Heart Surgeries Can Trigger Strokes Seizures And Other Neurological Complications
- Date:
- Loyola University Health System
- Summary:
- Strokes, seizures and other neurological complications related to heart surgery account for “considerable morbidity and mortality,” researchers report.
Strokes, seizures and other neurological complications related to heart surgery account for “considerable morbidity and mortality,” Loyola University Health System neurologists report in the November issue of the journal Hospital Practice.
Other complications include delirium, central nervous system infections, pituitary gland problems, spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries, residual effects of anesthesia and medication toxicity.
Complications can involve any part of the central and peripheral nervous systems. “Neurologic complications are always a risk with cardiac surgery, especially in older patients who have other health problems,” said Dr. José Biller, first author of the article and chairman of the Department of Neurology at Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine.
Strokes are the most common neurologic complication after cardiac surgery in adults. In children, seizures are the most common neurologic complication.
However, Biller said patients should not be afraid to undergo cardiac procedures. Many complications are rare. And despite the risks, cardiac surgeries generally “are highly beneficial and life-saving,” he said.
Story Source:
Scope Of The Statement
A key area addressed by the statement is identification of high-risk patients and methods of assessing risk. The preoperative workup should include assessment of the aorta with CT, taking a history of cerebrovascular disease and doing a physical exam for possible neurologic symptoms, says Dr. Bakaeen.
Discussion is then devoted to considerations in intraoperative management to prevent stroke, including :
- Left atrial appendage closure and ablation to reduce atrial fibrillation
- Blood transfusion strategies
A final section addresses diagnosis and treatment of perioperative stroke, including clinical and radiographic evaluation and strategies for medical, endovascular and surgical management.
The document concludes with a figure outlining 19 suggested actions for lowering stroke risk, from intraoperative measures to measures for early stroke diagnosis, treatment of perioperative stroke and prevention of postoperative stroke.
With mortality outcomes for cardiac and cardio-aortic surgery continuing to improve, it is increasingly important that we expand focus from not only extending lives but to optimizing our patients quality of life, observes Eric Roselli, MD, Chief of Adult Cardiac Surgery at Cleveland Clinic. The authors of this statement provide practical recommendations based on literature review to minimize risk and improve rescue from intraoperative and perioperative stroke.
Stroke After Surgery Everything To Be Aware Of
Without a doubt, surgeries following serious health issues have shown major results in improving a survivors quality of life. For those who suffer from heart conditions, forms of cancer, and even joint pain, a variety of operations can offer great recovery possibilities, but these procedures can also have their fair share of complications in the process.
What is important for all patients to know is that having surgery leaves one vulnerable to a range of health concerns, and suffering from a possible stroke is one of them. Especially for surgeries involving the heart, the odds of having a stroke afterward are considerable, whereas surgeries that are not cardiac have been related to decreases in strokes. Learning about a patients susceptibility under both circumstances can provide better understanding of and preparation for any health issues that you or a loved one may face.
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure Edema
Preparing For The Surgery
Preparation for open heart surgery starts the night before. A person should eat an evening meal as usual but must not consume any food or drink after midnight.
It is a good idea to wear loose, comfortable clothing to assist with restricted movement following surgery, but wear whatever is comfortable.
Be sure to have all personal medical information on hand. This might include a list of medications, recent illness, and insurance information.
It is normal to feel anxious before an anesthetic, and people should not hesitate to seek reassurance from the healthcare team.
The doctor may request that the person washes their upper body with antibacterial soap. A member of the healthcare team may need to shave the persons chest area before they can have the anesthetic.
The doctors may also need to run tests before surgery, such as monitoring the heart or taking blood samples. A doctor or nurse might place a line into a vein to enable the delivery of fluids.
After the medical team has completed the preliminary tasks, the anesthesiologist will administer general anesthesia.
