What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is a severe progressive condition that affects the pumping power of heart muscles. Because of decreased cardiac output, the organs get inadequate blood, oxygen, and nutrients. Congestive heart failure usually affects the lungs, heart, and kidneys. A decrease in cardiac output causes kidneys to retain water and salt. Because of the increased water retention, other organs get congested, leading to increased pressure on the heart.
What Causes Pediatric Congenital Heart Defects
In most cases, the reasons defects happen are not known, but some connections have been identified:
- Women who get German measles during their first trimester of pregnancy have a higher risk of having a baby with a congenital heart defect.
- The risk may also be higher if the woman has some types of viral infections, is exposed to industrial solvents, takes certain kinds of medications, drinks alcohol, or uses cocaine while pregnant.
- Women who have given birth to a child with a congenital heart defect are at higher risk of giving birth to another child with a heart defect.
Heart defects can also occur along with other types of birth defects.
Stage A Treatment Options
Treatment options in stage A mainly focus on promoting your overall health and disease prevention. If you meet the stage A criteria, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to slow or stop disease progression.
Heart Failure Doctor Discussion Guide
You May Like: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and, in part, what caused it. Medications and lifestyle behaviors are part of every treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment is the same, regardless of gender.
As heart failure gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. Since you cant move backward through the heart failure stages, the goal of treatment is to keep you from moving forward through the stages or to slow down the progression of your heart failure.
Stage A treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage A heart failure includes:
- Regular exercise, being active, walking every day.
- Stopping the use of tobacco products.
- Treatment for high blood pressure .
- Treatment for high cholesterol.
- Not drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker if you have coronary artery disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
- Beta-blocker if you have high blood pressure.
Stage B treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage B heart failure includes:
Stage C treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage C HF-rEF includes:
If the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression to Stage D.
Stage D treatment
What Are The Symptoms Of Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Often, there are no symptoms associated with these defects. The defects are usually found during routine physical examinations. In cases where there are symptoms, they may include:
- Trouble breathing.
- Bluish tones to the skin .
- Poor eating habits.
- Swelling in the abdomen or around the eyes.
- Rapid heartbeat.
Also Check: What Causes Congestive Heart Failure
Advanced Cardiology What Are The 4 Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure, or CHF, is a heart condition that impacts millions of Americans. CHF means that the heart cannot pump sufficient blood to the rest of the body. Its essential to be proactive about your heart health, and that starts with education. This article will explain the four stages of congestive heart failure, the risk factors and signs of CHF, and the treatment options available to manage the condition.
Stages Of Heart Failure
When you’re diagnosed with heart failure, your doctor will usually be able to tell you what stage it is.
The stage describes how severe your heart failure is.
It’s usually given as a class from 1 to 4, with 1 being the least severe and 4 being the most severe:
- class 1 you don’t have any symptoms during normal physical activity
- class 2 you’re comfortable at rest, but normal physical activity triggers symptoms
- class 3 you’re comfortable at rest, but minor physical activity triggers symptoms
- class 4 you’re unable to carry out any physical activity without discomfort and may have symptoms even when resting
Knowing the stage of your heart failure will help your doctors decide which treatments they think are best for you.
Page last reviewed: 19 May 2022 Next review due: 19 May 2025
Also Check: Why Is It Important To Know Your Target Heart Rate
What Medications Treat Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary vasodilators are medications that treat PAH and CTEPH. They cant be used for other types of PH, including those caused by underlying heart or lung issues.
Pulmonary vasodilators help your pulmonary arteries relax. This lowers blood pressure and eases the load on the right side of your heart.
People with PH may take a variety of other medications based on their underlying conditions.
What Is The Treatment For Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension treatment depends on the type of PH you have and your other medical conditions. Your healthcare team will tailor treatment to your individual needs.
Right now, only two types of PH can be treated directly:
- Pulmonary artery hypertension .
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension .
Treatment for other types of PH involves managing the underlying medical conditions.
Treatment for pulmonary arterial hypertension includes:
- Calcium channel blockers. These medications can help lower the blood pressure in your pulmonary arteries and throughout your body.
- Diuretics. These water pills help your body clear out extra fluid.
- Oxygen therapy. You may need this treatment if you dont have enough oxygen in your blood.
- Pulmonary vasodilators. These medications help your pulmonary arteries relax and open up better. This improves blood flow and lowers the strain on your heart.
