Components Of The Aorta
The aortic arch contains peripheral baroreceptors and chemoreceptors that relay information concerning blood pressure, blood pH, and carbon dioxide levels to the medulla oblongata of the brain. This information is processed by the brain and the autonomic nervous system mediates the homeostatic responses that involve feedback in the lungs and kidneys. The aorta extends around the heart and travels downward, diverging into the iliac arteries. The five components of the aorta are:
Easy Way To Remember Blood Flow Through The Heart
The blood flow of the heart is something you will have to learn in nursing school . When I was in nursing school I hated learning about the heart and promised myself that I would never enter into cardiology. Well, to make a long story short, I entered into cardiology and have never left it. I learned to heart the heart.
In this article, I am going to show you how to easily remember the blood flow of the heart. I found that learning the blood flow of the heart is best done by actually visualizing how the heart is set-up and how it flows through the muscle to the body.
After reviewing these notes, dont forget to take the heart blood flow quiz.
Blood Flow Positive And Negative Effects
A healthy heart normally beats anywhere from 60 to 70 times per minute when you’re at rest. This rate can be higher or lower depending on your health and physical fitness; athletes generally have a lower resting heart rate, for example.
Your heart rate rises with physical activity, as your muscles consume oxygen while they work. The heart works harder to bring oxygenated blood where it is needed.
Disrupted or irregular heartbeats can affect blood flow through the heart. This can happen in multiple ways:
- Electrical impulses that regulate your heartbeat are impacted, causing an arrythmia, or irregular heartbeat. Atrial fibrillation is a common form of this.
- Conduction disorders, or heart blocks, affect the cardiac conduction system, which regulates how electrical impulses move through the heart. The type of blockan atrioventricular block or bundle branch blockdepends on where it occurs in the conduction system.
- Damaged or diseased valves can become ineffective or leak blood in the wrong direction.
- A blocked blood vessel, which can happen gradually or suddenly, can disrupt blood flow, such as during a heart attack.
If you experience an irregular heartbeat or cardiac symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath, seek medical help immediately.
Also Check: List The Steps Of How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
Where Is Your Heart And What Does It Look Like
The heart is located under the rib cage, to the left of your breastbone and between your lungs.
Looking at the outside of the heart, you can see that the heart is made of muscle. The strong muscular walls contract , pumping blood to the arteries. The major blood vessels connected to your heart are the aorta, the superior vena cava, the inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery , the pulmonary veins , and the coronary arteries .
On the inside, the heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ. It is divided into the left and right side by a wall called the septum. The right and left sides of the heart are further divided into two top chambers called the atria, which receive blood from the veins, and two bottom chambers called ventricles, which pump blood into the arteries.
The atria and ventricles work together, contracting and relaxing to pump blood out of the heart. As blood leaves each chamber of the heart, it passes through a valve. There are four heart valves within the heart:
- Mitral valve
- Aortic valve
- Pulmonic valve
The tricuspid and mitral valves lie between the atria and ventricles. The aortic and pulmonic valves lie between the ventricles and the major blood vessels leaving the heart.
The heart valves work the same way as one-way valves in the plumbing of your home. They prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
Your Aorta Pumps Oxygenated Blood Out Of Your Heart To Your Body
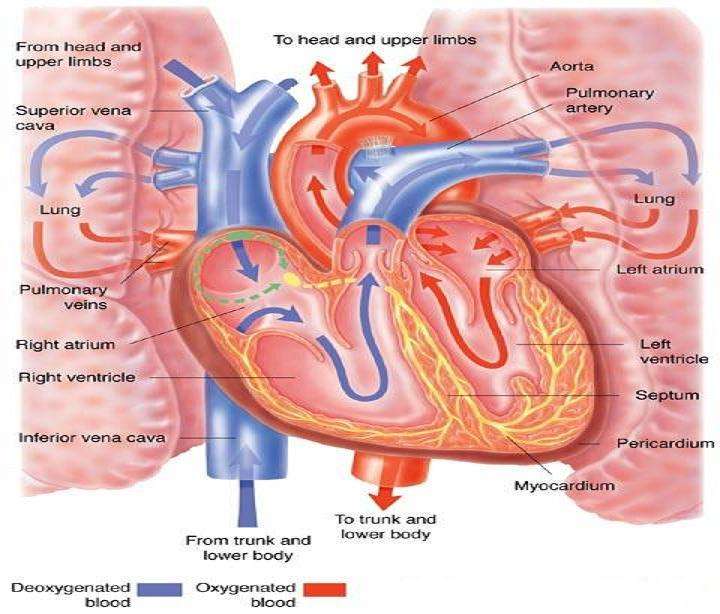
- The aorta stretches across the back of your heart and pumps blood both above and below your heart to your upper and lower body
- As oxygenated blood goes to your cells, it drops off oxygen and picks up waste
- Cells in your body need oxygen so that they can perform cellular respiration to get energy
- Blood also picks up carbon dioxide from the cells as the waste product of cellular respiration
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
What Kind Of Blood Comes Back Into The Heart & Then Goes To The Lungs
The heart consists of four chambers in which blood flows. Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. The oxygenated blood is brought back to the heart by the pulmonary veins which enter the left atrium.
