Why Was This Study Needed
Heart failure is a condition where the heart cannot pump blood efficiently enough to meet the needs of the body. It has many causes, commonly, previous heart attack or high blood pressure. The 2010 National Heart Failure Audit estimated that one in 100 people in the UK has heart failure. It has a poor prognosis around a third of people admitted to hospital with heart failure die within one year. Management currently costs the NHS around £625 million a year. The number of cases is expected to rise with the ageing population.
BNP is released from the heart muscle when it is stretched and under tension. Titrating medication to a pre-defined BNP target is a potential way to optimise treatment. However, it is unclear whether this is better than relying on symptoms alone, particularly in older adults and those with other illnesses.
This programme of work set out to assess the clinical and cost-effectiveness of BNP-guided therapy for people with a new diagnosis of heart failure between January 2007 and March 2013.
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is a dangerous condition in which the heart fails to adequately pump blood throughout the body. As a result, the bodys tissues and organs do not get enough nutrients and oxygen.
CHF is failure of the heart muscle and inability to perform properly. Heart failure can be either acute, happens quickly, or chronic, develops slowly over a long period of time.
Heart failure does not mean that the heart has stopped beating, it simply means the heart is not functioning properly. It can affect one or both sides of the heart. Specifically, congestive heart failure is a type of heart failure however, the terms are often used interchangeably.
Congestive heart failure is specifically when blood returning to the heart backs up and causes congestion in the body resulting in edema. The fluid can also back up into the lungs causing pulmonary edema. CHF affects the bodyâs inability to function properly including the kidneysâ ability to dispose of sodium and water.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 6.2 millionadults in the United States have heart failure.
Medical conditions that can increase risk associated with CHF include but are not limited to:
- Coronary artery disease
Availability Of Data And Materials
According to hospital regulations it is prohibited to publicly release datasets. Data release would cause concern from local ethical committees based on current institution regulations. Data are available from the Wonju Severance Christian Hospital Institutional Data Access/Ethics Committee for researchers who meet the criteria for access to confidential data. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Also Check: When Are Heart Palpitations Serious
Monitoring Patients With Heart Failure
BNP measurement is a potential tool for monitoring treatment response in patients with heart failure because of the tests ability to diagnose heart failure, predict prognosis, and correlate with more invasive clinical measures .36 Prognostic studies have shown that BNP levels measured after treatment took effect were more predictive of the risk of death or further cardiovascular events than those initiated at first presentation.37,38
Ideally, randomized trials would offer definitive evidence however, only two small trials have evaluated BNP-guided treatment.39,40 The first trial showed a nearly twofold decrease in cardiovascular events,39 and the second trial showed a decrease in BNP levels with BNP-guided treatment.40 However, according to the ACC/AHA guideline on the management of heart failure, the value of serial BNP measurements in guiding therapy for patients with heart failure is not well established.32 Larger randomized controlled trials are needed before routine BNP monitoring of heart failure can be recommended.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
You May Like: Typical Resting Heart Rate For A Healthy Individual
What Causes The Bnp To Be High
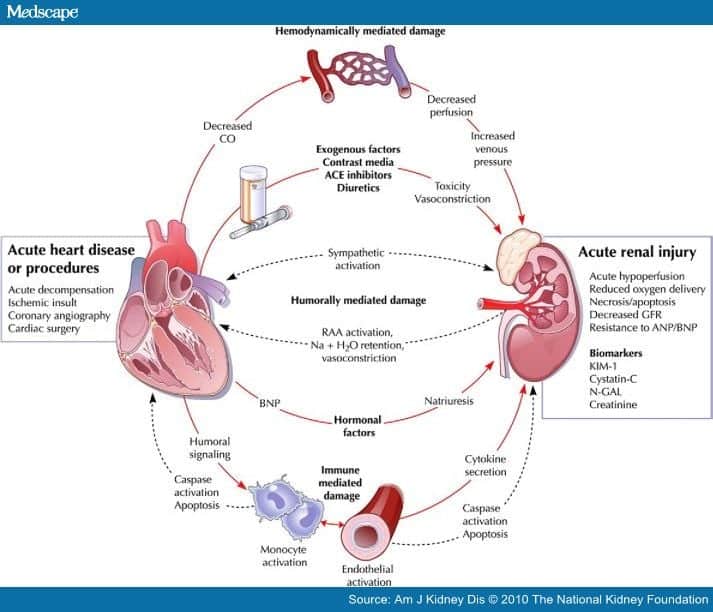
BNP levels may rise due to intrinsic cardiac dysfunction or as a result of other factors such as pulmonary or renal illness . BNP levels are linked to various indicators of heart health, such as the New York Heart Association classification. As people get older, their hearts become more efficient at pumping blood, so they require a higher percentage of their maximum activity to pump the same amount of blood. This is why patients over 40 years old with cardiovascular disease often have higher BNP levels than those without significant blockages in their arteries.
