Treating Chf In Louisiana
For patients suffering from CHF, skilled medical treatment is critical to managing the condition and maintaining health. Cardiovascular Institute of the South is home to many renowned and respected cardiologists. Our physicians are experienced and highly-qualified in the treatment of congestive heart failure, along with all other forms of cardiovascular disease. To request an appointment at any one of our locations across south Louisiana and Mississippi, click the button below.
What Happens If You Have Heart Failure
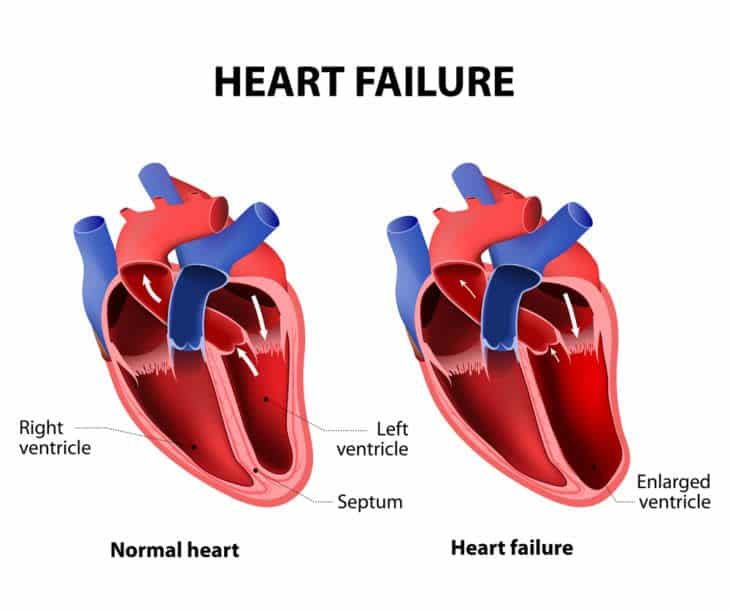
People with heart failure have weak hearts that dont work as well as they should. Over time, the illness causes significant damage to the body.
In the first stages, the heart is less effective. It stretches, grows bigger, and pumps faster to compensate for the lack of strength. The body also changes, with arteries getting smaller and blood being directed away from certain body parts. Many people with heart failure dont know they have a problem in these early stages.
Towards the end stages of CHF, symptoms will worsen even if lifestyle changes are made, and the body will be unable to compensate for the loss of blood flow. As soon as that happens, the person may start to feel tired, have trouble breathing, and have other problems.
People can get help managing their end stages congestive heart failure symptoms and slowing down the progress of their condition with a variety of treatments. Its a long-term condition that cant be cured, as well as heart failure. People will eventually reach the end stages of heart failure.
Even when the person is lying down, they feel a shortness of breath. Their symptoms can change rapidly over a short period of time.
What Are The Symptoms Of End
Heart Failure: Quick Facts
1. More than 6 million U.S. adults have heart failure.
2. About half of people who develop heart failure die within 5 years of diagnosis.
3. Most people with end-stage heart failure have a life expectancy of less than 1 year.
4. The leading causes of heart failure are diseases that damage the heart, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Heart failure worsens over time, so symptoms are most severe during the final stages. It causes fluid to build up in the body, which produces many of these symptoms:
- Shortness of breath . In the final stages of heart failure, people feel breathless both during activity and at rest.
- Persistent coughing or wheezing. This may produce white or pink mucus. The cough may be worse at night or when lying down.
- Weight gain or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
- Tiredness, weakness.
In addition, people in the final stages of heart failure may suffer from:
- depression, fear, insomnia, and isolation
- anxiety about their future
- trouble navigating the health care system
Recommended Reading: Does Drinking Raise Your Heart Rate
Stage B Treatment Options
While stage A CHF is managed with lifestyle changes, the treatment plan for stage B typically includes taking medications regularly. People at this stage should still make the same lifestyle changes as those appropriate for stage A. However, your doctor may also prescribe additional treatments such as:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Beta blockers if youve had a heart attack and your EF is 40% or lower, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Possible surgery or intervention as a treatment for coronary artery blockage, heart attack, valve disease, or congenital heart disease
When To Seek Help
Patients with a life expectancy shorter than six months are eligible for hospice care. A hospice provides additional aid and resources to assist the person in living comfortably and with the highest possible quality of life. Hospice caregivers can also help patients and their families plan for future needs and circumstances. They have a unique insight into how to assist those with these difficulties.
