How To Check Your Pulse And Heart Rate
Exercise is an important part of cancer prevention. You need 150minutes of moderate physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorousexercise each week to help lower your cancer risk. Your heart rate canhelp you determine if the exercise youre doing is moderate orvigorous.
If youre working at 50 to 70% of your maximum heart rate, then thatexercise is considered moderate. If youre working at 70 to 85% ofyour heart rate then its vigorous exercise.
How Are Arrhythmias Treated
Many arrhythmias don’t need treatment. For those that do, these options might be used:
- Medicines. Many types of prescription anti-arrhythmic medicines are available to treat arrhythmia. Sometimes, these can increase symptoms and cause side effects, so the patient will be closely watched by the doctor.
- Pacemakers. A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device implanted into the body through a surgical procedure. Connected to the heart by a wire, a pacemaker can detect if the heart rate is too slow and send electrical signals to speed up the heartbeat.
- Defibrillators. A small battery-operated implantable cardioverter defibrillator is surgically placed near the left collarbone. Wires run from the defibrillator to the heart. The ICD senses if the heart has a dangerously fast or irregular rhythm and sends an electrical signal to restore a normal heartbeat.
- Catheter ablation. A catheter is guided through a vein in the leg to the heart. Arrhythmias often are caused by microscopic defects in the heart muscle. Once the problem area of the heart is pinpointed, the catheter heats or freezes the defective muscle cells and destroys them.
- Surgery. Surgery is usually the treatment recommended only if all other options have failed. In this case, a person is put under anesthesia and a surgeon removes the tissue causing the arrhythmia.
Ii Sleep And Cardiovascular Disease
Sleep and sleep disorders both play a role in cardiovascular disease . The exact role that they play is still not quite clear. One thing that is certain is that there is a higher risk of sudden cardiac death in the first few hours after you wake up. This may be due to the amount of work your heart has to do when your body gets up and moving again. CVD is a leading cause of death in the U.S. It takes the life of nearly 2,600 Americans every day.
Common forms of CVD include the following:
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Congenital heart defects
People with obstructive sleep apnea have been shown to have higher rates of coronary heart disease and strokes. People who have had a heart attack are more likely to have OSA than those without heart disease. It can be even harder for someone to fully recover from a heart attack if their OSA is not treated.
OSA is a sleep disorder that occurs when the tissue in the back of the throat blocks the airway. This is very common, because the muscles inside the throat relax as you sleep. You stop breathing, keeping the oxygen you need from getting to the lungs. When you stop breathing, your body wakes up. It happens so quickly, you aren’t even aware of it. You can stop breathing hundreds of times in one night. Being treated for OSA reduces your risk of death due to CVD.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Heart Rate To Spike
What Causes Heart Palpitations At Night
Usually, heart palpitations are harmless and dont result from an underlying health problem. They happen when the heart beats out of rhythm or contracts too soon. Providers call this a premature ventricular contraction or premature atrial contraction . Nearly everyone has a PVC or PAC from time to time. But not everyone feels them.
Some people get heart palpitations when lying down because of the position in which they sleep. Sleeping hunched over on your side can increase pressure inside your body, causing palpitations. Many other common causes of heart palpitations include:
- Myocarditis, inflammation of the hearts muscles that results from a viral infection.
- Thyroid problems, such as hyperthyroidism.
- Structural problems in the heart, including valve disease.
