What Is Heart Rate
The cardiovascular system circulates blood throughout the body in order to supply oxygen and other nutrients and to remove waste products. Each time the heart beats blood is pumped out of the heart and into the body to supply oxygen to working muscles or to the lungs for re-oxygenation. Heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute, and is directly related to the workload being placed on the heart. When the body is in a resting state , resting heart rate is measured. A normal resting heart rate ranges from 60-100 beats per minute . Resting rates higher than 100 bpm suggest that the heart is working too hard to circulate blood, and thus may indicate a serious problem that should be monitored by a physician. Resting rates lower than 60 bpm occur more often with endurance-trained athletes whose bodies are more efficient at utilizing oxygen from the blood.
Herbal Remedies To Control Heart Rate
Herbal Remedies to Control Heart Rate Are you witnessing any signs of fast heart speed? Is your heart beating slowly? Do you feel any shortness of breath? This could a sign of warning for you. The heart is a delicate organ of our cardiovascular system. Todays life may be modern with technology to serve us but our body has been affected a lot by our careless and lazy attitude towards our health. This has lead to the increasing concerns of this miraculous organ of our body and emergence of heart ailments such as Heart attack, Tachycardia, and Palpitations etc. So in this blog, we are sharing herbal remedies to control heart rate.
Exercise Moderately At Least Two And A Half Hours Each Week
If youd rather go hard, you can get the same heart-healthy benefits with 75 minutes of vigorous activity. Exercise intensity is unique to you. Exercise thats moderate intensity for you may be vigorous for someone else. Moderate exercise should feel somewhat difficult, but you should still be able to carry on a conversation. Vigorous exercise should feel very challenging and youll only be able to get a few words out at a time between breaths.
Don’t Miss: Can Benadryl Cause Arrhythmias
Breathing Rate As The Driving Force
Owing to the design of the experiment, the breathing rate during guided intervals was intended to be constant. However, experiments demonstrated that individuals were unable to follow the metronomes rate exactly, so there was a variability in instantaneous breathing rate. Additionally, swallowing or coughing were observed in a few cases. However, the mean breathing rates matched the guided values set by the metronome. Figure highlights how closely volunteers followed the metronome: relative to the normalised interval 2 , the mean rates for interval 1 and 3 are very close to values of 0.9 and 1.2 , as intended by the experimental procedure. For this volunteer , the deviation from the mean for each interval is less than 4%. The mean and standard deviation of the breathing rate for all intervals and volunteers are shown in Table of Supporting Information . For most intervals, the standard deviation is less than 10%. The standard deviation of the breathing rate defines the minimal possible step increments between guided breathing rates. The values for the standard deviation of breathing rates obtained for our cohort confirm that the selected 10% and 20% incremental changes with respect to the RHR guarantee a statistically significant change in the mean value of the breathing rate between intervals of guided breathing.
Figure 2
Influences From The Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular centres
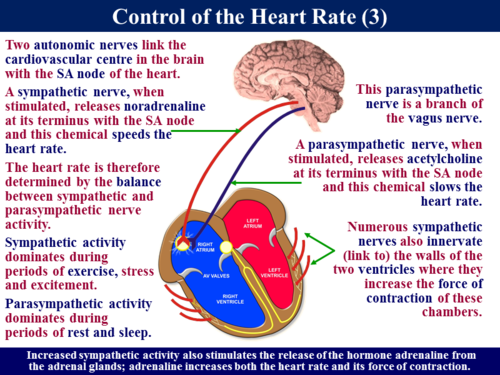
The heart rate is rhythmically generated by the sinoatrial node. It is also influenced by central factors through sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Nervous influence over the heart rate is centralized within the two paired cardiovascular centres of the medulla oblongata. The cardioaccelerator regions stimulate activity via sympathetic stimulation of the cardioaccelerator nerves, and the cardioinhibitory centers decrease heart activity via parasympathetic stimulation as one component of the vagus nerve. During rest, both centers provide slight stimulation to the heart, contributing to autonomic tone. This is a similar concept to tone in skeletal muscles. Normally, vagal stimulation predominates as, left unregulated, the SA node would initiate a sinus rhythm of approximately 100 bpm.
Norepinephrine binds to the beta1 receptor. High blood pressure medications are used to block these receptors and so reduce the heart rate.
Input to the cardiovascular centres
Increased metabolic byproducts associated with increased activity, such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen ions, and lactic acid, plus falling oxygen levels, are detected by a suite of chemoreceptors innervated by the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. These chemoreceptors provide feedback to the cardiovascular centers about the need for increased or decreased blood flow, based on the relative levels of these substances.
Don’t Miss: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
What Happens In Atrial Fibrillation
When the heart beats normally, its muscular walls contract to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, so the heart can fill with blood again. This process is repeated every time the heart beats.
Atrial fibrillation occurs when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start firing in the atria .
These impulses override the heart’s natural pacemaker, which can no longer control the rhythm of the heart. The atria contract randomly and sometimes so fast that the heart muscle cannot relax properly between contractions. This reduces the heart’s efficiency and performance and causes a highly irregular pulse rate.
