If I Have Systolic Heart Failure What Are My Medication Options
Systolic heart failure needs to be treated with several types of medication. The goal of therapy for this type of heart failure is to reduce the burden on the heart and interrupt the chemicals that can lead to weakening of the heart over time. In turn, your heart should work more efficiently and improve your quality of life.
Medications include:
Isosorbide Dinitrate And Hydralazine
Action:
- Dilate blood vessels to improve the amount of blood the heart pumps to the body.
- Combination may be particularly beneficial in African American patients.
- Effective for heart failure even in patients without high blood pressure.
Side effects:
- Headache. Common after this combination is started can take Tylenol® to control. Should become less intense with time.
- Low blood pressure. Check your blood pressure at home.
- Medications for erectile dysfunction interact with isosorbide dinitrate, and should be avoided.
- Dizziness. Take separately from other medications that cause dizziness.
- Get up more slowly from lying or seated position.
- Nausea. May take with small frequent meals.
Angiotensin Ii Receptor Blockers
This medication, often shortened to ARB, has very similar benefits to ACE inhibitors as it works on the same pathway. If you cant tolerate ACE inhibitors because of a reaction such as a cough or swelling, your doctor may prescribe angiotensin II receptor blockers instead. ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers are not used together.
Don’t Miss: Does Stress Increase Heart Rate
Including Infliximab Etanercept And Adalimumab
Use with caution in patients with mild HF or decreased left ventricular function. Infliximab doses > 5 mg/kg are contraindicated with moderate to severe HF . In a scientific statement from AHA, TNF blockers have been determined to cause either direct myocardial toxicity or exacerbate underlying myocardial dysfunction, 2016 .
5. Antiarrhythmic medications:
Class I: Flecainide, disopyramide
Class III: Dronedarone, Sotalol
6. Anti- Cancer medications:
Anthracyclines: doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, Mitoxantrone
US Boxed Warning: Myocardial damage can occur with doxorubicin with incidences from 1% to 20% for cumulative doses from 300 mg/m2 to 500 mg/m2 when administered every 3 weeks è monitor LVEF before, during and after treatment
Targeted therapy: Bevacizumab, Lapatinib, Trastuzumab
US Boxed Warning: Trastuzumab is associated reductions in left ventricular ejection fraction and heart failure the incidence is highest in patients receiving trastuzumab with an anthracycline-containing chemotherapy regimen è Evaluate LVEF in all patients prior to and during treatment discontinue for cardiomyopathy
7. Cilostazol
This is a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase type 3, antiplatelet and vasodilatory agent used primarily in patients with intermittent claudication and peripheral arterial disease .
US Boxed Warning: Cilostazol is contraindicated in patients with heart failure of any severity è causing decreased survival in patients with class III to IV heart failure .
9. 1 -Blockers:
Be The Star Of Your Team
It takes a team to manage heart failure, and you are the key player. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members, including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers, will also lend a hand. But it’s up to you to take your medicine, change your diet, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
Show Sources
Read Also: Normal Exercising Heart Rate
Classes Of Medications For Heart Failure
Doctors use a variety of medicines to manage heart failure. This includes drugs that reduce the hearts workload, help the heart pump more blood, and reduce fluid buildup in the body. Your doctor may also recommend drugs to prevent blood clots and reduce cholesterol. Most people with heart failure take more than one medication.
Classes of heart failure drugs include:
To help doctors choose the best treatment, they follow expert guidelines and recommendations. Your doctor will consider your symptoms, test results, and stage of heart failure. After starting treatment, your doctor will monitor your response. It may be necessary to adjust your dose, change drugs, or add another drug for optimal treatment.
What Are Heart Failure Medications
Heart failure medications are prescription drugs that help your heart work better. Heart failure, also called congestive heart failure, is a long-term condition. It affects nearly 6 million people in the U.S.
If you have heart failure, your heart cant pump blood as well as it should. Over time, this leads to fluid buildup in different parts of your body, including your legs, feet and lungs. You may also feel other symptoms including shortness of breath and fatigue.
Heart failure is progressive, meaning it gets worse over time. Treatment is essential to lower your risk of serious complications, like organ damage and sudden cardiac arrest. Treatment involves both lifestyle changes and medications. Some people need surgery.
Medications cant cure heart failure. But they can slow down its progression and improve your quality of life. People with heart failure usually need to take several different medications. Thats because each drug does a different job within your body to manage heart failure and its symptoms.
Your healthcare provider will decide the best medications for you based on your symptoms, your other medical issues and how far your condition has progressed. Your provider may change your treatment plan as you go along. For example, they may adjust your dose or change medications. Many of these medicines lower your blood pressure, so your provider will work with you to find a combination that works for you and keeps your blood pressure normal.
