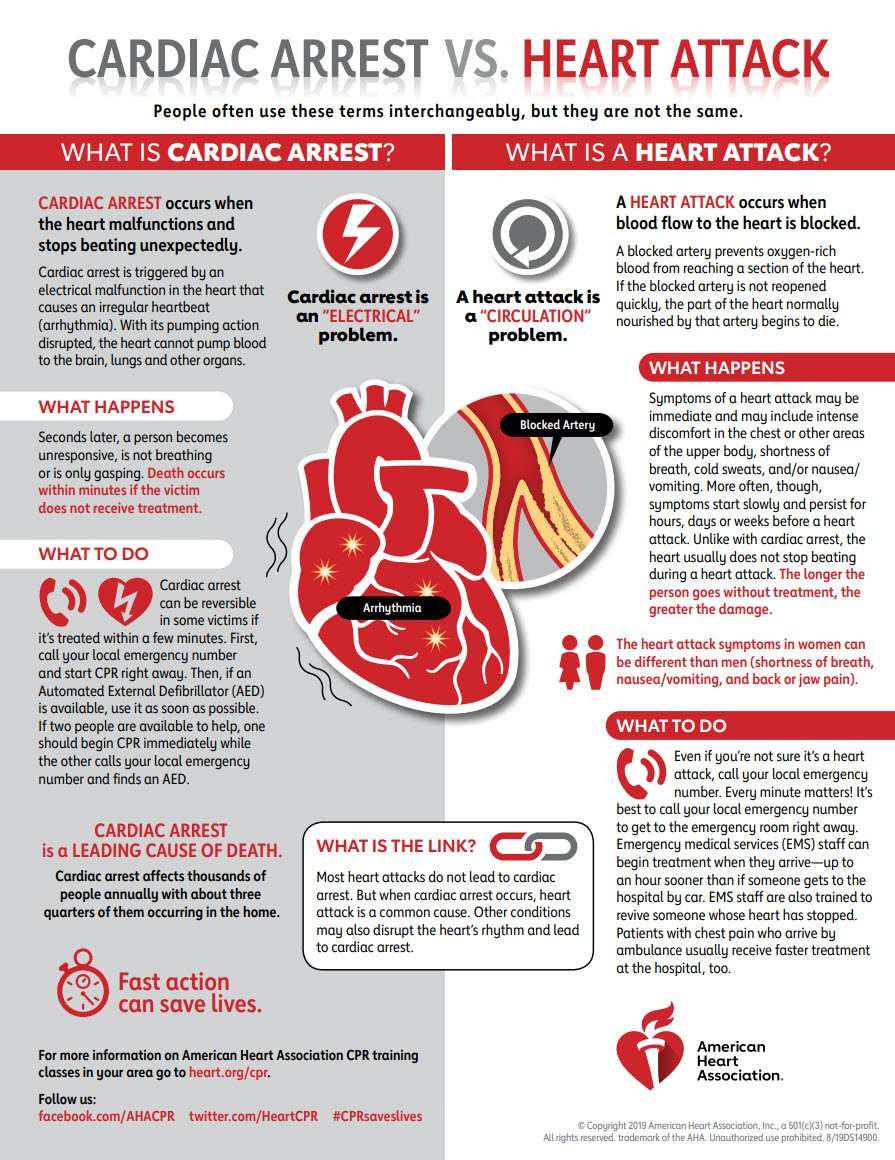
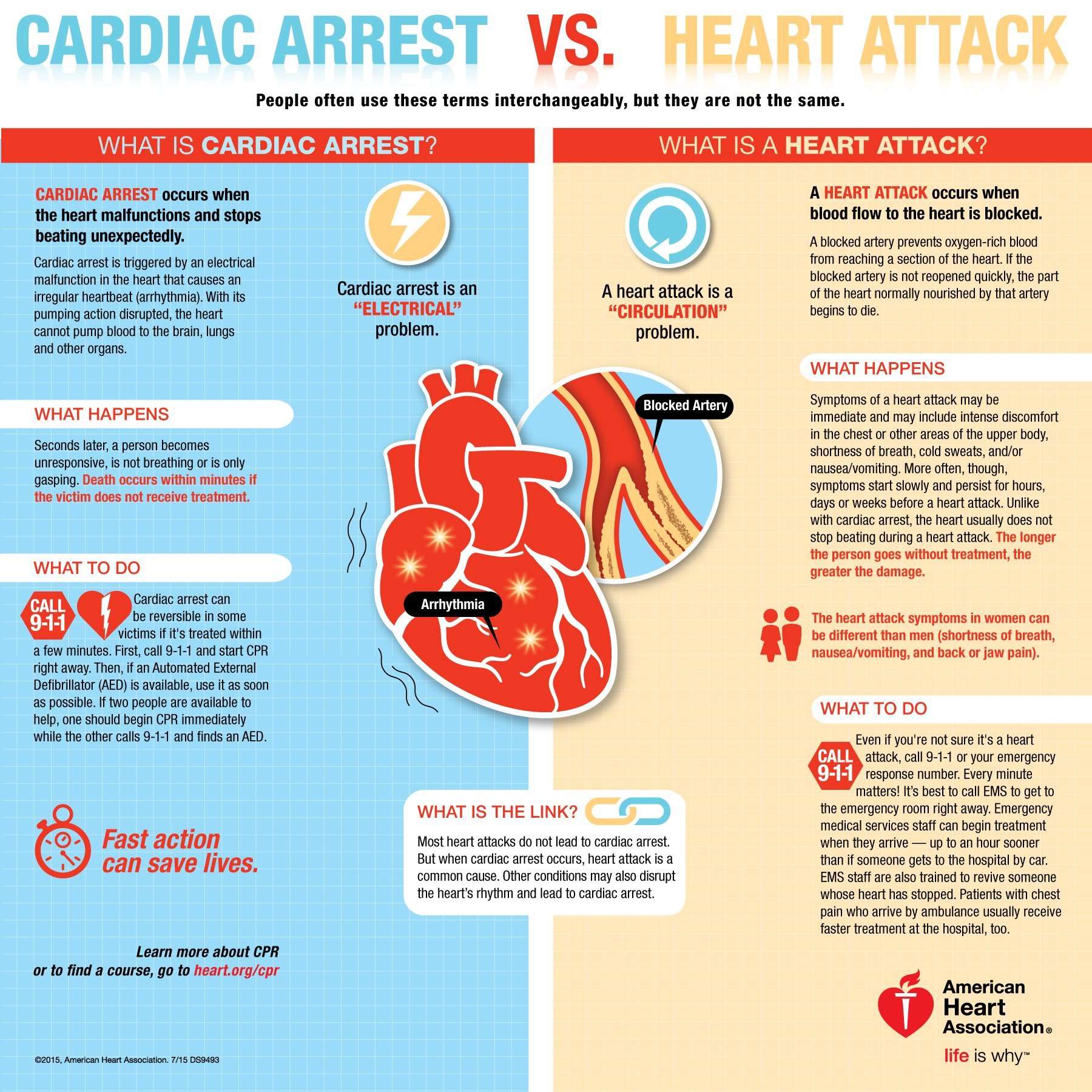
Whats The Difference Between Heart Failure And A Heart Attack
Both heart failure and a heart attack are forms of heart disease. While they share some similarities, many differences exist between them as well. One of the biggest differences is that heart disease happens gradually over time while a heart attack occurs suddenly and is an emergency.
Heart failure occurs when the muscles of the heart become weak and have difficulty pumping enough blood to nourish your bodys many cells. It is a chronic condition, which means that it doesnt go away and typically gets worse over time. However, you can manage heart disease with medication and lifestyle changes. Both can improve the quality of your life as well as your longevity.
A heart attack can come on with no previous warning.
Difference Between A Heart Failure And Heart Attack
Heart failure and heart attack are two different types of heart diseases. Heart attacks happen suddenly when an artery connected to the heart is blocked and cuts off the blood flow. This causes the oxygen supply to stop, leading to degeneration of the heart muscles. Heart failure, on the other hand, develops gradually. In this case, the heart muscle becomes weaker and has trouble pumping blood to the rest of the body. This is a chronic condition and it gradually gets worse. However, medications and therapy can help a patient live longer and better with it. Both heart failure and heart attack can be fatal depending on the severity of the condition.
Women Have Unique Heart Attack Symptoms
A significant challenge for diagnosing women with heart disease is the lack of recognition of symptoms that might be related to heart disease, or that don’t fit into classic definitions. Women can develop symptoms that are subtler and harder to detect as a heart attack, especially if the physician is only looking for the “usual” heart attack symptoms.