To calculate your risk of having a heart attack or stroke, use the Framingham Risk Score. It’s based on things like age, gender, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diabetes status, and smoking history. Your risk will change over time depending on what you do. If you maintain an active lifestyle and keep blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels within recommended limits, then you should reduce your risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood into the circulatory system to meet the body’s needs. Heart failure can be chronic or acute. With chronic heart failure there is damage to the heart muscle that prevents it from working efficiently. With acute heart failure there is some reversible cause for the malfunction – usually an infection or severe stress on the heart.
About Article Author
Also Check: Acute Systolic Congestive Heart Failure
Results Reporting Critical Findings
BNP and NT-proBNP levels elevate in patients with cardiac disease due to myocardial stress and volume overload. Patients with a BNP elevation of over 100 pg/ml should be assessed further for the signs and symptoms of cardiac disease. Though BNP is traditionally used in the diagnosis of left ventricular systolic function, it can be elevated through other processes as well, for example, in the setting of right ventricular failure, acute myocardial infarction, congenital heart disease, and valvular disease.
Review Question: In People With Suspected Heart Failure What Thresholds Of Pro
For full details see review protocol in .
Clinical
Plasma BNP
Five studies explored the diagnostic test accuracy of plasma BNP for diagnosing chronic heart failure. The quality of the included evidence ranged from high to very low. Evidence was downgraded due to risk of bias and imprecision due to the range of the confidence interval around the point estimate. A number of studies were also downgraded due to indirectness as a result of the study population having a prevalence of CHF much higher than that of a representative sample or due to a lack of information regarding the reference standard used in the study. Two high quality studies reported a high sensitivity of plasma BNP at the thresholds 30pg/ml and 77pg/ml and 97 respectively) which met the pre specified threshold of 95% set by the committee for possible recommendation. A further single study reported a high specificity of 100 at the threshold 400pg/ml. The committee placed an emphasis on specificity for the very high ârule inâ threshold of 400pg/ml of which this study met the specificity threshold. Very low quality evidence was found for plasma BNP at the threshold of 178pg/ml which reported a poor sensitivity of 47 . A further single study of very low quality reported an AUC 0.69. This study did not accurately report the threshold at which this accuracy data was collected.
Plasma NT-pro BNP
You May Like: Tests For Congestive Heart Failure
Uncertain Benefits Of Bnp Blood Tests To Monitor Heart Failure Treatment
This is a plain English summary of an original research article
In specialist clinics, using B-type natriuretic peptide blood levels to guide treatment in people with chronic heart failure shows promise but did not improve survival for all groups. In this review, the benefit was only seen in patients aged less than 75, who survived an extra 1.5 years on average, and possibly those with poor heart function . However, there was a reduction in hospital admissions for heart failure for everyone.
BNP is a hormone released from the heart muscle, and higher levels may indicate more severe disease. It is currently used for diagnosis, but its use in monitoring treatment has become the subject of recent research interest.
This research pooled data for 3,074 patients in 13 trials who were randomised to the blood test-guided or symptom-guided therapy and separately studied general practice data for a further 17,095.
The research was limited by the quality of the previous trials, the availability of data and the scarcity of monitored patients in general practice. Furthermore, there was no apparent mechanism found that could explain the small benefit. So, these findings should be regarded as tentative and are not conclusive enough to support a change in practice. Other research is underway that may better define the place for this test.
How Common Is Heart Failure
According to the American Heart Association, more than 6 million people in the United States are living with heart failure and the number is growing. It is estimated that one in five American adults age 40 and older will develop heart failure in their lifetime. You may be at increased risk of developing heart failure if you have conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes, or if you have had a heart attack. Other risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol use, and obesity.
You May Like: Afrin Heart Palpitations
Recommended Reading: Can Low Blood Pressure Cause Heart Palpitations
Role Of Bnp As A Diagnostic Biomarker
There are many randomised trials and systemic reviews conducted over a decade to research the potential value of BNP for diagnosis of HF. The following trials were performed in different clinical settings to examine the impact of BNP/NT-proBNP to rule in or rule out HF.
