Diagnosing Systolic Heart Failure
Systolic heart failure is diagnosed with a noninvasive test called transthoracic echocardiography. This test involves an ultrasound that can generate pictures of the heart and evaluate the heart’s pumping function , as well as the valves and flow of blood.
Other tests to help determine the cause and complications of heart failure include:
- Blood tests, including blood counts, electrolytes, and kidney, liver, and thyroid function
- Electrocardiogram
- Stress testing such as a nuclear stress test
- Coronary angiography
Etiology Congestive Heart Failure
There are numerous causes for systolic heart failure, but the most common is related to coronary artery disease and prior myocardial infarctions. This entity is termed an ischemic cardiomyopathy and accounts for nearly half of systolic heart failure cases in the United States.
Dilated cardiomyopathy is the second leading cause of systolic HF. This can be idiopathic , a viral cardiomyopathy, peripartum and hypertensive heart disease . These include doxorubicin therapy, stress-induced , alcohol-related, selenium or thiamine deficiency, tachycardia-mediated, giant cell arteritis, hyperthyroidism, cocaine use, obstructive sleep apnea and familial cardiomyopathies.
The third leading cause of systolic HF is valvular heart disease. This includes aortic valve stenosis, aortic valve regurgitation, mitral valve stenosis and mitral regurgitation. In many developing nations, the most common cause of systolic HF is Chagas disease, which is related to Trypanosoma cruzi and transmitted by triatomine bugs.
Recall that right heart failure and diastolic heart failure are different entities from the left-sided systolic heart failure reviewed here. The most common cause of right HF is pressure overload related to left HF. Diastolic HF is most commonly caused by hypertension as a part of hypertensive heart disease. Aging of the heart contributes to diastolic HF as well.
Severe Congestive Heart Failure
Despite conventional treatment with diuretics and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, hospital admission may be necessary in severe congestive heart failure. Fluid restriction is importantfluid intake should be reduced to 1-1.5 litres/24 h, and dietary salt restriction may be helpful.
Weighing the patient daily is valuable in monitoring the response to treatment
You May Like: Causes Of Left Sided Heart Failure
Indications And Contraindications To Cardiac Transplantation In Adults
Indications
- End stage heart failurefor example, ischaemic heart disease and dilated cardiomyopathy
- Rarely, restrictive cardiomyopathy and peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart disease
Absolute contraindications
- Recent malignancy
- Active infection
- Systemic disease which is likely to affect life expectancy
- Significant pulmonary vascular resistance
- Psychosocial problemsfor example, lack of social support, poor compliance, psychiatric illness
Correction of valve disease, most commonly in severe aortic stenosis or mitral incompetence , relieves a mechanical cause of heart failure closure of an acute ventricular septal defect or mitral valve surgery for acute mitral regurgitation, complicating a myocardial infarction, may be lifesaving. Surgical excision of a left ventricular aneurysm is appropriate in selected cases. Novel surgical procedures such as extensive ventricular reduction and cardiomyoplasty have been associated with successful outcome in a small number of patients, although the high mortality, and the limited evidence of substantial benefit, has restricted the widespread use of these procedures.
Causes And Symptoms Of Acute Heart Failure
The most common cause of acute heart failure is a heart attack . This is caused by blockages in the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle. Other causes include viruses, severe infections, allergic reactions, blood clots in the lungs, certain medications, or an illness that can attack the heart muscle.1
Shortness of breath is the most common symptom of AHF. Acute heart failure can also present with symptoms of rapid swelling and fluid retention characterized by sudden weight gain, up to several pounds in a 24-hr period. Coughing, wheezing, difficulty laying flat to sleep, as well as an irregular heartbeat can also be symptoms. In some cases, it is related to pre-existing cardiomyopathy. AHF often requires unexpected hospital admission. This tends to have a poor prognosis, with a high risk of readmission and death post-discharge.1 Seek emergency medical treatment if sudden or painful symptoms develop.
