What Is Shared Decision
When heart failure progresses to an advanced stage, there are still many treatment options. The decisions ranging from do everything possible to strive for comfort arent easy. Thats why the American Heart Association released recommendations that serve as a roadmap to decision-making in advanced heart failure.
The goal? A partnership between you and your doctor, where medical options are honestly discussed, and decisions are made based on what you want. Shared decision-making means you dont have to make decisions on your own.
Doctor-patient conversations about treatment options, their risks and benefits as well as future what-if scenarios should happen early and often, according to experts who helped draft the AHA recommendations. This early dialogue means youre not blindsided when a big medical event happens that requires tough decision-making.
Doctors provide the medical facts and figures, while you provide your personal goals and preferences. Together and often with input from family and friends you and your doctor build a care plan.
What Is Heart Failure
Heart failure, or congestive heart failure, is a long-term condition that gets worse over time. Although the name sounds like your heart has stopped working, heart failure means your heart isnt able to pump blood as well as it should. When your heart has less pumping power, that can damage your organs and fluid can collect in your lungs.
Prognosis At Each Stage
The outlook for CHF varies greatly between people, as there are many contributing factors for every individuals situation. However, generally speaking, if CHF is discovered in its earlier stages and properly managed, you can expect a far better outlook than if its discovered much later.
Some people whose CHF is discovered early and treated promptly and effectively can hope to have a nearly standard life expectancy.
Also Check: What Is A Normal Heart Rate For A Woman In Her 50’s
Summary Of How Heart Failure Develops
The heart muscle is weakened by conditions or diseases that damage the heart. The hearts pumping action becomes less efficient. The body tries to compensate for the hearts reduced pumping action by
- Increasing hormonal stimulation
- Enlargingthe heart chambers stretch and enlarge and the muscle mass may increase in size.
For a time, these adaptations will help continue normal or near-normal heart functions. But sooner or later, these adjustments can actually make matters worse by putting extra strain on the heart.
Request A Hospice Evaluation
The primary physician may recommend hospice when the time is right. But as anyone who has faced a serious illness knows, patients and family members often must act as their own advocates to receive the care they need and deserve.
You, your loved one or your trusted physician may request an evaluation to see if hospice is an appropriate option for care.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Weak Heart Valves
You May Like: Can Pneumonia Cause Congestive Heart Failure
Top Tips For Caring For Someone Who Needs Help Eating:
- Face the person so they can see you and their food.
- If the person normally wears glasses or hearing aids, help them to put them on. This will help them to see what youre doing and to hear what youre saying.
- Offer smaller meals or portions that dont overwhelm the person.
- Let the person eat slowly. Allow plenty of time for them to chew their food and swallow it. They might need to catch their breath before each mouthful.
- Watch for clues to help you tell when they have finished swallowing. If its hard to tell, ask the person if theyve finished or to open their mouth to see if there is any food left inside.
- For drinks, use a wide cup or glass, so the drinker doesnt have to tilt their head back. You could also use a straw, for cold drinks.
- Dont rush the meal. This could increase the risk of food entering the persons airways.
- Look out for signs of tiredness. If the person is getting sleepy, it is best for them to stop eating even if they havent finished their meal. This is because people are more likely to cough or choke on food.
- If possible, try and make sure the person waits at least 15 minutes before going back to bed or lying down. This reduces the chances of food and drink coming back up the throat and causing them to choke.
What You Can Do
Some risk factors of heart failure, like age, cant be modified. Still, people with CHF can take steps to improve the long-term prognosis. The first thing to do is to be familiar with any family history of heart disease. You’ll also want to learn about all the possible symptoms. Don’t ignore any symptom that you think is cause for concern. Tell your healthcare provider about them right away.
Regular exercise, along with managing any other health issues you may have, can also help to keep CHF under control.
Also Check: Can Smoking Cause Heart Attack
Life Expectancy An Individual Matter
“The exact reasons for this incongruity are unknown but they may reflect hope or may result from inadequate communication between clinicians and their patients about prognosis,” write the researchers. “Because differences in expectations about prognosis could affect decision making regarding advanced therapies and end-of-life planning, further research into both the extent and the underlying causes of these differences is warranted.”
In an editorial that accompanies the study, Clyde W. Yancy, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas, writes that predicting life expectancy in people with heart failure is not an exact science and many questions remain about clinical prediction models.
Therefore, until these issues are fully addressed, people should embrace an individualized decision-making process regarding end-of-life care guided by physician input.
Show Sources
National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey
NHANES, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute reports that gender and age are key influential factors in predicting life expectancy after a diagnosis of heart failure.3 This means the lifetime risk of HF is increasing. For example, for people between ages 45 and 95, the lifetime risks for HF are between 20%45%.3 Gender and racial disparities in HF persist. They influence lifetime risks and projected life expectancy. In the most recent report, the risks for developing HF were 30% to 42% in white males, 20% to 29% in black males, 32% to 39% in white females, and 24% to 46% in black females. Of note, the lower lifetime risk in black males may be attributable to competing risk factors.3
Although the rates of rehospitalization or death were greatest for those previously hospitalized for HF, the length of survival from heart failure in the older population has improved.3 They do differ by HF subtype and stage. The overall 1-year mortality rate is nearly 30% it has improved only slightly from 2008. Fatality rates, death after hospitalization for HF, were 10.4% at 30-days, 22% at 1-year, and 42.3% at 5-years. There is still a higher rate of death in blacks than whites.3
You May Like: What Is Your Max Heart Rate
Heart Failure Expectations Unrealistic
In the study, researchers surveyed 122 people with moderate to advanced congestive heart failure about their perception of their life expectancy.
