Classes Of Drugs Used To Treat Arrhythmias
Classes of drugs used in the treatment of arrhythmias are given below.; Clicking on the drug class will link you to the page describing the pharmacology of that drug class and specific drugs. Please note that many of the drugs comprising the first five listed classes have considerable overlap in their pharmacologic properties.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Block
Symptoms of heart block vary depending on the type of block.
First-degree heart block:
- May not have any symptoms.
- May be found during a routine electrocardiogram although heart rate and rhythm are usually normal.
First-degree block is common in athletes, teenagers, young adults and those with a highly active vagus nerve.
Second-degree heart block symptoms:
- Feeling tired.
- Shortness of breath.
Symptoms of third-degree heart block are more intense due to the slow heart rate. If you have severe symptoms, get medical attention right away.
Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressure
Throughout the cardiac cycle, the arterial blood pressure increases during the phases of active ventricular contraction and decreases during ventricular filling and atrial systole. Thus, there are two types of measurable blood pressure: systolic during contraction and diastolic during relaxation. Systolic blood pressure is always higher than diastolic blood pressure, generally presented as a ratio in which systolic blood pressure is over diastolic blood pressure. For example, 115/75 mmHg would indicated a systolic blood pressure of 115 mmHg and a diastolic blood pressure or 75 mmHG. The normal range for blood pressure is between 90/60 mmHg and 120/80 mmHg. Pressures higher than that range may indicate hypertension, while lower pressures may indicate hypotension. Blood pressure is a regulated variable that is directly related to blood volume, based on cardiac output during the cardiac cycle.
The Cardiac Cycle: Changes in contractility lead to pressure differences in the hearts chambers that drive the movement of blood.
Recommended Reading: How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
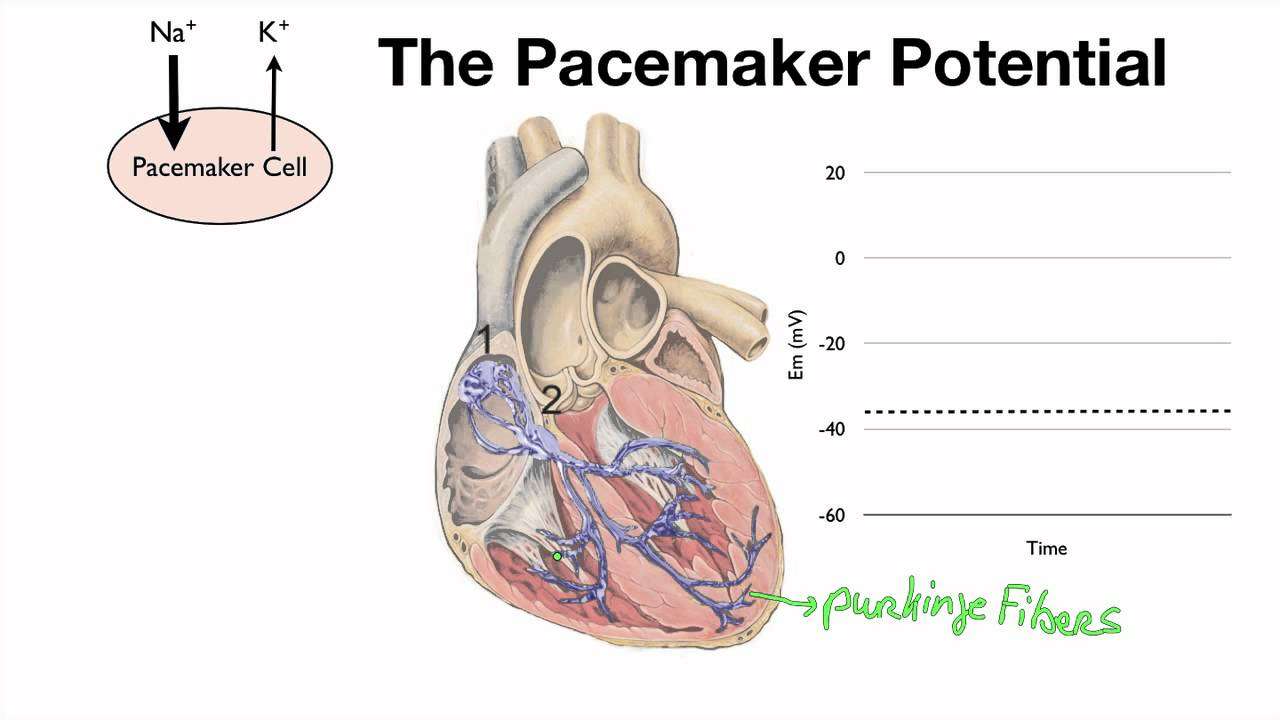
The Heart’s Electrical System
The atria and ventricles work together, alternately contracting and relaxing to pump blood through your heart. The electrical system of your heart is the power source that makes this possible.