Read Also: How Long Can Heart Attack Last
Causes Of Systolic Heart Failure
Systolic heart failure is usually caused by another cardiovascular condition that weakens the heart muscle. For example:
- Aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the valve in the large blood vessel that branches off the heart
- Arrhythmia, an irregular heart rhythm
- Cardiomyopathy, any condition affecting the heart muscle
- Coronary artery disease, narrowing of the blood vessels that bring blood to the heart
- Heart attack, which occurs when the heart doesnt get enough blood
- High blood pressure , the force of blood pushing against arteries
- Mitral regurgitation, when a valve in the heart doesnt close tightly, allowing blood to flow backward in the heart
- Myocarditis, inflammation of the heart muscle
What Is Systolic Heart Failure
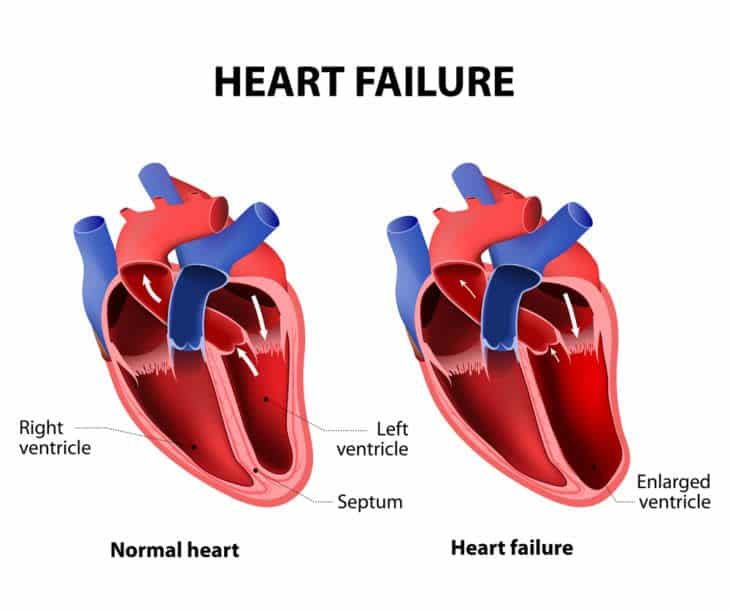
Systolic heart failure is a condition in which the left ventricle of your heart is weak.
Your left ventricle is the largest and strongest chamber of your heart. Its responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood from your lungs to the rest of your body.
When the left ventricle is weak it can cause fluid to build up in your lungs, resulting in shortness of breath or fatigue. It can also cause swelling in your body, including your belly, feet and legs.
Systolic heart failure can result from coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, previous heart attack, abnormal heart rhythm, alcohol use disorder and many other causes.
Its important to recognize symptoms of heart failure and identify the cause. There are many treatments available that can improve your heart function, quality of life and how long you live.
You May Like: What Is An Abnormal Heart Rate
Acute On Chronic Systolic Or Diastolic Congestive Heart Failure Admission
Scenario:
Patients have a history of CHF most of the time. New onset CHF is also seen in ER. They develop pedal edema gradually at home but recently they might have had more shortness of breath, tiredness, more swelling, cough, PND or orthopnea, etc. Not uncommonly, patients ate lot of salted chips, pretzels, or drank soup bought from store with high salt content immediately before they present in ER. This is relatively common. Some patients keep drinking a lot of water like they always did when they were young.
EMS:
Oxygen via Nasal cannula or Non Rebreather mask depending on necessity.
Lasix if diagnosis is very clear to the EMS staff.
Routine labs plus BNP, EKG, CXR
Oxygen
IV Lasix 40-80 mg x 1, Foley catheter placement
ABG, BiPap or Intubation if necessary> ICU if intubated
Observe in Telemetry floor. Can make them inpatient if patient has severe electrolyte disturbances, tachycardia, hypotension, worsening kidney function or if requiring BiPap etc.
Low salt diet-2gm Sodium diet, fluid restriction to 1500ml.
Continue IV Lasix 40-60mg Q 2-3 times a day .
Input/Output.
Cardiac Enzymes Q3hrs 2 or 3 times.
2D ECHO
Lipid Panel in AM labs.
Elevate legs with pillows above heart level and also elevate head of the bed to help with breathing
Cardiology consult
ACEI or ARB if EF < 40%-for after load reduction.
Coreg or Toprol XL, Start Beta Blockers at low doses and when patient is euvolemic.
Hydralazine and Nitrates esp. if African American Patients.
IV Lasix +/-Metolazone.
Airway Structure And Lung Function
Pulmonary function exhibited both restrictive and obstructive changes in HF patients in this study . Previous studies have shown approximately 20% reductions in FVC, FEV1, and FEF2575 with the development of HF . However, in both the control and HF groups, the airway luminal area in at least one generation was significantly related to each of the four spirometry variables, FEV1, FVC, FEF2575, and PEF at baseline. It is possible that the airway generations most responsible for modulating lung function with disease and after ADRB2 agonist administration are located below the resolution of CT scanning this is discussed in more depth below . Furthermore, the location of the equal pressure point, or the point of airway narrowing or collapse during a maximal expiration, is dependent on the resistance and luminal area of the airways leading to limitations of flow through that segment independent of driving pressure . This study suggests that it is necessary to quantify smaller airways to properly characterize the relationship between airway structure and function.
Recommended Reading: Aha Heart Failure Stages
What Is The Outlook For People With Systolic Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic serious condition that can shorten your lifespan. Prognosis depends on several factors, including:
- How advanced heart disease is.