Impact Of Other Perioperative Variables
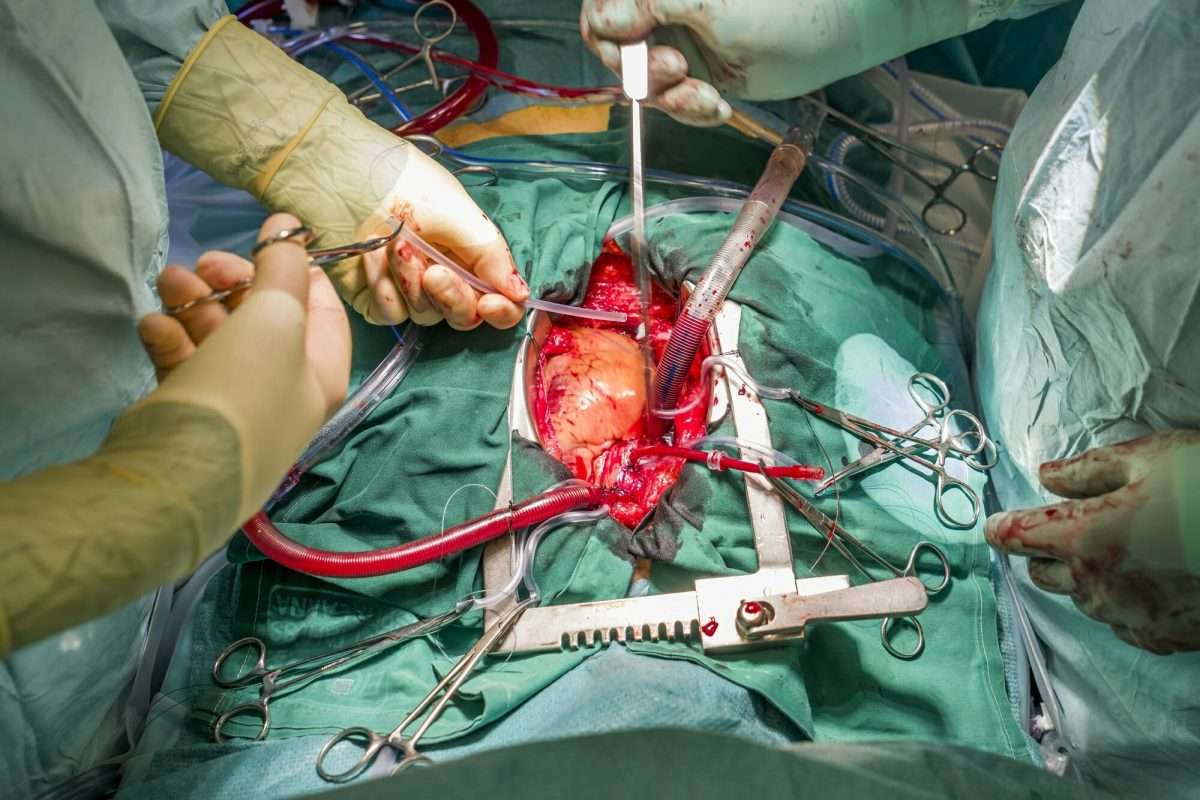
Our finding of a protective effect of hypertension on perioperative outcomes was unexpected but not implausible. These patients may well have been on more aggressive primary and secondary prevention regimes. Alternatively, these patients may have been perceived as being at higher risk and therefore given better perioperative care ., Unfortunately, our database does not contain further pharmaceutical or perioperative data to corroborate these explanations.
Renal failure was the second biggest risk factor for perioperative mortality but increased the odds of a prolonged LOS the most . The magnitude of this effect is in line with previous data and supports the importance of renal failure in determining perioperative outcomes. We have recently shown that chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is an important risk factor for perioperative mortality in orthopedic, but not vascular, surgical patients. However, given previous evidence, we were surprised that it only emerged as a risk factor for mortality for uncomplicated CABG surgery . Nonetheless, similar to diabetes mellitus, respiratory disease increased the risk of prolonged LOS even with inclusion of complicated surgery and so should be considered an important factor in judging perioperative risk.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Heart Rate To Burn Fat
Definition Of Ischemic Stroke
The objective of the present study was to estimate how frequently postoperative ischemic stroke may occur within 30 days of the procedure. Following the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association, ischemic stroke was defined as an acute episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal cerebral, spinal, or retinal infarction with a diagnosis based on symptoms persisting 24 or more hours or until death on pathological imaging, or other objective evidence of ischemic injury in a defined vascular distribution, and excluding other pathologies .
S Outlined To Reduce The Risk Of Stroke During After Heart Surgery
Statement Highlights:
- A stroke during or soon after heart surgery, called a perioperative stroke, increases the risk of death and can result in major disability for survivors.
- Stroke is one of the most feared complications of heart surgery.
- In general, the risk of stroke during or after heart surgery is low. However, pre-screening, measures taken during surgery, and immediate diagnosis and treatment of a stroke can improve patient survival and quality of life.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT / 5 a.m. ET, Wednesday, August 26, 2020
DALLAS, August 26, 2020 Steps for reducing the risk of stroke in patients undergoing heart surgery are detailed in a new American Heart Association Scientific Statement, Considerations for Reduction of Risk of Perioperative Stroke for Adult Patients Undergoing Cardiac and Thoracic Aortic Operations, published today in the American Heart Associations flagship journal Circulation. Pre-screening, surgical technique changes, early diagnosis while in surgery and quick team response all contribute to better survival rates and reduce the risks of major disability for patients.