Your heartbeat is triggered by electrical impulses that travel down a special pathway through your heart:
At rest, a normal heart beats around 50 to 99 times a minute. Exercise, emotions, fever and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster, sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute.
What Happens During The Pacemaker Implantation
Pacemakers can be implanted two ways:
Inside the heart : This is the most common and simple technique used. A lead is placed into a vein , and then guided to your heart. The tip of the lead attaches to your heart muscle. The other end of the lead is attached to the pulse generator, which is placed under the skin in your upper chest. This technique is done under local anesthesia .
Outside the heart : Your chest will be opened and the lead tip is attached to the outside of the heart. The other end of the lead is attached to the pulse generator, which is placed under the skin in your abdomen. This technique is done under general anesthesia by a surgeon.
Your doctor will decide which approach is best for you, although almost all patients receive the transvenous approach.
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Neurohumoral Control Of Sinoatrial Node Activity And Heart Rate: Insight From Experimental Models And Findings From Humans
- 1Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
- 2Cumming School of Medicine, Libin Cardiovascular Institute of Alberta, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
- 3School of Biomedical Engineering, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
The sinoatrial node is perhaps one of the most important tissues in the entire body: it is the natural pacemaker of the heart, making it responsible for initiating each-and-every normal heartbeat. As such, its activity is heavily controlled, allowing heart rate to rapidly adapt to changes in physiological demand. Control of sinoatrial node activity, however, is complex, occurring through the autonomic nervous system and various circulating and locally released factors. In this review we discuss the coupled-clock pacemaker system and how its manipulation by neurohumoral signaling alters heart rate, considering the multitude of canonical and non-canonical agents that are known to modulate sinoatrial node activity. For each, we discuss the principal receptors involved and known intracellular signaling and protein targets, highlighting gaps in our knowledge and understanding from experimental models and human studies that represent areas for future research.
Control By The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system alters the slope of the pacemaker potential, in order to alter heart rate.
Heart rate is affected by both the parasympathetic and sympathetic branches of the ANS, which innervate both the SA and AV nodes.
- Parasympathetic activity is mediated via;acetylcholine;acting on;M2;muscarinic receptors at the SA node. This lengthens the interval between pacemaker potentials, hence slowing heart rate.
- Sympathetic activity is mediated via noradrenaline acting on B1;adrenoceptors. This shortens the interval between impulses by making the pacemaker potential steeper, hence increasing the heart rate.
If all autonomic inputs are blocked, the intrinsic heart rate is about 100 beats per minute . The normal resting rate of about 60bpm is produced because the parasympathetic system dominates at rest. Initial increases in heart rate are brought about by a reduction in the parasympathetic outflow. Increasing sympathetic outflow allows for further increases in heart rate.
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Are There Special Instructions Or Information I Need To Share With Others If I Have A Pacemaker
If you have a pacemaker:
- Avoid close contact with magnetic devices and any device that sends out an electrical field. This includes staying at least six inches from cell phones.
- When going through security screening stations at airports, courthouses or any place that requires security screening, use the backscatter screener or get a hand check. Don’t allow the technicians to use the hand held wands. If you must go through the scanning stations it will likely indicate that you have metal, but it will not harm the pacemaker. Tell security screeners that you have a pacemaker. Always carry a card that states the type of pacemaker you have.
- Tell all of your doctors, your dentist and other healthcare providers that you have a pacemaker. Some medical procedures, such as magnetic resonance imaging , can interfere with pacemakers. However, provision for an MRI can often be made.
How Blood Flows Through The Heart
The heart consists of two upper chambers, atria, and two lower chambers, ventricles. Blood flows into the atria through veins.
The atria then contract to move the remainder of the blood into the ventricles. Once the ventricles are completely full the atrioventricular valves close. These valves are tissue flaps found between atrial and ventricular chambers.
The sound of these valves snapping shut is the lub sound that a doctor hears through a stethoscope. Once the ventricles are full of blood they then contract to force blood up and out into arteries that leave the heart.