“Women are much more likely to have atypical heart attack symptoms,” says Dr. Lili Barouch, director of the Johns Hopkins Columbia Heart Failure Clinic. “So while the classical symptoms, such as chest pains, apply to both men and women, women are much more likely to get less common symptoms such as indigestion, shortness of breath, and back pain, sometimes even in the absence of obvious chest discomfort.”
You May Like: Does A Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
What Are The 4 Stages Of Heart Failure
There are four stages of heart failure – stage A, B, C and D – which range from high risk of developing heart failure to advanced heart failure.
The four stages of heart failure are different to the four classes of heart failure symptoms also described in New York Heart Association , which illustrates the severity of symptoms, ranging from class one to the most severe, which is class four .
Determining Heart Disease Risk In Women
Women and men share many heart disease risk factors, but recent studies are showing what previous male-focused studies have not shown: Women also have their own unique heart disease risk factors.
Traditional risk factors common to both women and men:
- Family history
- Metabolic syndrome the co-existence of high blood pressure, obesity, and high glucose and triglyceride levels
- High levels of C-reactive protein a sign of inflammatory disease that can occur along with other cardiovascular risk factors
Some risk factors that relate specifically to women or that can affect women disproportionately include:
- Relatively high testosterone levels prior to menopause
- Increasing hypertension during menopause
- Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis more common in women than in men
- Stress and depression also more common among women
- Low risk factor awareness Lack of recognition of many of the above conditions as risk factors for heart disease is a risk factor in itself
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Types Of Cardiac Problems Seen With Stroke
Several kinds of heart problems are commonly seen in people who suffer a stroke. These include myocardial infarction , heart failure, and cardiac arrhythmiasespecially atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
Heart problems associated with strokes may be caused by the stroke itself, or may be caused by the same underlying process that produced the stroke, most commonly thrombosis of an artery. Or, the heart problem may occur first, and the stroke may result from it. This is most often seen when atrial fibrillation produces an embolus to the brain.
So whenever a stroke is complicated by a heart problem, it is very important for the healthcare provider to make every effort to sort out cause and effect. This understanding is necessary so that the most effective therapy can be chosen to hasten recovery and prevent more problems in the future.
Living With Heart Failure
There are five things patients diagnosed with heart failure need to do every day at home to manage their heart failure. The following MAWDS acronym may help you remember and follow these basic steps:
- Medications: Take your medications as prescribed by your doctor and heart care team, let them know if you dont tolerate your medications and dont run out of them.
- Activity: Stay active every day, do what you can to keep your body strong.
- Weight: Weigh yourself each day, recognize when changes in your weight mean you are retaining more fluid.
- Diet: Follow your die, that means low salt and limit fluid intake .
- Symptoms: Recognize your symptoms and know when to call for help.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Frequently Asked Questions For Treatment Of Heart Failure
What has the success rate of these LVAD devices been in comparison to heart transplant? Are there enough trained experts in the country to take this therapy further?
An LVAD is a feasible, safe and accessible option for patients in the advanced stage of heart failure. And due to persistent shortage of donors, LVADs can be used as both bridge to transplant and as destination therapy. It is also an option for patients who are not eligible for a heart transplant or are unable to undergo the same owing to other factors. An LVAD also requires fewer consultations post treatment compared to a heart transplant. Further, a study conducted by the NCBI has shown that there are no differences between a heart transplant and LVAD for patients with regards to late mortality.
How can one improve their lifestyle through this treatment? What are the things one must practice post treatment to extract the most benefits?
An LVAD device helps a patient lead a more active life. It increases the blood flow to the body, improves the function of the kidneys, liver, brain and other organs. It also impacts the patient’s strength and ability to participate in activities such as cardiac rehabilitation. Post treatment, a patient can continue following the precautions suggested above to manage heart failure. They must also seek medical consultations with their doctor and stay alert for any symptoms.
