How Long Can You Live With Stage 4 Heart Failure
Although there have been recent improvements in congestive heart failure treatment, researchers say the prognosis for people with the disease is still bleak, with about 50% having an average life expectancy of less than five years. For those with advanced forms of heart failure, nearly 90% die within one year.
Exercise And Maximum Cardiac Output
In healthy young individuals, HR may increase to 150 bpm during exercise. SV can also increase from 70 to approximately 130 mL due to increased strength of contraction. This would increase CO to approximately 19.5 L/min, 45 times the resting rate. Top cardiovascular athletes can achieve even higher levels. At their peak performance, they may increase resting CO by 78 times.
Since the heart is a muscle, exercising it increases its efficiency. The difference between maximum and resting CO is known as the cardiac reserve. It measures the residual capacity of the heart to pump blood.
Neural And Hormonal Factors
Heart rate and stroke volume are also influenced by the central nervous system and hormonal release. The book “Physiology of Sport and Exercise” reports that impulses from the brain travel through the nervous system and can increase cardiac output. For example, when psychologically stressed, the hormone cortisol is released into the bloodstream and heart rate is increased to prepare the body for action. Further, excitement can lead to the release of the hormone epinephrine, causing a constriction in the blood vessels, which in turn lowers stroke volume and increases heart rate.
Recommended Reading: How Much Blood Does An Adult Heart Pump Every Day
Cardiac Output And Blood Pressure
Cardiac output and blood pressure are two important measures of the health and function of the cardiovascular system. You need to understand these measures as a fitness professional in order to design and deliver safe, effective exercise sessions, and in the case of blood pressure, be able to conduct and interpret blood pressure measurements for your clients.
Consider Factors Affecting Stroke Volume
One anatomical explanation for the increase in stroke volume during exercise is the Frank-Starling mechanism, as explained in a June 2018 article published by Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology.
Blood is pumped to the body from the left ventricle and when this ventricle fills more completely, it stretches further and produces a more forceful contraction.
In other words, more blood entering the heart results in more blood being ejected. This mechanism results in a greater amount of blood being circulated through your body during exercise which is essential for delivering oxygen to your hard working muscles.
An increase in stroke volume is most commonly seen during aerobic exercises or endurance-type activities like running, swimming or cycling.
You May Like: Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate Accuracy
What Is Already Known On This Topic
Research data on the stroke volume response to incremental exercise are conflicting. Early research supports a plateau in stroke volume in healthy untrained and trained subjects. Recent research has documented that stroke volume progressively increases to Vo2max in both trained and untrained subjects, but this finding has not been consistently reported.
Ferguson and colleagues suggested that, in endurance trained women, the increase in stroke volume at higher exercise intensities was due to an enhanced ventricular preload, not myocardial contractility. In contrast, Jensen-Urstad and colleagues reported that training induced increases in myocardial contractility, and possibly a decreased afterload, were the main contributing factors to the increase in stroke volume during incremental exercise in elite male runners. Similarly, Vanfraechem reported that left ventricular ejection times decreased at each workload in male soccer players. The author hypothesised that the continued increase in stroke volume, despite the decrease in ventricular ejection time, may be due to an increase in ejection fraction during exercise of increasing intensity.
When Should You Worry About Your Heart Rate
Some people never notice the rate or rhythm of their heart, while others notice every minor irregularity . In the absence of symptoms , that’s not an indication of trouble. An abnormal rate or rhythm may be discovered during a physical exam, ECG, or other testing, even in healthy people who have no symptoms.
Common symptoms of a slow heart rate include:
- fatigue
- dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting or near-fainting
- confusion
Read Also: Tylenol Heart Palpitations
What This Study Adds
This is the first review of stroke volume responses to exercise in healthy subjects. This study adds to the understanding of the various stroke volume responses to increasing exercise intensity, the effects of endurance training, sex, and age on the stroke volume response to exercise, and the mechanisms responsible for a progressive increase in stroke volume during exercise.
Health And Performance Considerations
Higher heart rates may be an indication of poor heart function and higher than usual stress being placed on the hearts ability to circulate blood. This may further indicate heart disease conditions.