Patients with end-stage heart failure need medical continuity throughout outpatient programs. These are just some of the symptoms that hospice care might help with. Positive inotropic drug infusions, anxiolytics, and sleeping medicines are all viable treatments. Its challenging for patients, families, and doctors caring for patients with end-stage heart failure to identify when treatment goals shift from survival to quality of life, allowing for a peaceful and dignified death.
Read Also: Does Covid Cause Heart Attacks
Interactive Multiple Choice Questions
This Education in Heart article has an accompanying series of six EBAC accredited multiple choice questions .
To access the questions, click on BMJ Learning: Take this module on BMJ Learning from the content box at the top right and bottom left of the online article. For more information please go to: Please note: The MCQs are hosted on BMJ Learningthe best available learning website for medical professionals from the BMJ Group.
If prompted, subscribers must sign into Heart with their journal’s username and password. All users must also complete a onetime registration on BMJ Learning and subsequently log in on every visit.
Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
Stages of congestive heart failure are based on the severity of a patients current symptoms.
In Stage 1, patients are determined to have weakness in their heart muscle, but do not yet have the symptoms or structure of congestive heart failure.
In Stage 2, patients have structural heart disease, but still do not present with the signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure.
In Stage 3, patients experience symptoms that limit their everyday activities. These can include shortness of breath, fluid in the lower extremities, chest pain, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and fatigue.
In Stage 4, symptoms will worsen for the patient and will not improve with treatment. This is the final stage of congestive heart failure.
There are a number of factors that influence how long a patient will remain in the earlier stages and consequently how long they can live with congestive heart failure. These include how well the heart is functioning, age, lifestyle changes, response to treatment, and comorbidities .
Conditions including high blood pressure, diabetes, alcoholism, a previous heart attack, heart valve disease, and coronary artery disease can all contribute to congestive heart failure.
Recommended Reading: Breathing Exercises To Lower Heart Rate
Living With Congestive Heart Failure: What To Expect
Yes, there are several lifestyle changes you should take into account if youve been diagnosed with congestive heart failure. But remember your diagnosis doesnt mean you should necessarily stop doing things you love.
You are supposed to be exercising walking, biking, swimming, or doing light weight exercises, says Mountis. The American Heart Association recommends at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity aerobic activity at least five days a week for optimal heart health. Avoid exercises that make you feel breathless, and make sure to talk to your doctor before starting a new exercise routine.
Your healthcare provider will also likely suggest dietary changes that can help reduce the swelling associated with congestive heart failure and slow the progression of the condition. Those changes may include following a low- or reduced-salt diet, or reducing how much fluid you drink to lessen the bodys water content.
Other lifestyle changes that can slow the progression of heart failure include:
Take Care Of Your Mental Health Too
While stress is never pleasant, it can be especially hard on your heart. Anger management is also an important aspect of heart health.
Talking with a therapist or joining a support group can help with keeping your stress levels down and giving you accountability for the lifestyle changes youre making.
You May Like: Which Of The Following Is Also Called A Heart Attack
What Do The Classifications Really Mean
Heart failure is staged and classified by healthcare providers but what do they really mean. HF exists along a continuum. It can go from non-existent to mild to moderate to advanced, all over a period of time. Managing heart failure depends on the stage and can include the use of medications, lifestyle behaviors, and cardiac devices.
Mild heart failure may be evident when you experience minimal symptoms, such as shortness of breath, when involved in certain kinds of physical activity or maybe present without any symptoms. With early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and medication, people with mild to moderate heart failure generally lead normal lives. Moderate heart failure is often classified along with mild HF. The same treatment approach is indicated.
Refractory congestive heart failure occurs when symptoms continue to be present even after routine treatment. This is also called advanced heart failure or end-stage heart failure. It occurs when a person is not responding to or getting worse despite treatment.
Prognosis At Each Stage
The outlook for CHF varies greatly between people, as there are many contributing factors for every individuals situation. However, generally speaking, if CHF is discovered in its earlier stages and properly managed, you can expect a far better outlook than if its discovered much later.
Some people whose CHF is discovered early and treated promptly and effectively can hope to have a nearly standard life expectancy.
Read Also: Why Does My Heart Rate Increase After Drinking Alcohol
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure is a severe progressive condition that affects the pumping power of heart muscles. Because of decreased cardiac output, the organs get inadequate blood, oxygen, and nutrients. Congestive heart failure usually affects the lungs, heart, and kidneys. A decrease in cardiac output causes kidneys to retain water and salt. Because of the increased water retention, other organs get congested, leading to increased pressure on the heart.
