Signs And Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
Symptoms of a heart attack can vary greatly from person to person. Theyre likely to be more severe if youre having a major heart attack, in which a blood clot completely blocks an artery leading to your heart.
- Pain or discomfort in your jaw or neck
- Pain or discomfort in your arms, shoulders, or back
- Indigestion or sense of choking
- Sweating, especially a cold sweat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Sudden chest pain is the most common heart attack symptom, but not all people experience it. Some people have only mild symptoms that come on gradually.
Because a heart attack is a medical emergency, dial 911 right away if you experience symptoms that you believe are caused by one.
What Happens During A Heart Attack
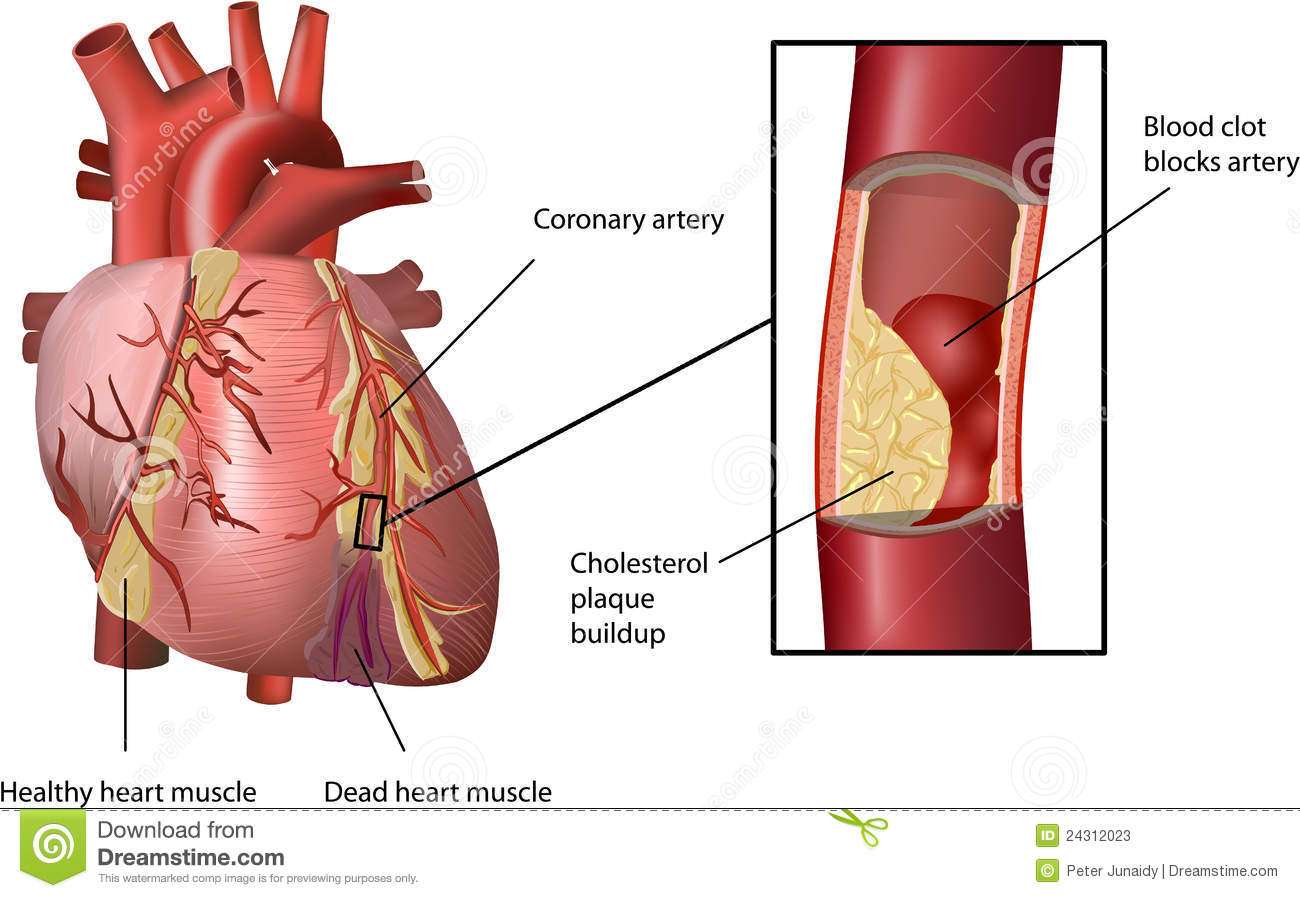
A heart attack happens when one or more of your coronary arteries suddenly becomes blocked, stopping the flow of blood to the heart muscle and damaging it causing a heart attack. Lets back up and learn more about your coronary arteries.
