Deoxygenated Blood Returns To Your Heart Through The Superior Vena Cava And Inferior Vena Cava To Your Right Atrium
- Capillaries separate oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood and arteries from veins
- After passing through the capillaries, blood is deoxygenated and needs to head back to the heart to be pumped to the lungs to pick up oxygen
- The Superior Vena Cava is the vein that gets deoxygenated blood from the upper body and returns it to the heart
- The Inferior Vena Cava is the vein that gets deoxygenated blood from the lower body and returns it to the heart
How Does Your Heart Work
Your heart is made up of 2 pumps. The pump on the right hand side receives blood that has already delivered its oxygen round the body and sends this blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen .
The pump on the left hand side receives oxygen-rich blood and then pumps it out into the arteries to deliver its oxygen around the body.
Supplying Oxygen To The Hearts Muscle
Like other muscles in the body, your heart needs blood to get oxygen and nutrients. Yourcoronary arteries supply blood to your heart. These arteries branch off from the aorta so that oxygen-rich blood is delivered to your heart as well as the rest of your body.
- The left coronary artery delivers blood to the left side of your heart, including your left atrium and ventricle and the septum between the ventricles.
- The circumflex artery branches off from the left coronary artery to supply blood to part of the left ventricle.
- The left anterior descending artery also branches from the left coronary artery and provides blood to parts of both the right and left ventricles.
- The right coronary artery provides blood to the right atrium and parts of both ventricles.
- The marginal arteries branch from the right coronary artery and provide blood to the surface of the right atrium.
- The posterior descending artery also branches from the right coronary artery and provides blood to the bottom of both ventricles.
Arteries supplying oxygen to the body. The coronary arteries branch off the aorta and supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. At the top of your aorta, arteries branch off to carry blood to your head and arms. Arteries branching from the middle and lower parts of your aorta supply blood to the rest of your body.
Some conditions can affect normal blood flow through these heart arteries. Examples include:
- The small cardiac vein.
Recommended Reading: Heart Bleeding Symptoms
Problems Of The Heart And Circulatory System
Problems with the cardiovascular system are common more than 64 million Americans have some type of cardiac problem. But cardiovascular problems dont just affect older people many heart and circulatory system problems affect children and teens, too.
Heart and circulatory problems are grouped into two categories: congenital and acquired .
Congenital heart defects. These abnormalities in the hearts structure are present at birth. Approximately 8 out of every 1,000 newborns have congenital heart defects ranging from mild to severe. These defects occur while the fetus is developing in the mothers uterus and its not usually known why they occur. Some congenital heart defects are caused by genetic disorders, but most are not. What all congenital heart defects have in common, however, is that they involve abnormal or incomplete development of the heart.
A common sign of a congenital heart defect is a heart murmur an abnormal sound thats heard when listening to the heart. Usually a heart murmur is detected by a doctor whos listening to the heart with a stethoscope during a routine exam. Murmurs are very common in children and can be innocent murmurs found in an otherwise healthy heart. Other murmurs can be caused by congenital heart defects or other heart conditions.
A blood test can measure if someones cholesterol is too high. A childs total cholesterol level is borderline if its 170 to 199 mg/dL, and its considered high if its above 200 mg/dL.
