How Are Heart Attacks Diagnosed
Healthcare providers usually diagnose heart attacks in an emergency room setting. Anyone with heart attack symptoms should undergo a physical examination, including checking pulse, blood oxygen levels and blood pressure and listening to heart and lung sounds.
A healthcare provider will diagnose a heart attack using the following:
- History and symptoms: The provider will ask you about the symptoms you experienced. They might also ask someone who was with you to describe what happened.
- Blood tests: During a heart attack, the damage to heart muscle cells almost always causes a chemical marker, a cardiac troponin, to appear in your bloodstream. Blood tests that look for that marker are among the most reliable methods to diagnose a heart attack.
- Electrocardiogram : This is one of the first tests you get when you come to an ER with heart attack symptoms.
- Echocardiogram: Using ultrasound , an echocardiogram generates a picture of the inside and outside of your heart.
- Angiogram: This test shows areas with little or no blood flow.
- Heart computed tomography scan: This creates a highly detailed scan of your heart.
- Heart MRI: This test uses a powerful magnetic field and computer processing to create an image of your heart.
- Nuclear heart scans: Similar to angiography, these scans use a radioactive dye injected into your blood. What sets them apart from an angiogram is that they use computer-enhanced methods like computed tomography or positron emission tomography scans.
When Can I Resume My Usual Activities
Recovery from a heart attack after leaving the hospital depends on the severity of the heart attack, how soon treatment began, the methods used and the health conditions you had if any before your heart attack. Your healthcare provider can explain the next steps for your recovery and what you can expect. In general, most people can return to work or resume their usual activities anywhere between two weeks to three months after their heart attack. Cardiac rehab can help people gradually and safely increase their physical activity back to its prior level.
The Prevention Of Heart And Vascular Disease Program
The Prevention of Heart and Vascular Disease Program at Brigham Healths Heart & Vascular Center is a world leader in treating high cholesterol and other risk factors that contribute to the development of heart and vascular disease. To make an appointment, please request an appointment online or call 307-4000.
Ron Blankstein, MD, is a preventative cardiology specialist and Associate Director of the Cardiovascular Imaging Program at Brigham Health.
Don’t Miss: What To Wear After Heart Surgery
Hearts And Bodies Change With Age Heart Disease Treatments May Need To Change Too
Statement Highlights:
- A new American Heart Association scientific statement provides updated information about how aging influences the diagnosis and treatment of heart attacks in people ages 75 and older.
- Changes in the cardiovascular system associated with normal aging and non-heart-related medical conditions that become more common with age should be considered when planning heart attack treatment and follow-up.
- Appropriate care for older people is increasingly important as the proportion of older people in the population continues to increase.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT / 5 a.m. ET Monday, Dec. 12, 2022
DALLAS, Dec. 12, 2022 For people ages 75 and older, age-related changes in general health and in the heart and blood vessels require consideration and likely modifications in how heart attacks and heart disease are treated, according to a new American Heart Association scientific statement published today in the Associations flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
The new statement,Management of acute coronary syndrome in the older adult population, highlights recent evidence to help clinicians better care for patients over age 75. According to the statement, 30-40% of people hospitalized with ACS are age 75 or older. ACS includes heart attack and unstable angina .
The statement is an update of a 2007 American Heart Association statement on the treatment of heart attacks in the elderly.