- Overall health and other health conditions.
- Response to treatments.
- Sudden and severe shortness of breath.
What else can I ask my healthcare provider?
Consider asking your healthcare provider:
- What is causing systolic heart failure?
- Is it affecting other organs?
- What is my ejection fraction?
- How can I improve my condition?
- What lifestyle changes or medications might help me?
- What should I avoid?
- When should we test my ejection fraction again?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Systolic heart failure is a serious, chronic condition that occurs when the left ventricle cant pump blood efficiently. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of heart failure. Treatment for any underlying causes and good lifestyle choices can ease symptoms and help you live a longer, fuller life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/14/2022.
References
Effects Of An Adrb2 Agonist On Lung Structure And Function
After ADRB2 agonist administration, the CT attenuation distributions for both groups shifted significantly to the left and were narrower relative to baseline . The mean, skew, kurtosis, full width half max , and percentage of voxels greater than 500 HU changed significantly with similar changes between the groups . Linear regression for baseline values versus percent change of mean attenuation, skew, kurtosis, FWHM, and percentage of voxels greater than 500 HU showed a statistically significant correlation for all values in both groups suggesting greater clearance in those with more fluid at baseline . Agonist administration increased the absolute size of the wall and decreased the fraction of the wall relative to the area significantly in all generations for the HF group and generations 3 through 6 for the control group . There was no statistical difference between the groups after agonist administration. After albuterol administration, neither the absolute nor the normalized airway areas changed for either group or between groups . After albuterol administration , FEV1, FEV1/FVC, and FEF2575 improved significantly for the HF group and FEV1 and FEF2575 improved for the control group . The HF group improved more than the control group for FEV1 and FEF2575 . There was no difference after albuterol for FVC, PEF, and TLC between groups. There were no statistically significant correlations between changes in pulmonary function and CT quantitative indices or airway areas.
Recommended Reading: Open-heart Surgery Survival Rate By Age
What Is Ejection Fraction
Systolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction .
Ejection fraction is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. Its a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood.
The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF under 40% may indicate systolic heart failure.
Tests For Acute Heart Failure
Your doctor will assess your medical history and perform a physical exam. Theyll listen to your heart and lungs with a stethoscope to detect any congestion or abnormal heart rhythms. Your doctor may also check for fluid buildup in your abdomen, legs, and the veins in your neck.
In addition, your doctor might request tests such as:
- Blood tests. These could include a BNP test, which measures a hormone related to heart failure.
- Electrocardiogram . During this test, your doctor will attach electrodes to your skin and record your hearts electrical activity.
- Stress test. This test measures your heart activity during physical exercise. Its not typically recommended if you already have signs and symptoms of heart failure.
Imaging tests that a doctor can use to help diagnose heart failure include:
- Chest X-ray. This test allows your doctor to better examine your heart and lungs.
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to form a live, moving image of your heart so your doctor can see which areas of your heart are affected.
- Angiogram. If your doctor thinks you may have a blocked artery, they will insert a thin tube into your groin or arm and into your coronary arteries. After injecting dye through a catheter, your doctor can see an image of your arteries.
When needed, other imaging tests can be used to look for underlying causes of heart failure:
Together, your physical exam and test results can help your doctor learn about the health of your heart.
Recommended Reading: What Heart Rate Is Considered Tachycardia
Precipitating Factors Of Ahf
The onset and increase in systemic congestion that precede AHF may develop over hours up to days, and can be triggered by several factors, either directly through stimulation of pathophysiological mechanisms leading to fluid accumulation or redistribution or indirectly through a worsening of cardiac diastolic or systolic function. The understanding of the pathophysiology involved in the development of AHF is important for providing the appropriate treatment. Although in many patients a progressive increase in body weight and pulmonary pressures may be observed as early as several days before hospital admission, in a relevant proportion of patients AHF is associated with only a minimal increase in body weight,. Several registries, including the North American OPTIMIZE-HF registry and the Euro-Asian registry of the GREAT network, have investigated the presence of precipitants in patients with AHF,. Acute coronary syndromes, arrhythmias , infections , uncontrolled hypertension and non-compliance with dietary recommendations and drug prescriptions are the most common identified precipitants,. Of note, in a relevant proportion of patients , no precipitants could be identified, whereas a combination of multiple factors were present in ~520% of patients,.
Management Of Chronic Heart Failure
General advice
- Ventricular assist devices
- Heart transplantation
Common features of chronic heart failure include breathlessness and reduced exercise tolerance, and management is directed at relieving these symptoms and improving quality of life. Secondary but important objectives are to improve prognosis and reduce hospital admissions.
Also Check: Left Side Vs Right Sided Heart Failure
Prognosis Of Systolic Heart Failure
In general, a diagnosis of heart failure is serious, since it can cause life-threatening arrhythmias and organ failure.