Prevention during surgery
- Monitor blood flow to the brain
- Intraoperative imaging of the aorta
- Tight blood pressure control and
- Closely monitor blood loss and the need for transfusion.
Early stroke diagnosis
Rapid treatment of perioperative stroke
Additional Resources:
- Follow AHA/ASA news on Twitter
- Follow news from the AHAs flagship journal Circulation
You May Like: Can Anemia Cause Heart Failure
Signs Of Mild Stroke After Surgery
Any type of surgery poses a series of possible risks and possible complications. Surgeries related to cardiology, neurology and pulmonary conditions run a much higher risk than others. Experiencing a mild stroke just before, during or after surgery may not be visible until the patient awakes and recovers from anesthesia 1. There are signs to look for that will help medical personnel evaluate whether the patient may have experienced a mild stroke 1.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
Effect Of Preoperative Stroke And Mi Or Heart Failure
As prior MI proved an important risk factor for perioperative mortality in patients with stroke we hypothesized that there may be an interaction between stroke and MI. Indeed, the combination far outweighed the risk of either condition individually . This may be due to an interaction between hemodynamic compromise and embolic injury of the brain. It has been proposed that emboli may lodge in areas of low cerebral blood flow and not be washed out certainly there is evidence that hemodynamic compromise exacerbates embolic brain injury from animal work. However, we cannot probe this proposed pathogenic explanation because we do not have data on either hemodynamic variables or embolic load. Furthermore, we did not find an interaction between prior stroke and heart failure therefore, we must be conservative in our conclusions about the cause of the interaction and merely suggest more work is required to validate this finding.
Nonetheless, interactions are important to recognize most perioperative risk scoring systems assume that comorbidities are additive in risk and thus may not adequately stratify individual patients who have different combinations of comorbidities. Studies are required to identify whether the combination of comorbidities exceeds the sum of each comorbiditys individual effect.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Arm Pain Heart Attack
No Silver Bullet For A Feared Complication
Perioperative mortality can be as high as 20% in patients who develop stroke during cardiothoracic surgery. Morbidity from stroke is also greatly feared: In a recent survey, 81% of patients said freedom from stroke was more important than length of life, hospital readmission or freedom from life in a nursing home.
In response to these challenges, the AHA convened the expert panel to review the literature and provide recommendations for reducing perioperative stroke risk in adults undergoing cardiac and proximal thoracic aorta procedures the guidance doesnt apply to carotid or other vascular operations, the authors note.
The document emphasizes the multiple contributors to stroke risk in this setting and the need for multifaceted strategies to mitigate the risk and consequences of stroke. The pathogenesis of perioperative stroke is multifactorial, notes Dr. Bakaeen, but having information on its mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment can help minimize the risk of stroke for an individual patient and improve the outcome if a stroke should occur.
Blurred Vision And Slurred Speech
When a mild stroke has occurred after surgery, vision and speech could be affected 1. If the patient is staring off to the side, not able to focus or has a droopy eyelid, these could be warning signals something went wrong during surgery. Slurred speech, having trouble pronouncing words and stuttering are signs as well.
Read Also: What Cause Low Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
Effect Of Preoperative Variables On Perioperative Outcomes
Prior stroke was associated with an increase in mortality , postoperative stroke and prolonged LOS . In addition, age, female sex, nonatrial fibrillation arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, heart failure, renal failure, peripheral vascular disease, unstable angina, and liver disease all increased perioperative mortality whereas prior MI did not . Despite occurring in only 0.4% of the population , liver disease exerted the most pronounced effect on mortality with 33.5% of liver disease patients dying. In contrast, a prior diagnosis of hypertension was shown to be protective .
