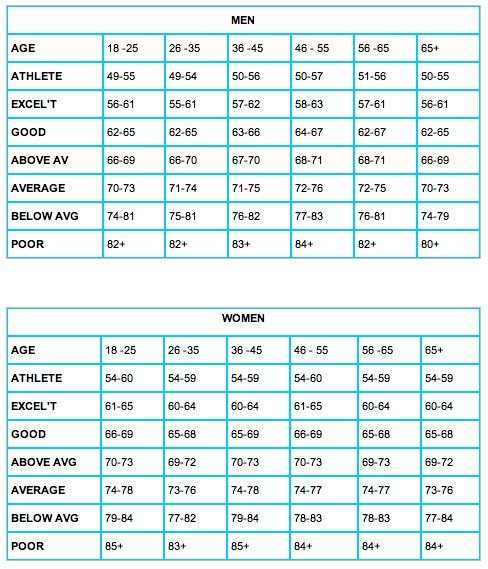
Know Your Numbers: Maximum And Target Heart Rate By Age
This table shows target heart rate zones for different ages. Your maximum heart rate is about 220 minus your age.3
In the age category closest to yours, read across to find your target heart rates. Target heart rate during moderate intensity activities is about 50-70% of maximum heart rate, while during vigorous physical activity its about 70-85% of maximum.
The figures are averages, so use them as a general guide.
Normal Resting Heart Rate
The heart rate measures how many times the heart beats in 60 seconds.
It is important to identify whether your heart rate sits within the normal range. If disease or injury weakens the heart, the organs will not receive enough blood to function normally.
The United States National Institutes of Health have published a list of normal resting heart rates.
The heart rate gets progressively slower as a person moves through childhood toward adolescence.
The normal resting heart rate for adults over the age of 10 years, including older adults, is between 60 and 100 beats per minute .
Highly trained athletes may have a resting heart rate below 60 bpm, sometimes reaching 40 bpm.
The following is a table of normal resting heart rates at different ages according to the NIH:
| Age | |
| Over 10 years | 60 to 100 |
The resting heart rate can vary within this normal range. It will increase in response to a variety of changes, including exercise, body temperature, emotional triggers, and body position, such as for a short while after standing up quickly.
How To Take Your Pulse
Count your pulse: _____ beats in 10 seconds x 6 = _____ beats/minute
Recommended Reading: What Causes Your Heart Rate To Drop
Meditation And A Relaxation Technique To Lower Blood Pressure
Several practices that help calm the mind can also lower blood pressure. All are types of meditation, which use different methods to reach a state sometimes described as “thoughtful awareness” or “restful alertness.”
But while researchers are now beginning to better understand how these mental changes affect the cardiovascular system, studying meditation has proved somewhat challenging. For one thing, some studies don’t include a good control treatment to compare with meditation. Second, the people most likely to volunteer for a meditation study are often already sold on meditation’s benefits and so are more likely to report positive effects.
Still, a number of well-designed studies show that meditation can modestly lower blood pressure, according to an American Heart Association scientific statement published in the journal Hypertension.
A related technique, designed to evoke the so-called relaxation response, was developed by Dr. Herbert Benson, director emeritus of the Harvard-affiliated Benson-Henry Institute for Mind Body Medicine. The relaxation response is the opposite of the stress-induced fight-or-flight response. This self-induced quieting of brain activity has aspects of both transcendental meditation and mindfulness meditation.
Dr. Benson recommends practicing the relaxation response twice a day, for 10 to 20 minutes, similar to what other meditation experts recommend. Here’s how to do it.
High Blood Pressure Vs High Heart Rate
Some individuals confuse high blood pressure with a high heart rate. Blood pressure is the measurement of the force of the blood against the walls of arteries, while pulse rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute.
There is no direct connection in between the two, and high blood pressure does not always lead to a high pulse rate, and vice versa. Heart rate goes up during laborious activity, however a vigorous workout may just modestly enhance high blood pressure.