Your coronary arteries are a network of blood vessels that surround your heart muscle and supply it with blood that is rich in oxygen and nutrients. Your heart muscle needs this continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients to function. Over time, sometimes one or more of your coronary arteries narrow because of a buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits on the inner walls. This is called atherosclerosis. Sometimes this plaque ruptures and forms a clot within the artery, which restricts blood flow to your heart. Blocked blood flow cuts off the needed supply of oxygen and nutrients, damaging or destroying that area of heart muscle.
Symptoms And Signs Of A Stemi
A STEMI has the classic symptom of pain in the center of the chest. This chest discomfort may be described as a pressure or tightness rather than a sharp pain. Some people who experience STEMIs also describe feeling pain in one or both arms or their back, neck, or jaw.
Other symptoms that may accompany chest pain include:
- nausea
- lightheadedness
- breaking out in a cold sweat
Don’t Miss: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Heart Attack Recovery And Outlook
Your recovery from a heart attack will depend on its severity and how it was treated. It can take anywhere from one week to several weeks before you can return to all your regular activities, especially anything involving heavy lifting.
Treating a heart attack promptly and effectively minimizes the damage. Your chances of a better outcome also improve if you do cardiac rehabilitation. Cardiac rehabilitation is a multiweek program of exercise routines, nutrition counseling, and learning about heart medications and lifestyle changes.
Get The Heart Care You Need When You Need It
Each year about 805,000 Americans have a heart attack, and about 655,000 die of heart disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This means heart disease is responsible for one in every four deaths, making it the leading cause of death for both men and women.
Remember, if you think youre having a heart attack:
- Chew one adult-strength aspirin to help keep your blood from clotting.
- Stay on the phone with the emergency operator as you wait for an ambulance. Do not try to drive yourself to the hospital.
A heart attack can be a scary experience. But remember that were here for you, and comprehensive heart care and recovery options are never far away.
Don’t Miss: Heart Palpitations Prednisone
When Do I Do If Someone Else Has A Heart Attack
An easy-to-use device called an AED is available in many public places and can be used by almost anyone to treat cardiac arrest. This device works by shocking the heart back into a normal rhythm.
Hereâs how to use an AED:
1. Check responsiveness
- For an adult or older child, shout and shake the person to confirm whether theyâre unconscious. Do not use AED on a conscious person.
- For an infant or young child, pinch their skin. Never shake a young child.
- Check breathing and pulse. If absent or uneven, prepare to use the AED as soon as possible.
2. Prepare to use AED
- Make sure the person is in a dry area and away from puddles or water.
- Check for body piercings or outline of an implanted medical device, such as a pacemaker or implantable defibrillator.
- AED pads must be placed at least 1 inch away from piercings or implanted devices.
3. Use AED
For newborns, infants, and children up to age 8, use a pediatric AED, if possible. If not, use an adult AED.
- Turn on the AED.
- Plug in connector, if necessary.
- Make sure no one is touching the person.
- Push the âAnalyzeâ button.
- If a shock is advised, check again to make sure no one is touching the person.
- Push the âShockâ button.
- Start or resume continue compressions.
- Follow AED prompts.
4. Continue CPR
Q What Is The Link Between Cardiac Arrest And Heart Attack
Don’t Miss: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
Is Chest Pain Normal After A Heart Attack
Once you’ve had a heart attack, you’re at higher risk for another one. Not everyone who has CHD will have chest pain , but if you do, it should be a light pain or pressure in your chest that quickly goes away. It will typically happen during or right after physical exertion, intense emotion or eating a heavy meal. If you’re having ANY chest pains, tell your doctor. There are exercises and medication that can help ease or prevent the pain. If you don’t know if your chest pain is angina or a heart attack, call 911.