Structure Of The Heart
The heart has four chambers . There is a wall between the two atria and another wall between the two ventricles. Arteries and veins go into and out of the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood to the heart. The flow of blood through the vessels and chambers of the heart is controlled by valves.
Read Also: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How Does The Heart Beat
The ventricles and atria work together and alternately relax and contract for making the blood flow through the heart. Your hearts electrical system provides them the power for accomplishing this goal.
The impulse begins in a little group of specialized and efficient cells known as the sinoatrial node situated in your right atrium. The SA node is also referred to as your hearts pacemaker. The electrical impulse spreads via the walls of your atria, stimulating them to instantly contract.
A group of cells lying in your hearts center between your ventricles and atria known as the atrioventricular node works like a door that reduces the speed of the electrical impulse before it moves to the ventricles. This slight delay gives your atria enough time to quickly contract prior to the contraction of the ventricles.
The His-Purkinje network refers to a path of numerous fibers that send that electrical impulse to your ventricles muscular walls, triggering them to quickly contract.
The Heart Rate
When you are resting, your heart beats about 50 to around 99 times per minute. Medications, emotions, fever and exercise can make your heart beat faster. At times, the heart can beat more than 100 beats/ minute.
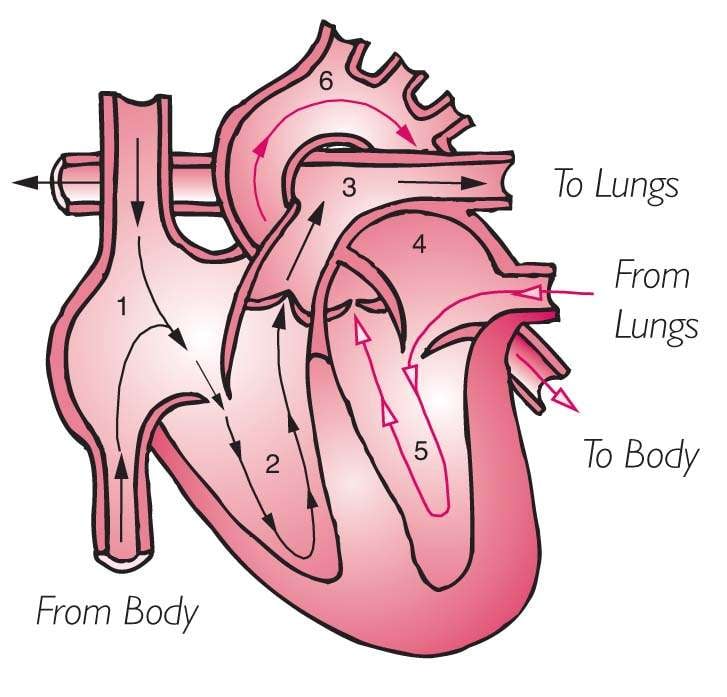
Left Side Of The Heart
Goal: to get the richly, oxygenated blood that LEFT the lungs to the body to feed the brain, tissue, muscles, organs etc.)
7. Blood enters from the lungs through the PULMONARY VEIN
8. Blood then enters into the LEFT ATRIUM
9. Down through the BICUSPID VALVE
10. Then blood is squeezed into the LEFT VENTRICLE
11. Up through the AORTIC VALVE
12. Lastly up through the AORTA, where it pumped throughout the body
Study Tip:
Many people get confused on if the blood enters the tricuspid or bicuspid valve first. Remember this saying, First always try, before you buy. By remembering this phrase, you will remember that the tricuspid is before the bicuspid ;valve.
Also, dont left the atriums and ventricles mess you up either. Try to remember that A is before V in the alphabet so atriums is above the ventricles .
