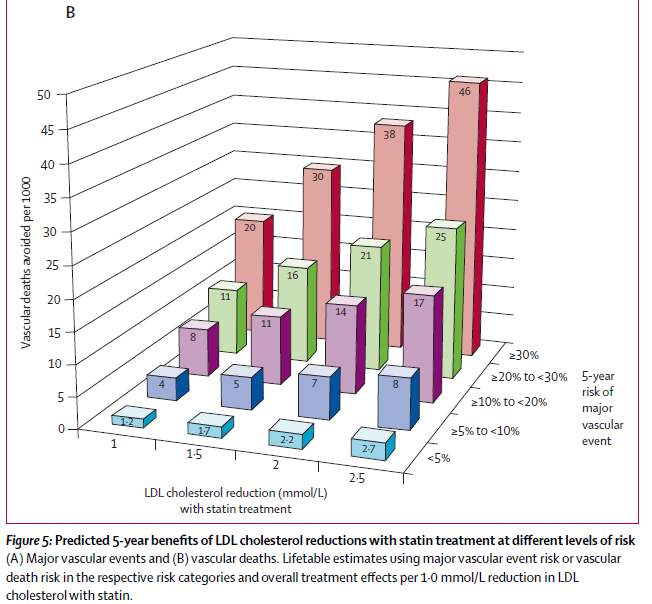
The authors were looking for two major outcomes: A Major Adverse Cardiovascular Event and mortality. Did statins save lives?
Here is what they found:
In this meta-analysis, only 1 of 8 randomized trials found that statins decreased all-cause mortality when used for primary prevention. We found that 100 adults aged 50 to 75 years would need to be treated for 2.5 years to avoid 1 MACE. This result suggests that statin treatment is most appropriate for adults aged 50-75 years with a life expectancy of greater than 2.5 years. For those with a life expectancy of less than 2.5 years, the harms of statins may outweigh the benefits. These results reinforce the importance of individualizing statin treatment decisions by incorporating each patients values and preferences.
OK, thats pretty technical. But the authors make it relatively simple.
They state unequivocally in their conclusions:
There is no evidence of a mortality benefit.
That means that for primary prevention there is little, if any, evidence that statins save lives. The drugs will prevent 1 MACE such as a heart attack out of 100 adults. It will take about 2.5 years for this benefit to show up. Another way of saying that is that 99 adults out of 100 will not avoid a MACE by taking a statin.
Read Also: Swollen Ankles Heart Failure
Cholesterol Confusion: Statins Have Little Impact On Heart Health Study Says
DUBLIN, Ireland How bad is bad cholesterol when it comes to heart health? A new study finds the link between the two may not be as strong as many doctors have thought.
In fact, a team from the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland says taking cholesterol-lowering statins appears to do very little to help prevent a heart attack or stroke. Their study is now questioning the use of LDL cholesterol-lowering statins for the purpose of cutting a patients heart disease risk.
Estimates show that more than 200 million people worldwide take statins to either lower cholesterol levels or improve heart health. Previous research has pointed to statins playing a role in improving cardiovascular disease outcomes including the risk of suffering a heart attack, stroke, or premature death from all causes.
The Evidence For Statins
Since lovastatin’s introduction in 1987, more than 100,000 people have participated in controlled trials of statins. Nearly six out of seven participants have been men, mainly because men develop heart disease earlier and make up a greater share of heart patients. These studies have found a 25% to 40% reduction in male cardiac events and cardiac deaths. Perhaps not surprisingly, they are less informative about the effects of statins on women. Many studies simply combined data for men and women, and others didn’t include enough women to permit statistically significant conclusions.
Hoping to get more definitive answers, researchers from the University of California at San Francisco and the University of North Carolina combined and re-analyzed the data for women in several major statin studies. Writing in the Journal of the American Medical Association , they offered these conclusions:
|
Statins |
Don’t Miss: What Is Open Heart Surgery
Are Statins Really Worth Taking For High Cholesterol
Apple Podcasts | | Stitcher | Spotify
Research has shown that statins are highly effective in reducing the risk of fatal heart attack and stroke. But some people are reluctant to take these life-saving drugs. They worry about taking medicine every day for the rest of their life or have heard that statins have undesirable side effects. What does science have to say about these concerns and others surrounding statins? We talked to UH interventional cardiologist Ian Neeland, MD, Director of the Center of Cardiovascular Prevention at University Hospitals, to learn more.
Inconsistent And Inconclusive Impact
However, these new findings reveal less-than-convincing evidence that this benefit is really significant. Specifically, researchers found statins had an inconsistent and inconclusive impact on CVD outcomes. Moreover, the true impact of taking LDL cholesterol-lowering statins may actually depend on each patients personal risk factors.
The message has long been that lowering your cholesterol will reduce your risk of heart disease, and that statins help to achieve this. However, our research indicates that, in reality, the benefits of taking statins are varied and can be quite modest, says lead author Dr. Paula Byrne in a media release.
Study authors add that health professionals should be communicating these new findings to patients who are making decisions about their heart health and which prescription drugs to take.
Along with cardiovascular disease, recent studies have also found inconsistent data surrounding statins and COVID-19. While some reports find evidence the cholesterol drug could lessen the severity of the virus, others find statins have little use as a coronavirus treatment.
The findings are published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine.
Also Check: How Is The Recovery Heart Rate Calculated