Also Check: How Long Can Heart Attack Last
Medical Tests For Heart Disease
Your doctor will check your blood pressure and do a fasting blood test to check your cholesterol, a type of fatty substance that can contribute to plaques in your arteries. He or she might also do a blood test to check the levels of proteins that are markers of inflammation in the body and suggest you have an electrocardiogram . This test looks at electrical activity in your heart. A chest x-ray will show whether your heart is enlarged or your lungs have fluid in them; both can be signs of heart failure. The doctor might do a blood test for brain natriuretic peptide , a hormone that increases in heart failure. If the cardiologist needs to determine your heart or valve function, he or she may order an echocardiogram, a painless test which uses sound waves to produce images of your heart in motion.
To learn more about heart disease, visit the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Target Heart Rates Chart
What should your heart rate be when working out, and how can you keep track of it? Our simple chart will help keep you in the target training zone, whether you want to lose weight or just maximize your workout. Find out what normal resting and maximum heart rates are for your age and how exercise intensity and other factors affect heart rate.
Recommended Reading: How Do Nsaids Cause Heart Attacks And Strokes
How To Calculate Your Maximum Heart Rate
It’s safe to say that getting older affects your max heart rate, which is the;highest heart rate you can safely hit during exercise. But how do you calculate your maximum heart rate and try to exercise at the right intensity? This is where heart rate zone monitoring comes into play. The general formula to calculate your maximum heart rate is to take 220 and minus your age. Then you’ll have to create your three target heart rate zones based off of that number:
These zones basically help explain how two people can do the same intensity workout at different heart rates and feel the same amount of effort in place. To put it in perspective: a 20 year old can reach a maximum bpm of 200 at 100%, while a 70 year old can only hit a threshold of 150 bpm. How’s that for the effects of heart rate and age?
Share;with us your take on heart rate and age by tagging us on Instagram;;and Facebook;.;Also, be sure to check out our new articles published daily!
-Gina
How To Check Your Heart Rate
You can check your heart rate by counting the pulse. A pulse can be felt at various sites on the body like over the sides of the neck, the wrist, and the top of the foot. To check your pulse on the wrist with the help of your middle finger and index finger, you need to:
- Keep your middle finger and your index finger over the inner part of the wrist and keep pressing gently until you can feel your pulse. The pulse is felt in your radial artery.
- After you have located your pulse, look at the watch, and start counting the beats for 30 seconds. Doubling this count will give you your heart rate. You can even count the beats for 10 seconds and multiply the number by six to get your heart rate.
If you find the rhythm of your heartbeat slightly irregular, you will have to count the beats completely until 60 seconds. You will have to visit your doctor if you keep getting a fast and irregular heart rate consistently.
Also Check: How Long Does End Stage Heart Failure Last
If You Slow Your Resting Heart Rate Can You Slow Down Aging
Having a lower resting heart rate is associated with having a longer lifespan.
Athletes generally have a lower resting heart rate due to their physical fitness.
One study found that the more physically fit you are, the lower the resting pulse. The same study found that even controlling for physical fitness, people with a higher resting heart rate had a shorter life expectancy compared to those with a lower resting heart rate.
So a high resting heart rate is not just a marker of risk, but a risk factor for premature death. The difference between a risk marker and a risk factor is that if you can control the risk factor, you can control the risk.
Why Is A High Resting Heart Rate Dangerous?
If your heart is beating fast 24 hours a day, all that circulatory stress can damage; the elastic fibers supporting your arterial walls causing them to become stiff. Your arteries do not have enough time to relax between beats.
Signs Of Heart Disease
Early heart disease often doesn’t have symptoms or the symptoms may be barely noticeable. That’s why regular checkups with your doctor are important.
Contact your doctor right away if you feel any chest pain, pressure, or discomfort. However, chest pain is a less common sign of heart disease as it progresses, so be aware of other symptoms. Tell your doctor if you have:
- Pain, numbness, and/or tingling in the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath when active, at rest, or while lying flat
- Chest pain during physical activity that gets better when you rest
- Lightheadedness
- Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, stomach, and/or neck
- Reduced ability to exercise or be physically active
- Problems doing your normal activities
Problems with arrhythmia are much more common in older adults than younger people. Arrhythmia needs to be treated. See a doctor if you feel a fluttering in your chest or have the feeling that your heart is skipping a beat or beating too hard, especially if you are weaker than usual, dizzy, tired, or get short of breath when active.
If you have any signs of heart disease, your doctor may send you to a cardiologist, a doctor who specializes in the heart.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of A Heart Attack For Women
What Is Resting Heart Rate
Your resting heart rate is how many times your heart beats in one minute while youre at rest. Its both a gauge of your heart health and a biomarker of aging.