Also Check: Vitamin D3 And Heart Palpitations
The Circulatory System Works In Tandem With The Respiratory System
The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to sustain the body with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide. Pulmonary circulation facilitates the process of external respiration: Deoxygenated blood flows into the lungs. It absorbs oxygen from tiny air sacs and releases carbon dioxide to be exhaled. Systemic circulation facilitates internal respiration: Oxygenated blood flows into capillaries through the rest of the body. The blood diffuses oxygen into cells and absorbs carbon dioxide.
Your Heart Beats To The Signals Of The Sa Node And Av Node As The Right Atrium Pumps It To The Right Ventricle
- From the superior and inferior vena cava, blood goes through the Right Atrium
- First, the SA Node sends electrical signals to pump blood from right atrium to right ventricle
- Then, as blood enters the right ventricle, the AV Node receives a signal to act as the gateway to the right ventricle and control the speed of blood flow there
- The SA and AV node combine to make the ba-bum sound of your heartbeat
- Blood goes through the tricuspid valve/right AV valve as it enters the right ventricle
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Anatomy Of The Heart And Blood Vessels
Reviewed byDr Jacqueline Payne
The heart is a muscular pump that pushes blood through blood vessels around the body. The heart beats continuously, pumping the equivalent of more than 14,000 litres of blood every day through five;main types of blood vessels: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins.
Read Also: Is 116 Heart Rate High
Where Are Your Blood Vessels Located
There are blood vessels throughout your body. The main artery is your aorta, which connects to the left side of your heart. It runs down through your chest, diaphragm and abdomen, branching off in many areas. Near your pelvis, your aorta branches into two arteries that supply blood to your lower body and legs.
The main vein in your body is the vena cava. The superior vena cava is in the upper right part of your chest. It carries blood from your head, neck, arms and chest back to your heart. The inferior vena cava is near the right side of your diaphragm. It brings blood from your legs, feet, abdomen and pelvis back to your heart.
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
The Heart Is A Muscle
Your heart is really a muscle. It’s located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it’s about the size of your fist. There are lots of muscles all over your body in your arms, in your legs, in your back, even in your behind.
But the heart muscle is special because of what it does. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste.
Your heart is sort of like a pump, or two pumps in one. The right side of your heart receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. The left side of the heart does the exact opposite: It receives blood from the lungs and pumps it out to the body.
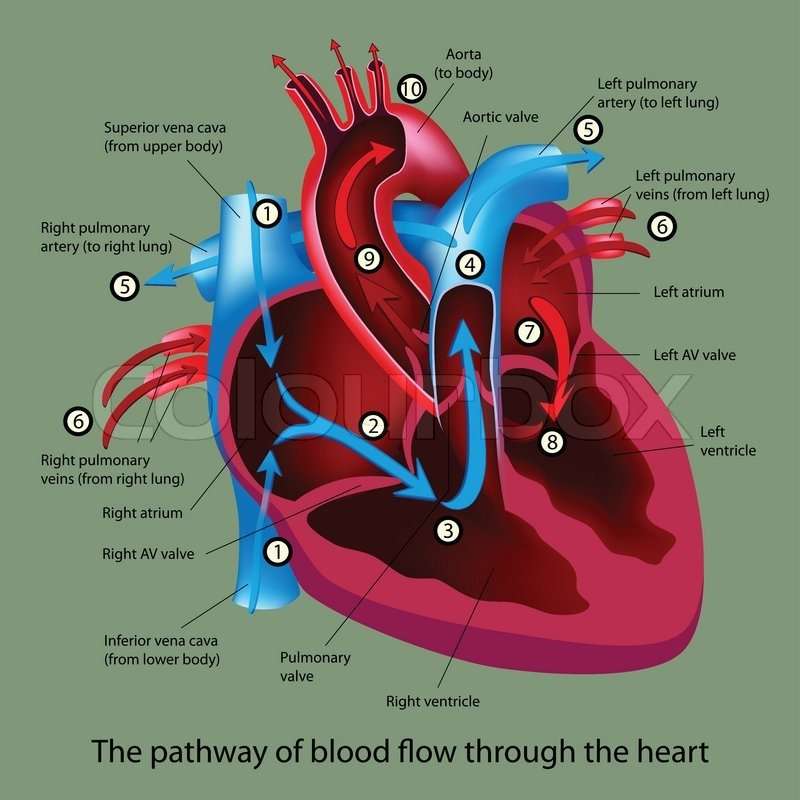
Heart Anatomy: By The Numbers
1. Superior vena cava: Receives blood from the upper body; delivers blood into the right atrium.
2. Inferior vena cava: Receives blood from the lower extremities, pelvis and abdomen, and delivers blood into the right atrium.
