Pathway Of Blood To The Brain
SKU: S02161
This exhibit depicts the pathways of blood from the heart to the brain. Blood leaves the heart through the aortic arch and enters the common carotid arteries. From there, it enters into the internal carotid arteries and travels through the carotid canal into the skull. Once it reaches the inferior brain, it branches out and enters into the cerebral arteries to supply the brain tissues.
Where Is Your Heart And What Does It Look Like
The heart is located under the rib cage, under and to the left of your breastbone , and between your lungs.
Looking at the outside of the heart, you can see that the heart is made of muscle. The strong muscular walls contract , pumping blood to the arteries. The major blood vessels that are connected to the heart include the aorta, the superior vena cava, the inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery , the pulmonary veins and the coronary arteries .
On the inside, the heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ. It is divided into the left and right side by a muscular wall called the septum. The right and left sides of the heart are further divided into two top chambers called the atria, which receive blood from the veins, and two bottom chambers called ventricles, which pump blood into the arteries.
The atria and ventricles work together, contracting and relaxing to pump blood out of the heart in a coordinated and rhythmic fashion. As blood leaves each chamber of the heart, it passes through a valve. There are four heart valves within the heart:
- Mitral valve
- Aortic valve
- Pulmonic valve
The tricuspid and mitral valves lie between the atria and ventricles. The aortic and pulmonic valves lie between the ventricles and the major blood vessels leaving the heart.
The heart valves work the same way as one-way valves in the plumbing of your home. They prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
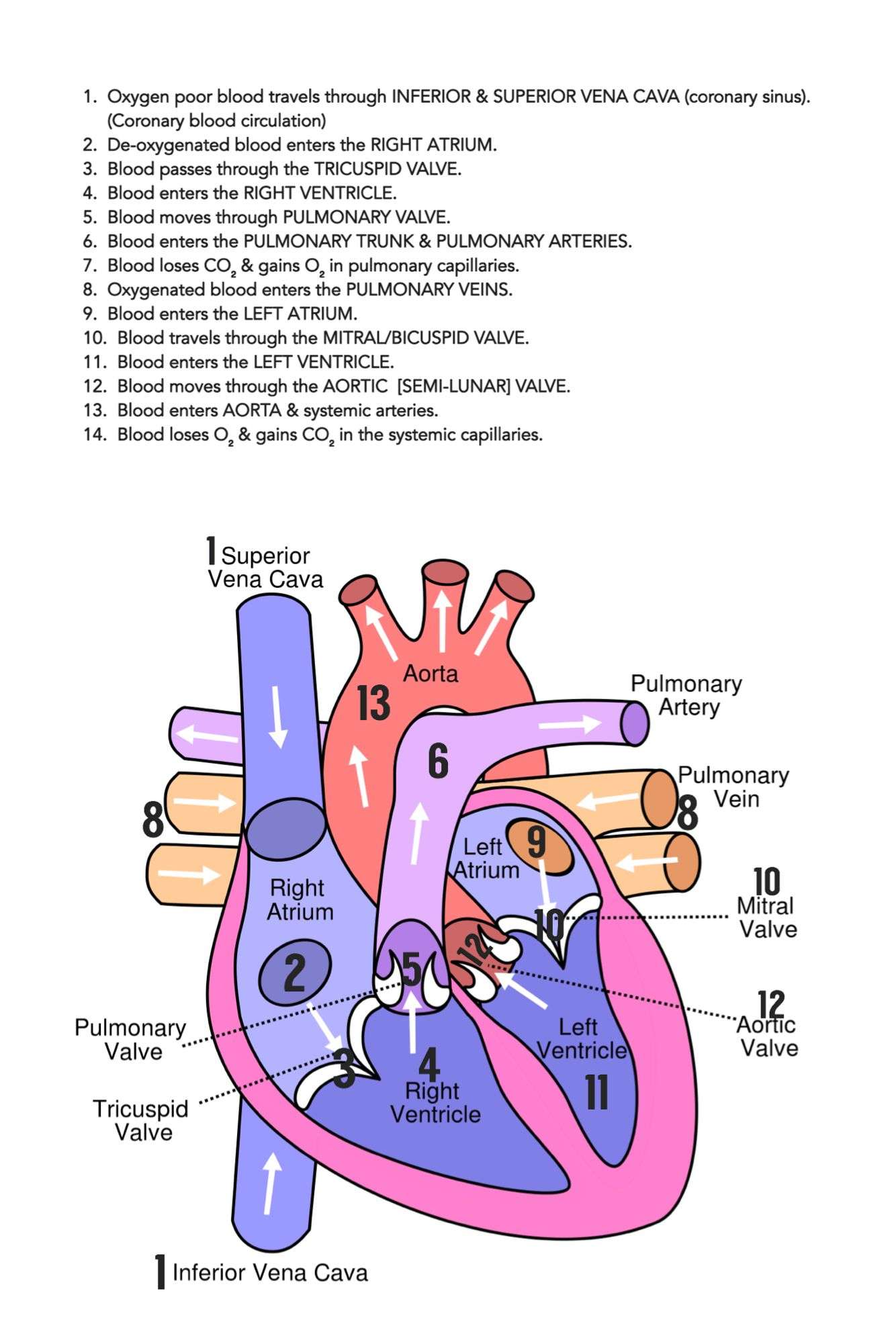
S Of Blood Flow Through The Heart
In summary from the video, in 14 steps, blood flows through the heart in the following order: 1) body > 2) inferior/superior vena cava > 3) right atrium > 4) tricuspid valve > 5) right ventricle > 6) pulmonary arteries > 7) lungs > 8) pulmonary veins > 9) left atrium > 10) mitral or bicuspid valve > 11) left ventricle > 12) aortic valve > 13) aorta > 14) body.
