Elevated Heart Rate Most Likely Caused By Medical Condition
May 6, 2011
What is sinus tachycardia? What causes it? How is it treated?
Answer:
Sinus tachycardia is the term used to describe a faster-than-normal heartbeat a rate of more than 100 beats per minute versus the typical normal of 60 to 70 beats per minute. Well over 99 percent of the time, sinus tachycardia is perfectly normal. The increased heart rate doesn’t harm the heart and doesn’t require medical treatment.
The term sinus tachycardia has nothing to do with sinuses around the nose and cheeks. Rather, it comes from the sinus node, a thumbnail-sized structure in the upper right chamber of the heart. This structure controls the heart rate and is called the heart’s natural pacemaker.
The sinus node signals the heart to speed up during exercise or in situations that are stressful, frightening or exciting. For example, a 10- to 15-minute brisk walk typically elevates the heart rate to 110 to 120 beats per minute. Also, the sinus node increases the heart rate when the body is stressed because of illness. In all of these circumstances, the heart rate increase is a normal response.
Likewise, the sinus node signals the heart to slow down during rest or relaxation.
For some patients, the elevated heart rate is the only symptom. Some have a lifelong history of sinus tachycardia in the 110 beats per minute range, and they lead a normal, healthy life. And often the inappropriate sinus tachycardia will improve in time without treatment.
What Is The Heart Rate
Heart rate or pulse rate is the number of times your heart beats in a minute. It is a simple measure to know how much your heart works during rest or activities.
Heart rate is one of the vital signs that are checked regularly whenever you visit your doctor, or when you get admitted to the hospital.
Your heart rate is lower when you are resting and higher when you are doing any kind of activity, or are feeling stressed or anxious.
When you exercise, your heart needs to work harder, which increases your heart rate. As soon as you rest, the heart rate starts decreasing gradually and returns to its normal level, usually within an hour.
Symptoms Of A Fast Heart Rate
Many people dont have symptoms when they find out they have a fast heart rate. They often just notice it when checking their pulse rate, or from a blood pressure machine or a Fitbit type accessory. Some patients may feel tired, short of breath, dizzy or fatigued. If the heart rate is particularly fast people may notice a thumping sensation or palpitations. If the heart rate is particularly fast, there may be a sensation of light-headedness or feeling of faintness. In the case of SVT that comes and goes at unpredictable times, there may be intermittent palpitations and light-headedness. When the palpitations come on, some patients may have associated chest pain that on occasion can point to underlying heart artery disease. If the palpitations are more serious, people may pass out as a result.
Recommended Reading: Benadryl Arrhythmia
When To Seek Care
An occasional fast pulse or pounding sensation that doesn’t last long, known as a palpitation, typically isn’t something to worry about.
But, says Dr. Gopinathannair, if your heart is going at a sustained 170 or 180 beats a minute and you’re having rapid palpitations, pounding and associated symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain or dizziness, you may need an immediate evaluation in the ER. That’s because some types of arrhythmias can lead to life-threatening complications, including stroke, heart failure and cardiac arrest.
If your heart rate is more like 105 or 110 beats a minute and you feel otherwise normal except for occasional palpitations, Dr. Gopinathannair advises going to an urgent care center or seeing your primary care doctor.
Another reason to see a doctor is if you have episodes of fast heart rate that are persistent or frequent or that involve other sensations, says Dr. Gopinathannair. Examples are having a regular fast heart rate of 100 beats per minute or symptoms such as skipped beats or a flip-flopping sensation.
