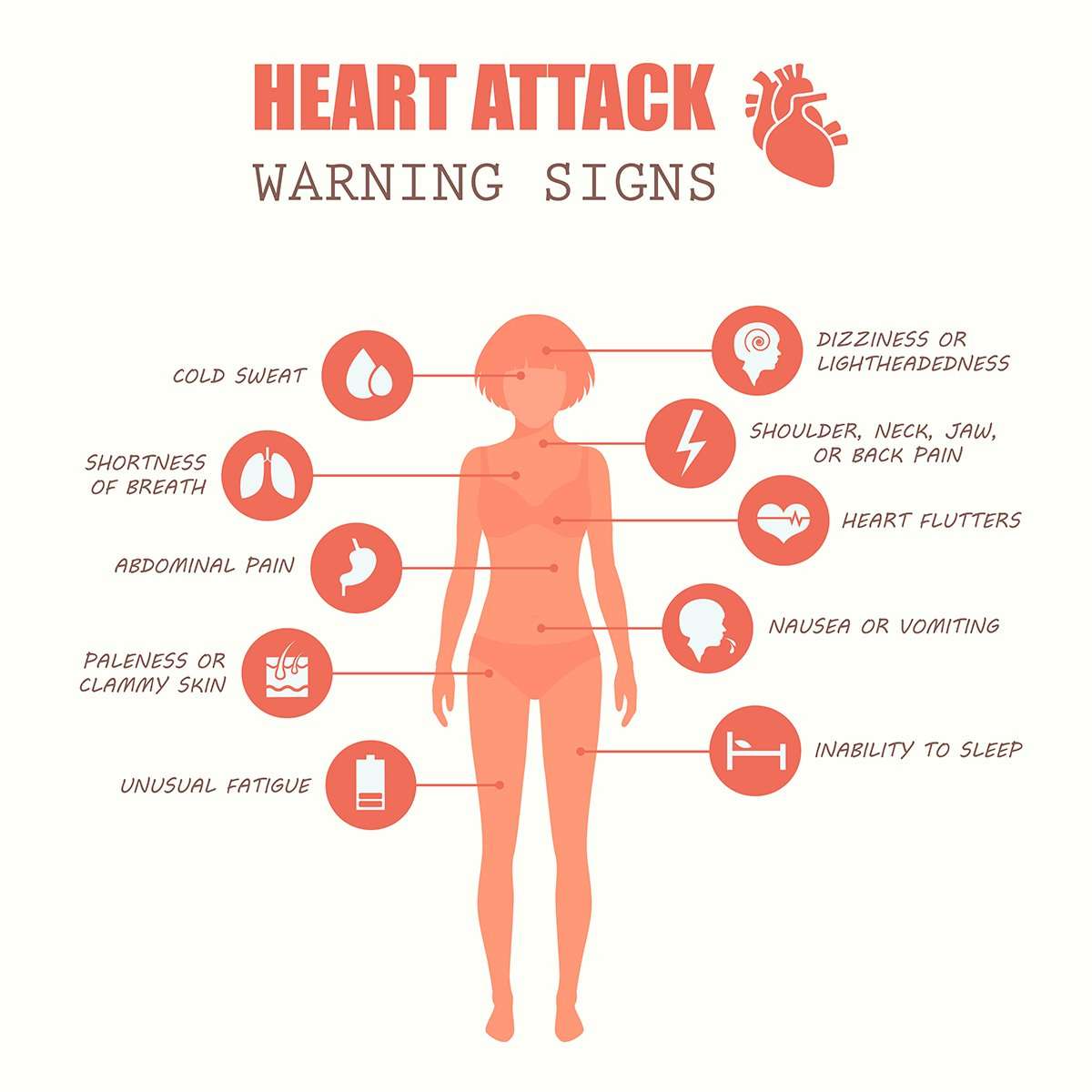
Symptoms That Should Accompany Left Arm Pain
Chest pain: Chest pain is the most commonly recognized symptom indicating that there is something wrong with the heart. But for some patients, chest pain does not occur as a symptom of a heart attack. You may experience pressure, tightness, or pain originating in the center of the chest spreading down the arm, to the back, or to the neck and jaw .
Unusual fatigue: We all get tired from time to time, but if fatigue is new, sudden, or dramatic, it could be a sign of a heart attack. This includes suddenly feeling worn out after your typical exercise routine, feeling fatigued even without physical exertion or after simple activities like making the bed, and experiencing sleep problems even though you feel exceptionally tired.
Sweating and/or shortness of breath: If you experience sudden sweating or shortness of breath without physical activity, breathlessness that worsens without activity, shortness of breath that worsens when lying down and improving when getting up, stress sweat with no apparent stress, or sweating or shortness of breath that is accompanied by the other symptoms listed here, then these are signs of a heart attack.
Neck, jaw, and head ache: As mentioned, chest pains can move to affect the neck or jaw, but pain in the jaw or neck can occur without the presence of chest pain during a heart attack.