Also Check: End Stage Coronary Artery Disease
Heart Contraction And Blood Flow
Almost everyone has heard the real or recorded sound of a heartbeat. When the heart beats, it makes a lub-DUB sound. Between the time you hear lub and DUB, blood is pumped through the heart and circulatory system.
A heartbeat may seem like a simple event repeated over and over. A heartbeat actually is a complicated series of very precise and coordinated events that take place inside and around the heart.
Each side of the heart uses an inlet valve to help move blood between the atrium and ventricle.
The tricuspid valve does this between the right atrium and ventricle. The mitral valve does this between the left atrium and ventricle. The lub is the sound of the mitral and tricuspid valves closing.
Each of the hearts ventricles has an outlet valve. The right ventricle uses the pulmonary valve to help move blood into the pulmonary arteries. The left ventricle uses the aortic valve to do the same for the aorta. The DUB is the sound of the aortic and pulmonary valves closing.
Each heartbeat has two basic parts: diastole and atrial and ventricular systole . During diastole, the atria and ventricles of the heart relax and begin to fill with blood.
At the end of diastole, the hearts atria contract and pump blood into the ventricles. The atria then begin to relax. Next, the hearts ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart.
Right Vs Left Side Of The Heart
The easiest way to understand the blood flow through the heart is to divide the heart into 2 sides.
We first have the right side of the heart shown in blue below.
There are 6 main steps or structures in which blood flows through the right side of the heart.
Next, we have the left side of the heart shown in red.
Similar to the right side, there are 6 main steps or structures in which blood flows through the left side of the heart.
Diagram: Blood flow steps through the right and left side of the heart, cardiac anatomy and structures, and cardiac circulation pathway.
Also Check: Does Tylenol Reduce Blood Pressure
Adding Oxygen To Blood
Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood enters the heart’s right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs.
The pulmonary artery then carries the oxygen-poor blood from your heart to the lungs. Your lungs add oxygen to your blood. The oxygen-rich blood returns to your heart through the pulmonary veins. Visit our How the Lungs Work Health Topic to learn more about what happens to the blood in the lungs.
The oxygen-rich blood from the lungs then enters the left atrium and is pumped to the left ventricle. The left ventricle generates the high pressure needed to pump the blood to your whole body through your blood vessels.
When blood leaves the heart to go to the rest of the body, it travels through a large artery called the aorta. A balloon-like bulge, called an aortic aneurysm, can sometimes occur in the aorta.
How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart
The right and left sides of the heart work together. The pattern described below is repeated over and over, causing blood to flow continuously to the heart, lungs, and body.
Right side of the heart
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the right atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
Left side of the heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
Read Also: Heart Failure Progression Timeline
Supplying Oxygen To The Hearts Muscle
Like other muscles in the body, your heart needs blood to get oxygen and nutrients. Yourcoronary arteries supply blood to your heart. These arteries branch off from the aorta so that oxygen-rich blood is delivered to your heart as well as the rest of your body.
- The left coronary artery delivers blood to the left side of your heart, including your left atrium and ventricle and the septum between the ventricles.
- The circumflex artery branches off from the left coronary artery to supply blood to part of the left ventricle.
- The left anterior descending artery also branches from the left coronary artery and provides blood to parts of both the right and left ventricles.
- The right coronary artery provides blood to the right atrium and parts of both ventricles.
- The marginal arteries branch from the right coronary artery and provide blood to the surface of the right atrium.