Structure Of The Heart
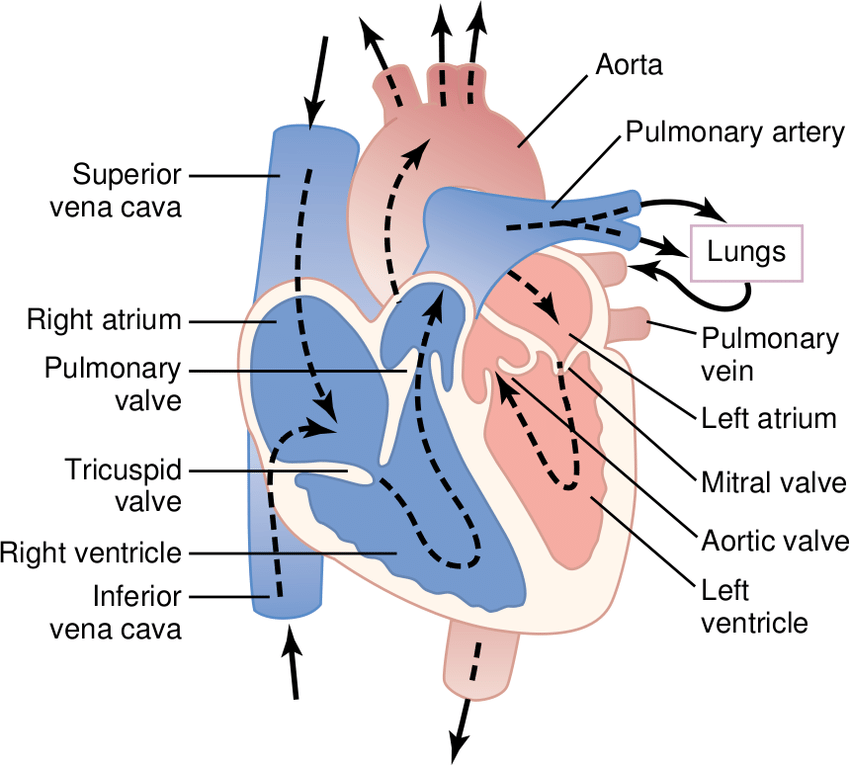
The heart has four chambers . There is a wall between the two atria and another wall between the two ventricles. Arteries and veins go into and out of the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood to the heart. The flow of blood through the vessels and chambers of the heart is controlled by valves.
Don’t Miss: Tylenol And High Blood Pressure
What The Heart And Circulatory System Do
The circulatory system works closely with other systems in our bodies. It supplies oxygen and nutrients to our bodies by working with the respiratory system. At the same time, the circulatory system helps carry waste and carbon dioxide out of the body.
Hormones produced by the endocrine system are also transported through the blood in the circulatory system. As the bodys chemical messengers, hormones transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. For example, one of the hormones produced by the heart helps control the kidneys release of salt from the body.
One complete heartbeat makes up a cardiac cycle, which consists of two phases:
In the systemic circulation, blood travels out of the left ventricle, to the aorta, to every organ and tissue in the body, and then back to the right atrium. The arteries, capillaries, and veins of the systemic circulatory system are the channels through which this long journey takes place.
Adding Oxygen To Blood
Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood enters the heart’s right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs.
The pulmonary artery then carries the oxygen-poor blood from your heart to the lungs. Your lungs add oxygen to your blood. The oxygen-rich blood returns to your heart through the pulmonary veins. Visit our How the Lungs Work Health Topic to learn more about what happens to the blood in the lungs.
The oxygen-rich blood from the lungs then enters the left atrium and is pumped to the left ventricle. The left ventricle generates the high pressure needed to pump the blood to your whole body through your blood vessels.
When blood leaves the heart to go to the rest of the body, it travels through a large artery called the aorta. A balloon-like bulge, called an aortic aneurysm, can sometimes occur in the aorta.
Read Also: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Flutters
Your Aorta Pumps Oxygenated Blood Out Of Your Heart To Your Body
- The aorta stretches across the back of your heart and pumps blood both above and below your heart to your upper and lower body
- As oxygenated blood goes to your cells, it drops off oxygen and picks up waste
- Cells in your body need oxygen so that they can perform cellular respiration to get energy
- Blood also picks up carbon dioxide from the cells as the waste product of cellular respiration
The Left Side Of The Heart
Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs passes through the pulmonary veins . It enters the left atrium and is pumped into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, the blood is pumped to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Like all of the organs, the heart needs blood rich with oxygen. This oxygen is supplied through the coronary arteries as its pumped out of the hearts left ventricle.
The coronary arteries are located on the hearts surface at the beginning of the aorta. The coronary arteries carry oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the heart.
Also Check: Can Tylenol Cause Heart Palpitations
Each Heart Beat Is A Squeeze Of Two Chambers Called Ventricles
The ventricles are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood empties into each ventricle from the atrium above, and then shoots out to where it needs to go. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, then pumps the blood along to the lungs to get oxygen. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium, then sends it on to the aorta. The aorta branches into the systemic arterial network that supplies all of the body.
