During Your Recovery Process It Is Important To:
- Take all medication as prescribed by your provider.
- Follow a heart-healthy lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and low stress.
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
Lifespan, Rhode Island’s first health system, was founded in 1994 by Rhode Island Hospital and the Miriam Hospital. A comprehensive, integrated, academic health system with The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Lifespan’s present partners also include Rhode Island Hospital’s pediatric division, Hasbro Children’s Hospital Bradley Hospital Newport Hospital Gateway Healthcare Lifespan Physician Group and Coastal Medical.
How Are Heart Attacks Diagnosed
Heart attacks are usually diagnosed in an emergency room setting. A healthcare provider will diagnose a heart attack using the following:
- History and symptoms: The provider will ask you about the symptoms you experienced. If someone was with you, the provider might also ask them to describe what happened.
- Lab testing: Heart attacks cause a specific chemical marker to show up in your blood.
- Heart-specific diagnostic tests: This includes tests that detect and record the electrical activity in your heart.
- Imaging tests: These tests give providers a way to see inside your heart. Many of these tests can also show the location of a blood flow blockage, which can guide treatment.
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better
In general, your heart attack symptoms should decrease as you receive treatment. You will likely have some lingering weakness and fatigue during your hospital stay and for several days after. Your healthcare provider will give you guidance on rest, medications to take, etc.
Recovery from the treatments also varies, depending on the method of treatment. The average hospital stay for a heart attack is between four and five days. In general, expect to stay in the hospital for the following length of time:
- Medication only: Patients treated with medication only have an average hospital stay of approximately six days.
- PCI: Recovering from PCI is easier than surgery because it’s a less invasive method for treating a heart attack. The average length of stay for PCI is about four days.
- CABG: Recovery from heart bypass surgery takes longer because it is a major surgery. The average length of stay for CABG is about seven days.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Soccer Players Have Heart Attacks
Changing Your Lifestyle Can Reduce Your Risk Of Heart Attack
Dealing with the lifestyle factors that contribute to CVD, which you can change, can help reduce your risk of heart attack. Things you can do include:
- take medicines as prescribed
- eat plenty of vegetables, fruits and wholegrains
- eat a variety of healthy protein sources especially fish and seafood, legumes , nuts and seeds. Smaller amounts of eggs and lean poultry can also be included in a heart healthy diet. If choosing red meat, make sure the meat is lean and limit to 1 to 3 times a week
- unflavoured milk, yoghurt and cheese if you have high blood cholesterol you should choose reduced fat varieties
- healthy fat choices with nuts, seeds, avocados, olives and their oils for cooking
- herbs and spices to flavour foods, instead of adding salt
- drink mainly water
Complications Of A Heart Attack

Complications of a heart attack can be serious and possibly life threatening.
These include:
- arrhythmias these are abnormal heartbeats. 1 type is where the heart begins beating faster and faster, then stops beating
- cardiogenic shock where the heart’s muscles are severely damaged and can no longer contract properly to supply enough blood to maintain many body functions
- heart rupture where the heart’s muscles, walls or valves split apart
These complications can happen quickly after a heart attack and are a leading cause of death.
Many people die suddenly from a complication of a heart attack before reaching hospital or within the 1st month after a heart attack.
The outlook often depends on:
- age serious complications are more likely as you get older
- the severity of the heart attack how much of the heart’s muscle has been damaged during the attack
- how long it took before a person received treatment treatment for a heart attack should begin as soon as possible
Read Also: How Much Aspirin Do You Take For A Heart Attack
Are The Symptoms Of Heart Attack Different For Women
The most common heart attack symptom for women is pain or discomfort in the chest. However, women are more likely to have a heart attack without having any chest pain. Therefore, women should pay close attention to other symptoms of heart attack. These include shortness of breath, sweating, fatigue, and dizziness.
Heart Attack Is A Medical Emergency
Call triple zero for an ambulance if you or someone you are with experiences the warning signs of heart attack.