You May Like: How Can A Heart Attack Be Prevented
How Do I Manage My Medications
Closely follow your healthcare providers guidance on how to take your medications. Review all your medication labels and ask your provider if anything is unclear.
Some important tips include:
- Dont wait to refill your prescription: Your pharmacy may not have your medication on hand. So you may need to wait several days for your refill. Keep track of how much medication you have left, and request a refill about a week before youd run out.
- Keep a list of your medications: Your list should include the names of all your medications as well as all dosage instructions . Include prescription drugs plus over-the-counter medications. Keep your list updated, and carry it with you wherever you go.
- Stay aware of your symptoms: If your heart failure symptoms get worse, call your provider right away. Your provider may need to adjust your medication. Also, make a note of any side effects that you notice, and tell your provider.
- Tell your provider if you cant get your medications: If your medications are too expensive, talk with your provider. They may be able to recommend more affordable options or connect you with resources that can help. Also, tell your provider if your pharmacy isnt able to provide the medications you need.
- Tell your provider if youre pregnant or could become pregnant: You cant take some medications during pregnancy. Talk with your provider right away so they can adjust your medications if needed.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Heart Failure
Signs and symptoms depend on the type of heart failure you have and how severe it is. You may have any of the following:
- Trouble breathing with activity that worsens to trouble breathing at rest
- Shortness of breath while lying flat
- Severe shortness of breath and coughing at night that usually wakes you
- Feeling lightheaded when you stand up
- Purple color around your mouth and nails
- Confusion or anxiety
- Periods of no breathing, then breathing fast
- Lack of energy , or trouble sleeping
- Swelling in your ankles, legs, or abdomen
- Heartbeat that is fast or not regular
- Fingers and toes feel cool to the touch
Read Also: Does Prednisone Cause Heart Palpitations
Manage Your Medications Safely
Knowledge Is the Best Medicine
1. When you receive a prescription from the doctor, make sure you ask:
- What is the brand name and chemical name of the medication?
- Why is it being prescribed?
- When and how should it be taken?
- How long will you need to take it?
- What side effects should you expect to have?
- What should you do about the side effects?
2. When you pick up your medication, ask your pharmacist to:
- Explain the best way to take the medication
- Describe what is written on the label
- Provide written information about the medication
3. Try to use the same pharmacy for all of your prescriptions. It is important for your pharmacist to have a complete list of your medications. Your pharmacist can then evaluate whether your medications can be safely taken together.
4. Carry your medication list with you. Make sure the list includes:
- All of your medications, as well as any vitamins, supplements and herbals
- Your allergies, immunizations and pharmacy phone number
Bring the pill bottles or a list of your current medications to all visits with your doctors.
5. Always ask your doctor or pharmacist before taking any medications or herbal products you can buy without a prescription. Medications you can buy over the counter at the drug store include pain medication, antacids, laxatives and cough medicines.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , such as ibuprofen and naproxen , may worsen your symptoms and/or make your prescription medication less effective.
- Phone: 1-800-575-5386
List Of Drugs That Can Cause Heart Failure
The term âheart failureâ can be frightening. It doesnât mean the heart has âfailedâ or stopped working. It means the heart doesnât pump as well as it should. Heart failure is a major health problem in the United States, affecting about 5.7 million Americans. About 550,000 new cases of heart failure occur each year. Itâs the leading cause of hospitalization in people older than 65.
Almost 6 million Americans have heart failure, and more than 870,000 people are diagnosed with heart failure each year. The condition is the leading cause of hospitalization in people over age 65. But now a study shows heart failure is on the rise in younger people too. And more are dying from it.
Heart Failure and Medications
Studies have found that most drugs can have adverse cardiovascular effects, ranging from abnormal heart rate to heart attack. Drug-induced heart failure should be regarded as a potentially preventable cause of heart failure.
A large body of evidence from controlled clinical trials has led to an improved understanding of well-established causes of drug-induced heart failure symptoms while implicating a wide range of other commonly used drugs and drug classes as having causal or contributory roles.
List of Medications and Recreational Drugs That Can Cause Heart Failure
The following medications can raise your risk of heart failure or related problems:
Over-the-Counter Drugs
Read Also: Prognosis Of Congestive Heart Failure
Maximizing Heart Failure Meds Within 2 Weeks Reduces Risk Of Hospital Readmission Death
Ramping up medication doses quickly after being hospitalized for acute heart failure resulted in a lower risk of dying or being readmitted for heart failure within the first six months after discharge, compared to usual care, according to a featured science research presentation today at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions 2022.
Millions of people are hospitalized for acute heart failure worldwide each year. There is a 20% risk of re-hospitalization and a 5% risk of death within one month after hospital discharge, and a 60% risk of re-hospitalization and a 25% risk of death within one year after discharge. Despite this increased risk, research suggests that many heart failure patients are not closely monitored after hospital discharge and may not be treated with full doses of all guideline-directed medications.