Treatment for CTEPH includes:
Treatment for PH caused by heart or lung problems focuses on managing the underlying conditions. Because so many different heart and lung conditions cause PH, treatment plans can be vastly different from person to person. Talk with your provider about whats best for you. In general, your provider may recommend:
- Dietary changes.
- Medication to manage problems like hypertension or heart failure.
- Oxygen therapy.
- Surgery, such as heart valve repair.
A last resort option for some people with severe pulmonary hypertension is a lung transplant.
Read Also: Early Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
What Are Heart Failure Treatments By Stage
Now for the good news: You can definitely make changes to both prevent heart failure and to keep it from progressing to advanced stages. The power is in your hands.
The habits you develop now will affect your heart 10, 20, or 30 years down the road, Dr. Shufelt says. Such habits include getting regular exercise, eating a Mediterranean-style diet, not smoking, and not being around people who smoke.
Your doctor will consider your heart failure stage or your personal riskslike having diabetes or smokingto make treatment recommendations. If you know youre in a certain stage, talk to your doctor about making the changes that make the most sense for you.
Its important to note that treatment guidelines are based on the ACC/AHA stages, as the NYHA system does not provide this information.4
Heres where youve really got to take a look at the lifestyle factors that could hurt your heart. According to Penn Medicine, this means:
- Stop smoking if you smoke.
- Engage in regular exerciseideally 150 minutes per week.
- Stop illegal drug use if you use drugs.
- Stop drinking or limit your alcohol intake to no more than two drinks a day for people with penises or one drink a day for people with vaginas.
- Seek treatments for high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- Take stock of other lifestyle behaviors and try to eat a balanced diet, get restful sleep, and manage everyday stress.
What Is Heart Failure
Heart failure, or congestive heart failure, is a long-term condition that gets worse over time. Although the name sounds like your heart has stopped working, heart failure means your heart isnt able to pump blood as well as it should. When your heart has less pumping power, that can damage your organs and fluid can collect in your lungs.
Recommended Reading: Stroke And Heart Attack
Other Causes Of Heart Failure Include:
- abnormal heart rhythms where your heart beats too fast, too slow or irregularly
- amyloidosis – a build-up of abnormal proteins in organs such as your heart and tissues. When it affects the heart it’s called cardiac amyloidosis – stiff heart syndrome – and can lead to heart failure
- anaemia a lack of red blood cells carrying oxygen in your blood
- congenital heart conditions different heart problems that youre born with
- endocarditis – a viral infection affecting the heart muscle
- heart valve disease – where blood struggles to flow through the heart properly, putting extra strain on the muscle
- pulmonary hypertension – raised blood pressure in the blood vessels that supply your lungs. This condition can damage the right side of your heart, leading to heart failure. Find out more about pulmonary hypertension on NHS Choices and PHA UK
- some cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy
- thyroid gland disease an underactive or overactive thyroid gland which produces too few or too many hormones
- too much alcohol .
How Do Doctors Diagnose Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is diagnosed with a physical exam and tests that may include:
- Electrocardiogram to measure the electrical activity in the heart
- Brain natriuretic peptide or N-terminal pro-BNP blood tests
- BNP or NT-proBNP level is high in people with heart failure
You May Like: Dog With Heart Failure
Neonatal Rat Ventricular Myocyte Hypertrophy
The protocol was as previously described . After isolation, NRVMs were plated in a six-well multi-well dish, transfected for 72 h with AAV6, and stimulated as indicated . NRVMs were then fixed in 3% PFA for 10 min, washed three times with ice cold PBS, and permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100. The cells were then incubated with 1% BSA for 30 min and incubated overnight at 4 °C with anti–sarcomeric actinin diluted 1:200 in 1% BSA. After washes, cells were incubated with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody anti-mouse . Cells were examined with a Nikon Eclipse Ni microscope, and images were acquired with a Nikon digital camera. For each sample, five to six fields were acquired.
Prognosis At Different Ages
In general, younger people diagnosed with CHF tend to have a better outlook than older people.
A report averaging several smaller studies found that people under age 65 generally had a 5-year survival rate of 78.8 percent following CHF diagnosis. The same report found that people over age 75 had an average 5-year survival rate of 49.5 percent following diagnosis.
Older people diagnosed with CHF may already have other chronic health conditions. This can make it difficult to manage CHF and create a more challenging outlook for them.
for congestive heart failure. The treatment thats best for you will depend on:
- your overall health
- any other health conditions you have
- how you respond to any medications
- what stage of CHF you have
Common options include:
There are lifestyle changes a person with CHF can make that have been shown to help slow the conditions progression. Talk with your doctor before making changes to your diet or starting an exercise routine.