Role of BNP in urgent care and emergency departments
Dao et al. evaluated the utility of BNP in the diagnosis of CHF . At a blood concentration of 80 pg/mL, BNP was an accurate predictor of the presence of CHF measurements less than this had a high negative predictive value . The measurement of BNP appears to be a sensitive and specific test to diagnose CHF in urgent care settings. The largest study of the diagnostic utility of BNP is the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study or . The diagnostic accuracy of BNP at a cutoff of 100 pg/mL was 83.4%. The negative predictive value of BNP with a cutoff point of 50 pg/mL was 96%. McCullough et al. further analysed the BNPMS data and stated that CHF is unlikely with BNP level < 100 pg/mL, possible with levels between 100 and 500 pg/mL and probable at levels > 500 pg/mL .
BNP> 400 pg/mL or NT-proBNP> 2000 pg/mL: patient should have an echocardiography and specialist clinical assessment within 2 weeks from the time of presentation.
BNP 100â400 pg/mL or NT-proBNP 400â2000 pg/mL: patient should have echocardiography and clinical assessment by the specialist within 6 weeks from the time of presentation.
Use of BNP in primary care
Diagnosis Using Bnp Or Nt
1) Patients in the emergency room or ones who are complaining of acute symptoms:
An accurate and rapid diagnosis is crucial for the diagnosis of patients who present to the emergency room or outpatient examination room with acute respiratory distress. The usability of a test greatly depends on its negative predictive value, which has vital significance as a differential diagnostic tool for serious acute respiratory distress syndrome, and can be very effective in the differential diagnosis of emergency room patients with heart failure. In general, the diagnostic accuracy is approximately 90% at the cut-off value of BNP or NT-proBNP . Due to its high accuracy, the negative predictive value is useful not only in diagnosing heart failure but also in differentiating it from respiratory disorders that lead to respiratory distress . In clinical reality, there are obvious differences in the cut-off values of cases of heart failure with acute symptoms and in those with stable chronic heart failure. The negative predictive value can greatly help in determining the cause of the patients respiratory distress.
2) Patients with stable chronic heart failure:
3) Treatment monitoring:
Percent reduction in N-terminal pro-brain BNP levels according to the clinical course during hospitalization .
4) Inadequate test results:
Don’t Miss: Heart Bypass Surgery Recovery
Low Bnp Levels In Up To 16% Of Heart Failure Patients
By Jamie L. W. Kennedy, MD, FACC
Associate Professor, Division of Cardiology, Advanced Heart Failure & Transplant Cardiology, University of California, San Francisco
SYNOPSIS: In patients with clinical heart failure and low B-type natriuretic peptide levels, the authors found these patients usually are young and obese, with higher ejection fraction and better renal function.
: Bachmann KN, Gupta DK, Xu M, et al. Unexpectedly low natriuretic peptide levels in patients with heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2021 9:192-200.
Interestingly, there is a subset of patients with clear heart failure with normal or even low BNP values. To further evaluate this phenomenon, Bachmann et al queried a de-identified version of their institutions electronic medical record to find patients with measured BNP values and heart failure based on echo or hemodynamic criteria or hospitalized with heart failure. Echo criteria included left ventricular ejection fraction 35% or lower or left ventricular hypertrophy based on estimated left ventricular mass . BNP measurement was required within 90 days of the study.
The authors identified 47,970 adult patients with a measured BNP value: 9,153 were associated with a heart failure hospitalization, 7,041 met echo criteria, and 363 met hemodynamic criteria . BNP levels below 50 pg/mL were present in 4.9% of patients hospitalized for heart failure, 14% of patients with abnormal echoes, and 16.3% of patients with abnormal hemodynamics.