Upper back pain: Pain from the chest may radiate to the upper back and can be experienced in-between the shoulder blades.
Medication Vs Cardiac Catheterization
Q: How effective are stents in the prevention of heart attacks?
A: Far and away, everyone should get the medicines and if you can, and on top of that, if its the right time frame, everyone will do much better if they get a stent if they’re having a heart attack. The effectiveness of stents has been shown through years and years of clinical trials since the 80s. Prior to stenting, the only treatment for heart attacks was to give people the medicines we already mentioned and have them rest for up to 2 weeks to prevent the heart from demanding more oxygen. But during those days, almost 30-50% of people could still die if their blood vessel wasnt opened in some way. The era of stenting really dropped that rate down significantly and thats definitely the preferred strategy in addition to medicines to treat someone who has a fresh heart attack.
Signs Of Heart Attack That You Shouldnt Ignore
About every 40 seconds, someone has a heart attack in the US. Most people imagine that having a heart attack is always intense. But the truth is that sometimes you may be unsure if your are suffering from a heart attack because the signs can be subtle and different from what you may typically think of.
This makes heart attacks very dangerous. In fact, 1 in 5 heart attacks goes unnoticed, meaning the heart muscle is damaged due to lack of blood supply but the person is not aware of that this has occurred.
So what are the signs of a heart attack both subtle and not-so-subtle? Here are 4 signs of heart attack to be on the lookout for:
Read Also: Why Is My Resting Heart Rate High
Cardiac Pain That Isnt A Heart Attack
Cardiac pain, or angina, refers to discomfort in the chest because of something going on with the heart. The first thing a cardiologist will try to determine in a patient with cardiac pain is whether the pain is caused by clogged arteries.
Several conditions of the heart can cause cardiac pain but arent related to clogged arteries, including:
- Pericarditis: inflammation of the two thin layers of tissue that surround the heart
- Dissection: when the aorta splits and causes severe chest and back pain
- Myocarditis: inflammation of the heart muscle
- Cardiomyopathy: diseases of the heart muscle
Anxiety And Panic Attacks
Some episodes of chest pain occur as part of an anxiety or panic attack.
In addition to chest pain and overwhelming feelings of anxiety, these attacks can cause symptoms such as heart palpitations, sweating, breathlessness and dizziness.
Most panic attacks last for 5 to 20 minutes. In the long-term, you may benefit from psychological therapy and medication, or both.
Recommended Reading: What Information Would Be Included In The Care Plan Of An Infant In Heart Failure
Another Reason Your Chest May Hurt
That pain in your chest could be linked to another kind of attack that has nothing to do with your heart.
A panic attack or anxiety can reveal itself with symptoms chest tightness, sweating, shortness of breath that mimic those of a heart attack. There are some key differences between a panic attack and a heart attack, though.
- Many heart attacks follow physical strain or exertion, an indicator not typically connected to panic attacks.
- Panic attacks often feature a stabbing pain as opposed to the elephant-on-your-chest squeezing feeling that often accompanies a heart attack.
- Pain from heart attacks frequently radiates to other areas. In a panic attack, it usually stays in the chest area.
What Are The Warning Signs Of A Heart Attack
There are several different warning signs of a heart attack, and they are not always sudden or severe. Whether or not your chest pain symptoms include mild to severe pain, they should be considered heart-related until proven otherwise.
People having a heart attack may have just one of these symptoms, or a combination of several. They can come on suddenly or develop over a few minutes and get progressively worse. Symptoms usually last for at least 10 minutes.
Warning signs could include:
- discomfort or pain in the centre of your chest a heaviness, tightness or pressure, like something heavy sitting on your chest, or a belt tightening around your chest, or a bad case of indigestion
- discomfort in your arms, shoulder, neck, jaw or back
- other problems such as:
- feeling dizzy or light-headed
Heart attacks are more common in older people than in younger people, but they can occur in people of any age.
The pain you have may not sound like that described above, but its still important to see a doctor. Remember, all chest pain should be checked out by a doctor as soon as possible.
Also Check: Is Congestive Heart Failure Reversible
So How Do You Know If Youre Having A Heart Attack What Does It Feel Like
- Pressure in the chest that feels like something heavy is pressing down on you. It could also feel like a big rope is being tightened around your chest.
- Chest pain or a squeezing sensation in the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes. It may go away and then come back.
- Pain in the left arm that seems to radiate down towards the chest. The pain can also be in both arms or move from right arm to left arm.
- Sudden intense clenching pain in the jaw, arm, neck, back or stomach.
- Breaking out in a cold sweat with unexplained nausea, indigestion, vomiting or dizziness.
Waiting For An Ambulance
If you have had a heart attack, it’s important that you rest while you wait for an ambulance, to avoid unnecessary strain on your heart.
If aspirin is available and you are not allergic to it, slowly chew and then swallow an adult-size tablet while you wait for the ambulance.
Aspirin helps to thin your blood and improve blood flow to your heart.