Normal aging and age-related changes in the heart and blood vessels
Smidt Heart Institute Study Shows Heart Attack Increase Has Been Most Prominent In Young Adults Especially Those Ages 25
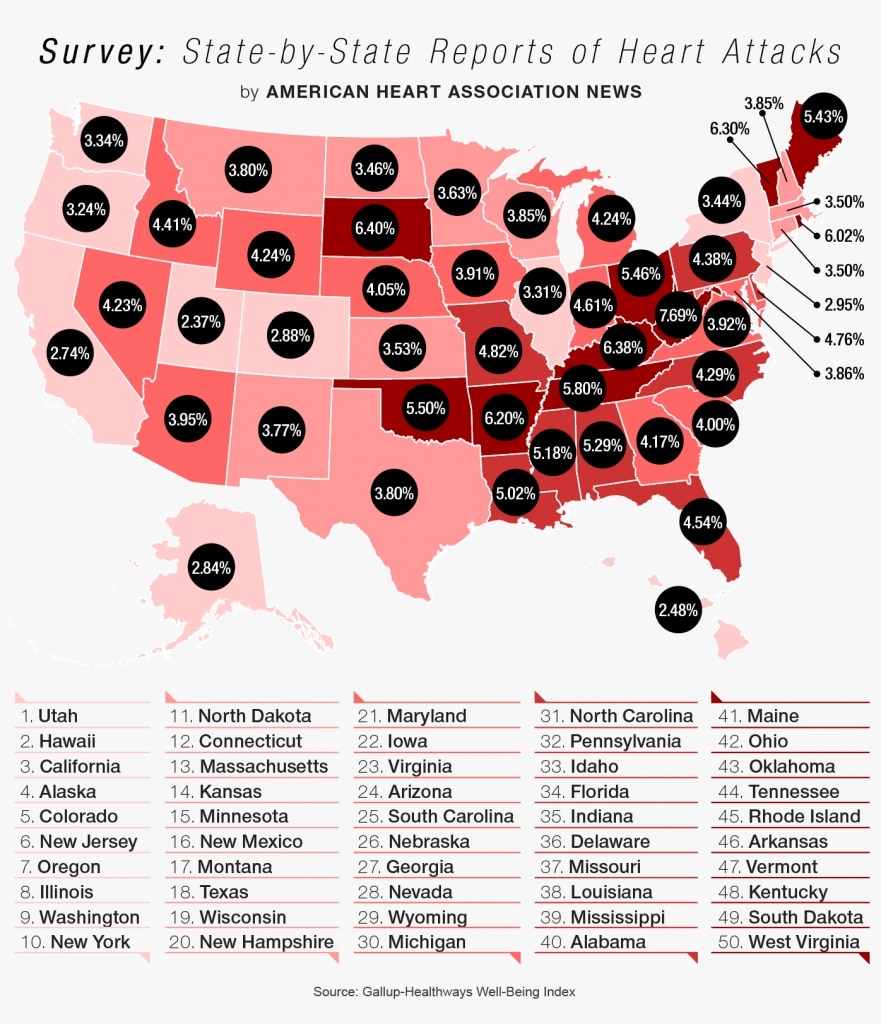
New data analysis from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai found that deaths from heart attacks rose significantly during pandemic surges, including the COVID-19 Omicron surges, overall reversing a heart-healthier pre-pandemic trend.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, heart attacks were the leading cause of death worldwide but were steadily on the decline. However, the new studyrecently published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Medical Virologyshows that heart attack death rates took a sharp turn and increased for all age groups during the pandemic.
The spikes in heart attack deaths have tracked with surges of COVID-19 infectioneven during the presumed less-severe Omicron phase of the pandemic. Furthermore, the data showed the increase was most significant among individuals ages 25-44, who are not usually considered at high risk for heart attack.
The dramatic rise in heart attacks during the pandemic has reversed what was a prior decadelong steady improvement in cardiac deaths, said Yee Hui Yeo, MD, first author of the study and a Cedars-Sinai physician-scientist. We are still learning the many ways by which COVID-19 affects the body, regardless of age, gender, ethnicity or race.
Using data from the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions National Vital Statistics System, the Cedars-Sinai researchers identified 1,522,699deaths from heart attacksmedically called acute myocardial infarctionsbetween April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2022.
Also Check: What Causes Heart Rate To Drop Suddenly
Major Risk Factors That Cant Be Changed
You may be born with certain risk factors that cannot be changed. The more of these risk factors you have, the greater your chance of developing coronary heart disease. Since you cant do anything about these risk factors, its even more important that you manage your risk factors that can be changed.
Increasing Age
The majority of people who die of coronary heart disease are 65 or older. While heart attacks can strike people of both sexes in old age, women are at greater risk of dying .
Male gender
Men have a greater risk of heart attack than women do, and men have attacks earlier in life.
Even after women reach the age of menopause, when womens death rate from heart disease increases, womens risk for heart attack is less than that for men.
Heredity
Children of parents with heart disease are more likely to develop heart disease themselves.
African-Americans have more severe high blood pressure than Caucasians, and a higher risk of heart disease. Heart disease risk is also higher among Mexican-Americans, American Indians, native Hawaiians and some Asian-Americans. This is partly due to higher rates of obesity and diabetes.
Most people with a significant family history of heart disease have one or more other risk factors. Just as you cant control your age, sex and race, you cant control your family history. So, its even more important to treat and control any other modifiable risk factors you have.
How Is A Heart Attack Diagnosed
To diagnose a heart attack, a doctor will ask you about your symptoms, your health, and your family health history. The doctor will also order tests.