From a performance stand point knowing specific heart rate training zones can optimize our bodys ability to adapt to performance requirements. Determining these zones can be done through many different methods, including VO2 or lactate testing, formulas and general training regimens. It then becomes necessary to monitor intensity in order to optimize your chances for success. To monitor your intensity there are several methods available to you. First is the perceived exertion method in which you rate your perception of how hard you are exerting yourself during a workout. The acronym for this is RPE . The scale on which to base your perceptions range from 1 – 10. See below.
The scale can be broken down as follows:
0: Nothing
Read Also: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
Chapter : The Cardiovascular System
- Relate heart rate to cardiac output
- Describe the effect of exercise on heart rate
- Identify cardiovascular centers and cardiac reflexes that regulate heart function
- Describe factors affecting heart rate
- Distinguish between positive and negative factors that affect heart contractility
- Summarize factors affecting stroke volume and cardiac output
- Describe the cardiac response to variations in blood flow and pressure
The autorhythmicity inherent in cardiac cells keeps the heart beating at a regular pace however, the heart is regulated by and responds to outside influences as well. Neural and endocrine controls are vital to the regulation of cardiac function. In addition, the heart is sensitive to several environmental factors, including electrolytes.
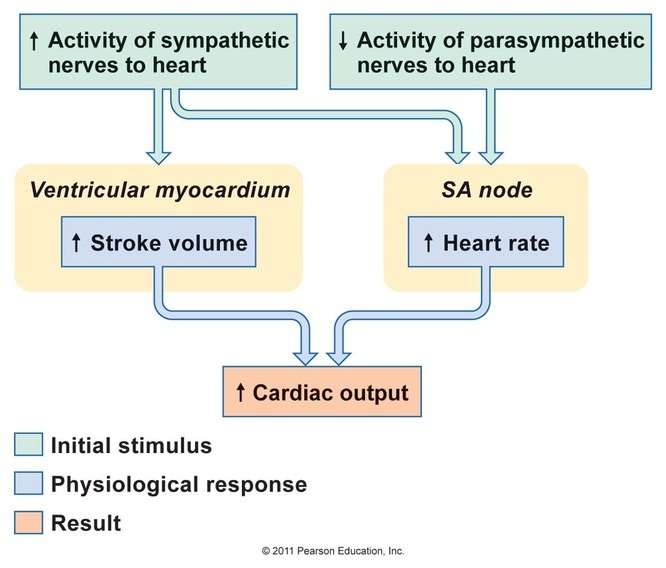
Factors Determining The Cardiac Output
The cardiac output = heart rate X stroke volume
Changes in cardiac output that are called for by physiologic conditions can be produced by changes in heart rate or stroke volume or both. The heart rate has a direct effect on the cardiac output, if increases, the cardiac output increase. However, if the heart rate increases so much to the extent that it shortens the diastolic time.
The cardiac output may decrease rather than increase. This is explained on the bases that the normal diastolic time in a person with an average heart rate of 70 beats/min is 0.5 sec. During this period, coronary and heart filling take place. Too much increase in heart rate shortens the diastolic time and decreases the end-diastolic volume, the force of contraction, and stroke volume. This results in decreased cardiac output.
Stroke volume: When the stroke volume is increased, it would increase the cardiac output, provided that the heart rate is unchanged
The stroke volume depends on preload, after load as well as myocardial contractility. The preload is proportionate to the end-diastolic volume, while the afterload is the resistance against which blood is expelled .
Factors affecting the cardiac output
- Venous return (preload.
The End diastolic volume
When the venous return is increased, the cardiac output will increase through the following mechanisms:
3. The diameter of arterioles: arteriolar dilation increases venous return, while arteriolar constriction decreases venous return.
Afterload
You May Like: Afrin Heart Palpitations
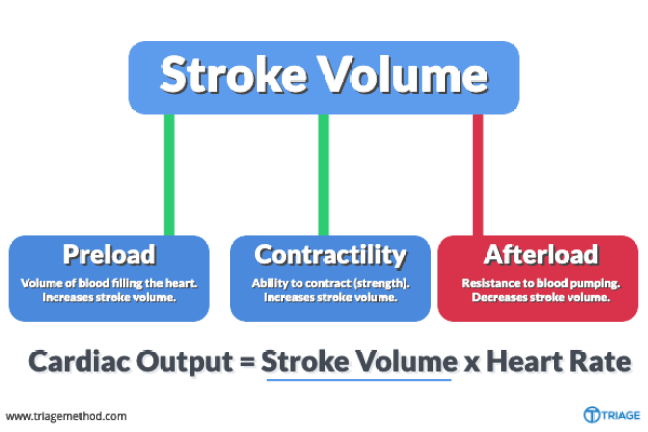
Whats A Normal Stroke Volume Value
Normal stroke volume in a healthy adult can be anywhere between 60ml and 120ml. Granted there are many things that can affect stroke volume, such as exercise and heart rate, but in general, a normal stroke volume for a healthy person will fall between these values.