Supporting Those Around The Patient
Those close to the patient may also need emotional and practical support. They may need:
- information about heart failure to help them understand the symptoms and treatment options
- support if they’re caring for the patient
- time to relax or look after their own health.
If the patient’s heart failure is due to an inherited heart condition, their family may have concerns about their own health. Talk to them about their worries. It might be appropriate to refer immediate family members to a clinic which specialises in inherited heart conditions. This may have been done when the patient was first diagnosed.
Inherited heart conditions services offer specialist assessment and investigations, genetic counselling and testing. GPs can refer to this service.
Recommended Reading: Best Hospitals For Heart Surgery
What Are The Stages Of Chf
Congestive heart failure is a progressive condition that can worsen over time. Depending on the severity of CHF and its associated symptoms, cases are classified into one of four potential categories:
|
Stage |
||
|
Stage I CHF can typically be managed through lifestyle modifications and medicaiton. |
||
|
Physical activity may lead to symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. |
Management of Stage II CHF is very similar to Stage I but may require more careful monitoring. |
|
|
Any physical activity is likely to result in notable symptoms, more severe than Stage II. |
Treatment of Stage III CHF is far more complicated than lower stages. Consult with a cardiologist to learn more. |
|
|
Symptoms are always present, even while at rest. Physical activity is likely not possible. |
Stage IV CHF has no cure, but there are options available to increase patient comfort. Speak with a cardiologist to learn more. |
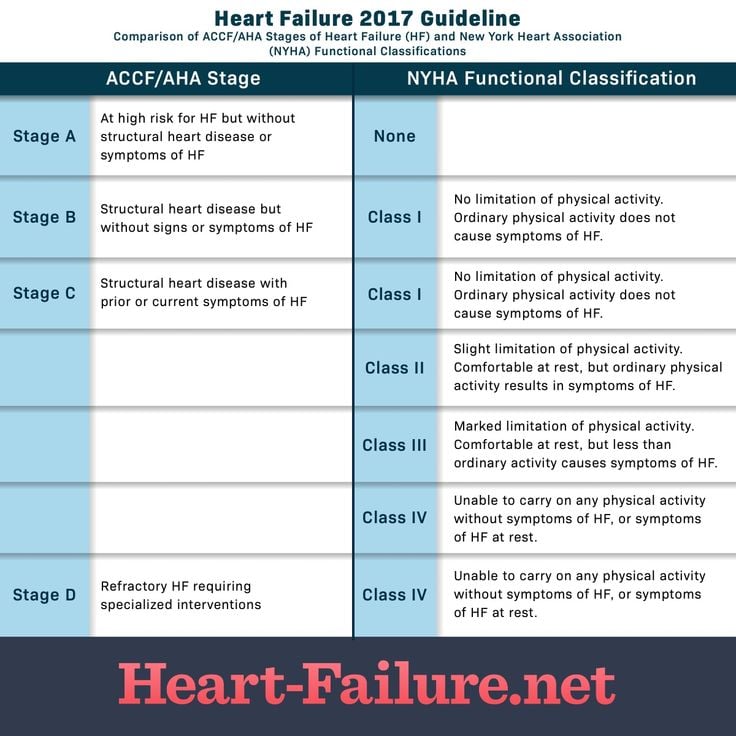
Classes Of Heart Failure
Doctors usually classify patients’ heart failure according to the severity of their symptoms. The table below describes the most commonly used classification system, the New York Heart Association Functional Classification1. It places patients in one of four categories based on how much they are limited during physical activity.
| Class | Patient Symptoms |
| I | No limitation of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not cause undue fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea . |
| II | Slight limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest. Ordinary physical activity results in fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea . |
| III | |
| IV | Unable to carry on any physical activity without discomfort. Symptoms of heart failure at rest. If any physical activity is undertaken, discomfort increases. |
| Class | |
| No objective evidence of cardiovascular disease. No symptoms and no limitation in ordinary physical activity. | |
| B | Objective evidence of minimal cardiovascular disease. Mild symptoms and slight limitation during ordinary activity. Comfortable at rest. |
| C | Objective evidence of moderately severe cardiovascular disease. Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms, even during less-than-ordinary activity. Comfortable only at rest. |
| D | Objective evidence of severe cardiovascular disease. Severe limitations. Experiences symptoms even while at rest. |
For Example:
- A patient with severe anginal syndrome but angiographically normal coronary arteries is classified:
- Functional Capacity IV, Objective Assessment A
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Heart Palpitations From Alcohol
What Does Moving To Hospice Care Involve
If you and your family have made the decision to pursue hospice care while receiving inpatient care, a case manager or social worker can help facilitate the process. If you are at home and would like to transition to hospice care, hospice agencies can help make the arrangements. Hospice agencies will review your needs and have a doctor order the appropriate medications for you. These medications will focus not on treating your condition, but on managing your symptoms and comfort as much as possible.