Doctors often use these types of tests to diagnose a heart attack and choose the best treatment.
- Blood tests. During a heart attack, heart muscle cells die and burst open. This process releases proteins into your blood. Heart attack blood tests measure the amount of these protein “markers” of heart damage. Common heart attack blood tests include:
- Cardiac troponin . This is the most common blood test. This marker is released from the injured heart muscle. It is not found in the blood of healthy people. Troponin levels go up three to six hours after your heart attack starts, so the test may not find a heart attack right away.
- Creatine Kinase-MB . The CKMB test measures the amount of damage to the heart because of blocked blood flow. The test can tell whether treatments to restore blood flow to the heart are working. CKMB levels rise about four to six hours after a heart attack starts and peak 24 hours later.
- Myoglobin. This test helps diagnose a heart attack in the very early stages. After a heart attack, myoglobin levels rise within one to four hours but peak after 12 hours.
Recommended Reading: Is Heart Failure And Heart Attack The Same
Young Adults Are Increasingly Diagnosed With Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is one of the biggest risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Unfortunately, just like the trend in heart attacks, the incidence of hypertension is rising faster in young adults than in older adults. High blood pressure makes your heart muscles thicken, harms your blood vessels, and increases your risk of a heart attack.
Heart Attacks Are Becoming More Common In Younger People Especially Women
Please note: This article was published more than two years ago, so some information may be outdated. If you have questions about your health, always contact a health care professional.
Heart attacks once characterized as a part of “old man’s disease” are increasingly occurring in younger people, especially women, according to new research.
The study presented Sunday at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions meeting in Chicago and published in the AHA journal Circulation, sought to investigate heart attacks in the young, a group frequently overlooked in cardiovascular research.
Past research has shown heart attack rates in the U.S. have declined in recent decades among 35- to 74-year-olds. But for the new study, researchers wanted to look specifically at how many younger people were having heart attacks.
They included data from a multi-state study of more than 28,000 people hospitalized for heart attacks from 1995 to 2014. The results showed 30 percent of those patients were young, age 35 to 54.
More importantly, they found the people having heart attacks were increasingly young, from 27 percent at the start of the study to 32 percent at the end.
“Women were not managed the same way as men, and that could be for a combination of reasons,” said Arora, a cardiology fellow at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine.
Piña and Arora both said they would like to see women better represented in future studies on heart disease.
Don’t Miss: Medication For Rapid Heart Rate
What If Youre At Risk
Heart attacks can happen to anyone but the risk isespecially high when genetics come into play. Primordial and primary preventionis crucial for those with a family history of heart disease.
Your hereditary risk of heart disease is defined by having afirst-degree male relative under the age of55 with heart attack or stroke history, or a first-degree female relative under the age of 65 with heart attack orstroke history.
When were talking about young people having heart attacks,its important to individualize the discussion based on risk factors, says Dr.Laffin. Its about having an honest conversation and not pushing things offand saying Oh, Im too young, especially if you have symptoms.
Guidelines recommend that people ages 20 to 39 withouthereditary risk have their cardiovascular health assessed every four to six years.
For those that have a genetic risk, its critical to beengaged in your health and speak with your doctor early.
How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Heart attack is most often treated with medicine or nonsurgical procedures that break up blood clots and restore normal blood flow to the heart. Some treatments will start right away, when the ambulance comes. You will get other treatments later, in the hospital.
Getting treatment right away for a heart attack can help prevent or limit damage to your heart muscle. This is one reason why it is important to call 911 if you think you are having a heart attack, rather than driving yourself to the hospital.
You May Like: How To Measure Your Heart Rate
Strong Family History Genetic Factors Increase Heart Disease Risk
Family history
Having a strong family history of heart disease is partly due to genetics and partly due to other factors. Approximately 10% to 15% of the U.S. population has a strong family history of heart disease. The risks in this group can include family traditions such as preferring sedentary instead of active family time or eating meals that typically include more unhealthy than healthy options.
Additionally, certain conditions that affect heart disease risk, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, tend to run in families. In others, the risk factor levels are OK and individuals are leading a healthy lifestyle, but there still are premature heart attacks in a family. These are the most challenging situations that can benefit from evaluation by a specialist. In fact, if both of your parents had a heart attack before they turned 50, you are seven times more likely to have one yourself.
Our health is strongly tied to our environment if we have been taught or cornered into a certain way of life, it can become “the norm.” Breaking that cycle can be a tough, but it’s absolutely possible with a support network and the guidance of a preventive cardiologist.