Read more:My Heartbeat Skips After Exercising
So How Much Does Low Blood Sugar Affect A Heart Beat
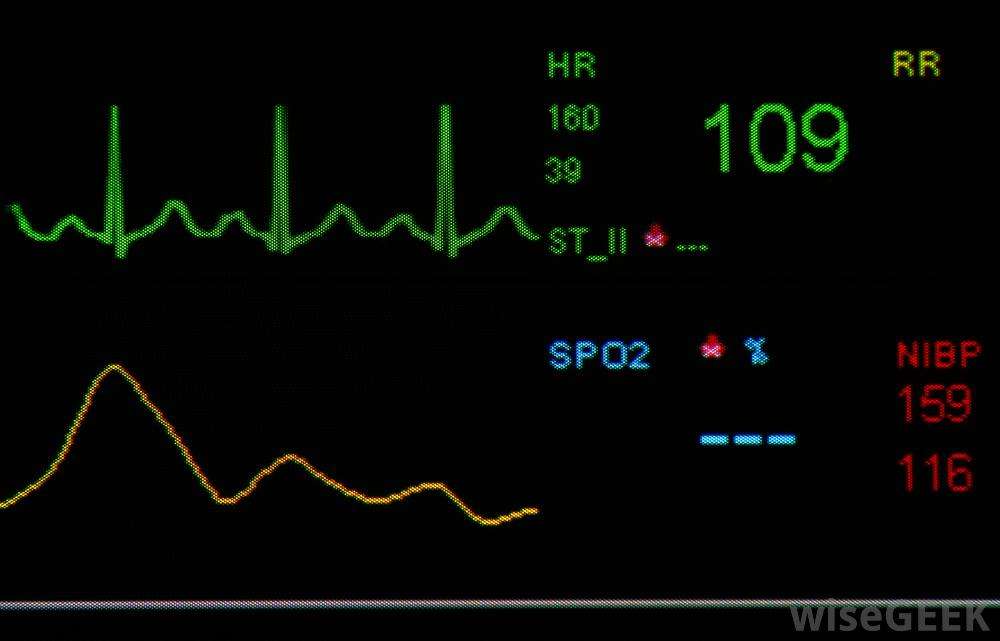
The researchers logged a total of 2,395 hours of ECG and CGM recordings. Of those hours, 159 were designated as low blood sugar and 1,355 as normal blood sugar.
A median duration of nighttime low blood sugar was 60 minutes and was longer than the daytime low blood sugar median of 44 min. Only 24.1 percent of nocturnal and 51 percent of daytime episodes were felt by the participants, the rest going unnoticed.
Bradycardia, or a low heart rate below 60 beats per minute, was more often found during nighttime lows compared with matched normal blood sugars. During daytime lows, bradycardia was not as frequent but atrial ectopics were more frequent.
Atrial ectopics, according to the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, are common and usually harmless and occur when there is an extra heartbeat caused by a signal to the upper chambers of the heart from an abnormal electrical focus. It is an electrical issue with the heart.
Researchers also wrote in their study abstract that Prolonged QTc, T-peak to T-end interval duration, and decreased T-wave symmetry were detected during nocturnal and daytime hypoglycemia. A prolonged QT is when your heart muscle takes longer than what is normal to recharge between beats and can lead to heart arrhythmias. A prolonged T-peak to T-end is associated with ventricular arrhythmogenesis.
This research shows that low blood sugar levels do alter the heart rate of people with type 1 diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Know What Different Heart Rate Zones Feel Like Stay Out Of The Danger Zone
Just because your heart is pumping and youre feeling fatigued doesnt mean youre working out in the danger zone. The key is understanding your running heart rate and those zones the aerobic system, the lactic threshold system, and the anaerobic system and what they feel like so you know when youve moved past them.
If you dont have a monitor , there are other physical markers to estimate which system youre training, such as the talking test.
Generally during a run, youre in one of those three zones. If youre working with a heart rate monitor, its easy to see what heart rate zone youre working within. But if you dont have a monitor , there are other physical markers to estimate which system youre training, such as the talking test.
If you can speak in full sentences, youre likely in the aerobic zone. If you can say a few words at a time, youre probably in the lactic threshold zone. And if you can barely get out one or two words, youve probably found yourself in the anaerobic zone.
If you start to hyperventilate or get dizzy, your heart rate is probably too high, and you should stop and rest, says Jason Lakritz, PT, DPT, physical therapist at Finish Line Physical Therapy in New York City and founder of Profunctional Running.
Diagnosing A Fast Heart Rate
Your doctor is likely to begin your evaluation with a physical exam, health history and an electrocardiogram , states the American Heart Association. If you’re not having an abnormal or elevated heart rate at the time, the machine may not pick up a problem.