- The posterior descending artery also branches from the right coronary artery and provides blood to the bottom of both ventricles.
Arteries supplying oxygen to the body. The coronary arteries branch off the aorta and supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. At the top of your aorta, arteries branch off to carry blood to your head and arms. Arteries branching from the middle and lower parts of your aorta supply blood to the rest of your body.
Some conditions can affect normal blood flow through these heart arteries. Examples include:
- The small cardiac vein.
Where Does A Drop Of Blood Start In The Circulatory System
To trace a drop of blood through the entire circulatory system, we will start in the right atrium. Deoxygenated blood flows from the right atrium, through the tricuspid valve, to the right ventricle. From the right ventricle the blood flows through the pulmonary valve, to the pulmonary artery, leading to the lungs where the blood picks up oxygen.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Enlarged Heart In Adults
The Exterior Of The Heart:
Below is a picture of the outside of a normal, healthy, human heart.
The illustration shows the front surface of the heart, including the coronary arteries and major blood vessels.
The heart is the muscle in the lower half of the picture. The heart has four chambers. The right and left atria are shown in purple. The right and left ventricles are shown in red.
Connected to the heart are some of the main blood vessels arteries and veins that make up the blood circulatory system.
The ventricle on the right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs.
When you breathe air in, oxygen passes from the lungs through blood vessels where its added to the blood. Carbon dioxide, a waste product, is passed from the blood through blood vessels to the lungs and is removed from the body when you breathe air out.
The atrium on the left side of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
The pumping action of the left ventricle sends this oxygen-rich blood through the aorta to the rest of the body.
What Is The Path Blood Travels Through Your Body
Bloodthroughbloodbodyofblood flowsyouryourthrough
. Regarding this, what is the correct order of the flow of blood?
Blood from right atrium enters right ventricle and pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs for oxygenation. Two pulmonary veins come from each lung and pass O 2-rich blood to left atrium. Blood enters left ventricle from the left atrium.
Similarly, in what order does blood flow through the heart? Blood enters the heart through two large veins the posterior and the anterior vena cava carrying deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium. Blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve.
Just so, what is the journey of the blood?
The pathway of blood through the heartOxygenated blood is carried to the heart from the lungs in the pulmonary vein. It goes into the left atrium, through the bicuspid valve and into the left ventricle. The ventricle pumps the blood through the semilunar valve, into the aorta and round the body.
Where does blood go after leaving the lungs?
Veins. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins, which return it to the left part of the heart, completing the pulmonary cycle. This blood then enters the left atrium, which pumps it through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
Also Check: Loratadine Heart Palpitations
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, as well as the side and back of the left ventricle. The left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
Anatomy Of Your Heart
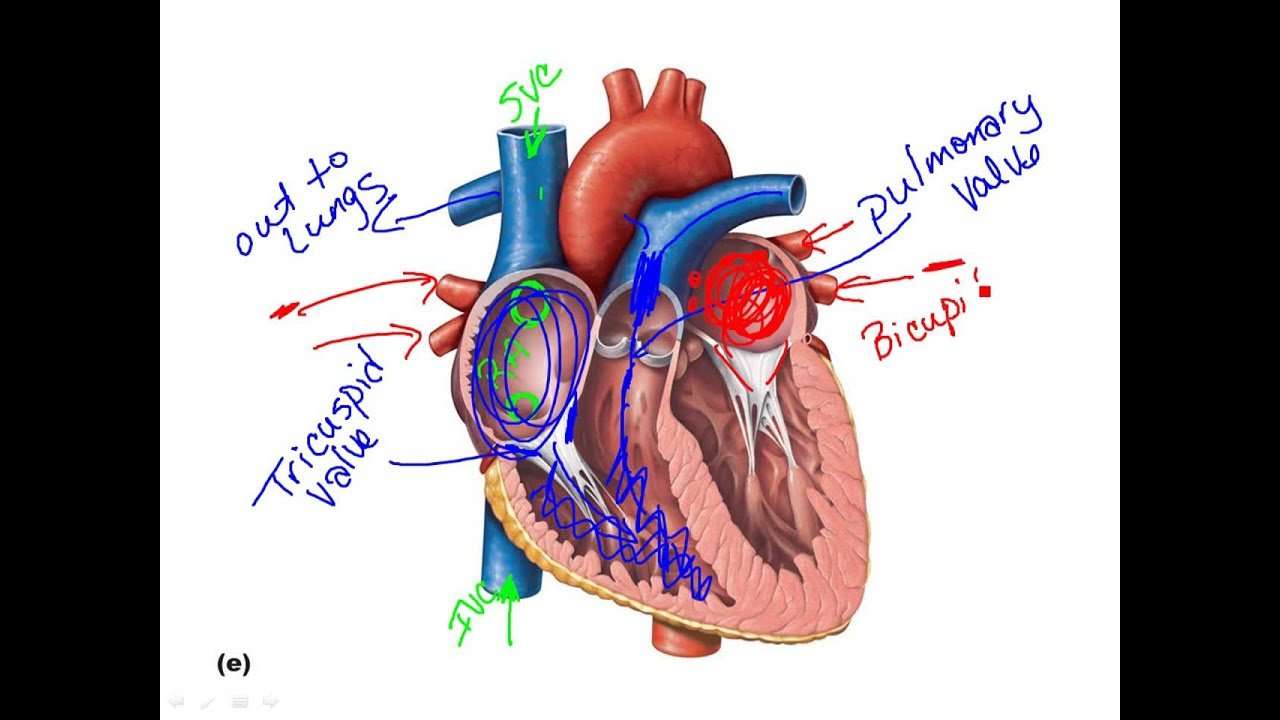
Your heart is in the center of your chest, near your lungs. It has four hollow heart chambers surrounded by muscle and other heart tissue. The chambers are separated by heart valves, which make sure that the blood keeps flowing in the right direction. Read more about heart valves in Blood Flow.
