Strengths And Limitations Of The Study And Method
Our study has a consistent and in-depth focus on the patients perspective. A major strength is the inclusion of very old patients . It is in the nature of qualitative studies to have a small number of participants. Therefore, the findings cannot be generalised, but they provide specific in-depth insights into the perception and personal experience of old and very old patients with severe heart failure. The patients were only recruited in an inpatient setting at two geriatric hospitals and not in general practice or other outpatient settings. Furthermore, the tendency towards socially desirable statements must be considered. To reduce social bias, the interviewer was not involved in the delivery of health care for the patients and was not employed by either of the geriatric hospitals.
Resources For Coping With Heart Failure
Living with heart failure usually means making some changes to your lifestyle. To thrive with heart failure, you need to do more than eat nutritious foods, exercise, and follow your doctors other advice. Youll also need to know the signs that your physical and mental health may be changing due to heart failure.
If youre a caregiver for someone with heart failure, you should learn about what to expect to prepare you for this role.
The following articles can help you learn more about heart failure and what to expect moving forward:
What Causes Congestive Heart Failure
There are several conditions that can impair the pumping efficiency of the heart. Below are a few common and rare conditions that can cause congestive heart failure:
- Coronary artery disease : This is the most common cause of congestive heart failure, as the arteries become blocked or severely narrowed, which decreases blood flow to the heart.
- Alcohol abuse
- Disorders of heart valves
- Thyroid abnormalities, viral infection, and heart rhythm abnormalities are a few rare cases that can cause congestive heart failure.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Exercise Increase Heart Rate
Talk To Them About Their Symptoms
People with heart failure may feel worried about their symptoms, treatment or risk of dying suddenly. Reassure them by talking openly and honestly about their concerns. Speak to their cardiac or palliative care team if you need support. If the patient has a plan for managing symptoms or emergencies, they may feel less anxious.
For Patients Speaking To Families
- Education is key. Educate yourself first. By now, youve probably done some research online. It may be helpful to read and share our Hospice Family Discussion Guide. This discussion guide is a tool for you to print out and use in a family discussion.
- Determine what your family members know. Before bringing up hospice, make sure your family members and caregivers have a clear understanding of your health status. People handle difficult information in different ways. If family members do not accept or understand your prognosis, ask your physician, clergy, a VITAS social worker or a trusted friend to speak with them on your behalf.
- Discuss your goals for the future, as well as theirs. As a patient, your greatest concern might be to live without pain, to stay at home or not to be a burden. Ask your family members/caregivers about their concerns as they consider the coming days, weeks and months. Explain that hospice is not giving up. It is an active choice to ensure that everyones needs are met.
- Take initiative. Remember, its up to you to express your wishes. Sometimes, out of concern for your feelings, your family or loved ones might be reluctant to raise the issue of hospice care for you.
You May Like: What Happens To Heart Rate During Heart Attack
What Are The Symptoms Of End
Heart Failure: Quick Facts
1. More than 6 million U.S. adults have heart failure.
2. About half of people who develop heart failure die within 5 years of diagnosis.
3. Most people with end-stage heart failure have a life expectancy of less than 1 year.
4. The leading causes of heart failure are diseases that damage the heart, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Heart failure worsens over time, so symptoms are most severe during the final stages. It causes fluid to build up in the body, which produces many of these symptoms:
- Shortness of breath . In the final stages of heart failure, people feel breathless both during activity and at rest.
- Persistent coughing or wheezing. This may produce white or pink mucus. The cough may be worse at night or when lying down.
- Weight gain or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
- Tiredness, weakness.
In addition, people in the final stages of heart failure may suffer from:
- depression, fear, insomnia, and isolation
- anxiety about their future
- trouble navigating the health care system
I Decline In Clinical Status Guidelines
These changes in clinical variables are listed in order of their likelihood to predict poor survival, the most predictive first and the least predictive last. No specific number of variables must be met, but fewer of those listed first and more of those listed last would be expected to predict longevity of six months or less.
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure Legs
Trouble Arises When The Heart Can’t Properly Relax
Relaxation is every bit as important for your heart as it is for the rest of you. If for some reason the heart has trouble relaxing between beats, then it can’t fill completely. Less blood pumped with each contraction sets the stage for a type of heart failure that goes by many names: diastolic heart failure, heart failure with normal ejection fraction, heart failure with preserved systolic function, and others.