Low Sleeping Heart Rate Learn Whats Normal
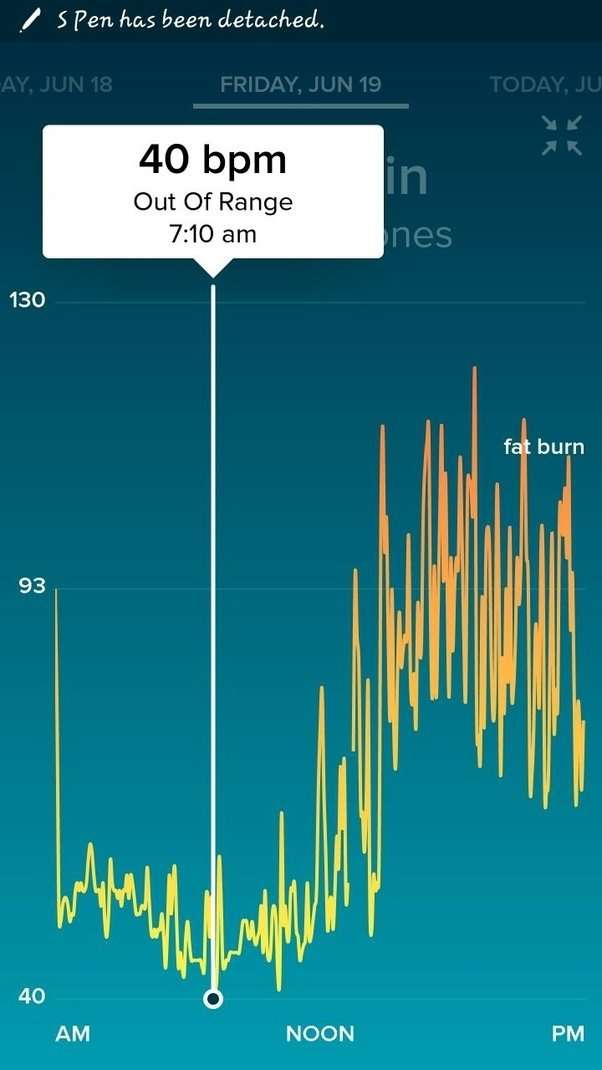
Your sleeping heart rate may be lower than your resting heart rate, according to the Cleveland Clinic. It may drop below 60 beats per minute. For most people, that is not a problem. However, bradycardia is a heart rate below 60 while you’re awake and active, and that could be a problem.
Video of the Day
“Your heart rate slows down during sleep. A normal resting heart rate for adults is anywhere between 60 to 100 beats per minute. During sleep, the normal rate can be anywhere from 40 to 100,” says Peter Santucci, MD, professor of cardiology at Loyola University Medical Center in Maywood, Illinois.
âRead more:â What Is Your RHR and Why Should You Care?
Read Also: How Long Does Open Heart Surgery Usually Take
What Is A Dangerously Low Heart Rate When Sleeping
A dangerously low heart rate when sleeping is medically known as bradycardia. It is a condition in which the heart beats fewer than 60 times per minute. Bradycardia can occur in people with or without heart disease and can cause lightheadedness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting. If left untreated, bradycardia can lead to cardiac arrest and death. There are a number of treatments for bradycardia, including medications and surgery.
What’s A Normal Heart Rate
Heart rate is measured by counting the number of beats per minute. Someone’s normal heart rate depends on things like the person’s age and whether he or she leads an active lifestyle.
The resting heart rate decreases as people get older. Typical normal resting heart rate ranges are:
- babies : 100150 beats per minute
- kids 13 years old: 70110 beats per minute
- kids by age 12: 5585 beats per minute
A doctor can determine whether a heart rate is too fast or slow, since the significance of an abnormal heart rate depends on the situation. For example, a teen or adult with a slow heart rate might begin to show symptoms when the heart rate drops below 50 beats per minute. But trained athletes have a lower resting heart rate, so a slow heart rate in them isn’t considered abnormal if it causes no symptoms.
Also Check: How To Lower Heart Rate And Blood Pressure
How Do I Stop Heart Palpitations When Lying Down
Heart palpitations often will pass on their own after a few minutes, but the effects of heart palpitations can be reduced by:
- Focusing on breathing: Inhale deeply through the nose, hold the breath for a moment then slowly exhale. Repeat this for a few minutes.