Slowing A Very High Heart Rate
You May Like: Tylenol Heart Rate
How To Slow It Down
Your doctor may suggest medical treatment if your heart races too often or it lasts too long. In the meantime, they might recommend the following things to slow it down:
- Cut back on coffee or alcohol.
- Get more rest.
- Close your eyes and gently press on your eyeballs.
- Pinch your nostrils closed while blowing air through your nose — a technique called the Valsalva maneuver.
How The Heart Beats 24/7
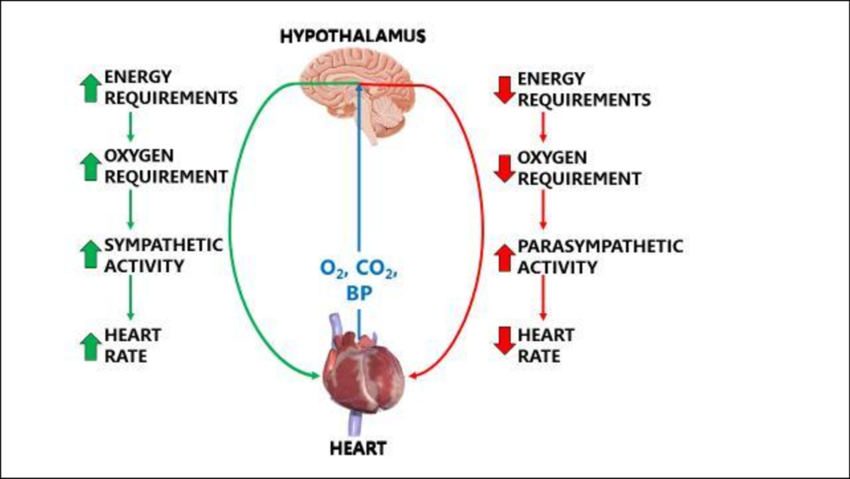
The heart doesn’t stop beating because two opposing mechanisms, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, work in sync to regulate the heart rate. The constant beating of the heart is the responsibility of the parasympathetic nervous system. When the sympathetic nervous system is activated, it causes the heart rate to speed up. The parasympathetic system brings the heart rate down again to the background level when the heart rate is high.
In a part of the brain called the medulla, a cardiac center receives information from different parts of the body and decides whether to activate the parasympathetic system to slow the heart rate or to stimulate the sympathetic system to increase the heart rate.
Also Check: Does Benadryl Increase Your Heart Rate
Improving Heart Rate While Running
If your heart rate reading is too rapid or you begin to feel dizzy, nauseated or breathless during your run, there are steps you can take to bring it down to a safe, comfortable range.
Reduce your intensity. Slowing your pace or taking walking breaks between intervals can help you catch your breath, so your body can more efficiently deliver oxygen-rich blood to the heart, organs and muscles. As you decrease intensity, aim for the lower range of your target heart rate, or about 50 to 70 percent of your maximum heart rate. You can also try the “talk test” if you’re able to speak without difficulty, you’ve lowered your intensity to a safe level.
Practice deep breathing techniques. Deep breathing, often referred to as “belly breathing” or “diaphragmatic breathing,” has been shown to slow the heartbeat and reduce blood pressure. If your heart rate is too high, stop running, find a comfortable place to sit down and try breathing deeply through your nose until your belly expands, then exhaling through your nose or mouth. Repeat until your heart rate has slowed.
Read More:Benefits of Deep Breathing
Avoid Stimulants Before a Run. Stimulants, like caffeine or nicotine, and alcohol can contribute to dehydration, which can put additional stress on the heart. If you must have your morning cup of coffee before your run, be sure to rehydrate by drinking 8 ounces of water before you leave, and 6 to 8 ounces every 20 minutes during your run.
The Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling many physiological functions. It induces the force of contraction of the heart and its heart rate. In addition, it controls the peripheral resistance of blood vessels. The ANS has both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions that work together to maintain balance.
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Raw Garlic And Other Herbs
Several herbs help benefit heart health, including cilantro, thyme, basil, oregano, parsley, and raw garlic. Research shows that garlic benefits people with uncontrolled hypertension. The polysulfides in garlic promote blood vessel health, blood pressure reduction, and hence also heart rate regulation. Garlic could also reverse early heart disease and plaque buildup in the arteries.
When Should One Be Concerned With Their High Heart Rate
A heart rate that is over 100 BPM at rest is clinically diagnosed as tachycardia. This is a condition in which the heart beats faster than normal due to conditions that are unrelated to physiological or emotional stress. There are three types of tachycardia: sinus, supraventricular, and ventricular. These types can result from different rhythm disorders that affect the hearts normal electrical impulses.
While tachycardia is a concern, sometimes it is also completely normal for a fast heart beat to occur. For example, it is normal for HR to rise during exercise, stress, trauma or illness.
If your heart rate is steadily increasing at rest, this is a marker of heart health worth watching.