You May Like: Cats With Congestive Heart Failure
How Common Is Pulmonary Hypertension
Some types of PH are rare, such as pulmonary arterial hypertension and PH caused by blood clots. But other types are much more common, especially PH caused by heart or lung problems.
We dont know exactly how many people around the world have pulmonary hypertension. But some estimates show PH may affect 1 in 100 people. This means 50 million to 70 million people are living with PH.
PH is even more common among older adults. Around the world, about 1 in 10 adults over age 65 have PH.
Researchers believe the number of people diagnosed with PH will rise in the next few decades.
Stage C Treatment Options
Treatment at this stage focuses on managing your symptoms, optimizing your heart function, and preventing worsening of your condition.
Medications to treat stage C heart failure include:
- Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
- Beta blockers to help make your heart work less hard
- SGLT2 inhibitors to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Entresto , which reduces the risk of death and hospitalization among patients with chronic heart failure
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Digoxin to help the heart beat stronger and more regularly
- Possible cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Possible implantable cardiac defibrillator therapy
In addition to the lifestyle changes for stages A and B, you may need to make the following changes:
- Reduce your sodium intake
- Restrict fluid intake
- Keep track of your weight daily
Remember that even if the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression of your condition to stage D.
Don’t Miss: Why Do I Keep Getting Heart Palpitations
How Palliative And Hospice Care Can Help With End
Both palliative and hospice care focus on the whole person, including their physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs. The main difference is that palliative care can be given at any time during a serious illness, and hospice care is given near the end of life typically when a persons prognosis is six months or less.
Palliative and hospice care can also provide help with making difficult treatment decisions, such as whether to be resuscitated if the persons heart stops, or whether to have a tube placed in their throat to help them breathe.