Your doctor may instead recommend you wear a portable EKG for a week or more, according to the Heart Rhythm Society. This provides a continuous readout that will catch a high heart rate whenever it happens.
Also Check: Does Benadryl Raise Heart Rate
Does This Really Matter If Youve Finally Got Low Blood Pressure
Heart rhythm problems that affect the upper heart chamber can put you at an increased risk for stroke, heart failure or death. Heres why:
If youre diagnosed with an irregular heart rhythm, you may need to take blood-thinning medications, plus one of the treatments above, to decrease your risk of stroke. Your doctor can help you get the right care to keep everything steady and stable so the only time your heart is racing is while youre watching Stranger Things.
High Pulse Rate Causes And Reasons
Tachycardia is brought about by something that usually disrupts the normal electrical impulses that usually control the rate of the hearts pumping action. Most of the things can lead to or even contribute to the problems with the hearts electrical system. These particular factors are:
- Damage to the heart tissues direct from heart disease
- Abnormal electrical pathways that are in the heart available at birth.
- Disease or even the congenital abnormality of heart
- Anemia
In some other cases, the exact reason behind tachycardia cant be determined.
You May Like: Which Of The Following Signs Is Commonly Observed In Patients With Right-sided Heart Failure
Running Or During Exercise
When you perform any aerobic activity, staying in the target heart rate range may assist ensure that you are working very hard enough so as to see results, but not working very hard that you are at a very high risk for injury or even an illness.
The optimal target heart rate much depends on the age and how fit a person is. A heart rate of about 170 while running can be very much high, depending on several factors.
Finding Your Heart Rate
To find out a heart rate, first find the pulse. You are able to locate it on the inside part of the wrist or on either side of the throat.
If you are not able to find it, try placing the hand across the middle of chest, slightly toward the left side. Using a stopwatch, measure a full minute and then count the number of beats. You may also count the number of beats in only 10 seconds and then multiply by six.
Figuring Out Your Target Heart Rate
You may figure out a possible estimate of the target heart rate for the exercise by understanding the theoretical maximum heart rate. The maximum heart rate is the number of beats per minute your heart can handle when working at its maximum.
There are several different methods that can be used to calculate your theoretical maximum heart rate. One way is to take your age and subtract it from 220. This particular number provides an average maximum heart rate for people in that age group, this is according to the cardiologists. Keep in mind also that the calculation has a very wide margin of error.
What To Expect At The Doctors
Your doctor may use a variety of diagnostic tools to help diagnose your condition, including:
- Electrocardiogram. Also referred to as an ECG or EKG, this diagnostic tool uses small electrodes to record the electrical activity of your heart. Your doctor can use the information collected to determine if heart abnormalities are contributing to your condition.
- Imaging tests. Imaging can be used to assess if there are any structural abnormalities in your heart that may be contributing to your condition. Possible imaging tests can include echocardiogram, CT scan, and MRI scan.
- Laboratory tests. Your doctor may order blood tests to determine if your condition is caused by something such as an electrolyte imbalance or thyroid disease.
Once a diagnosis is made, your doctor will work with you to develop a plan to treat and manage your condition.
Depending on the findings from the diagnostic tests, your doctor may refer you to a cardiologist. A cardiologist specializes in treating and preventing diseases of the heart and circulatory system.
Also Check: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Is A Heart Attack More Likely After Covid
That depends: Post says that heart attack has several different forms. A type 1 heart attack, caused by a blood clot blocking one of the hearts arteries, is rare during or after COVID-19 infection.
Type 2 heart attacks are more common with COVID-19, she says. This heart attack can be caused by increased stress on the heart, such as a fast heartbeat, low blood oxygen levels or anemia, because the heart muscle isnt getting enough oxygen delivered in the blood in order do this extra work. We have seen this in people with acute coronavirus disease, but it is less common in those who have survived the illness.
Blood tests have shown that during COVID-19, some people have elevated levels of a substance called troponin in their blood, along with EKG changes and chest pain. Elevated troponin levels are a sign of damaged heart tissue. Sometimes this is from a heart attack. This is less commonly seen after COVID-19.