Diastolic heart failure isn’t really new. It’s just that doctors now have tools that let them see how this form of heart failure differs from “regular” heart failure. At least half of the people who develop heart failure each year have diastolic heart failure. Both types of heart failure result in the same thing the heart has trouble supplying the body’s organs and tissues with the oxygen-rich blood they need.
|
Key points
|
Stiffening and bulking up
What to do
In the meantime, the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology recommend controlling:
Nitrates Apresoline Beta Blockers And Inotropes Drugs For Congestive Heart Failure
Nitrates are venous vasodilators that include isosorbide mononitrate and isosorbide dinitrate . They are commonly used in combination with an arterial vasodilator, such as hydralazine .
- Nitroglycerin is a nitrate preparation that is administered to treat acute chest pain, or angina.
Hydralazine is a smooth muscle arterial vasodilator that may be used for congestive heart failure. Clinical trial data has shown hydralazine plus nitrates to be especially effective in African-Americans with heart failure, when used in addition to ACE inhibitors or ARBs.
- Isosorbide dinitrate and hydralazine is a fixed dose combination of isosorbide dinitrate and hydralazine . This drug is indicated for heart failure in African-Americans based in part on results of the African American Heart Failure Trial .
- Hydralazine is also especially valuable in patients who have poor kidney function and/or are intolerant to ACE inhibitors and ARBs.
Beta-blockers: These drugs slow down the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and have a direct effect on the heart muscle to lessen the workload of the heart. Specific beta-blockers, such as carvedilol and long-acting metoprolol , have been shown to decrease symptoms, hospitalization due to congestive heart failure, and deaths. Other beta-blockers include bispropolol , atenolol , propranolol , and , but they are generally not used with significant congestive heart failure.
Getting the most out of congestive heart failure medications involves the following:
You May Like: Can Low Blood Sugar Cause Heart Palpitations
Signs It Might Be Time For Hospice
Patients are considered to be in the terminal end stage of heart disease when they have a life expectancy of six months or less. Only a doctor can make a clinical determination of congestive heart failure life expectancy. However, look for these common signs that the disease has progressed to a point where all involved would likely benefit from hospice services:
- The patient has advanced congestive heart failure or advanced coronary disease with frequent episodes of angina .
- The patient has an abnormal heart and suffers significant symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath or functional decline.
- Optimal treatment for the patients condition has already been provided and he or she is not a candidate for further surgical or medical intervention.
- The patient has tried optimal treatment and made the personal choice not to pursue any further specialized treatment.
People often say, I wish I had asked about hospice sooner.1 Reports show early referral to hospice results in greater satisfaction for the patient and their caregivers. In 2015, seriously ill patients received hospice services for an average of 69.5 days, but given more time, hospice resources can supplement care provided by doctors and loved ones through a patients last six months of life.
How Does Heart Failure Impact People At End Of Life
Heart failure can have a serious psychological impact on people, leading to feelings like worry, sadness or anger. Patients may experience a mix of good and bad days, and the lack of control over their limitations can be very frustrating. As the disease advances, symptoms can fluctuate dramatically, which makes evaluating how long the patient is expected to live more challenging.
Read Also: How Long Can Heart Attack Symptoms Go On
What Are The Survival Rates For Heart Failure
Survival rates are based on studies of large groups of people with certain diagnoses and generally presented as a 5-year survival rate, which is the percentage of people who lived for at least 5 years after diagnosis.
You can find online calculators that ask you to submit information to get a life expectancy prediction. However, these calculators are not always accurate since they are based on studies of certain population groups over a period of time .
Table: Survival rates for patients with heart failure
| Survival | |
|---|---|
| 10 | About 24.5% on average |
For example, the 5-year survival rate for patients with heart failure is about 76%. This means that about 76 out of 100 people who were diagnosed with heart failure could live for at least 5 years.
Generally, young patients with heart failure have a better prognosis than older patients. Early diagnosis and treatment help increase life expectancy as well.
You May Like: Can Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
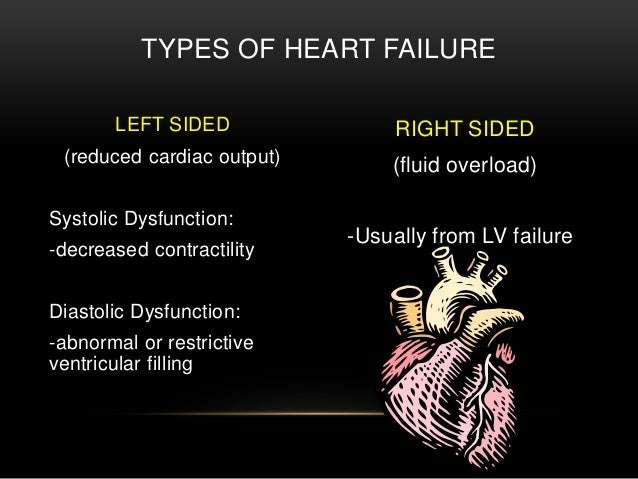
What Are The Types Of Heart Failure

There are many causes of heart failure, but the condition is generally broken down into these types:
Left-sided heart failure
Heart failure with reduced left ventricular function The lower left chamber of your heart gets bigger and cannot squeeze hard enough to pump the right amount of oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body.