Read Also: Heart Palpitations Prednisone
Chemicals Regulate Heart Beat
Neurotransmitters are substances or chemicals that activate nerve cells and allow them to communicate with other nerve and muscle cells. Norepinephrine and epinephrine activate the sympathetic nervous system and cause the heart rate to speed up. Acetylcholine stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system and lowers the heart rate. Thyroid hormones, which affect almost all cells in the body, increase the heart rate. During hyperthyroidism, thyroid hormone levels are abnormally high and force the heart to beat at a rate that can harm the heart muscle.
Heart Rate And Its Regulation
Normal heart rate is about 60-90 beats per minute. On an average, the rate at which the heart beats is about 75 per minute. It depends on the balanced activity between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve influence that are acting on it.
Heart rate can be increased because of either an increased activity of sympathetic nerve fibers or a decreased activity of parasympathetic nerve fibers and vice versa for a decrease in heart rate.
In a newborn infant, the heart rate is about 120 beats per minute. The rate at which the heart beats is proportionate to the metabolic rate of the body. In canary birds, it can be as much as 1000 beats per minute.
An increase in heart rate is known as tachycardia and a decrease is known as bradycardia.
Innervations to the Heart :
i. The efferent nerve supply to the heart is from both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
ii. The parasympathetic nerve supplying the heart comes along the vagus whereas sympathetic is from the lateral horn cells of T1-T5 segments of spinal cord. The sympathetic fibers reach heart as superior, middle and inferior cardiac nerves.
iii. Vagus nerve takes origin from the cardioinhibitory center present in the reticular formation of the brainstem. The preganglionic fibers synapse in the ganglion cells present in the walls of the atria. From these the short postganglionic fibers supply almost all parts of heart except the apex.
Phases of Respiration and Heart Rate:
Mechanism:
Regulation of Heart Rate:
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Easy Things You Can Do To Lower Your Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is dangerous. It can lead to many health problems, including heart attack, stroke, heart failure, angina, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, kidney disease, vision loss, sexual dysfunction and more.
Fortunately, high blood pressure can often be prevented or controlled.
Here are some easy things you can do to lower your blood pressure or help prevent high blood pressure in the first place.
Set small, easily attainable goals, and when you reach them, set bigger ones. Step by step, you will take control of your health and your blood pressure.
How Is Atrial Fibrillation Defined
Atrial fibrillation is defined in various ways, depending on how it affects you:
- paroxysmal atrial fibrillation – this comes and goes, usually stopping within 48 hours without any treatment.
- persistent atrial fibrillation – this lasts for longer than seven days, or less when it is treated.
- longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation – this means you have had continuous atrial fibrillation for a year or longer.
- permanent atrial fibrillation – this is when atrial fibrillation is present all the time and no more attempts to restore normal heart rhythm will be made
Read Also: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
When Should You Worry About Your Heart Rate
Some people never notice the rate or rhythm of their heart, while others notice every minor irregularity . In the absence of symptoms , that’s not an indication of trouble. An abnormal rate or rhythm may be discovered during a physical exam, ECG, or other testing, even in healthy people who have no symptoms.
Common symptoms of a slow heart rate include:
- fatigue
- dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting or near-fainting
- confusion
Signs Of High Heart Rate
There are countless benefits to aerobic exercise from reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, to stronger muscles and bones, to improved mood but working too hard can put stress on your heart, lungs and muscles, and potentially lead to serious health complications. That’s why it’s important to monitor your heart rate during your run and ensure it doesn’t reach your maximum heart rate.
In addition to monitoring your heart rate with your activity tracker or manually, look out for uncomfortable symptoms such as:
- Light-headedness or dizziness
- Shortness of breath
If you experience any of these symptoms, stop exercising and take the necessary steps to reduce your heart rate. If you experience chest pain, heart palpitations or fainting, seek emergency medical care immediately.
It’s important to note: Exercising in hot, humid weather can also raise your heart rate to potentially dangerous levels, so always check the temperature and humidity before heading out on your run. Being prepared can help you ensure you’re properly dressed and hydrated for warm weather running.
Read More:What is the Average Heart Rate While Running?
Read Also: Does Benadryl Increase Heart Rate
How To Lower Your Resting Heart Rate
How can you dial down a resting heart rate? Lifestyle changes can boost heart health and lower your pulse.
1. Get moving
Exercise is the number one way to lower resting heart rate, says Dr. Singh. The most common cause of a high resting heart rate is a sedentary lifestyle, one where you spend a lot of time not moving.
And being in poor shape can increase the risk of other problems, including obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes. To give your heart a healthy workout, the American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes per week of vigorous activity.
The more you exercise, the stronger your heart becomes. Since its pumping more blood with each beat, it wont need to pump as hard, which will lower your heart rate, she says.
2. Manage stress
Anxiety and stress can elevate the heart rate, too. To help bring it down, try to bring calm to your day, Dr. Singh says. Practice mindfulness, try to meditate or do breathing exercises.
3. Avoid caffeine and nicotine
Stimulants like caffeine and cigarettes can drive your heart rate up, Dr. Singh says. Cutting back may help lower your resting heart rate.
4. Maintain a healthy weight
The more weight you carry, the harder your body has to work to move blood through the body especially if you dont have a lot of muscle mass, Dr. Singh says. Losing weight can help bring down your heart rate.
5. Stay hydrated
6. Sleep well