During acute COVID-19, elevated troponin levels with an abnormal EKG are linked to higher mortality, but not in patients with a normal EKG, Post says.
Shortness Of Breath Or Chest Pain After Covid
Shortness of Breath
You want to consult a doctor if any of your symptoms are severe, especially shortness of breath, Post says. She recommends using a commercially available O2 saturation monitor.
Shortness of breath by itself is not always a sign of a serious problem, but if you have that symptom along with low O2 , that is a reason to be concerned. Sometimes people are short of breath with exertion after COVID-19 because they have been less active for a long time and need to gradually build their fitness level back up.
COVID-19 Chest Pain
What about lingering chest pain, another common post-COVID complaint? Chest pain may be nothing serious, but if you are having severe chest pain, get help, especially if it is persistent or if you are also having nausea, shortness of breath or lightheadedness: These could be symptoms of a heart attack.
If you have chest pain when you inhale, you might have lung inflammation. Sudden, severe chest pain could be a blood clot in the lung , Post says.
Family doctor or cardiologist?
If your symptoms are not severe but you want to be checked out, Post says a cardiologist doesnt need to be your first stop if youve never had heart problems before and are not at risk. For nonemergency post-COVID-19 symptoms, your primary care practitioner can advise you, she says.
Heart Failure and COVID-19
- Shortness of breath, especially with exertion
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath when lying down
- Leg swelling
- Frequent urination at night
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
What Causes Them
Your heart has its own electrical system that sends electrical signals around the heart, telling it when to contract and pump blood around the body. The electrical signals start in a group of cells, called the sinus node, located in the right atrium. The sinus node is the heart’s pacemaker and makes sure the heart beats at a normal and consistent rate. The sinus node normally increases your heart rate in response to exercise, emotions, and stress, and slows your heart rate during sleep.
But sometimes the electrical signals don’t “communicate” properly with the heart muscle, and the heart starts beating in an abnormal rhythm this is an arrhythmia .
Arrhythmias can be congenital or happen later, and they can be temporary or permanent.
Arrhythmias also can be due to chemical imbalances in the blood infections diseases that irritate the heart medicines injuries to the heart from chest trauma or heart surgery use of illegal drugs, alcohol, or tobacco caffeine and stress. Arrhythmias also can happen for no apparent reason.
What You Can Do
You should always aim to take good care of your heart. This includes doing things like exercising regularly, eating a heart-healthy diet, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Additionally, you should plan to visit your doctor regularly for physicals. Not only is it good practice, but it can also help with early detection of things like high cholesterol or blood pressure abnormalities.
If you already have heart disease, you should carefully monitor your condition and stick to your treatment plan. Take all medications as instructed by your doctor. Be sure to promptly report any new or worsening symptoms.
Some additional preventative health tips to help keep your heart healthy and happy include:
- Find ways to reduce stress. Examples of ways to do this can include things like yoga or meditation.
- Limit your caffeine intake. Using too much caffeine can lead to increases in heart rate.
- Moderate your drinking. Women and men over 65 should only have one drink per day. Men under 65 should only have two drinks per day.
- Quit smoking. Smoking increases your heart rate and quitting can help bring it back down.
- Be aware of medication side effects. Some medications can affect your heart rate. Always be aware of possible side effects before taking a medication.
Your heart is a muscular organ that works to pump oxygen-rich blood and nutrients to the tissues of your body. The muscles of your heart contract and relax to push blood through your blood vessels.
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Increase Heart Rate
How Are Arrhythmias Diagnosed
Arrhythmias can be diagnosed in several ways. The doctor will use a person’s medical history information, along with a physical examination, to begin the evaluation. If an arrhythmia is suspected, the doctor will probably recommend an ECG/EKG to measure the heart’s electrical activity.
There’s nothing painful about an ECG/EKG it’s just a procedure where a series of electrodes are attached to the skin with sticky papers. The electrodes have wires attached to them, which connect to the EKG machine.
The electrical signals from the heart are then briefly recorded, usually for just 10 seconds. This information is sent to a computer, where it’s interpreted and drawn as a graph.
A doctor might recommend these types of ECG/EKG tests:
P
