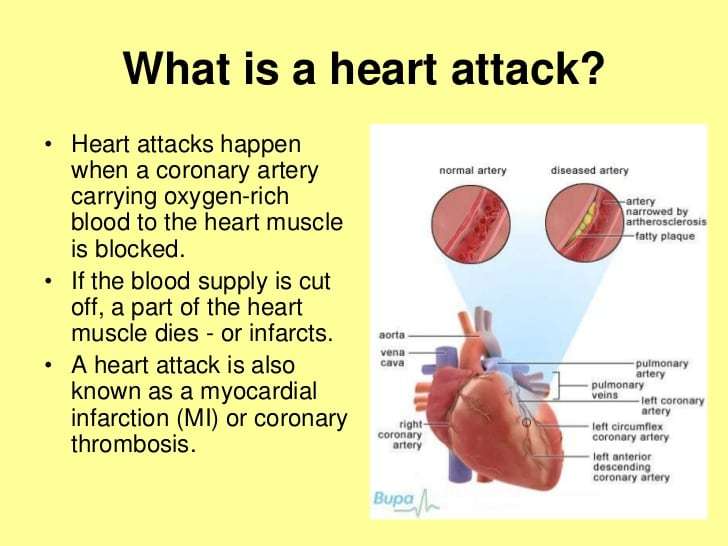
Causes Of A Heart Attack
Coronary heart disease is the leading cause of heart attacks.
CHD is a condition in which the major blood vessels that supply the heart get clogged with deposits of cholesterol, known as;plaques.
Before a heart attack, 1 of the plaques bursts , causing a;blood clot to develop at the site of the rupture.
The clot may block the supply of blood to the heart, triggering a heart attack.
Emergency Testing For A Heart Attack
After you call 911 for a heart attack, paramedics will quickly assess your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. They also will place electrodes on your chest for an electrocardiogram to check your heart’s electrical activity.
When you arrive at the hospital, the emergency room doctor will take your history and do a physical examination, and a more complete ECG will be done. A technician will draw blood to test for cardiac enzymes, which are released into the bloodstream when heart cells die.
If your tests show that you are at risk of having or are having a heart attack, your doctor will probably recommend that you have cardiac catheterization. The doctor can then see whether your coronary arteries are blocked and how your heart functions.
If an artery appears blocked, angioplastyâa procedure to open up clogged arteriesâmay be done during the catheterization. Or you will be referred to a cardiovascular surgeon for coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Some treatments and tests, such as cardiac catheterization, may be available only at regional medical centres. The tests and treatment your doctor chooses may depend on how close you are to a regional centre and the time it would take to transport you to the centre for treatment.
Recovering From A Heart Attack
You’ll usually stay in hospital for about two to five days after having a heart attack. This depends on what treatment you’ve had and how well you’re recovering.
Many people make a full recovery after a heart attack, but you might not be able to do everything you used to. Going to cardiac rehabilitation can help you get back to normal as quickly as possible.
A heart attack can be a frightening experience and it can take time to come to terms with what’s happened. Its natural to be worried about your recovery, feel scared, frustrated and isolated.;
For support and advice, visit our emotional support page.Practical matters like driving, going back to work or finances might be a worry after a heart attack. You can get support and advice on these topics and more on our practical support page.
- Hear from Mark who was 39 when he had a heart attack.;
Don’t Miss: What Does Heart Rate Mean
How Are Heart Attack And Stroke Diagnosed
If you have stroke symptoms, your doctor will get a quick summary of symptoms and a medical history. Youll likely get a CT scan of the brain. This can show bleeding in the brain and areas of the brain that may have been affected by poor blood flow. Your doctor may also order an MRI.
A different set of tests is done to diagnose a heart attack. Your doctor will still want to know your symptoms and medical history. After that, theyll use an electrocardiogram to check on the health of your heart muscle.
A blood test is also done to check for enzymes that indicate a heart attack. Your doctor may also perform a cardiac catheterization. This test involves guiding a long, flexible tube through a blood vessel into the heart to check for blockage.
What Happens After A Mild Heart Attack

After experiencing a mild heart attack, other symptoms may make themselves known and affect your physical and mental state. You might feel fatigued, as the episode will have weakened your heart muscle and made it more difficult for the heart to pump blood throughout the rest of the body. You may also experience some discomfort in your chest, as damage to the heart impairs blood flow and can result in chest pain.
Depression is another side effect of experiencing a mild heart attack, as after such a traumatic event, you may feel a fear of death or mortality as well as a loss of control over your life. Finally, heart arrhythmias may develop after a mild heart attack, as part of the muscle that conducts the impulse to beat may be damaged and cause the heart to beat irregularly.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Your Heart Rate Go Up When You Exercise
What Procedures Treat A Heart Attack
The most common procedures to treat a heart attack include:
- Angioplasty and stenting. Angioplasty, also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a nonsurgical procedure that opens blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. A thin, flexible tube with a medical balloon on the end is threaded through a blood vessel to the narrowed or blocked coronary artery. Once in place, the balloon is inflated to open the artery to allow blood flow to the heart. The balloon is then deflated and removed. A small mesh tube called a stent may be permanently placed in the artery. The stent helps prevent new blockages in the artery.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting. The surgeon uses a healthy blood vessel from another part of your body to re-route blood around the blockage in your artery. You may need this surgery if more than one artery is blocked, or if angioplasty and stenting did not work to restore blood flow to the heart.