There are 3 things that affect stroke volume. Those things are:
Preload: The filling pressure of the heart at the end of diastole.
Contractility: The inherent vigor of contraction of the heart muscles during systole.
Afterload: The pressure against which the heart must work to eject blood during systole.
Pulseco Algorithm Technology Overview
The PulseCO algorithm provides continuous beat-to-beat CO and SV by analyzing a blood pressure waveform. The algorithm is based on physics and physiological principles and focuses on pulse power analysis rather than waveform shape or contour. Unlike other arterial pressure algorithms, PulseCO is not based on statistics and assumptions about vascular compliance, nor on the detection of the dicrotic notch, which is often a challenge with peripheral arterial signals. As a result, the PulseCO algorithm avoids the limitations of other pulse pressure or contour-based hemodynamic monitoring technologies.
The current gold standard in hemodynamic monitoring, although not as commonly used due to its invasiveness, is the pulmonary artery catheter . The PulseCO algorithm has been validated against the PAC demonstrating a good agreement between the two methods.8,9
In addition, the precision of the PulseCO algorithm to trend changes in stroke volume has been evaluated in a number of clinical situations, including on: general surgical patients10 and during high cardiac output,11 hyperdynamic liver transplant,12 post-operative care,13,14 congestive heart failure,15,16 pre-eclampsia,17 and intensive care.18-20
You May Like: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
Disorders Of The Heart: Broken Heart Syndrome
Extreme stress from such life events as the death of a loved one, an emotional break up, loss of income, or foreclosure of a home may lead to a condition commonly referred to as broken heart syndrome. This condition may also be called Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, transient apical ballooning syndrome, apical ballooning cardiomyopathy, stress-induced cardiomyopathy, Gebrochenes-Herz syndrome, and stress cardiomyopathy.
