Thicker Heart Walls *
As well as causing the cavity of heart chambers to increase in volume, regular exercise also thickens the walls of our heart chambers. This results from a process called hypertrophy an increase in size of individual heart muscle cells . The benefit of this response is that it allows the heart to contract more forcefully and pump harder.
Interestingly, the exact nature by which your heart muscle increases in size differs according to what type of exercise you perform. Strength training tends to lead to what is known as concentric hypertrophy. This leads to more pronounced increases in thickness of heart chamber walls, particularly the walls of the left ventricle.
By contrast, endurance exercise tends to elicit eccentric hypertrophy. This is characterised by a lengthwise increase in size in individual heart muscle cells, which gives rise to a larger heart chamber and less pronounced wall thickening.
Nevertheless, both concentric and eccentric hypertrophy involve enlargement of heart muscle cells. Moreover, lots of sports and exercises will probably cause a mixture of both types of adaptation.
Average Resting Heart Rate By Age
Keep in mind, your heart rate during exercise is unique to you and only tells you how hard you’re working – not how fit you are. Therefore it isn’t accurate to compare heart rates between two different people. Besides having different target heart rates by age, your average resting heart rate will also differ. For adults 18 years old and older, a normal resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute . Keep in mind this does depend on the persons physical condition and age though. For children ages 6 to 15, the normal resting heart rate is between 70 and 100 bpm. A good time to check this is in the morning after youve had a good nights sleep, and before you eat or drink anything. When it comes to resting heart rate, lower is better because it means your heart muscle is in better condition and doesnt have to work as hard to maintain a steady beat. That’s why an athlete or more active person may have a resting heart rate as low as 40 beats per minute. If your heart rate is higher or lower than average and you don’t exercise regularly, be sure to see a doctor to see if it’s another underlying issue.
What Is Recovery Time
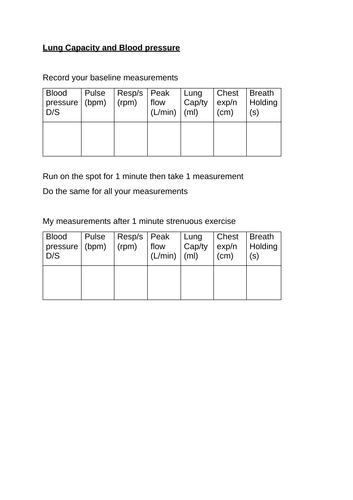
Recovery time is the time taken for heart rate to return to normal. If you have time, can you work out how long this is for you?
The pulse rate and breathing rate of a fitter person rise much less than in an unfir person during exercise, fitter people also have a shorter recovery time.
Links to Maths
Design a method of recording your results? Can you work out the average heart rate for 10 participants before and after exercise?
Calculate the difference between a persons heart rate before and after exercise.
Links to English
Can you write a letter to a friend telling them about your findings?
Also Check: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Whats A Normal Heart Rate During Exercise
When it comes to your heart rate, there is no normal. For a variety of reasons, its pointless comparing your heart rate during exercise to someone elses. As you will discover below, there are many factors that influence our heart rate, making each of ours different and it will continue to change over the course of your life and fitness journey.
Measuring Your Heart Rate

Figure 2.
Example graph from phyphox records a person saying a word each time they feel their pulse. The minimum decibel level recorded was 33 dB and the maximum was 73 dB.
Figure 3.
Figure 4.
You May Like: Chronic Systolic Heart Failure Life Expectancy
What Is The Best Exercise For Heart Rate
While interval-style exercise training is a popular choice for people who are time-poor, the intermittent nature of the exercise means heart rate will fluctuate, providing not much more benefit than traditional steady-state exercise.
Read more:Health Check: high-intensity micro workouts vs traditional regimes
From a scientific perspective, athletes typically use heart-rate ranges to train at specific intensities during aerobic exercise, like cycling or long-distance running.
Exercising at certain intensities are known to elicit adaptive responses from the body, for example, exercising at or below the lactate threshold.
These intensities are called training zones and are expressed relative to HRmax. For instance, a light aerobic training session would be prescribed below 75% HRmax, while training at threshold will induce physiological change.
Overall, some exercise is better than no exercise for your cardiovascular health. Accumulating 150 minutes of exercise per week is the minimum requirement for health benefit. Exercising at your maximal heart rate is not necessary to achieve these benefits. Athletes can use training zones, relative to HRmax, to achieve optimal adaptation and enhance endurance performance.
The Meaning Of Moderate
Exercise intensity levels are very subjective and depend partly on your current fitness level. These descriptions will give you a sense of the different levels. Moderate to vigorous exercise may be especially helpful for your heart, thanks to a phenomenon known as ischemic preconditioning.