Congestive Heart Failure Stages
There are four stages of congestive heart failure. Stage 1 is often known as Pre-CHF and can consist of heart disorders that are not directly related to CHF, or a weakness in the heart that is noticed but has not yet caused any symptoms. Patients with Stage 2 CHF might experience some symptoms but are otherwise still healthy. Often, these patients have existing heart complications but lack the symptoms that make it immediately clear that they are dealing with congestive heart failure. Stage 3 of CHF often includes symptoms that are experienced regularly, and patients in this stage may or may not be able to keep up with their regular, everyday tasks. Patients with Stage 4 CHF experience severe or debilitating symptoms, even while at rest.
Don’t Miss: How To Rule Out Heart Attack At Home
Mechanical And Surgical Management Of End Stage Heart Failure
Fig 11 presents a suggested algorithm for the treatment of patients with end stage heart failure. In patients with reduced LV function , sinus rhythm, left bundle branch block or echocardiographic signs of ventricular dyssynchrony and QRS width 120ms, who remain symptomatic despite optimal medical treatment, cardiac resynchronisation therapy using biventricular pacing improves symptoms and exercise capacity while decreasing hospitalisations and mortality.1,2,3,23,24,25 In the COMPANION trial, heart failure patients in NYHA class IIIIV with LVEF 35% and QRS width 120ms were randomised to optimal pharmacological treatment alone or in combination with either CRT or CRT plus implantable cardioverterdefibrillator .23 Importantly, while mortality was reduced in both device arms there was no significant difference in mortality between CRT and CRT/ICD. Therefore, currently available data indicate that the use of an ICD in combination with CRT should be based on the indications for ICD therapy.3
Table 3Absolute and relative indications for heart transplantation
What Is An Ejection Fraction
An ejection fraction is a measurement of the blood pumped out of your heart with each beat, expressed in a percentage. It can be measured using an echocardiogram , multigated acquisition scan, nuclear stress test, magnetic resonance imaging , or during a cardiac catheterization. A normal ejection fraction is between 50% and 70%.
You May Like: Does Lack Of Sleep Increase Heart Rate
Emotional Symptoms Towards The End Of Life
People with heart failure may experience different emotions and feelings. They may feel:
- up and down, with good days and bad days
- like they lack control over their life
- like it’s hard to cope with the reactions of others.
People may not think heart failure is as serious as other illnesses, such as cancer. Patients with heart failure can look well even when they feel very ill.
If a patient has anxiety or depression, their healthcare team will assess how it affects them and whether they need treatment, such as cognitive behavioural therapy or medication.
You can support the patient by providing emotional care and helping them with activities to make them feel better, such as reading, going outside and listening to music or audio books. Find out more about providing emotional care.
Talk To Them About Their Symptoms
People with heart failure may feel worried about their symptoms, treatment or risk of dying suddenly. Reassure them by talking openly and honestly about their concerns. Speak to their cardiac or palliative care team if you need support. If the patient has a plan for managing symptoms or emergencies, they may feel less anxious.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Slow Heart Rate Mean
Prognosis At Different Ages
In general, younger people diagnosed with CHF tend to have a better outlook than older people.
A report averaging several smaller studies found that people under age 65 generally had a 5-year survival rate of 78.8 percent following CHF diagnosis. The same report found that people over age 75 had an average 5-year survival rate of 49.5 percent following diagnosis.
Older people diagnosed with CHF may already have other chronic health conditions. This can make it difficult to manage CHF and create a more challenging outlook for them.
for congestive heart failure. The treatment thats best for you will depend on:
- your overall health
- any other health conditions you have
- how you respond to any medications
- what stage of CHF you have
Common options include:
There are lifestyle changes a person with CHF can make that have been shown to help slow the conditions progression. Talk with your doctor before making changes to your diet or starting an exercise routine.