Anatomy of the interior of the heart. This image shows the four chambers of the heart and the direction that blood flows through the heart. Oxygen-poor blood, shown in blue-purple, flows into the heart and is pumped out to the lungs. Then oxygen-rich blood, shown in red, is pumped out to the rest of the body, with the help of the heart valves.
Don’t Miss: Massive Heart Attack Definition
What Is The Path Blood Takes In The Circulatory System
The purpose of the Circulatory System is to deliver oxygen and nutrients to all the cells in the body. The circulatory consists of the heart and all the bood vessels in the body . Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood to the heart. The smallest blood vessels are the capillaries and they deliver the blood and oxygen to the cells. The blood vessels is said to resemble the branches of a tree with the main artery being the aorta which leaves the heart. The aorta then branches into smaller arteries which then branch into capillaries.
See also:
Image of path blood takes through circulatory system National Library of Medicine NIH.
What Does The Heart Do
The heart is a pump, usually beating about 60 to 100 times per minute. With each heartbeat, the heart sends blood throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen to every cell. After delivering the oxygen, the blood returns to the heart. The heart then sends the blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen. This cycle repeats over and over again.
Don’t Miss: What Happens Inside The Heart To Cause A Heart Attack
Each Heart Beat Is A Squeeze Of Two Chambers Called Ventricles
The ventricles are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood empties into each ventricle from the atrium above, and then shoots out to where it needs to go. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium, then pumps the blood along to the lungs to get oxygen. The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium, then sends it on to the aorta. The aorta branches into the systemic arterial network that supplies all of the body.
Basics Parts Of The Heart
Understanding the function of the heart is helpful to learn more about its anatomy. Here are the basic parts of the heart:
1. Right Atrium
The heart can be divided into right and left halves, as well as into the upper and lower chambers. There are two upper chambers called atria and two lower chambers called ventricles. On each side of the heart, there are one atrium and one ventricle. Blood from the body goes back to the heart via the right atrium.From the right atrium, blood will then pass through a valve called the tricuspid valve, to go to the next chamber. Valves are structures that make sure there is a one-way forward flow, thus keeping the blood from passing backward.
2. Right Ventricle
The right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries, which are guarded by another valve called the pulmonic valve.
3. Pulmonary Circulation
The pulmonary arteries distribute blood to the lungs. Blood circulates in the lungs, where oxygen is added to the bloodand carbon dioxide is removed. Blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins, which go into the left chambers.
4. Left Atrium
The left atrium receive blood from the lungs and pushes it through the mitral valve to pass it into the left ventricle.
5. Left Ventricle
The left ventricle pumps blood to the rest of your body through the aorta, with blood passing through to theaortic valve.
6. Aorta
Read Also: Will Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure
What Causes Blood To Flow Through The Heart
Blood flows through our heart because of the Right and left side of our heart works in a specific pattern.
Explanation:
The Process of blood passage throughout our heart-
Right Side-
1) Blood enters the heart through two large veins. They are –Inferior vena cava and Superior vena cava. Which emties Oxygen poor blood into the Right atrium of heart.
2) Now, as the atrium contracts blood flows from right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
3) When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atria while the ventricle contracts.
4) As the ventricle contracts blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs where it is oxygenated.
Left Side –
1) The pulmonary vein empties oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart.
2)As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
3) When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
4) As the ventricle contracts blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