Type of walking
Read Also: Ejection Fraction At Rest
Using Exercise To Tune Up Your Cardiovascular Health
If we compare a persons initial fitness response to testing, to responses three to six months later, we see progress, says Dr. Stewart. The oxygen consumption will be higher. The time on the treadmill will be longer. The heart rate and blood pressure will be lower. Its like tuning up your engine. Only the engine is your heart and the bodys circulatory system for distributing blood, and its working more efficiently.
Johns Hopkins Women’s Cardiovascular Health Center
The Johns Hopkins Womens Cardiovascular Health Center provides education, comprehensive treatment and diagnostic services to prevent and manage heart disease in women.
Aubrey Bailey Pt Dpt Cf
With all the attention paid to the effect that aerobic exercise has on heart rate, you might think the only requirement for an effective workout is to increase your heart rate. If that were true, watching a scary movie would do the trick.
Effective exercise occurs when the lungs, heart and muscles work harder together. So why all the focus on heart rate? It’s easy to measure and, more importantly, it changes directly with the metabolic requirements of the muscles.
Tip
Heart rate typically increases when you begin to work out. However, as your physical condition improves, heart rate at rest often decreases as this muscle become more efficient.
Also Check: Reflux Palpitations
What Happens To Your Heart When You Exercise
Published on Sep 29, 2021 | Fitness & Wellness, Fitness & Wellness, Heart Health, Men’s Health, Sports Medicine, Stay Well, Women’s Health |
When we workout, we typically think about muscles in our arms, legs, back or abdomen. However, these arent the only muscles that get stronger with regular exercise.
Your heart, which is a muscular organ, gets a workout during exercise, too. Your hearts full-time job is to distribute blood throughout your entire body. When it beats harder and faster, it can grow stronger and more resilient.
When youre stationary, your heart should beat between 50 to 100 times per minute to fall within the normal range. To narrow this down a little, most peoples hearts beat between 60 to 80 times per minute.
When you start your exercise, your muscles will start to work harder and demand more oxygen. This demand will cause sympathetic nerves to stimulate the heart to beat faster and with more force to increase overall blood flow. The sympathetic nerves will also stimulate the veins, causing them to compress. These narrower veins will increase the velocity at which blood flows through your body. This will ultimately increase the amount of blood returning to the heart.
How fast your heart pumps during exercise depends on numerous factors such as:
- Your age
- Intensity of the workout
- Your hearts overall strength
Once you are done with your exercise, your heart rate will begin to slow to a normal pace.
Finding Your Current Heart Rate For Maximizing Your Exercise Plan
It’s not enough to know “Why does heart rate increase during exercise?” You should know your current heart rate for maximizing your exercise regimen. This helps you strengthen your heart to derive maximum benefit from it. With more exercise, it becomes easier to reach closer to the targeted heart rate that is around 90 percent of the maximum heart rate. When you start exercising, your target should be to reach 50 percent of your greatest heart rate.
To determine the heart rate you should aim for, you should subtract your current age from 220. The answer is your greatest heart rate and refers to the number of heart beats per minute. If you are 30, then your answer will be 190 , or 190 beats per minute.
While exercising, the heart rate can be checked with a heart rate monitoring device or by examining your pulse. Exercise machines such as treadmills or exercise bicycles have heart rate monitoring devices built on their handlebars.
So, find out your heart rate and begin maximizing it to become stronger. By now, you must be fully aware of the reasons why heart rate increases during exercise and why it is beneficial for you.
Don’t Miss: Bottom Part Of Heart Not Working
How Does Cardiovascular Exercise Affect Your Heart
When performing cardio, blood flow is directed toward working muscles and away from areas that aren’t doing much . There is increased blood flow, and blood volume returning to the heart.
As the heart registers a larger blood volume, over time the left ventricle adapts and enlarges. This larger cavity can hold more blood, and ejects more blood per beat, even at rest.
More: Calculate your Target Heart Rate.
Over time, with chronic cardio training, our resting heart rate drops because each beat delivers a bigger burst of blood, and fewer beats are needed. This takes work off your heart and is why cardio exercise is recommended for heart health.
However, cardiovascular exercise can also produce stress. If we get into over-training, we may hit a point where we are drowning in cortisol. This eventually leads to immune-suppression and fat gain around the abdomen and face.
People who spend a significant part of their day in stress, who have poor digestion or other sources of physiological stress, should not further their stress levels by overtraining. Always think of your goals, moderate your exercise if necessary, and work to reduce your stress levels.
More Science For Kids
Make a pumping model of a heart, or try one of our sports science investigations.
Suitable for:
Key Stage 1 Science: Animals including Humans
Describe the importance for humans of exercise, eating the right amounts of different types of food, and hygiene.