Similarly, people with end-stage heart failure may need to decide when to disable certain medical devices implanted in their body:
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator . Patients can have the shock function turned off, or not replace the battery when the current one runs out. Electrical shocks from ICDs can cause unnecessary distress for patients and loved ones at the end of life.
- Left ventricular assist device . Typically, the patient decides when this heart pump will be shut off before it is implanted. The decision can be discussed again as the end of life nears.
What Is Shared Decision
When heart failure progresses to an advanced stage, there are still many treatment options. The decisions ranging from do everything possible to strive for comfort arent easy. Thats why the American Heart Association released recommendations that serve as a roadmap to decision-making in advanced heart failure.
The goal? A partnership between you and your doctor, where medical options are honestly discussed, and decisions are made based on what you want. Shared decision-making means you dont have to make decisions on your own.
Doctor-patient conversations about treatment options, their risks and benefits as well as future what-if scenarios should happen early and often, according to experts who helped draft the AHA recommendations. This early dialogue means youre not blindsided when a big medical event happens that requires tough decision-making.
Doctors provide the medical facts and figures, while you provide your personal goals and preferences. Together and often with input from family and friends you and your doctor build a care plan.
Read Also: Congestive Heart Failure And Erectile Dysfunction
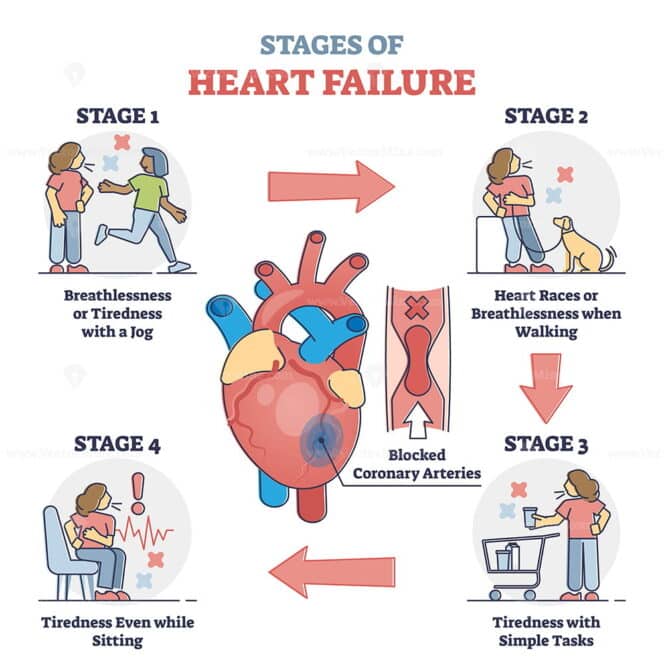
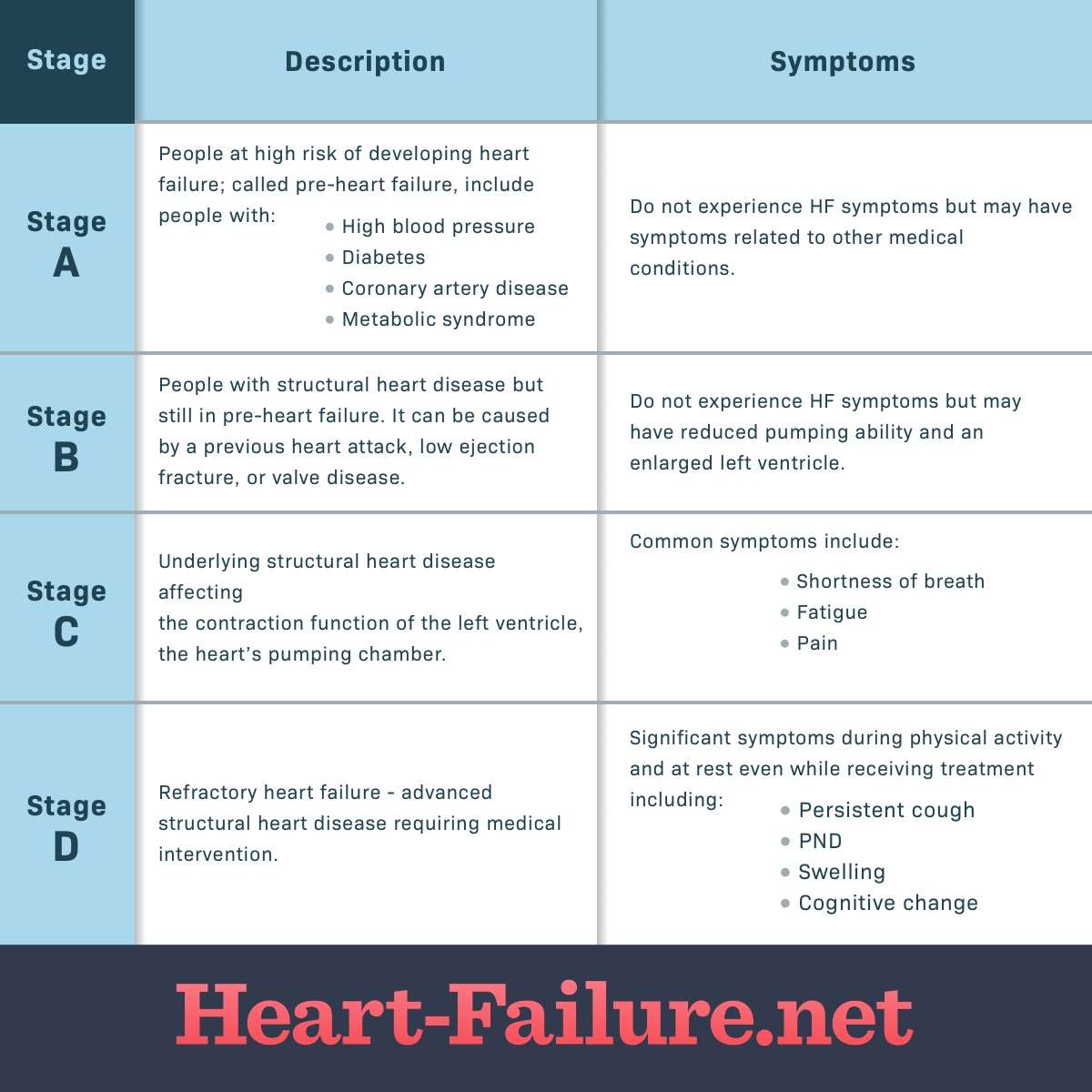
What Are The 4 Stages Of Heart Failure
There are four stages of heart failure – stage A, B, C and D – which range from high risk of developing heart failure to advanced heart failure.
The four stages of heart failure are different to the four classes of heart failure symptoms also described in New York Heart Association , which illustrates the severity of symptoms, ranging from class one to the most severe, which is class four .