Sacubitril: A Problem For Measuring Natriuretic Peptides
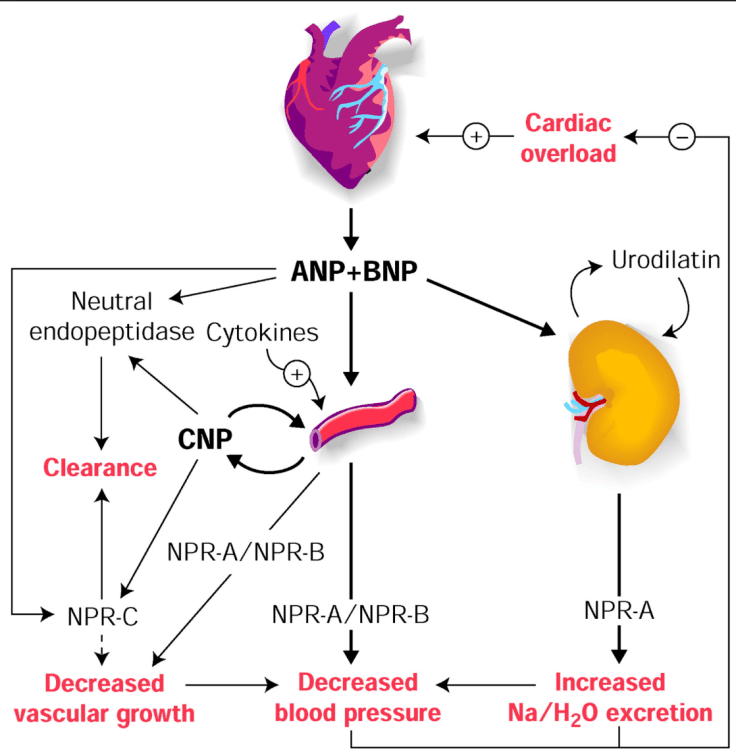
Among the bioactive peptides, sacubitril reduces the breakdown of the biologically active NPs by inhibiting the enzyme neprilysin, a circulating neutral endopeptidase involved in the degradation of NPs. This is true for both ANP and BNP, but BNP is a poorer substrate for neprilysin than ANP. Therefore, the increase of BNP may be less. The increase in BNP was only small although significant whereas the increase in urinary cGMP was much larger with sacubitril/valsartan in the PARADIGM-HF study.
Sacubitril has no direct influence on NT-proBNP because neprilysin has no effect on cleavage of NT-proBNP. However, it might be speculated that an increasing level of BNP results in a negative feedback regarding production of proBNP, thereby reducing NT-proBNP. To the best of our knowledge, this has not been properly tested. In clinical trials, sacubitril/valsartan resulted in a reduction of NT-proBNP, as well as a small increase in BNP as mentioned above. This reduction was accompanied by a better outcome. Therefore, it is likely that the decrease in NT-proBNP is, at least in part, related to more effective treatment of HF. To what extent NT-proBNP levels are influenced by a negative feedback mechanism remains to be determined.
Read Also: Is 116 Heart Rate High
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About A Natriuretic Peptide Test
Your health care provider may order one or more of the following tests in addition to or after youâve had a BNP or NT-proBNP test:
- Electrocardiogram, which looks at heartâs electrical activity
- Stress test, which shows how well your heart handles physical activity
- Chest x-ray to see if your heart is larger than normal or if you have fluid in your lungs
You may also get one or more of the following blood tests:
- ANP test. ANP stands for atrial natriuretic peptide. ANP is similar to BNP but it is made in a different part of the heart.
- Metabolic panelto check for kidney disease, which has similar symptoms to heart failure
- Complete blood count to check for anemia or other blood disorders
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Are Test Results Accurate
Many variables affect the accuracy and interpretation of the BNP and NT-proBNP tests, which is why it is so important to discuss your results with your physician.
For example, some factors that may affect test accuracy include:
- Type of test: There can be some variation in results from rapid tests and tests analyzed by a laboratory. Reference ranges may also differ by laboratory.
- Individual factors: The expected BNP and NT-proBNP level in healthy people varies by age. A doctor will also take into account your sex, genetics, and body mass index when interpreting your results.
- Other health conditions: More than one type of health problem can cause BNP or NT-proBNP levels to be elevated, which means that this test alone may not be able to diagnose congestive heart failure or another condition.
If you have any questions about the accuracy of your test results, talk with your health care provider to learn more about the type of test you had and its significance for your health.
Don’t Miss: Congestive Heart Failure Feeling Cold
Bnp Blood Test Results Explained
Your results will indicate if your BNP levels are high enough to suspect a diagnosis of heart failure. If you already have a diagnosis of heart failure, the results can help your doctor find out whether heart failure treatments are working.
Generally, BNP levels below 100 picograms per milliliter are considered normal. But normal BNP levels may vary depending on your age and sex.
What Happens During A Natriuretic Peptide Test
For a BNP test or an NT-proBNP test, a health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
You May Like: How Can You Tell If You Had A Heart Attack
What Did It Find
The systematic review found:
- BNP-guided therapy had no overall effect on risk of death from any cause . Sub-group analysis found it reduced mortality for participants aged less than 75 years but not for older patients.
- BNP-guided therapy reduced the risk of hospital admission for heart failure but did not affect overall hospital admission .
- In the cohort study, the overall death rate was 142 patients per 1,000 per year. Death rates were higher in the BNP-monitoring group than in the BNP-testing and never-tested groups . This probably reflects that this small group were sicker than other patients.