What Is The Long
Cardiomyopathy can be life-threatening and can shorten your life expectancy if severe damage occurs early on. The disease is also progressive, which means it tends to get worse over time. Treatments can prolong your life. They can do this by slowing the decline of your hearts condition or by providing technologies to help your heart do its job.
Those with cardiomyopathy should make several lifestyle adjustments to improve heart health. These may include:
- maintaining a healthy weight
- limiting alcohol intake
- getting support from their family, friends, and doctor
One of the biggest challenges is sticking with a regular exercise program. Exercise can be very tiring for someone with a damaged heart. However, exercise is extremely important for maintaining a healthy weight and prolonging heart function. Its important to check with your doctor and engage in a regular exercise program thats not too taxing but that gets you moving every day.
The type of exercise thats best for you will depend on the type of cardiomyopathy you have. Your doctor will help you determine an appropriate exercise routine, and theyll tell you the warning signs to watch out for while exercising.
Also Check: Does Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
Q What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Attack
Is My Heart Permanently Damaged
When a heart attack occurs, the heart muscle that has lost blood supply begins to suffer injury. The amount of damage to the heart muscle depends on the size of the area supplied by the blocked artery and the time between injury and treatment.
Heart muscle damaged by a heart attack heals by forming scar tissue. It usually takes several weeks for your heart muscle to heal. The length of time depends on the extent of your injury and your own rate of healing.
The heart is a very tough organ. Even though a part of it may have been severely injured, the rest of the heart keeps working. But, because of the damage, your heart may be weakened, and unable to pump as much blood as usual.
With proper treatment and lifestyle changes after a heart attack, further damage can be limited or prevented.
Learn more about heart damage detection.
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Black American Communities And Heart Attacks
While the overall risk of heart disease varies among different racial and ethnic groups in the United States, there is less data on heart attacks specifically.
According to the American Heart Association, the rate of cardiovascular disease in Black Americans is about 23 percent higher in men, and 33 percent higher in women, compared with the overall U.S. population.
Non-Hispanic Black Americans have the highest rate of death from heart disease at 208 per 100,000 people, according to the CDC. Next come non-Hispanic white Americans at 169, Hispanic Americans at 114, and Asian Americans at 86.
Researchers have found that among U.S. hospitals with sufficient data, the rate of death from heart attacks in Black patients was nearly identical to that of white patients. But the hospital readmission rate for Black patients was 4.3 percentage points higher than for white patients, according to an investigation published September 2018 in JAMA Open Network.
Area Of The Heart Wall
It is important to understand the coronary circulation and coronary artery dominance as outlined under blood supply to the heart. Most infarcts affects the wall of the left ventricle and this is dependent on the artery that is compromised as indicated by the area of risk in the diagram above. Majority of heart attacks associated with occlusion of the coronary artery involves the anterior descending branch of the left coronary artery followed by the right coronary artery and the minority of cases involve the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery. An obstruction may occur more proximally or distally in the coronary circulation but is not as common.
Picture from Wikimedia Comons
- When the left anterior descending coronary artery is blocked, then the infarct may affect the anterior wall of the left ventricle, anterior aspect of ventricular septum and/or apex of heart.
- When the right coronary artery is blocked, then the infarct may involve posterior wall of the left ventricle, posterior aspect of the ventricular septum and may extend to the posterior wall of the right ventricle.
- When the left circumflex coronary artery is blocked, then the infarct may involve the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
Also Check: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
Risk Of A Repeat Heart Attack
Once you’ve had a heart attack, you’re at higher risk for another one. Knowing the difference between angina and a heart attack is important. Angina is chest pain that occurs in people who have ischemic heart disease.
The pain from angina usually occurs after physical exertion and goes away in a few minutes when you rest or take medicine as directed.
The pain from a heart attack usually is more severe than the pain from angina. Heart attack pain doesn’t go away when you rest or take medicine.
If you don’t know whether your chest pain is angina or a heart attack, call 911.
The symptoms of a second heart attack may not be the same as those of a first heart attack. Don’t take a chance if you’re in doubt. Always call 911 right away if you or someone else has heart attack symptoms.
Unfortunately, most heart attack victims wait 2 hours or more after their symptoms start before they seek medical help. This delay can result in lasting heart damage or death.
