What Is The Outlook For Heart Failure Patients
Very good, particularly now compared to prior generations, says Dr. Jacoby. We have medicines and treatments that reverse many cases of heart failure, and in most cases, the outlook is generally very good.
In cases where reversal of damage to the heart and affected areas is not possible, Dr. Jacoby says that the Yale Medicine team follows the patient closely and works to optimize quality of life while treating him or her.
Causes Of Congestive Heart Failure:
Most of the time, CHF is caused by damage in the heart valves. In the heart of a healthy individual, the valve automatically closes between two pumps. This ensures that the blood continues to flow in the right direction. However, if the valve is damaged and it doesnt close properly, then the blood also cannot circulate like it should. This, in turn, can lead to CHF. That said, other causes also exist, including atherosclerosis, birth defects, infections, and heart attacks, to name but a few.
Atherosclerosis is of particular concern. Not only can it directly cause CHF, but it can also increase blood pressure. With high blood pressure, people are more likely to develop CHF as it means their heart has to work harder to pump the blood in the body. In fact, scientists agree that some 75% of people who have been diagnosed with CHF, also have a high blood pressure. Needless to say, it is of incredible importance that someone with CHF maintain a normal blood pressure, so as not to make the heart work even harder.
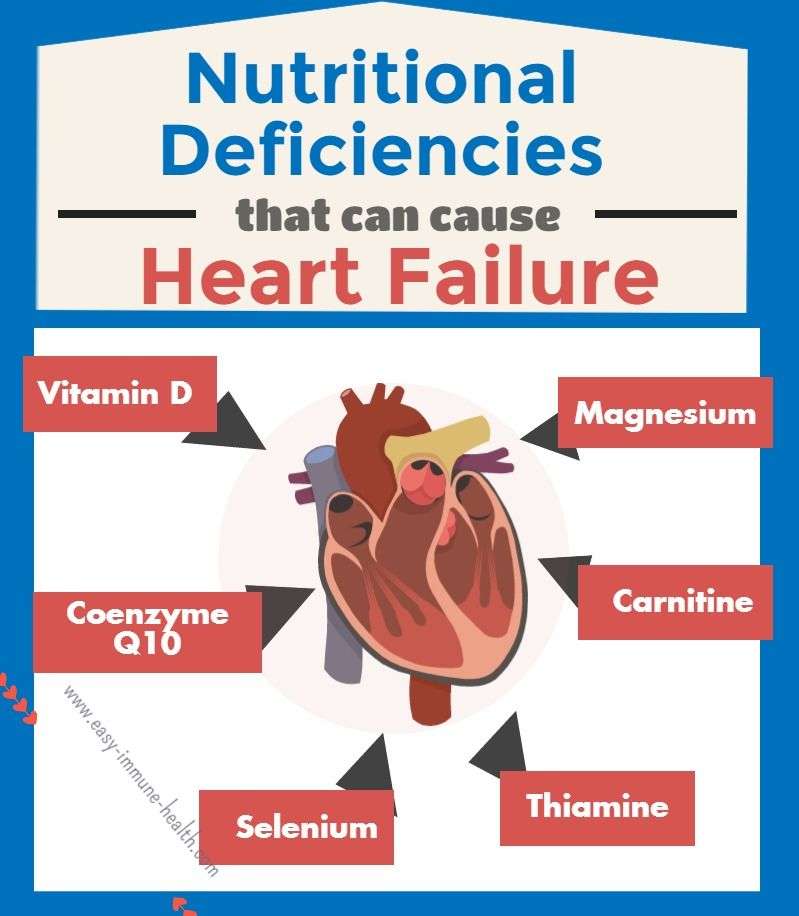
Various other factors increase the chances of someone developing CHF. These include things, such as various nutritional deficiencies, excessive salt intake, emotional stress, liver disease, and kidney disease. Essentially, if you have ever done anything that placed your heart under abnormal stress and strain, there is a chance that you will develop CHF.
Women And Heart Failure
Women are just as likely as men to develop heart failure, but there are some differences:
- Women tend to develop heart failure later in life compared with men.
- Women tend to have heart failure caused by high blood pressure and have a normal EF .
- Women may have more shortness of breath than men do. There are no differences in treatment for men and women with heart failure.
Don’t Miss: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
Congestive Heart Failure Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment can help people who have heart failure live longer, more active lives. Treatment for heart failure depends on the type and severity of the heart failure.
Heart failure is a chronic disease needing lifelong management. However, with treatment, signs and symptoms of heart failure can improve, and the heart sometimes becomes stronger. Treatment may help you live longer and reduce your chance of dying suddenly.
Doctors sometimes can correct heart failure by treating the underlying cause. For example, repairing a heart valve or controlling a fast heart rhythm may reverse heart failure. But for most people, the treatment of heart failure involves a balance of the right medications and, in some cases, use of devices that help the heart beat and contract properly.
