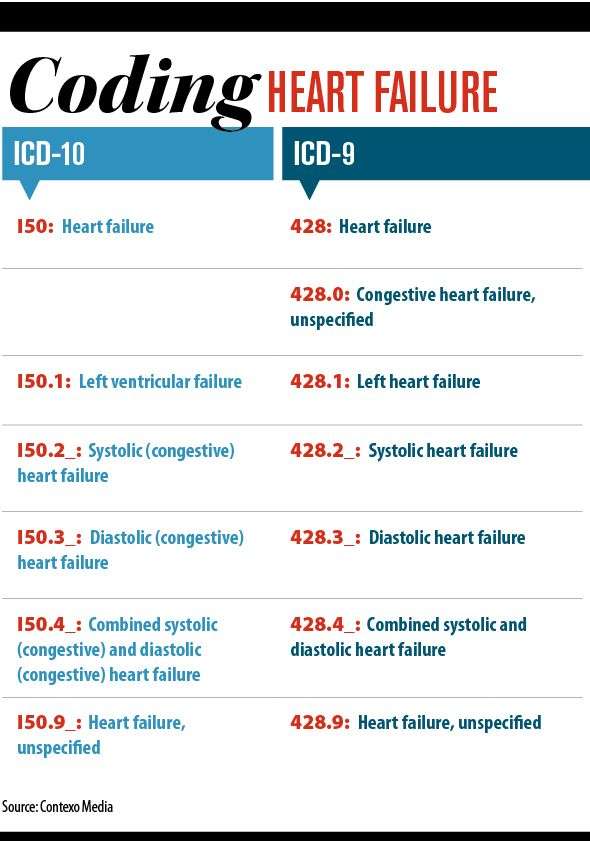
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized head to toe into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I50.9:
Inclusion Terms
Read Also: Can Ibs Cause Palpitations
What Is The Icd 10 Code For Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
3.9/5codeheart failureheart failureheart failureCodingacute
Consequently, what is the ICD 10 code for decompensated heart failure?
Acute on chronic diastolic heart failureI50. 33 is a billable/specific ICD10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD10-CM I50. 33 became effective on October 1, 2019.
Likewise, what is the code for congestive heart failure? ICD-10 has no code for congestiveheart failure the term is included in code I50. 9 Unspecified heart failure.
Beside this, what does decompensated mean in heart failure?
Specialty. Cardiology. Acute is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress.
What is stage a heart failure?
Stage A is considered pre-heart failure. It means you are at high risk of developing heart failure because you have a family history of heart failure or you have one of more of these medical conditions: Hypertension. Diabetes. Coronary artery disease.
Acute On Chronic Systolic Chf Icd 10
The Acute On Chronic Systolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.23.
ICD 10 has a different subcategory of codes for both systolic and diastolic heart failures, I50.2 for systolic, and I50.3 for diastolic heart failure. If the diagnosis is described as only systolic but acute and chronic, the code, under this subcategory I50.23, is complete code for this condition. If the provider has not mentioned systolic or diastolic, never use code from the I50.3 or I50.2 category.
Also Check: How To Cure Congestive Heart Failure
Acute On Chronic Diastolic Chf Icd 10
The Acute On Chronic Diastolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.33.
When looking at diastolic under failure/heart in the alphabetic index, the ICD 10 system provides subcategory I50.3 for diastolic heart failure. Under this category, several codes according to different specified descriptions are provided I50.33 at the bottom of this subcategory is the code of choice to fully describe the condition acute on chronic diastolic heart failure.
How To Code If No Cause For Heart Failure Is Documented
If no cause for heart failure is spcified in the note, it is better to code just the heart failure diagnosis alone , even if a secondary diagnosis is present in the note, such as hypertension. In other words, the medical coder does not have the liberty to makes the connection between another condition and heart failure, unless it is already present in the chart. In such a case, the coder should assign separate codes for the two conditions.
Also Check: How To Lower Resting Heart Rate Immediately
Acute Systolic Chf Icd 10
If the patients condition is acute, the second code under this subcategory should be used for reimbursement purposes. If the medical note states that the patients condition has been worsening or there is an emergency condition of chronic failure but does not document it as acute, do not presume it as an acute condition.