What Is Cardiac Arrest
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs suddenly and often without warning. It is triggered by an electrical malfunction in the heart that causes an irregular heartbeat . With its pumping action disrupted, the heart cannot pump blood to the brain, lungs and other organs. Seconds later, a person loses consciousness and has no pulse. Death occurs within minutes if the victim does not receive treatment.
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System Heart Disease Working Group Members
- Camille Adams, Saskatchewan Ministry of Health
- Claudia Blais, Institut national de santé publique du Québec
- Jill Casey, Nova Scotia Department of Health and Wellness
- Charmaine Cooke, Department of Health and Wellness
- Jennifer Covey, Department of Health and Wellness
- Yana Gurevich, Canadian Institute for Health Information
- Karin Humphries, University of British Columbia
- Helen Johansen, University of Ottawa
- Douglas Lee, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences
- Lisa M. Lix, University of Manitoba
- Kathy Marcotte, Canadian Institute for Health Information
- Pat McCrea, British Columbia Ministry of Health
- Jim Nicol, Saskatchewan Ministry of Health
- Céline Plante, Institut national de santé publique du Québec
- Rolf Puchtinger, Saskatchewan Ministry of Health
- Hude Quan, University of Calgary
- Drona Rasali, British Columbia Provincial Health Services Authority
- Kim Reimer, British Columbia Ministry of Health
- Sue Schultz, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences
- Larry W. Svenson, University of Calgary, Alberta Ministry of Health, University of Alberta
- Jack Tu, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences
- Karen Tu, Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences, University of Toronto, University Health Network
Don’t Miss: Benadryl Heart Arrhythmia
What Is The Difference Between Heart Disease And Cardiovascular Disease
Heart disease is a catch-all phrase for a variety of conditions that affect the hearts structure and function. Keep in mind all heart diseases are cardiovascular diseases, but not all cardiovascular diseases are heart disease. The most common type of heart disease is coronary heart disease.
What are the 4 types of Cardiovascular Disease?
- Coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle is blocked or reduced.
- Strokes and TIAs.
- Peripheral arterial disease.
- Aortic disease.
What causes heart disease or cardiovascular disease? High blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors for heart disease. Several other medical conditions and lifestyle choices can also put people at a higher risk for heart disease, including: Diabetes. Overweight and obesity.
What are 3 types of heart disease?
- Arrhythmia. An arrhythmia is a heart rhythm abnormality.
- Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a hardening of the arteries.
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Heart infections.
Risk Factors You Can Control
The major risk factors for a heart attack that you can control include:
- High blood sugar due to insulin resistance or diabetes
Some of these risk factorssuch as obesity, high blood pressure, and high blood sugartend to occur together. When they do, it’s called metabolic syndrome.
In general, a person who has metabolic syndrome is twice as likely to develop heart disease and five times as likely to develop diabetes as someone who doesn’t have metabolic syndrome.
For more information about the risk factors that are part of metabolic syndrome, go to the Health Topics Metabolic Syndrome article.
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Can You Have Sex After A Heart Attack
A heart attack can take a toll on your romantic relationships and sex life, but that doesnt mean you should give up on sex afterward.
It may take some recovery time before you can resume sexual activity, and you may need to make certain modifications to your sexual practices.
Impaired sexual function is common after a heart attack, yet many people are reluctant to discuss this problem with their doctor. You may improve your sexual function by working on your overall fitness and endurance.
Many doctors tout the benefits of sex and intimacy for heart attack survivors, such as stress reduction, improved emotional well-being, and lower blood pressure.
Exercise And Heart Attack Prevention

Certain studies suggest that getting enough exercise may not only help prevent a heart attack, but also increase your chances of survival if you have one.
It even appears that the more exercise you get and the more intense your exercise, the better your odds are of surviving a heart attack.
One possible explanation for this connection is that when you exercise a lot, extra blood vessels may grow around the heart. Known as collateral blood vessels, they provide a way for blood to flow even if an artery gets blocked.
Exercise may also help lower your blood pressure, as well as raise levels of HDL cholesterol, notes Michigan Medicine.
You May Like: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Family History And Genetics
A family history of early heart disease is a risk factor for coronary heart disease. This is especially true if your father or brother was diagnosed before age 55, or if your mother or sister was diagnosed before age 65. Research shows that some genes are linked with a higher risk for coronary heart disease.