“The American Heart Association and the European Society of Cardiology both recommend that patients hospitalized with acute heart failure should receive optimal doses of three main classes of heart failure medicine and regular follow-up visits post-discharge,” said Alexandre Mebazaa, M.D., Ph.D., the study’s lead researcher and a professor of anesthesia and critical care at Université de Paris and chair of the department of critical care at Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris, both in Paris, France.
More information:
Studies Have Shown That Several Classes Of Drugs Are Best To Treat Heart Failure
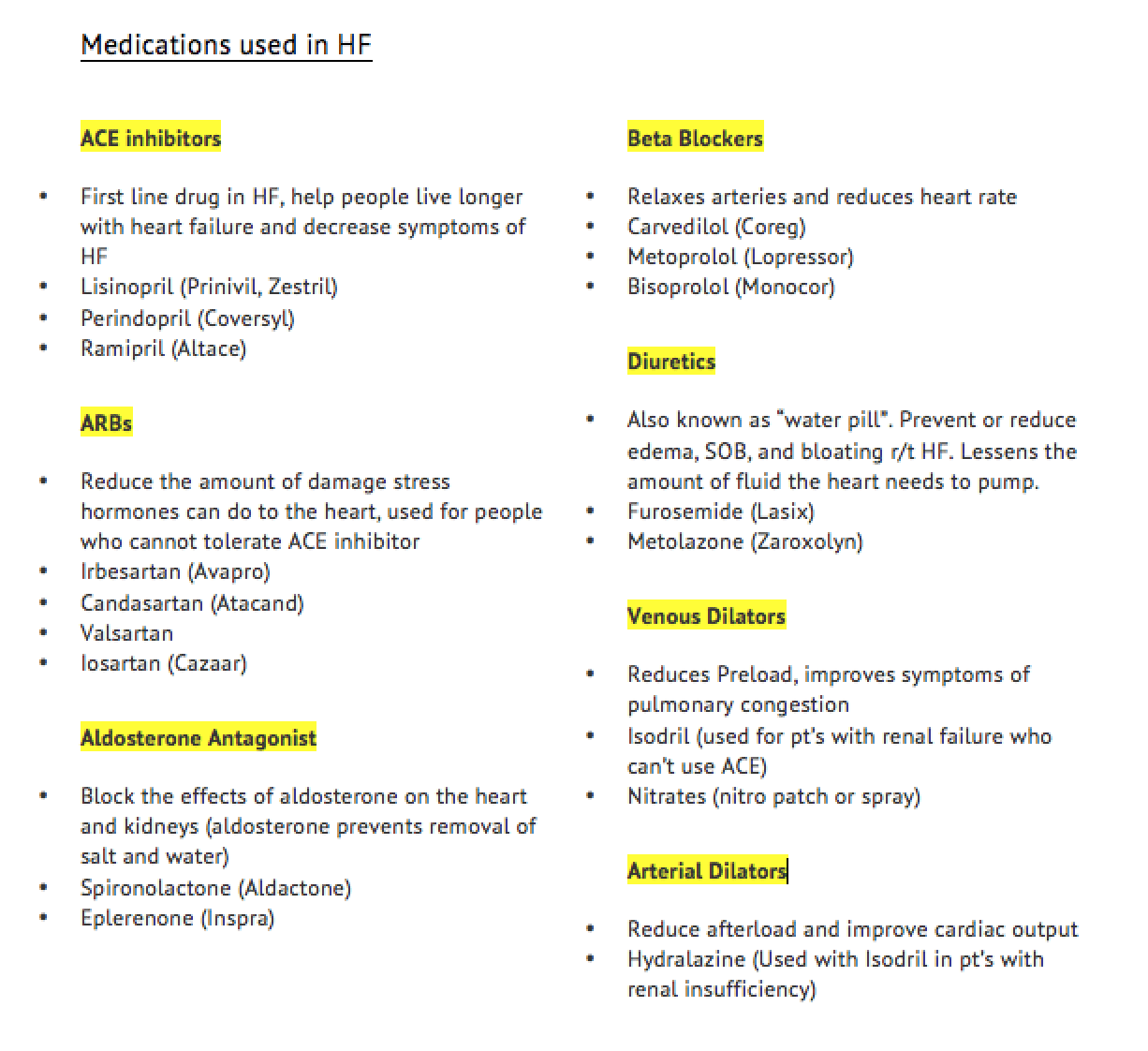
Heart failure patients may need multiple medications. Each one treats a different symptom or contributing factor and comes with its own instructions and rules.
You and your caregivers should work with your healthcare team to understand the medications and when, how often and in what dosage to take them.
Its important to discuss all of the drugs you take with your doctor and understand their desired effects and possible side effects. Your doctor and your pharmacist are your best sources of information. Dont hesitate to ask them questions about your medicines.