A query to the medical doctor would work here best asking about the exact condition. The ICD 10 code for acute systolic CHF is I50.21.
What Is Htn With Chf
Hypertension can be defined as chronic high blood pressure, causes can be environmental or genetics but it mostly leads to heart failure in most patients. The most important effect of hypertension is on the left ventricle making it weak and causing hypertrophy of the ventricle. Whenever HTN becomes the developmental factor of CHF, its called hypertensive heart disease.
You May Like: How Many People Died From Heart Disease In 2020
Unspecified Systolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.20 other international versions of ICD-10 I50.20 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Coding For Congestive Heart Failure
April 23, 2021 / By Rebecca Caux-Harry
I was reading an article the other day about a young man who developed severe biventricular heart failure after consuming a large quantity of an energy drink every day for 2 years. I remember my days as a college student and the need to be mentally alert for my classes and studies. We didnt have energy drinks at that time, but there were, and still are, caffeine pills. I tried them once or twice and found myself so overwhelmed by the caffeine side effects that there was no benefit. I guess I was lucky in that way.
While the young British student is expected to make a partial to full recovery with ongoing treatment, the article got me thinking about the ICD-10 codes for congestive heart failure . CHF is when the heart muscle doesnt pump blood to the rest of the body as it should. The condition is usually progressive, meaning most people arent cured, but rather managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
When I first started coding, we only had 3 ICD-9 codes for CHF: 428.0, 428.1 and 428.9. A few years later, those codes were expanded with specificity for acuity and type . Now, with ICD-10 we have a wide variety of codes to choose from, but as always, selection of the most accurate and specific code depends entirely on the physicians documentation.
Rebecca Caux-Harry, CPC, is a professional fee coding specialist with 3M Health Information Systems.
You May Like: Does Fever Increase Heart Rate
Validity Of Heart Failure Diagnoses
The validation statistics reported by each of the included studies are provided in Table 2. Sensitivity was reported by 14 studies, and was â¥69% in half of them . PPV was undefined in one of the studies , but was at least 87% in nine of the 17 remaining studies . Specificity was â¥95% in all 13 studies reporting this statistic, and NPV was â¥88% in all but two of the 14 studies where this data was available. Kappa was only reported in six studies , , , , , . The values in three of the studies indicated there was moderate agreement between the diagnostic codes and reference standard, while those in the other three indicated there was substantial to almost perfect agreement.
What Is Acute On Chronic Chf
When heart muscles are damaged chronically, the term Chronic is used to define such a condition but sometimes, a chronically damaged heart can get a viral infection, certain vessels blockage, or shortness of breath leading to acute heart failure of chronic CHF. Medical professionals call it acute on chronic heart failure. The simple definition could be Sudden onset of chronic heart condition.
You May Like: What Is A Normal Heart Rate
Acute On Chronic Chf Icd 11
The Acute On Chronic CHF ICD 11 codes are BD10 and XT5R/XT8W.
Currently, there is no combination code available to describe acute on chronic diastolic heart failure. The main stem code BD10 is used with either acute XT5R or chronic XT8W as available extension codes.
Other extensions for severity and type of heart failure with complexity are available to extend the diagnosis code in ICD-11 but the main stem code is the same for all conditions related to congestive heart failure.