RHR changes as you age and varies from person to person. Its important to know your RHR as it can help you assess your heart health over time. Being aware of changes in your RHR can help you uncover a heart condition early.
Resting Heart Rate Versus HRV and Blood Pressure
Resting heart rate, heart rate variability, and blood pressure are all important measures of heart health.
- Resting heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute.
- Heart rate variability is a measure of the variation in the time between consecutive heartbeats.
- Blood pressure is the force of blood flowing through your blood vessels .
What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate
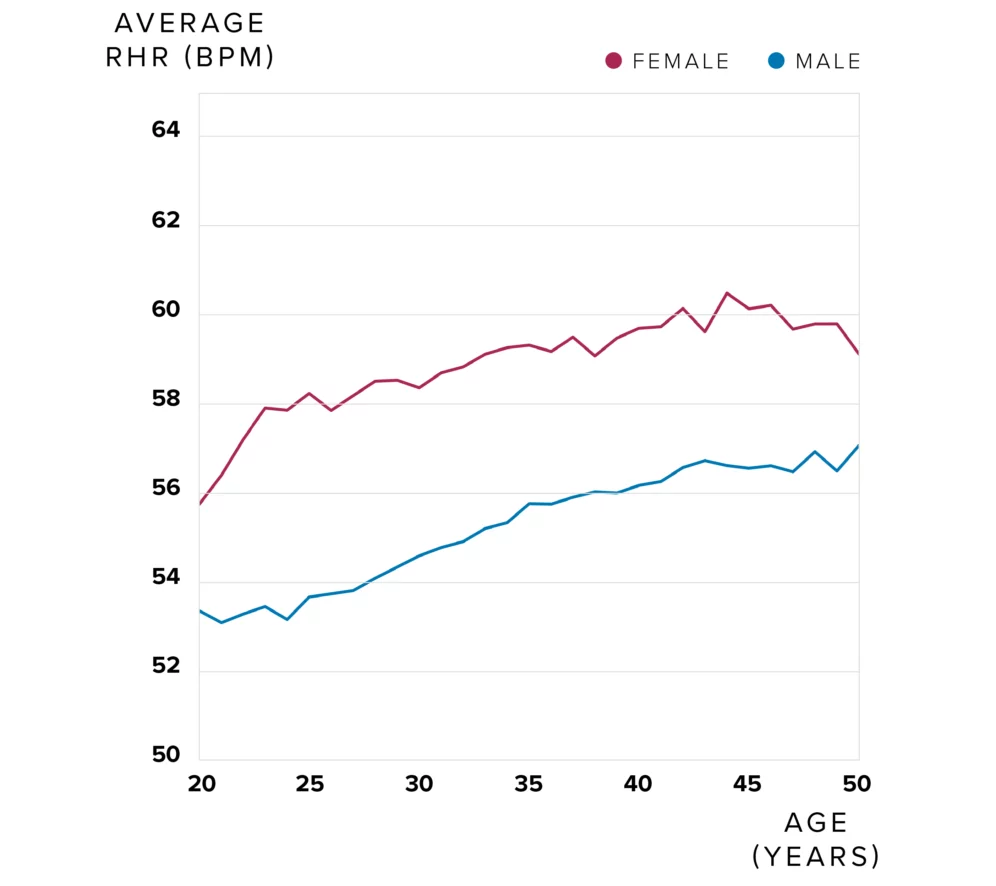
A normal resting heart rate for adults is between 60 beats per minute and 100 bpm. An abnormal pulse rate below 60 bpm or above 100 bpm could increase your risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, or early death.
Normal Resting Heart Rate for Women
The normal resting heart rate for adult women is similar for men, between 60 bpm and 100 bpm. Age and activity level are more important factors for heart rate.
Studies show that having high resting heart rate increases your risk even after controlling for other factors such as physical fitness, blood pressure, and lipid levels.
Is a resting heart rate of 80 bad? A bpm of 80 is still within the normal range, but over 90 can be dangerous.
For example:
One study tested the resting heart rate of about 3,000 men over 16 years. The study found that, after accounting for other risk factors, men with a resting heart rate over 90 bpm were three times more likely to die than the men with the lowest RHR.