After a heart attack, you may also need to recover from the damage the heart attack did to your heart.
What Is The Outlook
Your outlook following a stroke or heart attack depends greatly on the severity of the event and how quickly you get treatment.
Some people who have a stroke will experience damage that makes walking or talking difficult for a long time. Others lose brain function that never returns. For many of those who were treated soon after symptoms began, complete recovery may be possible.
Following a heart attack, you can expect to resume most of the activities you enjoyed before if you do all of the following:
- follow your doctors orders
- participate in cardiac rehabilitation
- maintain a healthy lifestyle
Your life expectancy will depend greatly on whether you adhere to heart-healthy behaviors. If you have a stroke or heart attack, its important to take the rehabilitation process seriously and stick with it. As challenging as it may be at times, the payoff is a much better quality of life.
Many of the same strategies that can help prevent a stroke can also help reduce your chances of having a heart attack. These include:
- getting your cholesterol and blood pressure levels into a healthy range
- not smoking
You May Like: How To Lower My Resting Heart Rate
Risk Factors You Can Control
The major risk factors for a heart attack that you can control include:
- High blood sugar due to insulin resistance or diabetes
Some of these risk factorssuch as obesity, high blood pressure, and high blood sugartend to occur together. When they do, it’s called metabolic syndrome.
In general, a person who has metabolic syndrome is twice as likely to develop heart disease and five times as likely to develop diabetes as someone who doesn’t have metabolic syndrome.
For more information about the risk factors that are part of metabolic syndrome, go to the Health Topics Metabolic Syndrome article.
What Should I Do If I Have A Heart Attack While I’m Alone
Call 9-1-1 immediatelydo not attempt to drive yourself to the emergency room. While you wait for help:
- If you’ve been prescribed nitroglycerin, take it as directed.
- Whether you have nitroglycerin or not, take 325 milligrams of aspirin. It will work faster if you chew the tablet rather than swallow it whole.
- Make sure your door is unlocked so the emergency team and friend or family member can get in.
- Wrap up in a blanket to stay warm.
- Sit comfortably propped up and try to stay calm.
Also Check: How Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate
Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention is the term for emergency treatment of an STEMI. It’s a procedure to widen the coronary artery .
Coronary angiography is done first, to assess your suitability for PCI.
You may also be given blood-thinning medicines to prevent further clots from forming, such as low-dose aspirin.
You may need to continue taking medicines for some time;after PCI.
Treatment And Medication Options For A Heart Attack
Once you arrive at a hospital after experiencing heart attack symptoms, doctors will confirm a heart attack through a combination of heart monitoring, blood tests, and imaging tests.
You may be started right away on an intravenous clot-busting drug, which will help dissolve the blood clot that caused your heart attack.
You may also undergo a procedure to open up your blocked artery and keep it open, known as coronary angioplasty and stenting.
In certain cases, you may require bypass surgery, in which doctors use blood vessels from other areas of your body to restore blood flow around blocked arteries to your heart.
You May Like: How To Calculate Resting Heart Rate
Heart With Muscle Damage And A Blocked Artery
A less common cause of heart attack is a severe spasm of a coronary artery. The spasm cuts off blood flow through the artery. Spasms can occur in coronary arteries that aren’t affected by atherosclerosis.
Heart attacks can be associated with or lead to severe health problems, such as heart failure and life-threatening arrhythmias.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats. Ventricular fibrillation is a life-threatening arrhythmia that can cause death if not treated right away.
How To Diagnose A Heart Attack

Because of the atypical nature of symptoms and the occasional difficulties in diagnosing heart attacks in women, women are less likely to receive aggressive thrombolytic therapy or coronary angioplasty, and are more likely to receive it later than men. Women also are less likely to be admitted to a coronary care unit.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Heart Palpitations Due To Anxiety
Returning To Normal Activities
After a heart attack, most people who don’t have chest pain or discomfort or other problems can safely return to most of their normal activities within a few weeks. Most can begin walking right away.
Sexual activity also can begin within a few weeks for most patients. Talk with your doctor about a safe schedule for returning to your normal routine.
If allowed by state law, driving usually can begin within a week for most patients who don’t have chest pain or discomfort or other disabling problems. Each state has rules about driving a motor vehicle following a serious illness. People who have complications shouldn’t drive until their symptoms have been stable for a few weeks.
Staff Were Unsure When His Heart Attack Occurred So He Had Warfarin To Thin The Blood Instead Of
Thrombolytic drugs help to dissolve the clot that is blocking the artery and are usually given immediately upon arrival in hospital. But in some parts of the country, people get them before they reach hospital, to speed up treatment. Ideally the injection should be given as soon as possible after the onset of symptoms of the heart attack. If the injection is delayed beyond six hours, the benefit is less and beyond 12 hours there is little or no benefit.