Chronic Systolic Chf Icd 10
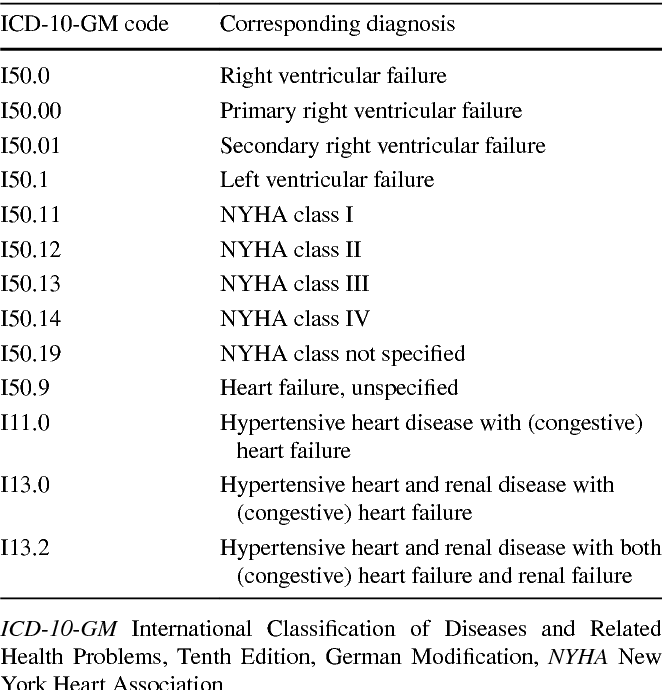
The Chronic Systolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.22. The third code in this category as chronic systolic heart failure I50.22 is the code of choice here. The main code has excluded notes beneath it that states that a code cannot be used here if there is a combination of the acute and chronic condition of systolic/diastolic heart failure.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Heart Attack
Q& a: Documentation For Coding Heart Failure
Sharme Brodie,RN, CCDS
Q: If the documentation states, diastolic heart failure euvolemic or diastolic HF hypervolemic, can we code chronic diastolic HF and acute diastolic HF, respectively?
A: Unfortunately, you may not like my answer, which is no, this documentation would not be acceptable to pick up either diagnoses of chronic or acute diastolic heart failure.
Code assignment is based on the physician documentation of the type and acuity of the HF. Euvolemic is a medical term that implies the patient appears to have normal circulatory or blood fluid volume. Hypervolemia or fluid overload is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood, because not every patient is in fluid overload or hypervolemia at the time of admission, many physicians are now use HF versus congestive heart failure in their documentation.
There are many types of HF, and CHF is just one type. There is a code in ICD-10-CM for fluid overload: E87.70, Fluid over, unspecified. This is also where hypervolemia would be coded.
Now, in AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2016, it did state that HFpEF could be referred to as diastolic heart failure and that HFrEF could be referred to as systolic heart failure. This advice supersedes information previously given in Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2014. This is why its very important to keep up with the advice given by Coding Clinic.
Fransoo Et Al And Fransoo Et Al
- In The 2013 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. and The 2019 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. residents were considered to have CHF if they met one of the following conditions:
- one or more inpatient hospitalizations in one year with a diagnosis for CHF: ICD-9-CM code 428 or ICD-10-CA code I50 OR
- two or more physician visits in one year with a diagnosis for CHF .
- section 4.10 Congestive Heart Failure Prevalence in the 2019 deliverable.
Only Manitoba residents aged 40 and older were included.For more information, please see:
Recommended Reading: Does Caffeine Increase Heart Rate
Treatment For Congestive Heart Failure
There are several medications that can be used to treat CHF. The first is ACE inhibitors. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors open up narrowed blood vessels to improve blood flow. Vasodilators are another option if you cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors. ACE inhibitors shouldnt be taken with the following medications without consulting with a doctor, because they may cause an adverse reaction. The second type of medication is beta-blockers. Beta-blockers can reduce blood pressure and slow rapid heart rhythm. Beta-blockers should be taken with caution with the following medications, as they may cause an adverse reaction. The third type of medication is diuretics. Diuretics reduce your bodys fluid content. CHF can cause your body to retain more fluid than it should. Thiazide diuretics cause blood vessels to widen and help the body remove any extra fluid. Loop diuretics cause the kidneys to produce more urine. This helps remove excess fluid from your body. Potassium-sparing diuretics help get rid of fluids and sodium while still retaining potassium. If medications arent effective on their own, more invasive procedures may be required. Angioplasty, a procedure to open up blocked arteries, is one option. Your cardiologist may also consider heart valve repair surgery to help your valves open and close properly.
The table below includes the most commonly used ICD-10 codes for Congestive Heart Failure:
| ICD-10 Chapter |
|---|
Acute On Chronic Combined Systolic And Diastolic Chf Icd 10
The acute on chronic combined systolic and diastolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.43.
A combined condition of systolic and diastolic CHF is not a very common but dangerous condition. In this abnormal situation, a heart neither contract nor relax properly between beats leading to a serious medical condition. If a medical note states that the patient has acute on chronic with combined diastolic and systolic heart failure, ICD-10 has provided a combination code to fully describe this condition.