Once all the blood has entered the arteries a second set of valves, the semilunar valves between the arteries and ventricles, snap shut. This is the second sound, the dub sound that a doctor hears.
It is very important that the heart muscle of the various chambers contract at the correct time in order for the heart to work efficiently and to ensure that the cardiac output is what it should be.
In order for the heart to contract correctly, the nerve impulses have to pass along a particular pathway. If people have problems with the cardiac nerve conduction pathways then they are vulnerable and may have arrhythmias or in the extreme case, sudden death.
Recommended Reading: Acid Reflux Heart Fluttering
What Happen If I Have Heart Block
Normally, electrical signals travel from the upper chambers of your heart to the lower chambers . The AV node is a cluster of cells that connect the electrical activity like a bridge from the top chambers of your heart to the bottom chambers. If you have heart block, the electrical signal does not travel through the AV node to the ventricles. The result is a heart that doesnt function effectively, meaning your heart beats slowly or skips beats and it cant pump blood through its chambers and out to the body as a normal heart would.
Therapeutic Use And Rationale
The ultimate goal of antiarrhythmic drug therapy is to restore normal rhythm and conduction. When it is not possible to revert to normal sinus rhythm, drugs may be used to prevent more serious and possibly lethal arrhythmias from occurring. Antiarrhythmic drugs are used to:
- alter the excitability of cardiac cells by changing the duration of the effective refractory period
- suppress abnormal automaticity
Because sympathetic activity can precipitate arrhythmias, drugs that block beta1-adrenoceptors are used to inhibit sympathetic effects on the heart. Because beta-adrenoceptors are coupled to ion channels through defined signal transduction pathways, beta-blockers indirectly alter membrane ion conductance, particularly calcium and potassium conductance.
In the case of AV block, drugs that block vagal influences are sometimes used. AV block can occur during beta-blocker treatment and therefore simply removing a beta-blocker in patients being treated with such drugs may normalize AV conduction.
Read Also: How To Calculate Resting Heart Rate
Can Heart Block Be Prevented
Some cases of heart block may be congenital . But most heart block develops after birth. Some causes cant be prevented. We also know that the risk of heart block increases with age and so does heart disease. Some causes of heart disease are preventable.
Steps you can take to keep your heart and body as healthy as possible include:
- Lead a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a heart healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting an adequate amount of sleep each night, reducing stress, limiting alcohol and stopping smoking and use of illicit drugs.
- Talk with your healthcare provider about reviewing medications and other supplements you are taking to determine if any change the normal levels of potassium, calcium and magnesium substances in your body that play a role with your hearts electrical system. Your provider can change your medication to a different drug class if needed.
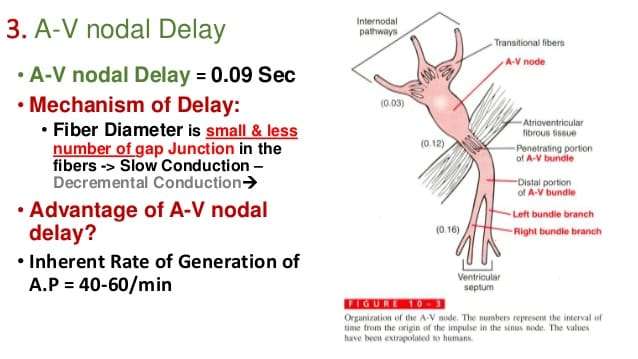
First And Second Degree Atrioventricular Block
-
Delays of impulse conduction at the atrioventricular node are classified as first, second, and third degree AV block. Second degree AV block is the most common physiological arrhythmia in horses. Third degree AV block is considered pathological and will be discussed below.
-
First-degree AV block occurs when the PQ interval exceeds the upper normal limit while the atrial impulse still transmits through the AV conduction system and activates the ventricle, causing a normal QRS-T complex on the ECG.
-
Diagnosis of first-degree AV block is difficult by auscultation, although a prolongation of the interval between the fourth and first heart sound may be heard.
-
During second-degree AV block, some P waves are not conducted to the ventricles, resulting in occasional P waves not followed by a QRS-T complex on the ECG. The underlying rhythm is usually a normal sinus rhythm .
-
Auscultatory findings include a regular underlying rhythm with intermittent pauses during which the fourth heart sound may be audible.
Colin C. Schwarzwald, … William W. Muir, in, 2009
Read Also: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Problems With The Conduction System
A person who has difficulties with how the nerve conduction system works can experience issues such as heart arrhythmias or even, in some cases, sudden death.