Taking medications as prescribed, monitoring fluid status, and close follow-up with a healthcare provider can help people with heart failure stay out of the hospital and improve quality of life.
Advanced treatments and heart transplant are also options for those with very severe heart failure.
Systolic Heart Failure Symptoms
The hallmark feature of systolic heart failure is shortness of breath, also called dyspnea.
A person with early systolic heart failure might get short of breath only when exercising. But a person with advanced systolic heart failure might have trouble breathing when simply walking across the room or even when resting.
Other signs of systolic heart failure are:
You May Like: Heart Rate When Working Out
Sacubitril/valsartan Treated Adult Patients With Chronic Heart Failure
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : November 14, 2022Last Update Posted : November 15, 2022 |
| Drug: sacubitril/valsartan |
This was a non-interventional, retrospective cohort study using secondary data sources from the Optum Clinformatics® Data Mart and 100% files of the CMS Medicare RIFs.
Two study cohorts were constructed to include adult Heart Failure with reduced ejection fraction patients who newly initiated sacubitril/valsartan and adult Chronic Heart Failure patients who newly initiated sacubitril/valsartan .
The date of first prescription fill for sacubitril/valsartan during the cohort identification period was defined as index date. A 12-month washout period was employed to ascertain the “new user” status. The Healthcare Resource Utilization and costs of care outcomes will be measured within both the 12 months post-index period and the 12 months pre-index period.
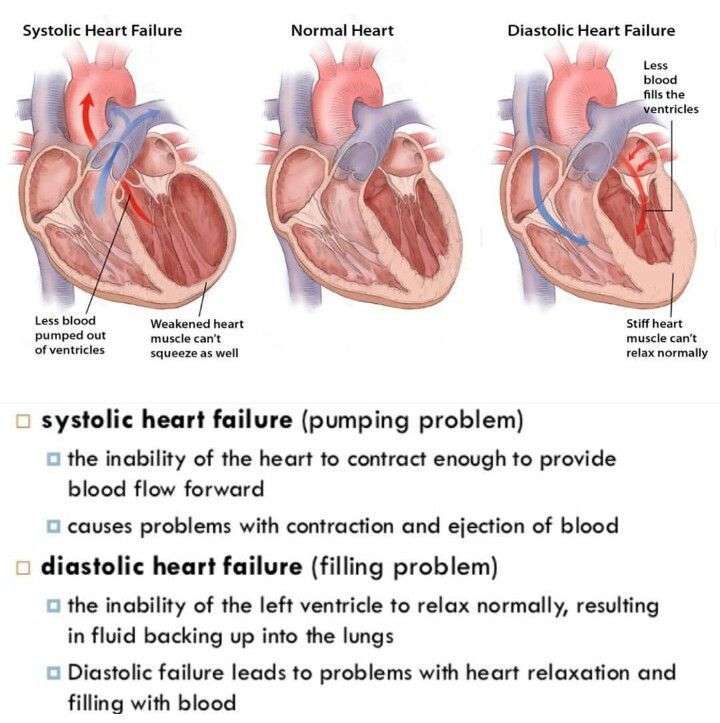
Vs Diastolic Heart Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure can occur in either side of the heart, but this article focuses on heart failure of the left ventricle.
Systolic heart failure means the heart is not strong enough to pump blood out.
Diastolic heart failure means the heart muscle is not relaxing properly between beats.
Recommended Reading: What Is Target Heart Rate
De Novo Acute Heart Failure
Acute heart failure is broadly defined as a rapid onset of new or worsening signs and symptoms of HF . It is often a potentially life-threatening condition, requiring hospitalisation, and emergency treatment is aimed predominantly at managing fluid overload and haemodynamic compromise. This umbrella term includes patients presenting for the first time with typical symptoms and signs of heart failure and also those with worsening of their pre-existing cardiomyopathy .
De novo AHF occurs when there is a sudden increase in intracardiac filling pressures and/or acute myocardial dysfunction which can lead to decreased peripheral perfusion and pulmonary oedema. The most common aetiology is cardiac ischaemia where -total coronary occlusion leads to decreased contractility in myocardium subtended by the affected coronary artery. In this case, management is focussed not only on haemodynamic compromise but also on reperfusion with the aim of restoring myocardial contractile function.
In addition to myocardial dysfunction, AHF can be precipitated by acute valvular incompetence. This most commonly occurs in an ischaemic context leading to acute mitral regurgitation but can also occur without ischaemia per se as is the case with infective and non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis. Extra-cardiac pathologies may also precipitate AHF as is the case with pulmonary embolism or pericardial effusion causing tamponade, both of which reduce LV output and therefore reduce peripheral perfusion