American College Of Cardiology/american Heart Association Classification
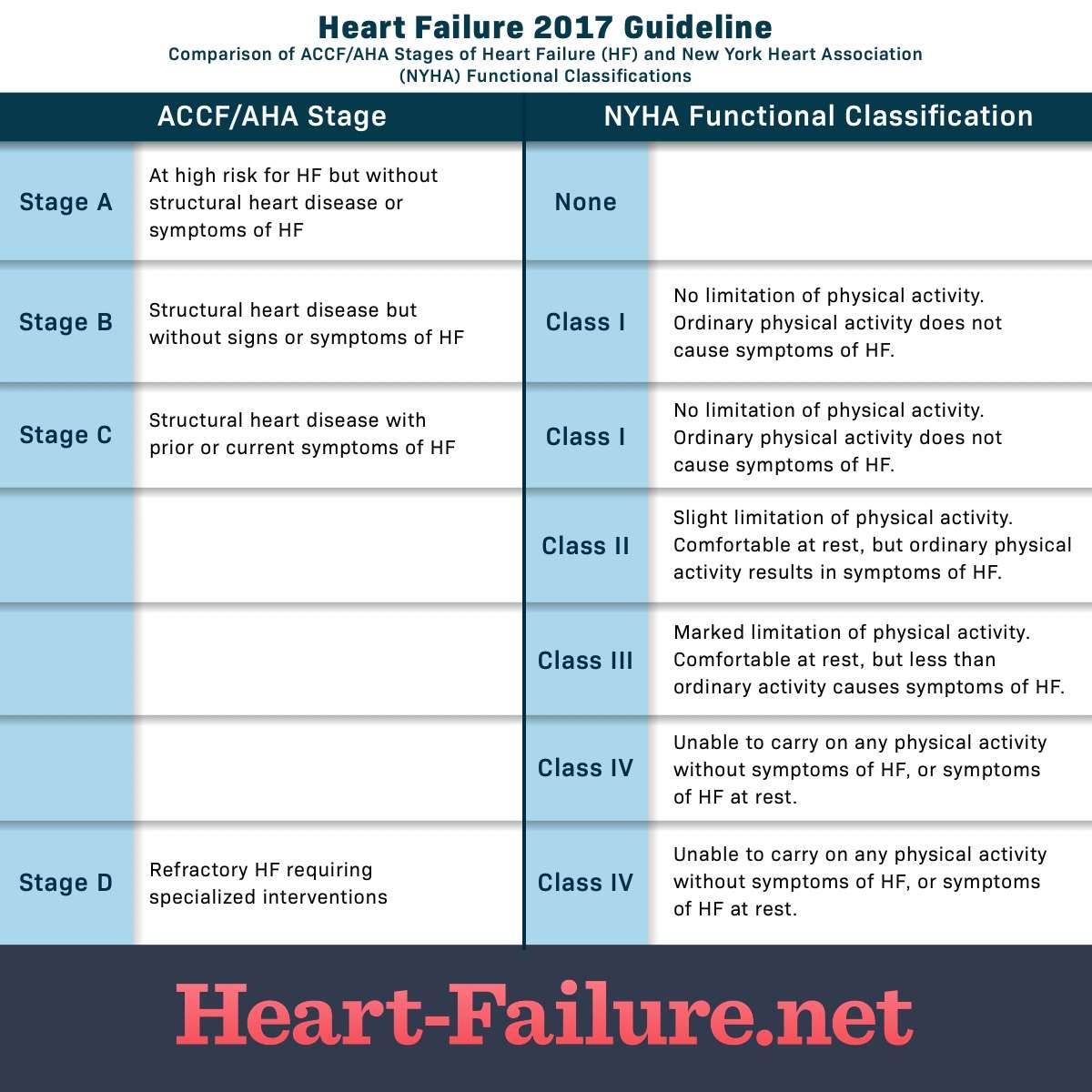
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association classification of heart failure stages focus more on the condition’s structural impact on the heart, such as the measurement of ejection fraction:
- Stage A: You do not have any structural disorder of the heart, but are at high risk for developing congestive heart failure due to a family history of heart failure or a personal history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, alcohol abuse, viral infections, or use of drugs that are toxic to the heart.
- Stage B: You have a structural disorder of the heart, but no symptoms of heart failure .
- Stage C: You have a structural disorder of the heart and you have currently or previously displayed symptoms of heart failure.
- Stage D: People in this final stage of heart failure do not get better with treatment.
Read Also: How Long Does Heart Surgery Take