- Drink water: Drinking a glass or two of water can help normalize your heart rate.
- Change position: If you are sleeping in a hunched position on your side, you might be at an increased risk of experiencing heart palpitations. Try lying on your back.
- Eat less before bedtime: Sometimes eating a large meal just before going to bed can result in heart palpitations. Try eating a few hours earlier or having a smaller meal at dinnertime.
Factors Affecting Your Heart Rate
So, what affects the speed of your heart? Thats down to your overall health:
- Activity levels: Trained athletes who do lots of exercise tend to have lower heart rates. The more exercise you do, the lower your heart rate will be.
- Cardiovascular health: High blood pressure and heart disease can contribute to a faster heart rate.
- Obesity: Your body size contributes to a faster heart, and this is particularly true if you are obese.
- Caffeine and tobacco: Both have been found to increase your heart rate, even during sleep.
- Bradycardia: The name for exceptionally slow heart rates. According to the American Heart Association, bradycardia is diagnosed in people who have a heart rate lower than 60 BPM.
- Weather: It might sound surprising, but in hot weather or high humidity, your heart rate will go up. This is perfectly normal.
- Emotions: Stress and anxiety can both have an impact on causing a fast heart rate, and studies have shown thats even when you sleep.
- Some medications, such as those for thyroid problems and high blood pressure , can affect your heart rate.
Also Check: Is Your Pulse And Heart Rate The Same Thing
What Is A Pulse At Rest
Heart rate is a measure of heart function and health. While the average resting heart rate for healthy individuals is between 60 and 80 bpm, obesity, medicines, anxiety, and other circumstances can influence your heart rate. Physical fitness levels are also important. In fact, a professional athletes resting heart rate may be significantly lower than normal, ranging from 40 to 70 beats per minute .
Because their heart muscle is healthy and robust, regular exercisers hearts have to work less to distribute a sufficient quantity of blood throughout the body. For individuals who dont have strong cardiac muscle, their heart has to pump much harder than usual in order to maintain normal blood flow, resulting in a greater than usual heart rate.
Your Sleeping Heart Rate
Your sleeping heart rate is simply the rate at which your heart beats while you sleep. If you dont have a device that can track your nocturnal heart rate, this can sometimes be difficult to calculate.
Typically, your heart rate drops by about 20% to 30% of your normal resting heart rate while you sleep. So, if your resting heart rate is 80, you can expect your sleeping rate to be between 56 and 64.
However, just as during the day your heart rate fluctuates, your sleeping heart rate changes during the night too. It is during deep sleep that you can expect your heart rate to reach this level, but there are other stages of sleep where youll have a different heart rate:
- Light sleep: During light sleep, your heart rate will not be as low as during deep sleep, studies show.
- REM sleep: During rapid eye movement sleep, you experience a high heart rate variability, and studies show that it can change even more than when you are awake. Thats because REM is when youre dreaming, and the qualities of your dreams affect your heart rate.
So, all sleep is not created equal. There are a lot of changes going on, and these affect your heart rate too.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Risk Of Heart Disease
When To Talk To Your Doctor
If you have concerns about your heart rate, or it seems above or below what is considered normal, talk to your doctor. They can diagnose whether an underlying condition is contributing to your heart rate, and suggest treatment options, lifestyle changes, and changes to medications to bring it closer to normal levels.
Also let your doctor know if you regularly experience an irregular heart rate, or if your heart rate does not go back to normal after resting or deep breathing. If you experience other symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, heart palpitations, or feeling faint, seek medical attention immediately. Those who have been diagnosed with diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol should monitor their heart rate carefully.
- Was this article helpful?
Can I Prevent Heart Palpitations At Night
You may not be able to prevent heart palpitations at night, but you can lower your risk. You should:
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol or caffeine, especially before bed. If you smoke, talk to your provider about a plan to quit smoking.
- Dont eat a big meal right before you go to bed.