Heart failure with preserved left ventricular function Your heart contracts and pumps normally, but the bottom chambers of your heart are thicker and stiffer than normal. Because of this, your ventricles can’t relax properly and fill up all the way. Because there’s less blood in your ventricles, your heart pumps out less blood to the rest of your body when it contracts.
Right-sided heart failure
Heart failure can also affect the right side of your heart. Left-sided heart failure is the most common cause of this. Other causes include certain lung problems and issues in other organs.
Also Check: Can Statins Cause Heart Palpitations
Prognosis At Different Ages
In general, younger people diagnosed with CHF tend to have a better outlook than older people.
A report averaging several smaller studies found that people under age 65 generally had a 5-year survival rate of 78.8 percent following CHF diagnosis. The same report found that people over age 75 had an average 5-year survival rate of 49.5 percent following diagnosis.
Older people diagnosed with CHF may already have other chronic health conditions. This can make it difficult to manage CHF and create a more challenging outlook for them.
for congestive heart failure. The treatment thats best for you will depend on:
- your overall health
- any other health conditions you have
- how you respond to any medications
- what stage of CHF you have
Common options include:
There are lifestyle changes a person with CHF can make that have been shown to help slow the conditions progression. Talk with your doctor before making changes to your diet or starting an exercise routine.
Request A Hospice Evaluation
The primary physician may recommend hospice when the time is right. But as anyone who has faced a serious illness knows, patients and family members often must act as their own advocates to receive the care they need and deserve.
You, your loved one or your trusted physician may request an evaluation to see if hospice is an appropriate option for care.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get A Heart Attack
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and, in part, what caused it. Medications and lifestyle behaviors are part of every treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment is the same, regardless of gender.
As heart failure gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. Since you cant move backward through the heart failure stages, the goal of treatment is to keep you from moving forward through the stages or to slow down the progression of your heart failure.
Stage A treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage A heart failure includes:
- Regular exercise, being active, walking every day.
- Stopping the use of tobacco products.
- Treatment for high blood pressure .
- Treatment for high cholesterol.
- Not drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker if you have coronary artery disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
- Beta-blocker if you have high blood pressure.
Stage B treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage B heart failure includes:
Stage C treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage C HF-rEF includes:
If the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression to Stage D.
Stage D treatment
Caring For Someone At The End Of Their Life
When someone you love is facing the end of life, its an extremely worrying and upsetting time. Given the current situation with coronavirus, you might have lots of questions about what youre allowed to do, especially if your loved one is in a hospice or care home. Many care homes are limiting visitors but government guidance has specified that visiting loved ones who are at the end of their life is important and should continue. Check with your loved ones hospice or care home about what restrictions they have in place. Unfortunately, if you have coronavirus symptoms, you wont be able to visit a loved one. Government guidance states that carers are still able to perform their caring duties if the carer doesnt have coronavirus symptoms. If you live with the person you care for and you have coronavirus symptoms, the government are advising you to ask friends and family for help with providing care or contact your local authority or healthcare provider. If someone you care for has a heart condition, they are at higher risk of severe complications of coronavirus. Be mindful of this when visiting and always follow NHS guidance around hand washing and hygiene.
Also Check: How Do You Determine Your Target Heart Rate
Read Also: Does Pain Increase Heart Rate
Can You Prevent Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure can be the ultimate result of a number of diseases, or lifestyle choices, that damage the heart. Some of these can be prevented. Others cannot be prevented but can be treated successfully.
Some examples of illnesses or lifestyle choices that can lead to congestive heart failure are as follows:
- Coronary heart disease , including heart attack
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Congenital heart disease
- Infection
- Damage to the heart valves
- Alcoholism
- Smoking
In some cases, a family history of heart failure can be present. Many cases are a combination of factors, and in other cases, the cause is unknown.
If a person has congestive heart failure, they are at increased risk of developing pneumonia. They probably should receive both the pneumonia vaccination and annual flu shots. Patients should ask their doctor or other health care professional to be sure.