Its important to call triple zero, because:
- The trained operator will decide if you need an ambulance.
- You will receive treatment as soon as you phone.
- You will receive advice on what to do while waiting for the ambulance to arrive.
Ambulance paramedics are trained to use special lifesaving equipment and to start early treatments for heart attack inside the ambulance. Early treatment can reduce the damage to your heart.
The ambulance is the safest and fastest way to get you to hospital. It gets you medical attention straight away.
Do not drive yourself to the hospital. This is dangerous for you and other road users.
If you live in a remote region and an ambulance is not available, make sure someone else drives you.
Its always better to go to hospital and be told its not a heart attack than to stay at home until its too late. Ignoring the warning signs can result in permanent damage to your heart muscle.
Also Check: Can Beer Cause Heart Attack
Anxiety As A Heart Attack Symptom
One other common heart attack symptom is anxiety, or a vague but undeniable feeling that somethings wrong.
Research shows that a heart attack causes victims to feel like theyre having a panic attack. But this is a dangerous assumption. Rather than get help immediately, some individuals having a heart attack want to chalk up their symptoms to indigestion or anxiety or feeling worn out from too much exertion.
In addition, if the pressure in your chest isnt too uncomfortable and youre just a little short of breath, you may think youre having some mild heart attack symptoms. This could lead you to not take them seriously.
see our posts Heart Attack Symptoms in Men: 5 Common Signs and Heart Attack Symptoms in Women.)
Diagnosing A Heart Attack
Our team of heart specialists are experienced in diagnosing and treating heart disease at all stages, including heart attacks. Our team will run tests to check if your signs and symptoms, such as chest pain, indicate a heart attack or another condition. Tests to diagnose a heart attack may include:
- Electrocardiogram This non-invasive test uses small sensors attached to your chest and arms to record your hearts electrical activity.
- Blood tests These tests can also rule out any issues with your thyroid, liver or kidneys.
- Chest X-ray This allows your doctor to see the condition of your lungs and heart, and potentially rule out other causes of your symptoms.
- Echocardiogram A wand-like device is placed on your chest and uses sound waves to create a video of your heart working.
- Cardiac catheterization During this minimally invasive procedure, a long, thin tube is inserted into your heart for diagnostic testing and to check for any blockages. Many people are able to remain awake during the procedure.
- Stress test This test involves monitoring your heart while you exercise.
Recommended Reading: Does Heart Rate Increase After Eating
After Having A Treatment Procedure For A Heart Attack
Once you have had treatment you will spend time recovering in a special hospital ward. This is called the Coronary Care Unit . You will be there for a few days. This is so that doctors and nurses keep an eye on you during your recovery.
The days after treatment are when you are at most risk of developing complications. Complications could be a very fast or very slow heart rate. There are other complications too.
During this period you will:
- be examined by a doctor or nurse at least once a day
- have regular ECG tests
- have blood tests to work out how much damage the heart attack caused
- have chest x-rays taken, if necessary
Your doctor might also carry out an echocardiogram . This is to find out how well your heart muscle is working. An ECHO is an ultrasound examination of your heart.
The number of monitors and drips attached to you may worry you and your family. But, remember this is normal. It should not alarm you.
Your Stay In Hospital After A Heart Attack
Once your condition is stable, you will move from the CCU to a cardiac ward. After that you will be able to go home.
At this stage, doctors will have a better idea of what caused your heart attack. You will then start receiving treatment for these conditions.
In some hospitals you will have a visit from a member of the cardiac rehabilitation team. They will discuss a cardiac rehabilitation programme with you.
Before you leave hospital you may also have an angiogram. An angiogram is a specialised x-ray.