Key Stage 2 Science: Animals including Humans
Recognise the impact of diet, exercise, drugs and lifestyle on the way their bodies function
Don’t Miss: How Does Fitbit Calculate Resting Heart Rate
An Insurance Policy For Your Heart
People at risk for heart disease often struggle with the uncertainty of knowing whether their arteries contain fatty plaque that might cause a heart attack. Unless they have symptoms, it’s hard to justify doing potentially invasive or expensive testing, says Dr. Wasfy. What may be reassuring, however, is to think of exercise as an insurance policy that may offer both short- and long-term protection for your heart. A single exercise session may protect the cardiovascular system for two to three hours, the authors postulate. “In essence, you’re training your heart to be more resilient,” says Dr. Wasfy.
But that protection likely depends on reaching a certain intensity of exercise, she adds. Simply puttering around all day long may not do the trick. To make your heart work hard enough to activate the metabolic molecular pathways responsible for preconditioning the heart, you need to engage in moderate to vigorous exercise .
As for duration, 30 minutes a day is the sweet spot for nearly maximal health protection, says Dr. Wasfy. But it’s fine to break that up into three 10-minute sessions. As always, if you’re not accustomed to getting any exercise, get clearance from your physician before starting.
What Is Heart Rate
The cardiovascular system circulates blood throughout the body in order to supply oxygen and other nutrients and to remove waste products. Each time the heart beats blood is pumped out of the heart and into the body to supply oxygen to working muscles or to the lungs for re-oxygenation. Heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute, and is directly related to the workload being placed on the heart. When the body is in a resting state , resting heart rate is measured. A normal resting heart rate ranges from 60-100 beats per minute . Resting rates higher than 100 bpm suggest that the heart is working too hard to circulate blood, and thus may indicate a serious problem that should be monitored by a physician. Resting rates lower than 60 bpm occur more often with endurance-trained athletes whose bodies are more efficient at utilizing oxygen from the blood.
Don’t Miss: Does Lack Of Sleep Increased Heart Rate
Concluding Remarks And Remaining Questions To Be Addressed
Overview of major cardiovascular effects of exercise. Abbreviations: HR, heart rate LV, left ventricle eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase NO, nitric oxide VSM, vascular smooth muscle BP, blood pressure HDL, high density lipoprotein LDL, low density lipoprotein VLDL, very low density lipoprotein TG, triglycerides EPC, endothelial progenitor cell.
Improving Your Heart Health
To keep your heart healthy, the American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise weekly. If you aren’t currently exercising regularly, talk with your doctor about how to get started safely and setting personal goals. Because hypertension typically causes no signs or symptoms, it’s also important to have your blood pressure checked regularly.
Seek medical care right away if you experience an unusually fast or slow heart rate, or a pounding or irregular heartbeat — especially if accompanied by chest pain, dizziness, fainting or shortness of breath.
Don’t Miss: Unsafe Heart Rate During Exercise
Sweaty Science: How Does Heart Rate Change With Exercise
A physical pursuit from Science Buddies
Exercise
IntroductionHave you ever wondered how many times your heart beats in a day, a month, a yearor will beat in total throughout your life? Over an average lifetime, the human heart beats more than 2.5 billion times. For a person to keep their heart healthy, they should eat right, not smoke and get regular exercise. In this science activity, you’ll measure your heart rate during different types of physical activities to find out which gives your heart the best workout to help keep it fit.
BackgroundA 150-pound adult has about 5.5 liters of blood on average, which the heart circulates about three times every minute. A person’s heart is continuously beating to keep the blood circulating. Heart health experts say that the best ways to keep our hearts healthy is through a balanced diet, avoiding smoking and regular exercise.
Materials Clock or timer that shows seconds or a helper with a watch Comfortable exercise clothes Simple and fun exercise equipment, such as a jump rope, bicycle, hula-hoop, two-pound weight, etc. Alternatively you can do exercises that do not require equipment, such as walking, doing jumping jacks, jogging in place, etc. You will want to do at least two different types of exercises, both of which you can sustain for 15 minutes. Calculator
More to explore
How Do You Know When Youre Making Progress
There are many ways to chart your exercise progress. Three of the most common are target heart rate for aerobic exercise, number of repetitions for weight training, and fat vs. muscle body composition.
- Target heart rate The more fit you are, the harder youll need to work to reach your target heart rate. For example, in the first month you may need to walk 3 mph to reach a heart rate of 120, while in the second month in order to reach the same heart rate, you need to walk 4 mph or find a steeper hill. Your fitness is improved and your heart is working more efficiently.
- Reps The more weight you can lift 12-15 times without straining, the stronger and more durable your muscles are. For example, you start out struggling to curl a 15-lb. dumbbell 15 times, and then add three to five pounds when it becomes easy.
- Body composition Exercise more and your body will change shape: youll lose fat, specifically around the waist, and gain muscle. A looser pair of pants or skirt is a distinct sign of progress.
Also Check: Can Dehydration Cause Increased Heart Rate