After initial diagnosis and treatment, people were cared for in the hospital’s coronary care unit , where further tests and decisions about treatment were made . Sometimes, people are transferred to another hospital for specialist treatment and care.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Heart Rate To Spike
Manage Stress And Get Help For Depression
- Manage stress. Stress can hurt your heart. Keep stress low by talking about your problems and feelings, rather than keeping your feelings hidden. Try different ways to reduce stress, such as exercise, deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Get help for depression. Getting treatment for depression can help you stay healthy.
How To Get Checked Out
Men may not be aware they had an SMI until weeks or even months later when they see their doctor for a regular visit, or because of persistent symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, or heartburn.
SMI is usually detected from an electrocardiogram or echocardiogram, which can highlight heart muscle damage. Another method is a blood test for the molecular footprints of troponin T, a protein released by injured heart cells. That test is often used in emergency departments for patients with heart attack symptoms.
Once an SMI is diagnosed, your doctor can identify your main risk factors and help design a treatment strategy, including changing your diet, exercising regularly, and taking a statin as well as other medication to help prevent a second heart attack .
“If you do notice any symptoms of a SMI, do not brush them aside, even if you do not think they are serious,” says Dr. Plutzky. “Playing it safe is always a better move than risking the potential harmful downside.”
Recommended Reading: What Branch Of Medicine Deals With Heart Disease
What Are The Risk Factors For Heart Attack
Several health conditions, your lifestyle, and your age and family history can increase your risk for heart disease and heart attack. These are called risk factors. About;half of all Americans have at least one of the three key risk factors for heart disease: high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking.2
Some risk factors cannot be controlled, such as your age or family history. But you can take steps to lower your risk by changing the factors you;can control.
Learn more about risk factors for heart disease and heart attack.
What Is The Difference Between A Heart Attack And Cardiac Arrest
A heart attack is not the same as cardiac arrest. In a heart attack, the heart keeps beating. The person has a pulse and usually stays conscious . During cardiac arrest, the heart stops beating. The person has no pulse and is unconscious .
A defibrillator is a machine that sends an electrical shock to the heart to restore normal rhythm. This treatment must be given as soon as possible. For cardiac arrest, call 911 and begin CPR right away. The American Heart Association says that with “hands only” CPR, anyone can give lifesaving treatment to someone having cardiac arrest. Push hard and fast in the center of the chest and keep going until emergency personnel arrive. Do not give CPR for a heart attack.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Calculate Heart Rate
What Is A Cardiac Rehabilitation Program
Before you leave the hospital, your doctor may talk to you about a cardiac rehabilitation program. These programs provide information that will help you understand your risk factors. It will help you live a healthy lifestyle that can prevent future heart problems. You will learn about exercise and;diet, and how to reach and maintain a healthy weight. You will also learn ways to control your stress level, your;blood pressure,;and your;cholesterol;levels.
Your cardiac rehabilitation program will probably start while you are still in the hospital. After you leave the hospital, your rehabilitation will continue in a rehab center. The rehab center may be at the hospital or in another location.
Most cardiac rehabilitation programs last 3 to 6 months. Your doctor will talk to you about how often you need to attend the program. Once you enroll in a cardiac rehabilitation program, regular attendance is important. The more lifestyle changes you make, the better your chances of preventing future heart problems.
The sooner you get medical help, the greater your chances of surviving a heart attack. Do not delay getting immediate medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of heart attack.
Life After A Heart Attack
A heart attack is often a devastating event that severely disrupts your life. Still, many people find ways to live a full, enjoyable life after having one.
Some people experience their heart attack as a wake-up call that they need to make certain lifestyle changes.
Eating habits may need to be changed after a heart attack, along with lifestyle factors like stress and physical activity.
Recovering from a heart attack can be physically and emotionally taxing, with some people experiencing depression stemming from their limitations.
Its important to reach out for any help you need to deal with recovery-related challenges.
Recommended Reading: Heart Rate When Having A Heart Attack
Assessing The Risk Factors For A Heart Attack
- Understand that there are different types of risk factors for heart condition. There are factors youll change by making changes to your lifestyle choices, and there are some that you simply cannot. Once you are aware that the alternatives that you make increases or decreases your risk of heart condition and of an attack , you create better choices.
- Understand the risk factors for developing a heart condition that you simply cannot change these are factors that cant be changed and will be considered when assessing your overall risk of an attack . Risk factors you cant change include:
- Age: Men over 45 and women over 55 have a better risk of heart attack.
- Family history: If your close blood relatives have had an early attack, youll be at a better risk.
- History of autoimmune disease: If youve got a history of an autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis or Lupus, youre at higher risk of getting an attack .
- Pre-eclampsia: this is often a condition in pregnancy
- Lower your risk of attack by striving to remain active a day choose a brisk walk for a quarter-hour after lunch and dinner. Eat a healthy diet low in salt, trans-fats and carbohydrates, high in healthy unsaturated fats and proteins.
- Stop smoking.
- Its important to follow your doctors recommendations for treatment and drugs if youre at risk of a heart attack, or if youre recovering from one.