Further Progress In Store
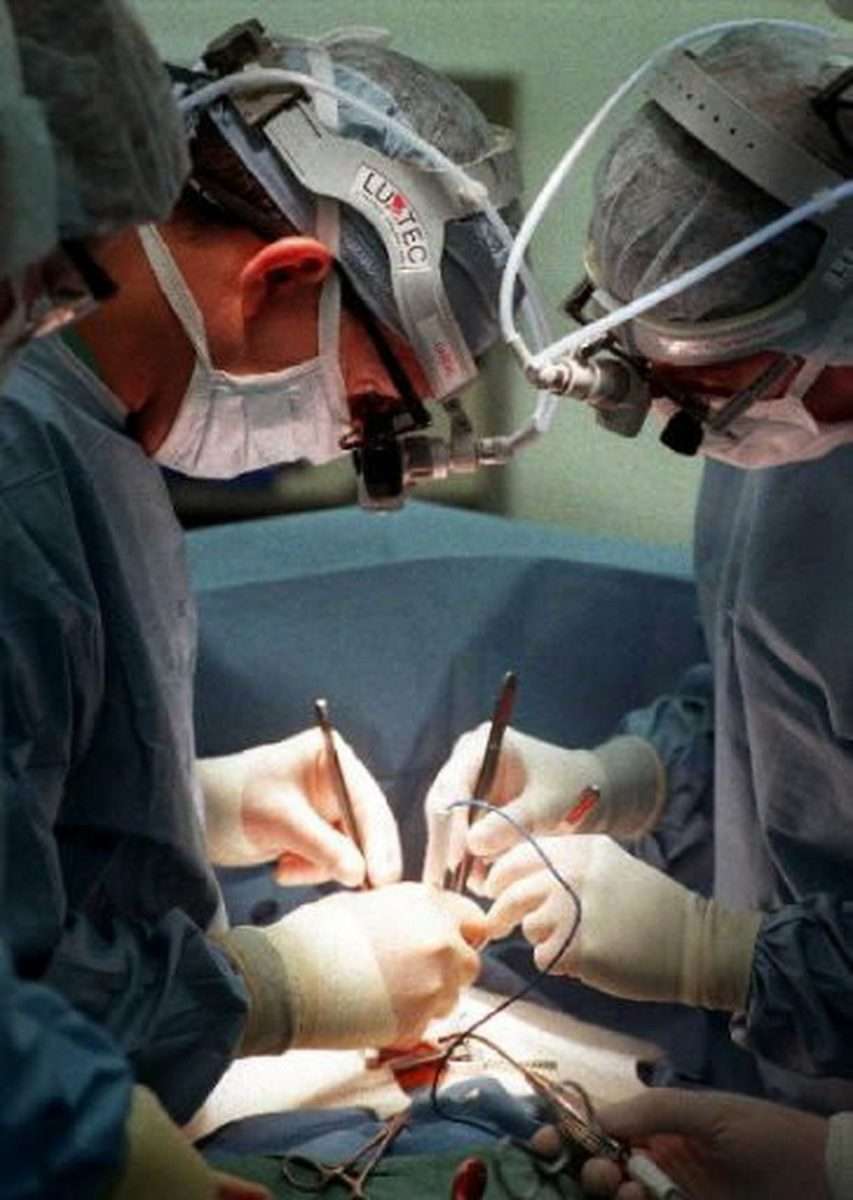
Dr. Roselli notes that theres good reason to expect progress against perioperative stroke to continue apace. As imaging quality and data analysis improve with advances in computer technology, we will progress from making decisions based on average treatment effect towards individualized precision medicine, he says. This will allow us to understand which techniques are best tailored to each patient around the time of cardiac surgery to further reduce strokes from complicating these life-saving operations.
Read Also: What Distinguishes A Heart Attack From Heart Failure
Thrombotic Or Embolic Strokes
To try to explain this increase, you must examine the process of cardiothoracic surgery and their relationship to ischemic strokes. The American Heart Association classifies an ischemic stroke into two categories: Thrombotic or Embolic. A Thrombotic stroke is caused by a blood clot that forms within an artery and then travels to the brain, where it cuts off blood flow. An Embolic stroke is a clot that wanders away from the heart or neck arteries through the bloodstream and eventually blocks a blood vessel within or connected to the brain. Considering that both types of stroke begin with clots formed elsewhere in the body, a correlation can be made that cardiothoracic surgeries have the potential to dislodge blood clots from their origin, causing them to lodge in other locations.
Justin And Hailey Bieber Make Out In Idaho Amid His Ramsay Hunt Recovery
Hailey Bieber underwent heart surgery after suffering a mini stroke last month.
The supermodel, 25, revealed she recently had a patent foramen ovale closure procedure performed to mend a hole in her heart.
It went very smoothly Im recovering really well, really fast, she said in a new YouTube video, titled telling my story.
After being rushed to a Palm Springs area hospital last month with stroke-like symptoms, Bieber discovered she had a blood clot which travelled to her brain and caused a transient ischemic attack .
However, doctors couldnt figure out how the blood clot ended up there.