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, as well as the side and back of the left ventricle. The left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
Also Check: How Does Blood Move Through The Heart
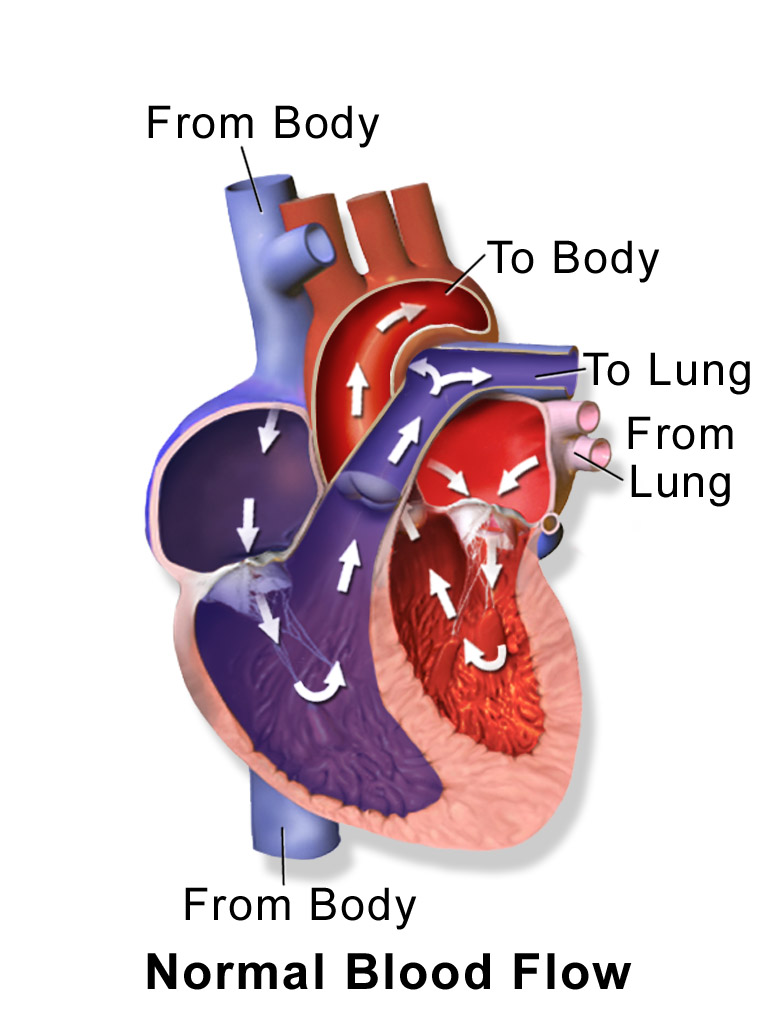
Blood Flow Through The Heart
Blood flows through the heart in 12 easy steps. Always remember that it must flow through 6 areas on the right side and then 6 areas on the left side . For better illustration, look at the picture below and note how the right and left side are separated.
The right side is in blue and the left side is in red. Study Tip: When you are having to memorize this for a test, think of the blood flow like this: There are 12 steps, 6 for the right and 6 for the left.
Blood Flow During Exercise
Blood flow within muscles fluctuates as they contract and relax. During contraction, the vasculature within the muscle is compressed, resulting in a lower arterial inflow with inflow increased upon relaxation. The opposite effect would be seen if measuring venous outflow.
This rapid increase and decrease in flow is observed over multiple contractions. If the muscle is used for an extended period, mean arterial inflow will increase as the arterioles vasodilate to provide the oxygen and nutrients required for contraction. Following the end of contractions, this increased mean flow remains to resupply the muscle tissue with required nutrients and clear inhibitory waste products, due to the loss of the inhibitory contractile phase.
You May Like: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How The Heart Works
The human heart pumps blood to every part of your body. Learn about the different parts of the heart and watch our video about how a healthy heart works.
Your heart is the pump which powers your body. It supplies blood carrying oxygen and nutrients to every cell, nerve, muscle and vital organ in your body.
It sits in your chest between your lungs, slightly to the left of centre, and is protected by your rib cage.
Your heart is about the size of your clenched fist and weighs about 300 grams .
Watch our step-by-step video of how the heart works
What Does The Circulatory System Do
The circulatory system is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart.
The circulatory system carries oxygen, nutrients, and to cells, and removes waste products, like carbon dioxide. These roadways travel in one direction only, to keep things going where they should.