The goals of treatment for all stages of heart failure include:
- Treating the conditions underlying cause, such as coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes
- Reducing symptoms
- Stopping the heart failure from getting worse
- Increasing your lifespan and improving your quality of life
Treatments usually include heart-healthy lifestyle changes, medicines, and ongoing care. If you have severe heart failure, you also may need medical procedures or surgery.
Lifestyle and home remedies
- Stop smoking. Smoking damages your blood vessels, raises blood pressure, reduces the amount of oxygen in your blood and makes your heart beat faster.
Medications
Surgery and medical devices
When Is Surgery Necessary For Congestive Heart Failure
Surgery can repair some underlying causes of heart failure, such as blockage of the coronary arteries, a valve problem, a congenital heart defect, or thickened pericardium. For patients with severe coronary artery disease, coronary artery bypass graft surgery can be conducted to circumvent blockages in vessels and ensure that the heart muscle maintains its blood supply. Valve replacement surgery can also be performed to repair malfunctioning heart valves. However, once the heart’s ability to pump blood is severely, permanently, and irreversibly impaired, no surgery can repair the damage. The only alternative is a heart transplant. This option is for patients who are not elderly and who do not have other medical conditions that would make it unlikely for a heart transplant to be successful. Heart transplant evaluations are done in specialized centers. Over the years there have been new innovations in the field of cardiac surgery and if a heart transplant is not available, a left ventricular assist device may be implanted to help prolong life.
Left ventricle assist device : This device is surgically implanted to mechanically bypass the left ventricle. It can be used as a âbridge to transplantâ until a heart transplant is available.
- Alternatively, LVADs are also being used as âdestination therapyâ in patients who are not eligible for a transplant, but only at approved specialized medical centers.
Congestive Heart Failure Follow-up
You May Like: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Clinicians Show Gender Racial Biases In Treatment Decisions For Heart Failure Patients
The Black community as a whole has a higher rate of heart disease, as well as a higher rate of many of the main risk factors for heart disease and heart failure, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity. While there is no one-size-fits all explanation for this increased risk, researchers believe a combination of socioeconomic factors, environment, education, stress levels, and culture are all at play, according to UT Southwestern Medical Center.
Researchers suggest Hispanic Americans are at a greater risk of heart failure, as well. A study published in 2016 in the American Heart Associations journal Circulation: Heart Failure found that about one-half of the middle-aged Hispanic adults studied had heart problems that could lead to heart failure. However, fewer than 1 in 20 participants knew they had a health issue. The researchers found these individuals also had higher rates of obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
How Long Can An 80 Year Old Live With Congestive Heart Failure
In a recent study, it was reported that patients hospitalized with moderate systolic heart failure faced a median expected survival time of 2.4 years if they were aged 71 to 80 years and 1.4 years if they were aged 80 years or more. In patients with more advanced systolic dysfunction, life expectancy was even shorter.
Don’t Miss: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
Social Determinants Of Health
Social determinants such as disadvantage, status, lack of , , access to play an important role in myocardial infarction risk and survival. Studies have shown that low is associated with an increased risk of poorer survival. There are well-documented disparities in myocardial infarction survival by , , , and census-tract-level .
Race: In the U.S. have a greater burden of myocardial infarction and other cardiovascular events. On a population level, there is a higher overall of risk factors that are unrecognized and therefore not treated, which places these individuals at a greater likelihood of experiencing adverse outcomes and therefore potentially higher and .
Socioeconomic status: Among individuals who live in the low- areas, which is close to 25% of the US population, myocardial infarctions occurred twice as often compared with people who lived in higher SES areas.
Immigration status: In 2018 many lawfully present who are eligible for coverage remain uninsured because immigrant families face a range of enrollment barriers, including fear, confusion about eligibility policies, difficulty navigating the enrollment process, and and challenges. Uninsured are ineligible for coverage options due to their immigration status.
Health care access: Lack of and financial concerns about accessing care were associated with delays in seeking emergency care for acute myocardial infarction which can have significant, adverse consequences on patient outcomes.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B
ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
You May Like: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
When Should I Call An Ambulance
If you have any of the symptoms below, call triple zero immediately and ask for an ambulance. If calling triple zero does not work on your mobile phone, try calling 112.
- chest pain thats severe or worsening, or has lasted longer than 10 minutes
- chest pain that feels heavy, crushing or tight
- other symptoms, such as breathlessness, nausea, dizziness or a cold sweat
- pain in your jaw or down your left arm
How Can I Prevent Heart Failure
You can prevent heart failure by preventing coronary heart disease and heart attack. The best way to do this is to reduce or eliminate the risk factors that lead to heart failure. You could:
- drink alcohol in moderation
- reduce stress and look after your mental wellbeing
If you have had a heart attack, its even more important to manage your risk factors and follow your treatment plan. Make sure you check in frequently with your healthcare team.