The recognized effects on the heart include congestive heart failure due to a profound weakening of the myocardium not related to lack of oxygen. This may lead to acute heart failure, lethal arrhythmias, or even the rupture of a ventricle. The exact etiology is not known, but several factors have been suggested, including transient vasospasm, dysfunction of the cardiac capillaries, or thickening of the myocardiumparticularly in the left ventriclethat may lead to the critical circulation of blood to this region. While many patients survive the initial acute event with treatment to restore normal function, there is a strong correlation with death. Careful statistical analysis by the Cass Business School, a prestigious institution located in London, published in 2008, revealed that within one year of the death of a loved one, women are more than twice as likely to die and males are six times as likely to die as would otherwise be expected.
Regulation Of Stroke Volume
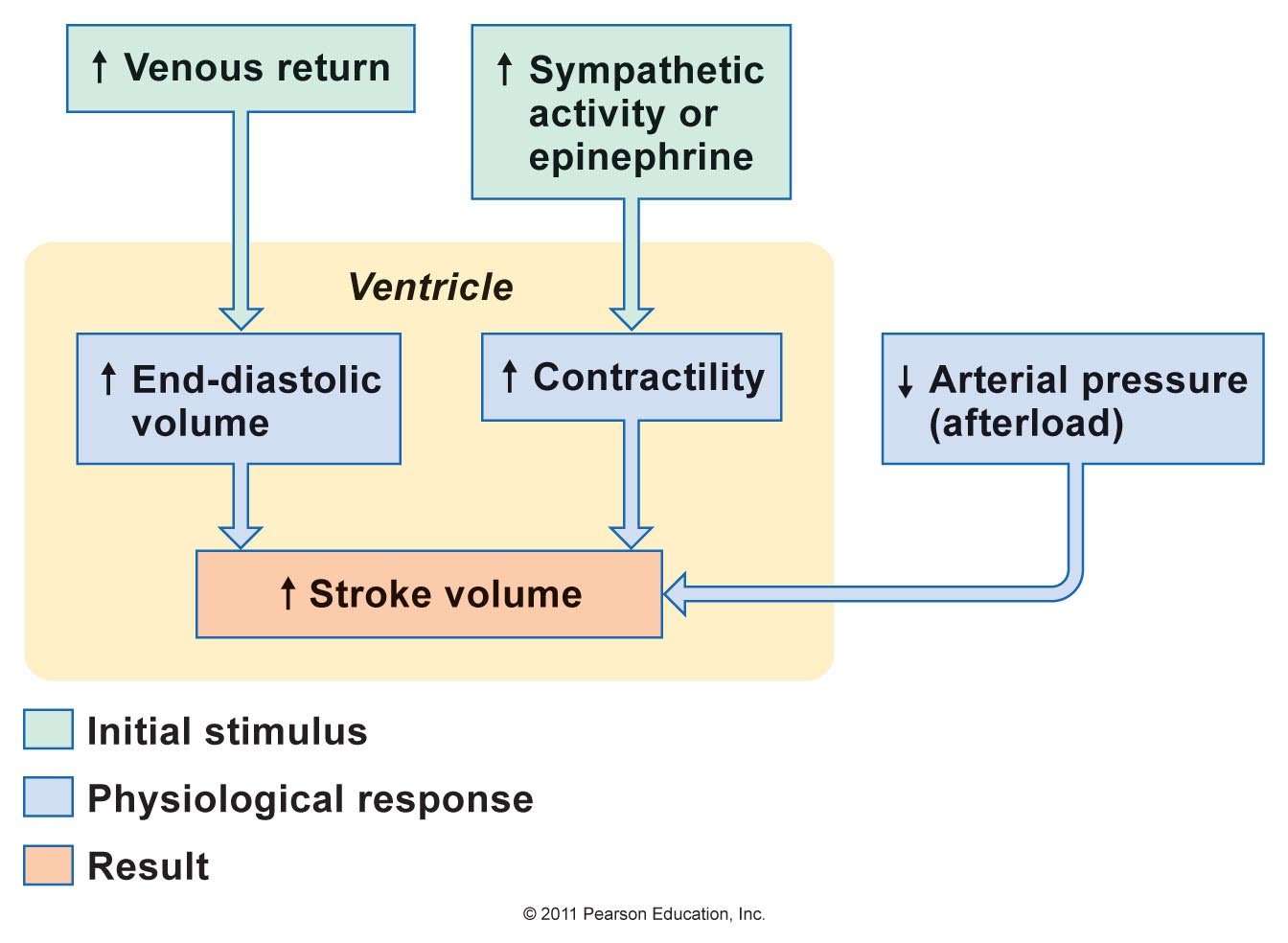
Ventricular stroke volume is often thought of as the the amount of blood ejected per beat by the left ventricle into the aorta . This assumes, however, that all the blood leaving the ventricle is ejected into the outflow tract, but this is not the case when there is or an . Therefore, a more precise definition for SV and one that is used in echocardiography when assessing ventricular function is the difference between the ventricular end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume . The EDV is the filled volume of the ventricle prior to contraction and the ESV is the residual volume of blood remaining in the ventricle after ejection. In a typical heart, the EDV is about 120 mL of blood and the ESV about 50 mL of blood. The difference in these two volumes, 70 mL, represents the SV. Therefore, any factor that alters either the EDV or the ESV will change SV.
SV = EDV – ESV
For example, an increase in EDV increases SV, whereas an increase in ESV decreases SV.
There are three primary mechanisms that regulate EDV and ESV, and therefore SV.
Read Also: Vitamin D3 And Heart Palpitations
Socm Study Guide Essay
Chapter 1 ELOsDescribe the basic functions of living organisms. A. Responsiveness organisms respond to changes in their immediate environment B. Growth over a lifetime, organisms grow larger through an increase in size or number of cells. Differentiation is when cells have specialized functions C. Reproduction Organisms reproduce, creating subsequent generations of similar organisms D. Movement Organisms are capable of movement
Starlings Law Of The Heart
Frank Starlings Law: This chart indicates stroke volume compared to ventricular preload, with labels for preload dependent zone, responsive patient SVV > 10%, and nonresponsive patient SVV < 10 %.