Genetic factors
It seems illogical that a healthy person who is active and strong can have a heart attack. But it happens, and when it does, the cause almost always is a genetic condition that runs in the family.
Related reading: 10 truths about statins and high cholesterol
Preventive Care In 2020 And Beyond
The greatest challenge we have in the immediate future is increasing public awareness around preventive services. Here in Dallas, patients can self-refer for guided support to determine their personal risks and work with us to sculpt achievable goals to improve their heart health.
Looking toward the future, we must continue to expand our view of heart disease as a metabolic and endocrine condition as well as a cardiovascular disease. Because the development of heart disease is influenced by so many conditions, the UT Southwestern preventive cardiology team and other cardiologists around the country have adopted the term “diabetocardiologist” to describe the shift in cause and treatments for heart disease.
Particularly in the middle age population, we must become more vigilant and proactive to help patients take control of their heart health. From intercepting genetic heart issues to guidance for making healthier lifestyle choices, we are here to support you.
Find out how you or a loved one might benefit from a preventive cardiology exam. Call or request an appointment online today.
You May Like: Wearable Heart Rate Monitor
Too Young To Worry About Heart Attack
A heart attack can occur at any age. Youre never too young to start heart-healthy living. If youre over 40, or if you have multiple risk factors, work closely with your doctor to address your risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Heart attack prevention is critical. It should begin early in life. Start with an assessment of your risk factors. Then develop a plan you can follow to maintain a low risk for heart attack.
For many people, their first heart attack is disabling or even fatal. Do everything you can to lower your risk.
Check Your Blood Pressure
As you get older, it’s important for you to have your blood pressure checked regularly, even if you are healthy. This is because aging changes in your arteries can lead to hypertension. You may feel fine but, if not treated, high blood pressure could lead to stroke and problems with your heart, eyes, brain, and kidneys. To manage high blood pressure, exercise, dietary changes, and reducing your salt intake can help, but as aging changes in the arteries often cause high blood pressure in older age, medication is often necessary. It is not uncommon to need more than one medication to control your blood pressure.
Age can cause other changes to the heart. For example:
Other factors, such as thyroid disease or chemotherapy, may also weaken the heart muscle. Things you can’t control, like your family history, might increase your risk of heart disease. But, leading a heart-healthy lifestyle might help you avoid or delay serious illness.
Don’t Miss: What Does Left Arm Pain From Heart Attack Feel Like
Heart Attack Risk Factors You Can Control:
Cholesterol. Healthy levels of LDL and HDL cholesterol help prevent arterial plaque buildup. Lifestyle changes can steady the balance, but you may also need medication.
Diet. Healthful food is a highly effective weapon against heart disease. Focus on fruits, vegetable and grains – as well as low-fat dairy, poultry and fish. Limit red meat and sugar.
Drinking. Alcohol can amplify cardiac health risks, raise triglycerides and cause irregular heartbeat. Consume safely by having no more than two drinks per day for men .
Blood Pressure. High blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, causing damage over time. If your blood pressure is higher than 120/80, your heart attack risk is considered elevated.
Diabetes. Patients with diabetes have twice the risk of coronary heart disease. That’s because high blood sugar, if uncontrolled, can lead to increased plaque in your arteries.
Smoking. Smoking is directly related to one in four heart attacks. People who smoke have a heart attack risk two to three times higher than nonsmokers.
Physical Activity. Exercise can lower blood pressure, cholesterol and weight. Be active every day – with three to four 40 minute sessions of moderate to vigorous activity each week.
Weight. Being overweight or obese is linked to several related heart attack risk factors. Your doctor can help you determine an ideal goal weight based on height and age.
Primordial Prevention: How Early Is Early Enough
Heart experts always thought about primary and secondary prevention when it comes to heart attacks, Dr. Laffin says. Thats trying to prevent the first heart attack and then trying to prevent the second heart attack.
But recently, theres been a shift to the idea of primordial prevention. This means trying to prevent the progression of the heart attack risk factors themselves. Dr. Laffin says it includes trying to change the social and environmental conditions that could develop and progress risk factors. These are things we have control over such as exercising, eating nutritious foods, not smoking, managing stress and blood pressure.
Primordial prevention also includes education about whatbehaviors put you at risk for cardiovascular disease. These include:
- Poor diet and lack of exercise.
- Type 2 diabetes.
- Family history of cardiovascular disease.
Read Also: What’s The Lowest Heart Rate