Some risk factors such as your age, whether you have other health conditions, or your genes may be outside your control. Speak with your doctor if you have concerns about developing heart failure, and how you can manage it.
Also Check: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Facts About Heart Failure In The United States
- About 6.2 million adults in the United States have heart failure.1
- In 2018, heart failure was mentioned on 379,800 death certificates .1
- Heart failure costs the nation an estimated $30.7 billion in 2012.2 This total includes the cost of health care services, medicines to treat heart failure, and missed days of work.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
People with , most commonly or , frequently have chronic shortness of breath and a chronic productive cough. An presents with increased shortness of breath and production. is a risk factor for thus this condition should be ruled out. In an acute exacerbation treatment is with a combination of , , and possibly .
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Surgical Treatments For Congestive Heart Failure
A variety of surgical procedures may be used in the treatment of some cases of congestive heart failure including:
- and stent placement or coronary artery bypass may be an option for people with congestive heart failure who have severely blocked coronary arteries.
- Heart transplant may be the only treatment option in severe cases of congestive heart failure in which medications and lifestyle and dietary changes do not improve heart function.
- Left is a device surgeons connect to the heart to improve heart function. It may be used as a “bridge treatment” while waiting for a or as a treatment in itself.
- may be used in some cases to control abnormal heart rhythms.
- Valve surgery repair or replacement of damaged heart valves
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
We assess the current health status of the patient to establish a baseline and develop a long-term health plan with the goal of improving the patients health, says Dr. Jacoby. This may involve the optimization of medicines and therapies, adding new medication or maybe enrollment in one of the clinical trials going on here.
Theres no quick fix, he says. Stabilizing and/or reversing a patients condition often involves long-term collaborative follow-up with a referring cardiologist or physician, Dr. Jacoby says.
In worst-case scenarios, we may offer advanced therapies, which include mechanical solutions, a heart transplant or hospice, Dr. Jacoby says. But first, we work very closely with our partners in cardiology and Interventional Cardiology Program at Yale to see if the patient would benefit from any interventional strategies.
“Yale has the best program in the area for heart transplants and artificial parts, but we want to exhaust all other options to avoid either if we can.
Also Check: Flonase Chest Pain
Congestive Heart Failure Procedures And Interventions
Other treatment or procedures may be offered, depending on the underlying cause of the heart failure.
Angioplasty: This is an alternative to coronary bypass surgery for some people whose heart failure is caused by coronary artery disease and may be compounded by heart damage or a previous heart attack. Angioplasty is performed to treat narrowing or blockage of a coronary artery that supplies the left ventricle with blood. The narrowing or blockage is caused by cholesterol deposits.
- Angioplasty begins with the cardiac catheterization procedure during which a long, thin tube called a catheter is inserted through the skin, into a blood vessel, and threaded into the affected artery. This procedure is performed while the person is under local anesthesia.
- At the point of the atherosclerotic narrowing or blockage, a tiny balloon and/or an expandable metal stent, attached to the end of the catheter, is inflated and/or deployed.
- The expanded stent pushes aside the cholesterol deposits that are blocking the artery so that blood can flow through in a more normal manner.
Pacemaker: This device controls the rate of the heartbeat. A pacemaker may keep the heart from going too slow, increasing heart rate when the heart is not increasing enough with activity. It also helps sustain regular rates when the heart is not beating in a coordinated way. Or, the pacemaker performs some combination of these.
Congestive Heart Failure Stages
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood through to meet the bodys needs for blood and oxygen 19). Basically, the heart cant keep up with its workload.
At first the heart tries to make up for this by 20):
- Enlarging. The heart stretches to contract more strongly and keep up with the demand to pump more blood. Over time this causes the heart to become enlarged.
- Developing more muscle mass. The increase in muscle mass occurs because the contracting cells of the heart get bigger. This lets the heart pump more strongly, at least initially.
- Pumping faster. This helps to increase the hearts output.
The body also tries to compensate in other ways 21):
- The blood vessels narrow to keep blood pressure up, trying to make up for the hearts loss of power.
- The body diverts blood away from less important tissues and organs , the heart and brain.
These temporary measures mask the problem of heart failure, but they dont solve it. Heart failure continues and worsens until these substitute processes no longer work 22).
Eventually the heart and body just cant keep up, and the person experiences the fatigue, breathing problems or other symptoms that usually prompt a trip to the doctor.
The bodys compensation mechanisms help explain why some people may not become aware of their condition until years after their heart begins its decline. Its also a good reason to have a regular checkup with your doctor 23).