- Get treatment for anxiety or depression. Talk to your provider about antidepressant medication and therapy.
- Take steps to reduce stress on a daily basis. Try meditation, yoga, diaphragmatic breathing and other relaxation techniques.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If you carry extra weight or have obesity, ask your provider about a weight loss plan.
Read Also: How To Increase Resting Heart Rate
Tips For Improved Sleep
When youre sound asleep, your body is wide awake. Welcome its feedback, listen closely to what it has to say, and take steps towards optimizing your sleep.
Use the following tips to help boost your sleep routine:
- Try to wake up at the same time seven days a week.
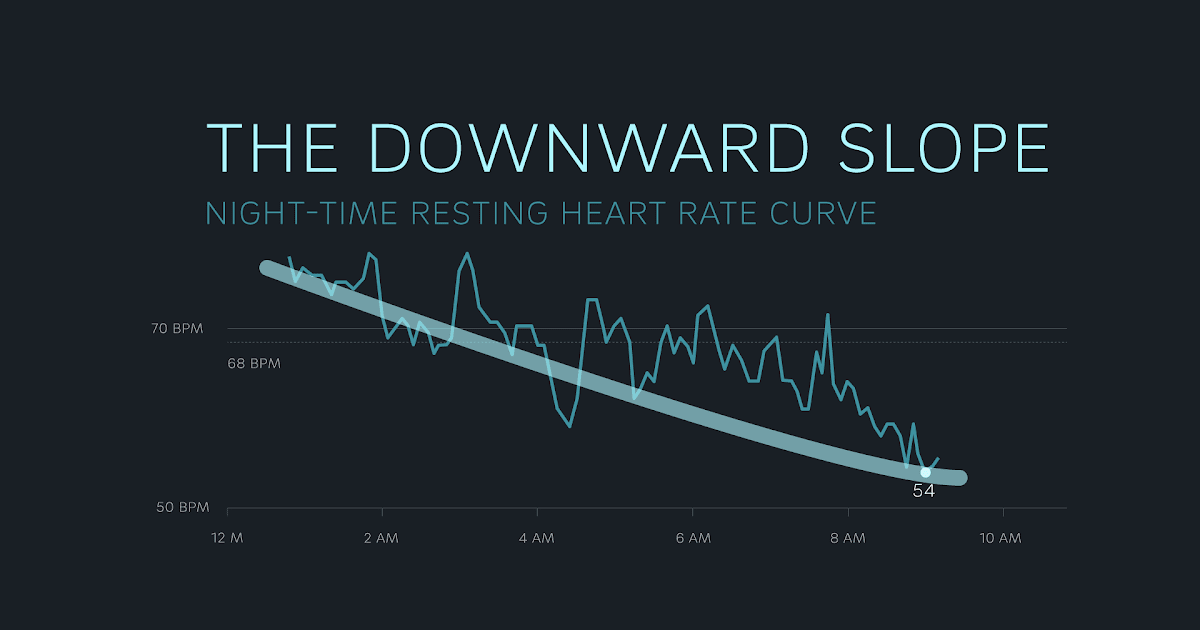
- Time your meals mindfully late meals may show up as the Downward Slope.
- If your sleep pattern is optimal , take notes. Think about what you did the previous day and continue to make similar choices.
Read More About What Your Sleeping Heart Rate Can Tell You:
What Is Heart Rate Variability
As the term suggests,heart rate variability is a measurementVerified SourceHarvard HealthBlog run by Harvard Medical School offering in-depth guides to better health and articles on medical breakthroughs.View sourceof the variation in time between each heartbeat. In other words, it expresses how well the heart changes speeds throughout the day.
For example, you may measure your heart rate and find its about 90 beats per minute. However, that doesnt mean that every single heartbeat takes about of a second. The interval between each heartbeat varies. In this same example, you may have of a second between beats and later a full second between beats.