They found the heart failure patients tended to overestimate their life expectancy by about three years. The average patient survival estimate was 13 years compared with a validated medical model estimate of 10 years.
Overall, 63% of people with heart failure overestimated their remaining life expectancy by an average of 40% compared with medical model predictions. Those who were younger and with more advanced disease were most likely to overestimate how long they had left to live.
During the three-year follow-up period, 29% of the people involved in the survey died. Researchers found no relationship between longer life expectancy perceptions and survival.
Facts About Heart Failure In The United States
- About 6.2 million adults in the United States have heart failure.1
- In 2018, heart failure was mentioned on 379,800 death certificates .1
- Heart failure costs the nation an estimated $30.7 billion in 2012.2 This total includes the cost of health care services, medicines to treat heart failure, and missed days of work.
Read Also: What Can Cause Congestive Heart Failure
Right Sided & Left Sided Heart Failure
When the right side of the heart is not pumping effectively, the blood returning to the heart from the body backs up in the veins. Right sided Heart Failure causes a backup of blood coming into the heart. Symptoms of right sided Heart Failure:
- Swelling in the liver
- Abdominal distention
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
The blood enters the left side of the heart from the lungs. When the left side of the heart is not pumping blood forward well enough, blood backs up, causing fluid accumulation in the lungs. This is also called congestive Heart Failure. Decreased forward blood flow results in less nourishment to the bodys organs and tissues. Symptoms of left sided Heart Failure:
Read Also: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
How Much Water Should You Drink With Heart Failure
Heart failure can cause fluid retention.
Those who are diagnosed with heart failure are usually instructed to limit their daily fluid intake to 2,000 to 2,500 milliliters or 2 to 2.5 liters per day. This includes all types of fluid intake, not just water.
However, too little fluid intake can increase dehydration and the risk of problems such as damage to the kidneys.
Your optimal fluid intake goal should be based on multiple factors, such as:
- the type of heart failure you have
- whether you take a diuretic medication
- your kidney function
- your sodium intake
- whether youve been hospitalized in the past for fluid retention
Based on these factors, you and your doctor can decide what your ideal fluid intake should be.
Dr. Kohli is an internationally recognized researcher and noninvasive cardiologist who specializes in preventive cardiology. She received two undergraduate Bachelor of Science degrees in biology and brain and cognitive science with a concentration in economics. She graduated with a perfect GPA, receiving the most outstanding academic record distinction. She went on to Harvard Medical School for her MD degree and again graduated at the top of her class with a distinction. She completed her internal medicine residency at Harvard Medical School/Brigham & Womens Hospital in Boston.
Recommended Reading: Treatments Congestive Heart Failure
What Are The Main Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure can have many causes. The most common causes are:
- Coronary heart disease this is where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances called atherosclerosis which may cause symptoms of chest discomfort called angina or heart damage from a heart attack.
- Hypertension high blood pressure can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure.
- Cardiomyopathy conditions affecting the heart muscle and can be hereditary or acquired condition that causes the changes in the heart muscle tissue leading to failure of function.
- Arrhythmias heart rhythm problems such as atrial fibrillation which impairs the contraction strength of the heart by the persistent fast heart rate is one of the many rhythm disturbances causing the heart to pump less efficiently.
- Heart valve disease valve defects and damage will increase volume and strain on the heart and weaken it.
- Congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart.
- Metabolic hyperthyroid with overactive thyroid and diabetes are endocrine causes of heart failure.
- Toxicity alcohol and certain chemotherapy drugs can be toxic to the muscle cells and damage their function.
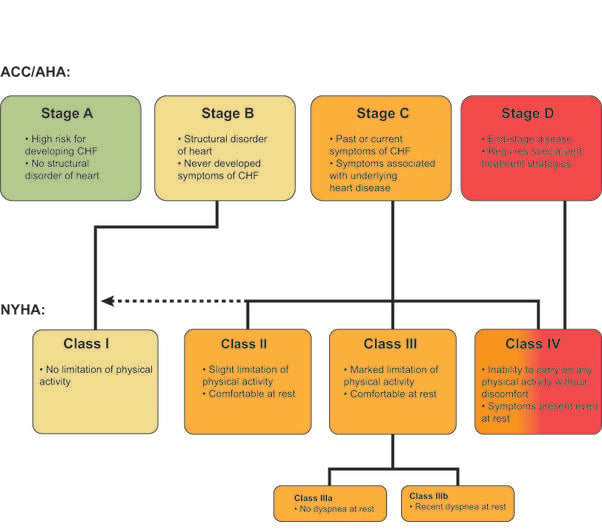
What Are The Heart Failure Stages
Heart failure is a chronic condition that gets worse with time. There are four heart failure stages . The stages range from “high risk of developing heart failure” to “advanced heart failure.”