It’s critical that people with heart failure take their medications exactly as directed by their healthcare provider, to optimize the benefits. The use of these drugs has saved lives, prolonged life and improved the hearts function.
The following list gives you a quick look at many typical medications to treat heart failure at different stages. Your prescription may have a different name from the ones listed here. Brand names commonly available in the United States are shown in parentheses after the generic name for each drug.
Also Check: Life Expectancy Congestive Heart Failure
Ace Inhibitors And Arbs
ACE inhibitors and ARBs work by opening blood vessels and lowering blood pressure. These medicines can:
- Reduce the work your heart has to do
- Help your heart muscle pump better
- Keep your heart failure from getting worse
Common side effects of these drugs include:
When you take these medicines, you will need to have blood tests to check how well your kidneys are working and to measure your potassium levels.
Most of the time, your provider will prescribe either an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Heart failure is often caused by damage or injury to your heart. The damage may be caused by other heart problems, diabetes, or high blood pressure. The damage may have also been caused by an infection. Your healthcare providers will help you manage any other health conditions that may be causing your heart failure. The goals of treatment are to manage, slow, or reverse heart damage. Treatment may include the following:
- Medicines may be given to help regulate your heart rhythm and lower your blood pressure. You may also need medicines to help decrease extra fluids. Medicines, such as NSAIDs, may be stopped if they are causing your heart failure to become worse. Do not stop any of your medicines on your own.
- Cardiac rehab is a program run by specialists who will help you safely strengthen your heart. In the program you will learn about exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition. Cardiac rehab may be recommended if your heart failure is not severe.
- Oxygen may help you breathe easier if your oxygen level is lower than normal. A CPAP machine may be used to keep your airway open while you sleep.
- Surgery can be done to implant a pacemaker or another device in your chest to regulate your heart rhythm. Other types of surgery can open blocked heart vessels, replace a damaged heart valve, or remove scar tissue.
Read Also: Rapid Heart Rate After Eating
Commonly Dispensed As Over The Counter Drugs Or As Anti
US Boxed Warning regarding Serious cardiovascular risk: cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction , and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in the treatment and may increase with duration of use. Celecoxib is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft surgery .
3. Some Oral Hypoglycemic Agents:
Thiazolidinediones such as Pioglitazone è are associated with fluid retention
US Boxed Warning: Thiazolidinediones may cause or exacerbate heart failure è closely monitor for signs and symptoms of HF particularly after initiation or dose increases. If HF develops, treat and consider dose reduction or discontinuation of pioglitazone. Initiation of therapy is contraindicated in patients with NYHA class III or IV HF .
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin
In a scientific statement from American Heart Association , saxagliptin has been determined to be an agent that may exacerbate underlying myocardial dysfunction , 2016 . The ADA recommends avoiding the use of saxagliptin in patients with HF, 2020) .
Bies is associated withguanid lactic acidosis, which can be fatal in patients with CHF
US Boxed Warning regarding Lactic acidosis: Risk factors include renal impairment, 65 years and hypoxic states, e.g: acute congestive heart failure. Metformin may be used in patients with stable heart failure, ADA 2020 .
Can I Ever Stop Taking Heart Failure Medications
Always follow the medication schedule your healthcare provider gives you. Never stop taking the medication without talking to your provider first. They’ll let you know if you should stop taking a certain drug or change its dose. Suddenly stopping your medication can be dangerous for your body.
Even if you feel better, you should keep taking your medications as prescribed. Feeling better is a good sign. It shows the medications are doing their job. But you need to keep taking them so they can keep doing their job.
Read Also: How Many Heart Attacks Has Bernie Sanders Had
Diuretic Therapy For Heart Failure
Diuretics are used to control symptoms of fluid retention and maintain euvolaemia. They should never be used as sole therapy for HFrEF as they do not improve survival in HF. Diuretics may be used in a flexible manner. Daily weight monitoring is an essential component in the assessment of fluid status and is useful in guiding diuretic dosing. Tools such as the Weight and symptom diary may assist patients to monitor changes in their weight.
Loop diuretics, such as furosemide , are potent diuretics and are often used in patients with HF. Bumetanide is another loop diuretic that may be beneficial in patients with reduced gut absorption due to HF as it has better oral bioavailability than furosemide .
Thiazide diuretics and potassium-sparing diuretics are rarely used in clinical practice for HFrEF patients except in the presence of ‘resistant fluid overload’. In these circumstances they may be combined with a loop diuretic such as furosemide cautiously and temporarily as prolonged use increases the risk of hypokalaemia and dehydration. Thiazides may also increase serum urate and hence contribute to gout, which is frequently experienced by patients with HFrEF.
Thiazide diuretics are sometimes used in HFpEF where they may have the advantage of treating mild fluid retention and hypertension, a common cause of HFpEF.