These increments between beats are called R-R intervals and are measured in milliseconds. The term R-R intervals comes from the heartbeats R-phase. These intervals are essentially the spikes you see on the results of anelectrocardiogram test.Verified SourceMedline PlusOnline resource offered by the National Library of Medicine and part of the National Institutes of Health.View source
During the R phase, most of the heart is activated resulting in the greatest wave shown by the ECG recording, according to a2016 review on heart rate variability in humans.Verified SourceNational Library of Medicine Worlds largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible.View source
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Resting Heart Rate Immediately
Tips For Managing Your Heart Rate
To change your sleeping heart rate and improve overall heart health, try these tips:
- Get better sleep: Follow a regular sleep schedule, and aim to get at least seven hours of sleep each day.
- Reduce stress and anxiety: Yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation may help induce a state of relaxation with slower breathing and a lower heart rate.
- Exercise regularly: Physical fitness is associated with a lower resting heart rate.
- Avoid nicotine and caffeine: Nicotine and caffeine can cause heart palpitations.
- Eat a healthy diet: To help control heart rate and overall heart health, you may want to consider including more nuts, seeds, and fish in your diet and cutting down on cholesterol and saturated fats.
Why Good Sleep Matters For Your Hearts Health
When you think about improving your heart health, food and exercise may come to mind. Sleep is just as crucial â even though many people treat it like a luxury, not a necessity.
âJust like we talk about eating a low-fat diet to minimize your cholesterol and maintain your heart health, maintaining your sleep health is important for your overall well-being,â says Susheel Patil, MD, PhD, director of the Sleep Medicine Program for University Hospitals.
And yet, many people view sleep as a luxury, not a necessity. âMost Americans are probably sleep-deprived to some extent,â Patil says. According to the CDC, 1 in 3 U.S. adults gets less than the recommended 7-9 hours of sleep a night. Over time, that could put them at higher risk for conditions that may impact the heart, including obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
Getting good-quality sleep on a regular basis lets your body get the restorative break it needs. Without it, youâre more likely to develop health problems. And that, in turn, can affect your heart.
People who get less than 6 hours of sleep a night are more likely to gain weight, develop diabetes, and be diagnosed with heart disease than those who get 7-8 hours of sleep, Patil says. And, he says, thereâs evidence that sleep-deprived people tend not to live as long as their well-rested peers.
Recommended Reading: How To Bring Your Heart Rate Down
Improve Your Nocturnal Heart Rate Reduce Your Risks
Nocturnal heart rate is an important metric that helps quantify the efficiency of your cardiovascular system. Tracking your nocturnal heart rate over time and gaining knowledge of how certain behaviors are impacting trends can help develop an individualized lifestyle plan on the journey to optimal health and life performance.
Additionally, tracking heart rate may provide valuable insight or early detection of health conditions such as sleep disorders that can not impact your sleep quality, but may facilitate or exacerbate other health-related issues.
Maintaining positive habits such as consistently engaging in physical activity may help strengthen the bodys most vital muscle- the heart.
- Tags
Improving Your Resting Heart Rate Score
If you have an elevated RHR, one of the best things you can do for your heart is to incorporate more cardiovascular exercises into your lifestyle.
Several research studies show a conclusive link between a high resting heart rate and a lower level of physical fitness. The RHR in most people also increases with body weight, and obese people have a significantly higher resting heart rate than the general population.
Hence, adopting a more fitness-oriented lifestyle and losing some weight are some of the best tactics for getting your RHR in control.
Adopting cardiovascular exercises like cycling, swimming, and walking into your daily routine can also strengthen your heart, improve your overall heart health, and reduce your risk of heart disease and other adverse cardiovascular events.
Note: Remember to hydrate properly and get enough sleep. Dehydration and sleep deprivation are two factors that can cause a consistent spike in your resting heart rate, even if you maintain optimal fitness levels.
You May Like: Can You Feel Heart Palpitations