CO can also predict blood pressure based on blood volume. Starlings law of the heart states that the SV of the heart increases in response to an increase in EDV when all other factors remain constant. Essentially, this means that higher venous blood return to the heart will increase SV, which will in turn increase CO. This is because sarcomeres are stretched further when EDV increases, allowing the heart to eject more blood and keep the same ESV if no other factors change.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Why Is Frank Starling Important To Heart Failure
4.9/5Heart FailureFrankStarlingheartheart
The Frank–Starling mechanism allows the cardiac output to be synchronized with the venous return, arterial blood supply and humoral length, without depending upon external regulation to make alterations. The physiological importance of the mechanism lies mainly in maintaining left and right ventricular output equality.
Also Know, how does Starling’s law affect cardiac output? The FrankStarling law of the heart indicates that the increased filling pressure of the right heart results in increased cardiac output. Any increase in output of the right heart is quickly communicated to the left heart as an increased filling pressure.
In this way, which of the following is a consequence of the Frank Starling law of the heart?
As impaired myocyte contractility results in depression of ventricular stroke volume and cardiac output, the Frank–Starling mechanism has compensatory effects. As the elevated ventricular diastolic volume increases the stretch on the myocardial fibers, there will be a subsequent increase in stroke volume.
What does the Frank Starling law state?
The Frank–Starling Law is the description of cardiac hemodynamics as it relates to myocyte stretch and contractility. The Frank–Starling Law states that the stroke volume of the left ventricle will increase as the left ventricular volume increases due to the myocyte stretch causing a more forceful systolic contraction.
How Do The Resting Stroke Volume Heart Rate And Cardiac Output Of A Well
The resting stroke volume of an athlete is greater than that of a sedentary individual because of hypertrophy of the cardiac muscle in the athlete, which results in an increase in contractility and an increase in venous tone that lead to more blood being returned to the heart. Both the increased contractility and increased venous tone cause an increase in the strength of contraction of cardiac muscle and in the stroke volume.
The resting heart rate of an athlete is lower than that of a sedentary individual .
The higher stroke volume of an athlete is canceled out by the lower heart rate, resulting in the resting cardiac output of an athlete being similar to that of a sedentary individual.
George J. Crystal, … Kai Kuck, in, 2019
Don’t Miss: How Does Anemia Cause Heart Failure
Correlation Between Heart Rates And Cardiac Output
Initially, physiological conditions that cause HR to increase also trigger an increase in SV. During exercise, the rate of blood returning to the heart increases. However as the HR rises, there is less time spent in diastole and consequently less time for the ventricles to fill with blood. Even though there is less filling time, SV will initially remain high. However, as HR continues to increase, SV gradually decreases due to decreased filling time. CO will initially stabilize as the increasing HR compensates for the decreasing SV, but at very high rates, CO will eventually decrease as increasing rates are no longer able to compensate for the decreasing SV. Consider this phenomenon in a healthy young individual. Initially, as HR increases from resting to approximately 120 bpm, CO will rise. As HR increases from 120 to 160 bpm, CO remains stable, since the increase in rate is offset by decreasing ventricular filling time and, consequently, SV. As HR continues to rise above 160 bpm, CO actually decreases as SV falls faster than HR increases. So although aerobic exercises are critical to maintain the health of the heart, individuals are cautioned to monitor their HR to ensure they stay within the target heart rate range of between 120 and 160 bpm, so CO is maintained. The target HR is loosely defined as the range in which both the heart and lungs receive the maximum benefit from the aerobic workout and is dependent upon age.
Other Measures Of Systolic Function
Stroke volume may be derived from the change in LV volume from end-diastole to end-systole, using the biplane method of discs. Stroke volume can also be obtained by pulsed wave Doppler at the left ventricular outflow tract , as shown in Fig. 3. Utilizing this method, stroke volume is calculated as the product of the cross-sectional area of the LVOT and the flow velocity at the LVOT over the duration of flow, or velocity-time integral . Stroke volume multiplied by heart rate results in cardiac output. Measurement of cardiac output by echocardiography can identify diminished cardiac function, even in the setting of normal LVEF, volume depletion, right ventricular dysfunction, or left ventricular hypertrophy.
Fig. 3. Stroke volume by LV outflow tract Doppler. Cross-sectional area of the LVOT can be calculated from the LVOT diameter measured from the parasternal long-axis view . Velocitytime integral is obtained from pulsed-wave Doppler across the LVOT in the apical 5-chamber view . Using the continuity equation, the LVOT cross-sectional area multiplied by the VTI yields stroke volume.
David Sidebotham, Ian J. Le Grice, in, 2007
You May Like: Acid Reflux Heart Fluttering