Stage A
Stage A is considered pre-heart failure. It means youre at high risk of developing heart failure because you have a family history of heart failure or you have one or more of these medical conditions:
- History of taking drugs that can damage your heart muscle, such as some cancer drugs.
Stage B
Stage B is considered pre-heart failure. It means your healthcare provider has given you a diagnosis of systolic left ventricular dysfunction but youve never had symptoms of heart failure. Most people with Stage B heart failure have an echocardiogram that shows an ejection fraction of 40% or less. This category includes people who have heart failure and reduced EF due to any cause.
Stage C
People with Stage C heart failure have a heart failure diagnosis and currently have or previously had signs and symptoms of the condition.
There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:
- Shortness of breath.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats .
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full or hard stomach, loss of appetite or upset stomach .
There may be times that your symptoms are mild or you may not have any symptoms at all. This doesn’t mean you no longer have heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
Don’t Miss: Is Blood Pressure The Same As Heart Rate
Heart Failure Survival Rates
The survival rates from heart failure have been improving over the years. The improvement is slow, but gradual. Clinicians measure overall patient survival from a disease by comparing large groups of people with the disease to large groups of the same age range without it. For example, a 1-year survival rate of 90% is good. It means people with the disease are 90% as likely as people without the disease to be alive for at least one year after diagnosis. For heart failure, the 1-year survival rate rose from 74% in 2000 to about 81% in 2016. The 5-year survival rate increased from 41% to 48%, and the 10-year survival rate rose from about 20% to 26%.
Keep in mind prognosis and life expectancy information is based on data registries from several years ago . Someone diagnosed with heart failure today may have a better prognosis because heart failure treatment, including heart transplant, improves with time.
If you or a loved one has heart failure and you would like to know more about your case, ask your doctor how your age, overall health, and treatment affect your prognosis and life expectancy. Knowing what to expect can help you make plans for the time you have.
What Are The Survival Rates For Heart Failure
Survival rates are based on studies of large groups of people with certain diagnoses and generally presented as a 5-year survival rate, which is the percentage of people who lived for at least 5 years after diagnosis.
You can find online calculators that ask you to submit information to get a life expectancy prediction. However, these calculators are not always accurate since they are based on studies of certain population groups over a period of time .
Table: Survival rates for patients with heart failure
| Survival | |
|---|---|
| 10 | About 24.5% on average |
For example, the 5-year survival rate for patients with heart failure is about 76%. This means that about 76 out of 100 people who were diagnosed with heart failure could live for at least 5 years.
Generally, young patients with heart failure have a better prognosis than older patients. Early diagnosis and treatment help increase life expectancy as well.
You May Like: Heart Attack In Men
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- breathlessness after activity or at rest
- feeling tired most of the time and finding exercise exhausting
- feeling lightheaded or fainting
- swollen ankles and legs
Some people also experience other symptoms, such as a persistent cough, a fast heart rate and dizziness.
Symptoms can develop quickly or gradually over weeks or months .
Does Walking Help Heart Failure
Walking helps congestive heart failure patients in several ways: Reduces heart attack risk, including cutting the risk of having a second heart attack. Strengthens their hearts and improves lung function. Long term, aerobic activity improves your hearts ability to pump blood to your lungs and throughout your body.
Also Check: Miracle Cure For Congestive Heart Failure
How To Use The Congestive Heart Failure Life Expectancy Calculator
To find a person’s survival odds with our heart failure life expectancy calculator, you’ll need the exact values of:
- The age of the patient
- The patient’s weight/height, or BMI
- Their creatinine levels – creatinine is a product of the muscles’ metabolism. It is found at increased levels when the kidneys do not work properly
- Ejection Fraction – the amount of blood that is pushed out of the heart during systole, out of the total amount of blood in the heart and
- Systolic blood pressure – the larger value of the blood pressure measurement made during a routine blood pressure check-up, given in mmHg.
In addition, you need to answer the following questions:
Signs It Might Be Time For Hospice
Patients are considered to be in the terminal end stage of heart disease when they have a life expectancy of six months or less. Only a doctor can make a clinical determination of congestive heart failure life expectancy. However, look for these common signs that the disease has progressed to a point where all involved would likely benefit from hospice services:
- The patient has advanced congestive heart failure or advanced coronary disease with frequent episodes of angina .
- The patient has an abnormal heart and suffers significant symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath or functional decline.
- Optimal treatment for the patients condition has already been provided and he or she is not a candidate for further surgical or medical intervention.
- The patient has tried optimal treatment and made the personal choice not to pursue any further specialized treatment.
People often say, I wish I had asked about hospice sooner.1 Reports show early referral to hospice results in greater satisfaction for the patient and their caregivers. In 2015, seriously ill patients received hospice services for an average of 69.5 days, but given more time, hospice resources can supplement care provided by doctors and loved ones through a patients last six months of life.
You May Like: What Should My Target Heart Rate Be
Also Check: What Should Your Heart Rate Be While Working Out