3. Right atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior vena cava; transmits blood to the right ventricle, which pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
4. Tricuspid valve: Allows blood to pass from the right atrium to the right ventricle; prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium as the heart pumps .
5. Right ventricle: Receives blood from the right atrium; pumps blood into the pulmonary artery.
6. Pulmonary valve: Allows blood to pass into the pulmonary arteries; prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle.
7. Pulmonary arteries: Carry oxygen-depleted blood from the heart to the lungs.
8. Pulmonary veins: Deliver oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
9. Left atrium: Receives blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary veins.
10. Mitral valve: Allows blood to flow into the left ventricle; prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium.
11. Left ventricle: Receives oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium and pumps blood into the aorta.
12. Aortic valve: Allows blood to pass from the left ventricle to the aorta; prevents backflow of blood into the left ventricle.
13. Aorta: Distributes blood throughout the body from the heart.
Also Check: How Much Blood Does An Adult Heart Pump Every Day
Right Side Of The Heart
Goal: to get the blood RIGHTto the lungs so it can become oxygenated.
1. The un-oxygenated blood enters the heart through the SUPERIOR AND INFERIOR VENA CAVA.
2. Blood enters into the RIGHT ATRIUM
3. Then it is squeezed through the TRICUSPID VALVE
4. Blood then enters into the RIGHT VENTRICLE
5. Then it is squeezed into the PULMONIC VALVE
6. Blood is then shot up through the PULMONARY ARTERY and then enters into the lungs for some oxygen
Study Tip: Since the goal of the right side is to get blood;to the lungs always remember that the pulmonic valve and pulmonary artery will be on the right side since it is associated with the lungs. Remember in medical terminology;pulmon means lungs.;This will help you keep from getting confused with the left side of the heart.
What Is The Name Of The Blood Vessels That Carry Blood To And From The Lungs
pulmonary arterypulmonary
Refering to the common carotid artery supplies blood to the head and face. The blood vessel that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. It is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood.
Also, what is the blood vessel that carries blood to the heart called? blood vessels: Blood moves through many tubes called arteries and veins, which together are called blood vessels. The blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called arteries. The ones that carry blood back to the heart are called veins.
People also ask, what carries blood away from the lungs?
Key terms
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Keep Your Heart Happy
Most kids are born with a healthy heart and it’s important to keep yours in good shape. Here are some things that you can do to help keep your heart happy:
- Remember that your heart is a muscle. If you want it to be strong, you need to exercise it. How do you do it? By being active in a way that gets you huffing and puffing, like jumping rope, dancing, or playing basketball. Try to be active every day for at least 30 minutes! An hour would be even better for your heart!
- Eat a variety of healthy foods and avoid foods high in unhealthy fats, such as saturated fats and trans fats .
- Try to eat at least five servings of fruits and vegetables each day.
- Avoid sugary soft drinks and fruit drinks.
- Don’t smoke. It can damage the heart and blood vessels.
Your heart deserves to be loved for all the work it does. It started pumping blood before you were born and will continue pumping throughout your whole life.
Deoxygenated Blood Returns To Your Heart Through The Superior Vena Cava And Inferior Vena Cava To Your Right Atrium
- Capillaries separate oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood and arteries from veins
- After passing through the capillaries, blood is deoxygenated and needs to head back to the heart to be pumped to the lungs to pick up oxygen
- The Superior Vena Cava is the vein that gets deoxygenated blood from the upper body and returns it to the heart
- The Inferior Vena Cava is the vein that gets deoxygenated blood from the lower body and returns it to the heart
Recommended Reading: What Branch Of Medicine Deals With Heart Disease
Which Side Is A Womans Heart
Although most of us place our right hand on our left chest when we pledge allegiance to the flag, we really should be placing it over the center of our chest, because thats where our hearts sit. Your heart is in middle of your chest, in between your right and left lung. It is, however, tilted slightly to the left.
3.9/5major blood vesselsheartarterymore about it
aorta : The aorta is the major blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
what type of artery carries blood away from the heart? Arteries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Pulmonary arteries transport blood that has a low oxygen content from the right ventricle to the lungs. Systemic arteries transport oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body tissues.
Herein, which vessel carries blood from heart to lungs?
The pulmonary artery channels oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle into the lungs, where oxygen enters the bloodstream. The pulmonary veins bring oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium.
What carries blood back to the heart?
The circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart. The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells, and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide.
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It usually branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, side, and back of the left ventricle, and the left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open called collateral vessels may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When Someone Has A Heart Attack