You May Like: What Is Resting Heart Rate
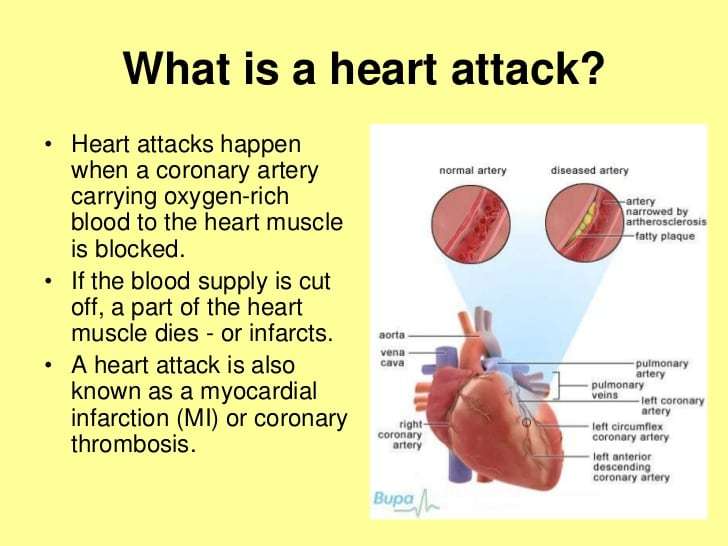
What Causes A Heart Attack
The vast majority of heart attacks occur because of a blockage in one of the blood vessels that supply your heart. This most often happens because of plaque, a sticky substance that can build up on the insides of your arteries . That buildup is called atherosclerosis.
Sometimes, plaque deposits inside the coronary arteries can break open or rupture, and a blood clot can get stuck where the rupture happened. If the clot blocks the artery, this can deprive the heart muscle of blood and cause a heart attack.
Heart attacks are possible without a blockage, but this is rare and only accounts for about 5% of all heart attacks. This kind of heart attack can occur for the following reasons:
- Spasm of the artery: Your blood vessels have a muscle lining that allows them to become wider or narrower as needed. Those muscles can sometimes twitch or spasm, cutting off blood flow to heart muscle.
- Rare medical conditions: An example of this would be any disease that causes unusual narrowing of blood vessels.
- Trauma: This includes tears or ruptures in the coronary arteries.
- Obstruction that came from elsewhere in the body: A blood clot or air bubble that gets trapped in a coronary artery.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Having too much or too little of key minerals like potassium in your blood can cause a heart attack.
- Eating disorders: Over time, an eating disorder can cause damage to your heart and ultimately result in a heart attack.
Risk Factors For Cardiovascular Disease
You can reduce your risk of developing CVD and having a heart attack by removing or reducing risk factors. These include:
- unhealthy eating
- smoking either being a smoker or inhaling other peoples smoke
- having high cholesterol
- having depression, being socially isolated or not having quality social support.
Other factors you cant change that can increase the risk of developing CVD include:
- getting older
- being male
- having a family history of early death from CVD, such as a first-degree relative younger than 60
- ethnicity Indigenous, Mori, Pasifika people and those from South Asian countries, are at higher risk of heart disease
- being a post-menopausal woman.
Also Check: Who Performed The First Open Heart Surgery In The World
What Are The Complications Of A Heart Attack
Complications associated with heart attacks include:
- Arrhythmias : Management options include medication, pacemaker placement, implantable cardioverter defibrillator placement and other options.
- Heart failure: If enough heart tissue has died, your heart is now weakened and cant pump blood effectively, which can lead to heart failure.
- Heart valve problems: Depending on the area of heart damage, your heart valves may be affected. Catheter-based procedures or surgery are treatment options for heart valve problems.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: This sudden stoppage of your heart can be caused by arrhythmia.
- Depression and anxiety: Talk to your healthcare provider. Management includes medication and counseling. Joining a support group can help.
Angina Vs Heart Attack
Chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle is called angina. Its a common symptom of heart disease. There are two main types of angina:
- stable angina, the most common type of angina and one that is predictable often occurring with physical exertion or stress
- unstable angina, which is unpredictable and should be treated as a medical emergency
An angina attack can feel like a heart attack, and in many cases especially with unstable angina it can be hard to tell angina from an actual heart attack.