When I went to UCLA we did more in-depth testing to find a PFO, she explained in the video, describing a PFO as a flap between the right and left chambers of the heart.
Typically at birth its supposed to close on its own, she added, noting hers didnt close.
They found that I had a grade five which is the highest grade you can have. Mine was fairly large. What typically happens is the heart will filter the blood clot to the lungs and the lungs will absorb it because theyre so big and they can handle it.
However, the blood clot, escaped through the hole in my heart and travelled to my brain and that is why I suffered a .
The wife of Justin Bieber said she was just grateful that they found it, and her doctors performed a procedure in which they use a button to close the flap in the heart.
You May Like: Can Drinking Too Much Alcohol Cause Heart Attack
Who Is In Theater For Open Heart Surgery
A team of doctors and other health professionals work together in the operating theater during open heart surgery.
The team is likely to include:
- the lead surgeon who will direct others surgeons who will assist during the operation
- the anesthesiologist, who is in charge of giving and anesthesia and monitoring vital signs
- the pump team, also known as perfusionists, operate the heart-lung machine and other technical equipment that supports open heart surgery
- nurses and technicians, who assist the surgical team and prepare the operating theater for surgery
Death And Stroke Risks After Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement: A Real World Perspective
With a rapidly rising proportion of aging population, aortic stenosis represents one of the most common valvular heart diseases affecting adults in the US and accounts for at least 92,000 aortic valve replacements annually in the US. Surgical AVR has been traditionally regarded as the treatment of choice for patients with severe symptomatic AS, who do not have a prohibitive risk for open heart surgery due to advancing age or other concomitant comorbidities. The current literature provides heterogeneous rates of adverse complications including in-hospital death and stroke following surgical AVR. This heterogeneity encountered in the literature especially from the clinical trials raises an issue whether real life stroke rate after surgical AVR in high-risk patients might as well be different from what is encountered in the trial setting. To that end, we aimed to assess the incidence of in-hospital death and adverse neurological events following surgical AVR , especially among the elderly and the high-risk patients, utilizing a large representative nationwide population sample of hospital discharges.
Adjusted comparison of study outcomes among the various age groups for isolated AVR. Comparisons have been made using odds ratio , which represent the ratio of odds of an outcome in a particular age category compared to the reference group
Shikhar Agarwal, Samir R Kapadia
Heart and Vascular Institute, Cleveland Clinic
Read Also: What Is Right Sided Heart Failure
Surgical Risk Factors For Ischemic Stroke Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting A Multi
- 1Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht – CARIM, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, Netherlands
- 2Cardiac Surgery Department, Vrije Universiteit Brussels, Brussels, Belgium
- 3Cardio-Thoraco-Vascular Department, Careggi Hospital, Florenze, Italy
- 4Division of Cardiac Surgery, University Hospital Center of Tirana, Tirana, Albania
- 5Cardiac Surgery, St. Michael’s Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 6Cardiac Surgery Unit, Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Florence, Firenze, Italy
Background: Ischemic stroke after coronary artery bypass has been often linked to aortic manipulation during surgery.
Objectives: The objective of the study was to estimate the rate of postoperative ischemic stroke within 30 days from CABG by surgical risk factors alone or in combination.
Methods: The multinomial propensity score for multiple treatments was used to create six models with a total of 16,255 consecutive patients undergoing isolated CABG. For each model, a different classification variable was used to stratify patients.
Aortic cross-clamping was found to be the primary cause of post-CABG ischemic stroke. Instead, additional aortic manipulation from a side-biting clamp, on-pump surgery, multiple aortic touches, number of proximal anastomoses, and aortic cannulation were found not to increase the estimate of stroke significantly. Further research on this topic is warranted.
Effect Of Preoperative Stroke
Our cohort of stroke patients undergoing CABG was smaller than anticipated and relatively smaller than other large studies . It may be that our definition of stroke is more stringent than other definitions used. Nonetheless, we did not find a relationship between the time interval between stroke and CABG and perioperative outcomes. Rather, our study emphasizes the importance of age and heart failure in stroke patients as further determining mortality risk, though the limited sample size means we should be cautious about ruling out other factors.
We initially hypothesized that there would be a window of vulnerability after stroke during which CABG should be considered high risk. However, our data do not support a higher risk period within 3 or 6 months of a stroke. The reader should note that we were limited by the few operations being conducted in patients with a recent stroke, possibly due to the clinical perception of increased risk. Therefore, we cannot definitively conclude that CABG is safe in the first few months after stroke.
Read Also: How Does Atropine Increase Heart Rate