The main term combined after following failure/heart in the alphabetic index will lead to subcategory I50.4. The combination code for reimbursement purposes is I50.43.
Also Check: What Should My Heart Rate Be Working Out
Index To Diseases And Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code. The following references for the code I50.9 are found in the index:
- cardiacSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- cardiovascularSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- heartSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- myocardialSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- cardiacSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- SyndromeSee Also: Disease
Dont Miss: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Chronic Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.32 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.32 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.32 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.32 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Don’t Miss: What Is My Resting Heart Rate
Unspecified Combined Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- Edema of lung with heart disease NOS
- Edema of lung with heart failure
- Left heart failure
- Pulmonary edema with heart disease NOS
- Pulmonary edema with heart failure
- edema of lung without heart disease or heart failure
- pulmonary edema without heart disease or failure
Determine The Cause Of Heart Failure
One of the most important things you understand, when coding for heart failure, is that there can be many very different reasons why somebody can develop heart failure, and the ICD-10-CM coding system, as complex as it is, allows for very fine granuation in this respect. Therefore, your first decision to make, when looking for a code to use, is to determine, from the note, what is the underlying cause for heart failure. To illustrate, I am listing a few of the more common ICD-10 codes for heart failure based on cause:
- I11.0 Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure
- I09.81 Rheumatic heart failure
- I97.131 Postprocedural heart failure following other surgery
- I97.130 Postprocedural heart failure following cardiac surgery
- I13.0 Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease
- P29.0 Neonatal cardiac failure
Note that none of the above conditions where heart failure is present use the root I50 for buidling the ICD-10 code.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If You Had A Heart Attack
Conquer All Your Heart Failure Icd
Hint: Report I50.21 for acute systolic heart failure.
Heart failure can be tricky to code because you may see numerous acronyms, and you need to decipher whether its chronic, acute, or acute on chronic. If you dont pay close attention to all of the details in the documentation, you run the risk of reporting the wrong code.
Learn which codes you will report for different types of heart failure to always report clean claims in your cardiology practice.
Differentiate Between Systolic, Diastolic Heart Failure
When a patient has heart failure, their heart does not adequately pump blood to meet their bodys need for blood and oxygen. This, in turn, can cause blood and fluids to back up in the patients body in their lungs, hands, or feet.
Heart failure can be categorized as systolic or diastolic, says Rebecca Sanzone, CPC, CPMA, quality assurance specialist at St. Vincent Medical Group/ Accension Health and coding consultant at the American College of Cardiology.
Systolic heart failure: HFrEF is the acronym for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, which is also known as systolic heart failure. When a patient has systolic heart failure, the left ventricle of their heart is not able to contract normally, so their heart cant pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation.
The clinical definition of systolic heart failure is an ejection fraction < 50%, Sanzone explains.
In diastolic heart failure, the ejection fraction > = 50%, Sanzone adds.
Diastolic Chf Icd 11 Code
The Diastolic CHF ICD 11 Code is BD10. ICD 11 does not have category and subcategory but these terms are named as stem code and extensions respectively. The main stem code is the same just like the category in ICD-10 BD10 there is no code for exacerbation.
There are some extensions about types of heart failure that are divided based on code rules of ICD-11 like if there is an effect on physical activity or not and others. Currently, BD10 with an acute extension should be used to code this condition.
Don’t Miss: What Is Good Resting Heart Rate
What Is Diastolic Chf
Diastolic heart failure occurs when a heart is unable to relax fully, making ventricles deprived of enough blood to pump the blood to other organs. The volume and pumping force decreases significantly making the heart as well as other body areas deprived of oxygenated blood significantly. Doctors use different medications as well as surgical options to treat this condition.
Acute Diastolic Chf Icd 10
When improper relaxation becomes an emergency condition, a doctor calls it an acute diastolic condition. The first code under the main subcategory, I50.31 is the most appropriate code for this condition.
If the provider has described the condition as an acute one, a coder cannot self-analyze the condition even if the treatment is described as an emergency one in medical notes. The ICD 10 code for acute CHF diastolic is I50.31.
You May Like: How Long After Open Heart Surgery Can You Travel