Further, an increase in heart rate over time is associated with an increased risk of death from heart disease and all-cause mortality.
;
Is A Low Resting Heart Rate Good Or Dangerous?
At the other extreme, one study found that having a low resting heart rate is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in athletes.
Having a heart rate below 60 bpm doesnt mean that youre not healthy. For example, a low RHR could be the result of taking a drug such as a beta-blocker. Moreover, athletes generally have lower heart rates.
Also Check: Is 190 Heart Rate Bad
Why Its Lower For Endurance Runners
In most cases, a low resting heart rate is synonymous with a healthy athlete. This is why there is often no need to panic if you have a resting heart rate lower than what is considered an average value between 60100 bpm. In fact, Richard Diaz, founder of Diaz Human Performance, says a well-trained athlete may even see resting heart rate values as low as 40 bpm.
In most cases, this is an indication of cardiac efficiency, he continues. Cardiac output relates to how many beats per minute X stroke volume . The more blood youre able to deliver per stroke lessens work the heart needs to do to satisfy the demand, whatever it might be.
Because of the efficiency of the heart in many endurance athletes, the heart has less work to do to pump blood through the body . Of course, resting heart rate is not just determined by fitness level; genetics have even been noted;to play a role. As mentioned above, there is often no need to panic if you have a low resting heart rate . Pyron notes that, at rest, a runners heart is so efficient it doesnt need to beat often, but there is a downside to this.
There is an association of very high-level endurance athletes with developing heart arrythmias, she notes. The heart mechanisms in place to control the normal rhythm are somewhat overridden by adaptations to exercise. This, however, happens mostly in the professional-level athlete, so the vast majority of athletes do not have this concern.
What Is A Healthy Heart Rate What Is Optimal
An optimal heart rate about one beat per second; at rest, or . Consequently, for every 10 beats per minute increase, theres a 10 to 20% increased risk of premature death.
Theres strong evidence showing that everyone with a high heart rate is at risk , even otherwise healthy individuals. But there are ways that you can slow your heart rate naturally.
First, check your resting heart rate before you make any changes using the method in section 2. This reading will be your baseline number to track your progress and test which programs work for you. Secondly, record your heart rate after any changes you make.
Recommended Reading: How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
How Age And Exercise Affect Your Max Heart Rate
The relationship between the heart and exercise has been studied for more than six decades and the research is clear: Max heart ratethe highest heart rate you can safely hit during exercisedecreases with age regardless of lifestyle or level of fitness.
Why the drop? The reasons arent completely known, but a 2013 University of Colorado Medical School study found that one reason could be slower electrical activity in the hearts pacemaker cells. Basically, your heart cant beat as often, says Roy Benson, running coach and co-author of Heart Rate Training.However, a lower max heart rate may not necessarily affect your splits. Its not a foregone conclusion that a decrease in heart rate max means a decline in performance, says Joe Friel, coach and author of Fast After 50 and The Triathletes Training Bible. Thats a very common but unsupported view of athletes who are ill informed about the science behind heart rate. They assume a high heart rate means a high level of performance. Not true.
Maximum Heart Rate For People Older Than 50
The formula for maximum heart rate works well for people under 40 but for older people it may overestimate their maximum heart rate, Bauman said. For older people, a much better formula for the optimal heart rate is:
208
- You can either manually compute your heart rate during exercise or use heart rate displays that wrap around the chest, or are consisted of in sports watches.
- Nevertheless, thats not to say that working out without getting the heart rate up to the target zone has no advantage, Bauman said.
So many individuals just arent doing any workout that I worry less about them reaching their target heart rate and more about them getting out and moving their body, Bauman said.
Reducing a fast heart rate.
Pulse rates can spike due to anxiety, stress, dehydration and overexertion. Taking a seat and taking sluggish, deep breaths can normally decrease your heart rate. Working out and getting trimmer will usually reduce heart rate, too.
Recommended Reading: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Baseline Characteristics In 1993
Participants in the higher RHR subgroups were more likely to be current smokers, had more often a sedentary lifestyle and mental stress, higher BMI, wider waist circumference, higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure and were more likely to have a medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidaemia and diabetes than participants in the lower RHR subgroup . Baseline characteristics according to different groups of RHR change are presented in .