If a problem with the pacemaker is diagnosed, a person can be treated by having an artificial pacemaker implanted under the skin. This can help to ensure that the heart does contract normally.
Atrioventricular block is when there is a problem with conduction between the SA node and the AV node. There are also cases where an extra electrical pathway is present, such as in Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome.
However, there may often be no symptoms at all and a person who appears perfectly healthy may suddenly drop dead.
Scientists have found that lethal arrhythmias are more likely to occur if the problems in conduction are related to the AV bundle and Purkinje fibers.
What Happens After The Pacemaker Is Implanted
Hospital stay: After the pacemaker implant, you will be admitted to the hospital overnight. The nurses will monitor your heart rate and rhythm. You will also have a monitor . It will record your heart rhythm while you are in the hospital. This is another way to check proper pacemaker function. The morning after your implant, you will have a chest X-ray to check your lungs and the position of your pacemaker and leads. Your pacemaker will be checked to make sure it’s working properly. The results of the test will be reported to your doctor.
Final pacemaker check: For your final pacemaker check, aà small machine known as a programmer is used to check your pacemaker. It has a wand that is placed directly over the device. This machine allows the technician to read your pacemaker settings and make changes during testing. With these changes, the function of the pacemaker and leads can be evaluated. You may feel your heart beating faster or slower. This is normal; however, report all symptoms to the technician. Results of the pacemaker check are discussed with your doctor who will then determine your pacemaker settings.
You May Like: Can Too Much Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
How Do I Care For My Wound
Keep the area where the pacemaker was inserted clean and dry. After about five days, you may take a shower. Look at your wound daily to make sure it is healing. Call your doctor if you notice:
- Increased drainage or bleeding from the insertion site
- Increased opening of the incision
- Redness around the incision site
- Warmth along the incision
- Increased body temperature
When Can I Do Normal Activities After A Pacemaker Implantation
After your pacemaker is implanted, you may move your arm normally and do not have to restrict its motion during normal daily activities. Avoid extreme pulling or lifting motions . Activities such as golf, tennis, and swimming should be avoided for six weeks after the pacemaker is implanted. Microwave ovens, electric blankets, and heating pads may be used. Cellular phones should be used on the side opposite your pacemaker. Ask your doctor or nurse for more specific information regarding types of equipment that may interfere with your pacemaker.
Pacemaker Identification: You will receive a temporary ID card that tells you what type of pacemaker and leads you have, the date of implant and the doctor who implanted it. In about three months following implantation, you will receive a permanent card from the company. It is important that you CARRY THIS CARD AT ALL TIMES in case you need medical attention at another hospital.
Recommended Reading: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How Fast Does The Normal Heart Beat
How fast the heart beats depends on the body’s need for oxygen-rich blood. At rest, the SA node causes your heart to beat about 50 to 100 times each minute. During activity or excitement, your body needs more oxygen-rich blood; the heart rate rises to well over 100 beats per minute.
Medications and some medical conditions may affect how fast your heart-rate is at rest and with exercise.
How Do I Prepare For A Biventricular Pacemaker Implant
Ask your doctor what medications you are allowed to take before your pacemaker is implanted. Your doctor may ask you to stop certain drugs several days before your procedure. If you have diabetes, ask your doctor how you should adjust your diabetic medications.
Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before the procedure. If you must take medications, drink only small sips of water to help you swallow your pills.
When you come to the hospital, wear comfortable clothes. You will change into a hospital gown for the procedure. Leave all jewelry and valuables at home.
Read Also: What Branch Of Medicine Deals With Heart Disease
How Is Heart Block Treated
Your cardiologist will determine how heart block is affecting your hearts ability to function and consider your symptoms to determine how to manage your condition. Symptoms and treatment vary from person to person.
Sometimes, making changes to medications or treatment for heart disease stops heart block.
- First-degree block: If you have first-degree heart block, you probably wont need treatment.
- Second-degree block: If you have second-degree heart block and have symptoms, you may need a pacemaker to keep your heart beating like it should. A pacemaker is small device that sends electrical pulses impulses to your heart.
- Third-degree block: Third degree heart block is often first discovered during an emergency situation. Treatment almost always includes a pacemaker.
If you need a pacemaker, your cardiologist/electrophysiologist will talk to you about the details, the type that is best for you, and what to expect before, during and after you get your pacemaker.