Also read: Exercising Is The Key To A Healthy Heart- Here’s Why
Watch Live News:
Are There Other Types Of Heart Attack
Yes and no. While heart attacks all involve some form of congestion in the heart, there are different classifications a heart attack and pain around the heart can fall under. The most common include:
- Angina
- This is where the hearts blood supply is restricted and results in chest pain. A person can have stable and unstable angina. You can find out more information about angina here.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Weak Heart Valves
Difference Between Heart Attack And Heart Failure
June 30, 2011 Posted by Dr.Guru
Heart Attack vs Heart Failure
Heart is a pump working continuously in our body. Heart circulates the blood throughout the body. Blood carries the oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, and the waste products from the tissue. Heart get the oxygen and nutrients via the coronary arteries. Heart is capable to function on its own, however, the sympathetic stimulation and parasympathetic inhibition may play a role in its function.
Heart needs continuous blood supply to work continuously. If the blood supply is deficient or stopped the cardiac muscles suffer with hypoxia and ultimately they die. Cardiac muscle cells cannot be replaced by new muscle cells. The dead tissue may be changed in to fibrous tissue. If the blood supply is partially occluded, the muscle will suffer. The nerve tissue will be stimulated and the intense pain may be felt. This pain is named as angina. If the blood supply is cut off critically, the muscle will die. This also cause severe, unbearable pain. This is called myocardial infarction or heart attack. Heart attack usually occurs suddenly. If the infarction is very extensive, and involved with most of the ventricular muscles, heart failure may occur. Severe chest pain with sweating will be the myocardial infarction.
What Are The Causes Of Heart Attack
Heart attack is an episode caused due to blockage in the coronary artery of the heart. Usually one may have an episode of heart attack when some parts of the plaque formation contributing to the blockage breaks and forms a clot thereby causing a hindrance to the blood flow. At times, even when there is no history of blockage in the arteries, a spasm occurring in it may lead to heart attack.
Recommended Reading: Ibs And Palpitations
Immediate Treatment Of A Heart Attack Patient
If you think you are having a heart attack, call 911 or the local emergency number right away and wait for an ambulance. DO NOT attempt to drive yourself to the hospital. After you call 911 or the local emergency number, chew an adult-size non-coated aspirin. Be sure to tell the paramedics so an additional aspirin dose is not given.
For a particular type of heart attack called ST-elevation myocardial infarction or STEMI, which is diagnosed by electrocardiography , guidelines recommend:
- Angioplasty , also called percutaneous coronary intervention , is a procedure that should be performed within 90 minutes of arriving at the hospital. People suffering a heart attack should be transported by emergency services to hospitals equipped to perform PCI, if possible.
- Fibrinolytic therapy should be given if a center that performs PCI is not available or if anticipated transfer time would exceed a certain window of time and there are no contraindications for fibrinolysis.
Women And Heart Failure
Women are just as likely as men to develop heart failure, but there are some differences:
- Women tend to develop heart failure later in life compared with men.
- Women tend to have heart failure caused by high blood pressure and have a normal EF .
- Women may have more shortness of breath than men do. There are no differences in treatment for men and women with heart failure.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Stage D And Reduced E
Patients with Stage D HF-rEF have advanced symptoms that do not get better with treatment. This is the final stage of heart failure.
Stage D treatment
The usual treatment plan for patients with Stage D heart failure includes:
- Treatments listed in Stages A, B and C.
- Evaluation for more advanced treatment options, including:
- Heart transplant.
- Research therapies.
Heart Problems That Go Hand In Hand With Strokes
As if having a stroke is not bad enough, strokes are often accompanied by additional medical complications. These may include pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, gastrointestinal bleeding, urinary tract infections, and cardiac complications. Complications like these often prolong hospitalization, delay rehabilitation, or worse.
Heart problems, in particular, are distressingly common in people who have a stroke. If you have a stroke, both you and your healthcare providers need to be particularly vigilant about your heart during the acute phase of the stroke, during the recovery periodand thereafter.
Read Also: Flonase Chest Pain
What To Do When Symptoms Occur
If you are having chest pain or other symptoms that may indicate a heart attack, you should:
- After you call 9-1-1, chew 1 adult-size or 4 baby non-coated aspirin. Be sure to tell the paramedics so an additional aspirin dose is not given.
- For people with angina, take one nitroglycerin dose as prescribed at the first onset of symptoms or as directed. Some people may be told to take up to three doses, 5 minutes apart. If symptoms DO NOT go away or worsen after the maximum number of tablets has been taken, call 9-1-1.