If you have stable angina thats brought on with exertion and eases with rest, you may assume a sudden but brief bout of chest pain is only an angina attack. If chest pain doesnt subside with rest or comes and goes for a period of 10 minutes or more, you may be having a heart attack.
Talking with your doctor about how to manage your angina will help you better understand the difference between angina and heart attack symptoms, and help prepare you if your chest pain is actually a symptom of a heart attack.
The leading cause of heart attacks is coronary heart disease. This is where plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. The general buildup of plaque in the arteries is also known as atherosclerosis.
There are two main types of heart attack.
In type II heart attacks the heart does not receive as much oxygen-rich blood as it needs, but there is not a complete blockage of an artery.
Other causes of heart attacks include:
Also Check: Resting Heart Rate Age Chart
How Heart Attack Symptoms May Differ For People With Diabetes
Research has shown that people with diabetes are more likely to have silent heart attacks compared to people who dont have diabetes. In other words, if you have diabetes, you may not experience the typical symptoms associated with a heart attack, especially chest pain.
Many studies have been done to better understand why people with diabetes are less likely to experience chest pain and other heart attack symptoms. One explanation is that the development of neuropathy a type of nerve damage thats a common complication of diabetes may interfere with the ability to feel chest pain caused by a heart attack.
According to research , approximately 55 percent of people with diabetes have coronary artery disease. Having impaired blood flow in the coronary arteries is a major risk factor for a heart attack.
Because of this risk, its important that people with diabetes keep their blood sugar levels under control, get frequent blood tests to check cholesterol levels, and work closely with a doctor to ensure their diabetes is managed well.
Heart Attack Early Treatment
Early Treatment Important for Heart AttacksChest pain is one of the most common symptoms of a heart attack and one of the most common reasons people visit the emergency room. Each year more than one million Americans have a heart attack, and more than one-third of those heart attacks are fatal. Emergency room physicians will tell you that for a heart attack to be treated effectively, the treatments must start within one hour from when the symptoms start.
Symptoms of a Heart AttackWhen it comes to heart attacks, knowing the symptoms and getting prompt medical attention can make a huge difference in the outcome. Here are the symptoms of a heart attack:
- Chest pain or discomfort. The pain is usually in the center of the chest and may last for a few minutes or come and go. People describe the feeling as uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain.
- Pain or discomfort in the upper body. Other places that may hurt include one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or even stomach.
- Shortness of breath. This may accompany the chest pain or begin before the pain starts.
- Other symptoms may include a cold sweat, nausea and fainting or feeling light-headed.Women are more likely to experience less common symptoms such as feeling short of breath, nausea or vomiting and pain in the back and jaw.
For blocked arteries, doctors may need to perform a bypass. In a coronary artery bypass graft operation, doctors take a healthy section of artery and use it to route around the blockage.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Good Resting Heart Rate By Age
Types Of Heart Medications
If you’ve had a heart attack, you will most likely be prescribed medication that you will take for the rest of your life.
There are many types and combinations of drugs used to treat coronary artery disease , and your doctor or other health care provider will decide the best treatment combination for your situation.
The following gives you a quick look at many typical cardiac medications. Your prescription may have a different name from the ones listed on this chart. Brand names commonly available in the U.S. are shown in parentheses after the generic name for each drug.
*Some of the major types of commonly prescribed cardiovascular medications are summarized in this section. For your information and reference, we have included generic names as well as major trade names to help you identify what you may be taking. However, the AHA is not recommending or endorsing any specific products. If your prescription medication isn’t on this list, remember that your healthcare provider and pharmacist are your best sources of information. It’s important to discuss all of the drugs you take with your provider and understand their desired effects and possible side effects. Never stop taking a medication and never change your dose or frequency without first consulting the prescribing doctor.
Commonly prescribed include:
What the Medication Does
Reason for Medication