Read Also: Does Tylenol Lower Blood Pressure
The Heart’s Control System
A heartbeat is caused by an electrical impulse traveling through the heart. The heart’s built-in electrical system controls the speed of its pumping. The electrical impulse originates in the sinus node which functions as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The sinus node is most often located in the top of the right atrium. The electrical signals travel through the heart tissue causing the atria and ventricles to contract and relax and the blood to be pumped to the body.
The Structure Of The Heart
The heart is a two-sided pump made up of four chambers: the upper two chambers called atria and the lower two called the ventricles.
- On the right side of the heart, the right atrium and right ventricle work to pump oxygen-poor blood returning from the body back to the lungs to be reoxygenated.
- On the left side of the heart, the left atrium and left ventricle combine to pump oxygenated blood back through the body.
- Muscular walls, called septa or septum, divide the heart into two sides and keep the two kinds of blood from mixing.
Read Also: Can Dehydration Cause Increased Heart Rate
Heart Trivia: How Much Blood Does Your Heart Pump Each Day
By Adam Pick on March 18, 2009
Any guesses as to how much blood your heart pumps each day?
Need a hint? Its more than 10 gallons.
Need another hint? Its more than 100 gallons.
To find out how much blood your heart pumps each-and-every day of your life Scroll down below the beating heart animation.
According to The Texas Heart Institute, most healthy hearts can pump up to 2,000 gallons of blood during each twenty-four hour period. Isnt that incredible?
I just did the math. During the time you just read this blog , your heart pumped 1.38 gallons of blood through your body!!!
Why am I writing about this? Well This is exactly why our heart valves need to function properly. If our valves do not open-and-close tightly, the heart needs to pump even more blood which puts additional strain on the heart. If the heart works overtime for long periods of time, the cardiac muscle can thicken, dilate and, ultimately, fail.
Keep on tickin!
Heart Diagram Parts Location And Size
Location and size of the heart
Normal heart anatomy and physiology
Normal heart anatomy and physiology need the atria and ventricles to work sequentially, contracting and relaxing to pump blood out of the heart and then to let the chambers refill. When blood leaves each chamber of the heart, it passes through a valve that is designed to prevent backflow of blood. There are four heart valves within the heart:
- Mitral valve between the left atrium and left ventricle
- Tricuspid valve between the right atrium and right ventricle
- Aortic valve between the left ventricle and aorta
- Pulmonic valve between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
How the heart valves work
Read Also: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
Left Side Of The Heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
Your Heart Beats To The Signals Of The Sa Node And Av Node As The Right Atrium Pumps It To The Right Ventricle
- From the superior and inferior vena cava, blood goes through the Right Atrium
- First, the SA Node sends electrical signals to pump blood from right atrium to right ventricle
- Then, as blood enters the right ventricle, the AV Node receives a signal to act as the gateway to the right ventricle and control the speed of blood flow there
- The SA and AV node combine to make the ba-bum sound of your heartbeat
- Blood goes through the tricuspid valve/right AV valve as it enters the right ventricle
Don’t Miss: Can Antihistamines Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are The Parts Of The Heart
Your heart is a bit like a house. It has:
- outer walls
- electrics .
Heart walls
The walls of your heart are made of powerful muscle tissue, which squeezes and relaxes to pump blood around your body. This muscle tissue is divided into three layers.
- The endocardium .
- The myocardium .
- The epicardium .
Heart chambers
Your heart is made up of four chambers, two on the right and two on the left. These are like the rooms of your house.
The top two chambers are called the left and right atrium and the bottom two are called the left and right ventricles.
They are divided by a thin wall called the .
Heart valves
There are four heart valves, which act like doors between the chambers of the heart. They open and close as your heart pumps.
The valves only open one way. This stops blood flowing in the wrong direction between the chambers of your heart.
The two valves that sit between the upper and lower chambers of the heart are called the atrioventricular, or AV valves.
The tricuspid valve is the door between the right atrium and ventricle.
The mitral valve is the door between the left atrium and ventricle.
The other two valves are the doors out of the ventricles. They are called semilunar, or SL valves.
The aortic valve is the door out of the left ventricle into the aorta.
The pulmonary valve is the door out of the right ventrical into the pulmonary artery.
The blood vessels
How the heart pumps
The heart’s conduction system
How the heart pumps
The coronary arteries