There Are Several Common Myths About Heart Failure That People Believe To Be True Roughly 8 To 10 Million Individuals In India Alone Suffer From Heart Failure It Is A Serious Chronic Progressive Condition With A Significantly Associated Burden
Representative image
Do you also think that heart failure means the heart has stopped? There are several common myths about heart failure that people believe to be true. Roughly 8 to 10 million individuals in India alone suffer from heart failure. It is a serious, chronic, progressive condition, with a significantly associated burden. However, despite heart failure being a major public health challenge in our country, it remains poorly understood and neglected. To better understand heart disease and bust common misconceptions, read on:
Vishal Rastogi, Additional Director, Cardiac Sciences, Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, New Delhi said, “Heart failure is a growing concern in India. In our hospital, we see about 20 patients visit the hospital with heart failure-related complications every month. However, there are several barriers to early diagnosis and care, including certain misconceptions and lack of awareness. Educating people on heart failure would help facilitate increased understanding and ability to identify symptoms and risk factors thus, enabling timely detection. This can support the effective management of heart failure in its early stages. Thereby alleviating patients’ symptoms and reducing hospital visits, empowering them to live longer with an improved quality of life.”
Read Also: 10 Second Trick To Prevent Heart Attack
No They Are Not Same Read To Know The Difference
Written by Debjani Arora | Updated : September 6, 2017 3:17 PM IST
Most people use the terms heart attack and heart failure interchangeably, but they are two different conditions that are equally fatal. While the symptoms and the causes might seem similar, they have different consequences and manifest in different ways. To understand the conditions better, we spoke to Dr Shirish Hiremath, president of Cardiological Society of India , who helps us to decode these two conditions.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack is a sudden, unexpected event resulting due to blockage in one of the main arteries supplying blood to the heart. In the absence of blood and oxygen, the heart muscles die slowly which could be life-threatening. Here are eight warning signs of heart attack that you should know.
Symptoms That Are Less Likely To Indicate Heart Attack
The following symptoms are less likely to be due to heart attack:
- Sharp pain brought on by breathing in or when coughing.
- Pain that is mainly or only in the middle or lower abdomen.
- Pain that can be pinpointed with the tip of one finger.
- Pain that can be reproduced by moving or pressing on the chest wall or arms.
- Pain that is constant and lasts for hours .
- Pain that is very brief and lasts for a few seconds.
- Pain that spreads to the legs.
However, the presence of these symptoms does not necessarily rule out a serious heart event.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Bleeding Around The Heart
Myth: Heart Failure Is The ‘end Of The Road’ And Cannot Be Managed
Fact: Heart failure does not mean your heart has stopped working and is definitely not the ‘end of the road’. Although there is no definite cure, it can be treated, and symptoms can often be managed effectively.
Now that these myths have been addressed, you can be better prepared to track your heart health! If you or a loved one is experiencing any heart failure symptoms — consult a doctor immediately.
What Is The Outlook
Your outlook following a stroke or heart attack depends greatly on the severity of the event and how quickly you get treatment.
Some people who have a stroke will experience damage that makes walking or talking difficult for a long time. Others lose brain function that never returns. For many of those who were treated soon after symptoms began, complete recovery may be possible.
Following a heart attack, you can expect to resume most of the activities you enjoyed before if you do all of the following:
- follow your doctors orders
- participate in cardiac rehabilitation
- maintain a healthy lifestyle
Your life expectancy will depend greatly on whether you adhere to heart-healthy behaviors. If you have a stroke or heart attack, its important to take the rehabilitation process seriously and stick with it. As challenging as it may be at times, the payoff is a much better quality of life.
Many of the same strategies that can help prevent a stroke can also help reduce your chances of having a heart attack. These include:
- getting your cholesterol and blood pressure levels into a healthy range
- not smoking
Recommended Reading: Thrz Calculator
Stroke And Cardiac Arrhythmias
Significant cardiac arrhythmias are seen during the first few days in 25% of patients admitted to the hospital with acute stroke.
The arrhythmia most frequently associated with stroke is atrial fibrillation, which accounts for more than half of stroke-related heart rhythm problems.
Life-threatening arrhythmias may also occur, including ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest. In many cases, such potentially lethal arrhythmias are due to long QT syndrome, which may result from a stroke.
Significant bradycardia can also occur after a stroke. Usually, the bradycardia is transient, but occasionally significant heart block may be seen, requiring insertion of a pacemaker.