Recommended Reading: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
What Is Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
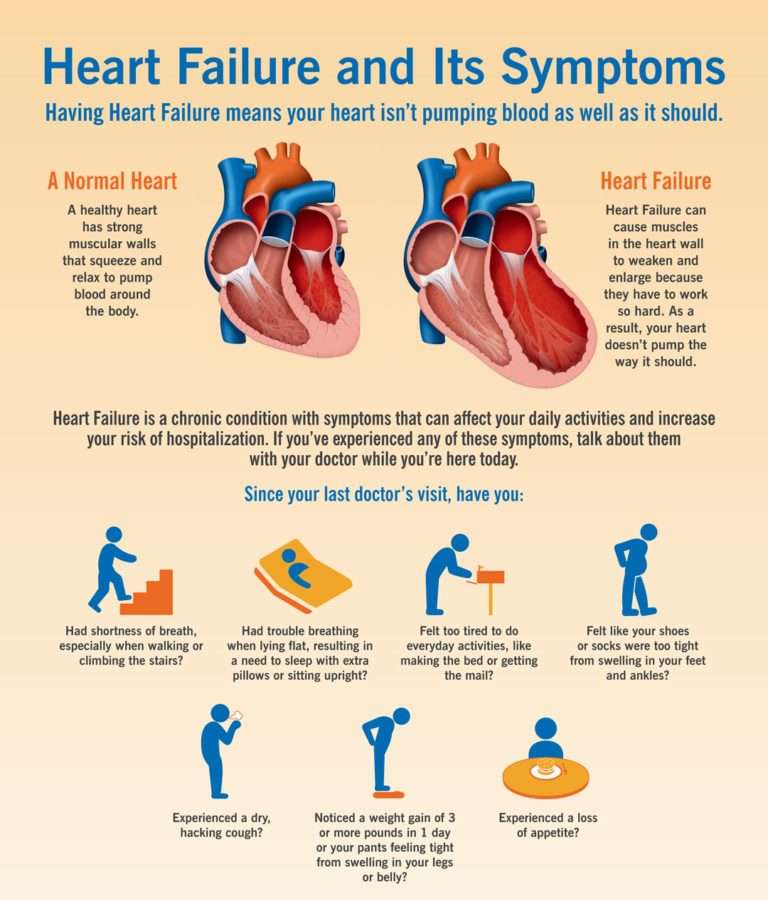
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart doesnt pump as well as it should.
While the term “heart failure” may sound like the heart has stopped working, that isn’t actually the case. It still pumps, just inefficiently.
As a result, there’s a reduction in blood flow to the body and a backup of fluid into the lungs, liver, abdomen, and lower extremities.
Heart failure is a serious condition that is often the end stage or final outcome of many cardiovascular conditions, according to the American Heart Association .
While there’s no cure for heart failure, medication and healthy lifestyle changes can help manage the condition and allow people to maintain a good quality of life.
What Medications Should I Avoid If I Have Heart Failure
There are several different types of medications that are best avoided in those with heart failure including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as Motrin or Aleve. For relief of aches, pains, or fever take Tylenol instead.
- Most calcium channel blockers
- Some nutritional supplements, such as salt substitutes, and growth hormone therapies
- Antacids that contain sodium
If youâre taking any of these drugs, discuss them with your doctor.
Itâs important to know the names of your medications, what theyâre used for, and how often and at what times you take them. Keep a list of your medications and bring them with you to each of your doctor visits. Never stop taking your medications without discussing it with your doctor. Even if you have no symptoms, your medications decrease the work of your heart so that it can pump more effectively.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Bleeding Around The Heart
Myocytes And Myocardial Remodeling
In the failing heart, increased myocardial volume is characterized by larger myocytes approaching the end of their life cycle. As more myocytes drop out, an increased load is placed on the remaining myocardium, and this unfavorable environment is transmitted to the progenitor cells responsible for replacing lost myocytes.
Progenitor cells become progressively less effective as the underlying pathologic process worsens and myocardial failure accelerates. These featuresnamely, the increased myocardial volume and mass, along with a net loss of myocytesare the hallmark of myocardial remodeling. This remodeling process leads to early adaptive mechanisms, such as augmentation of stroke volume and decreased wall stress and, later, to maladaptive mechanisms such as increased myocardial oxygen demand, myocardial ischemia, impaired contractility, and arrhythmogenesis.
As heart failure advances, there is a relative decline in the counterregulatory effects of endogenous vasodilators, including nitric oxide , prostaglandins , bradykinin , atrial natriuretic peptide , and B-type natriuretic peptide . This decline occurs simultaneously with the increase in vasoconstrictor substances from the RAAS and the adrenergic system, which fosters further increases in vasoconstriction and thus preload and afterload. This results in cellular proliferation, adverse myocardial remodeling, and antinatriuresis, with total body fluid excess and worsening of heart failure symptoms.