Read Also: How Do You Calculate Heart Rate
Chest Pain And Heart Attack Symptoms
Chest pain is only one of the possible signs of an impending heart attack. If you notice one or more of the signs below in yourself or someone else, call 911 or your local emergency number right away.
-
Uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, burning, tightness, or pain in the center of the chest
-
Pain, numbness, pinching, prickling, or other uncomfortable sensations in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach
-
Shortness of breath
-
Heat/flushing or a cold sweat
-
Sudden heaviness, weakness, or aching in one or both arms
Shoulder Pain And Its Link To Heart Attack
Chest pain is one of the most common signs of a heart attack that many people recognize easily. But sometimes, there are other symptoms as well, which you may not associate with a heart event. Case in point, shoulder pain can be a sign of a heart attack.
The shoulder can begin to hurt as a result of the pain radiating from the chest. This is most commonly experienced on the left side where your heart resides.
Its important to be aware of this type of pain as a symptom of a heart attack, as well as other strong and weak indicators of a heart attack. The below chart will help you distinguish between the two.
| Strong Indicators of a Heart Attack | Weak Indicators of a Heart Attack |
|---|---|
| Burning, squeezing, tightness, pressure, or pain sensation | Knifelike or sharp pain felt when coughing or sneezing |
| Gradual increase of pain over a few minutes | Pain concentrated on one point. |
| Pain in the diffuse area, including middle of the chest | Pain occurring distinctly on one side of the body |
| Pain extending to back, jaw, neck, and left arm | Abrupt stabbing pain that lasts for a very short moment |
| Pressure or pain accompanied by other symptoms like sudden nausea, cold sweat, problems breathing | Pain lasting for days or hours without any other symptoms |
| Pressure or pain that is felt during emotional stress or physical exertion or when you are resting | Pain caused by pressing the chest or body movement |
Don’t Miss: Can You Live With Heart Failure
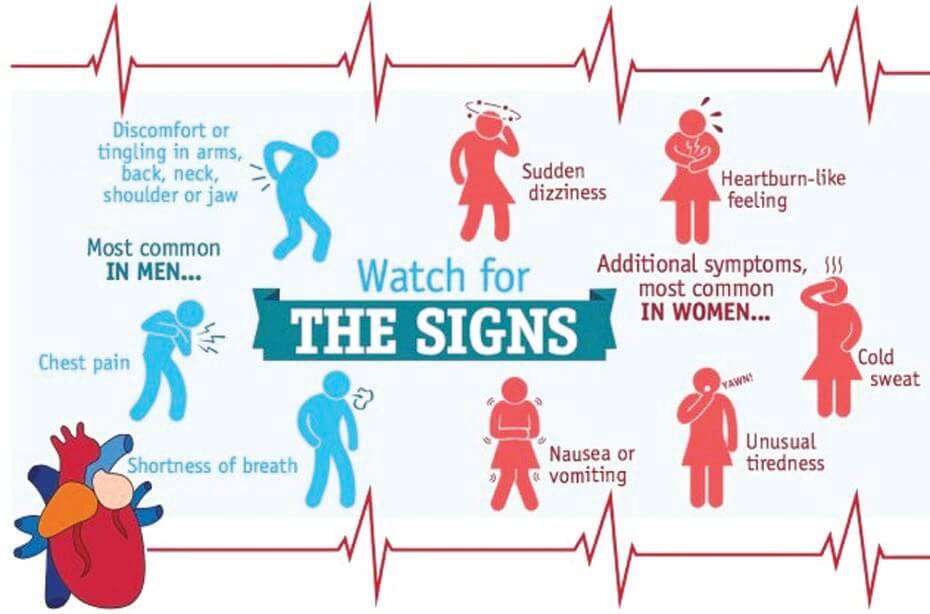
Symptoms Can Be Different For Men And Women
Men and women experience heart attack symptoms in slightly different ways. The main difference is how pain radiates.
- For men: Pain will spread to the left shoulder, down the left arm or up to the chin.
- For women: Pain can be much more subtle. It may travel to the left or right arm, up to the chin, shoulder blades and upper back or to abdomen . Women are also more likely to experience these accompanying symptoms: shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting and back or jaw pain. Read an in-depth overview of heart attack symptoms for women here.
Some heart attacks are sudden and intense, but most start slowly with mild pain and discomfort. Surviving a heart attack depends upon how well you recognize and react to these symptoms. Remember that “time is muscle.” The sooner you receive medical care, the sooner heart muscle can be saved.
What Does A Heart Attack Actually Feel Like
And Heart Attack Warning Signs
When it comes to heart attacks, most people immediately think chest pain with pain in the left arm. While those are two of the main warning signs of a heart attack, there are actually an abundance of other symptoms people experience that indicate theyve suffered a heart attack.
According to WebMD, More than 1 million Americans have heart attacks each year. Also called myocardial infarction, or MI, heart attacks can be deadly if medical care isnt received quickly.
Luckily, medical research is paving the way to a quicker diagnosis that can save more lives. Did you know when someone goes to the hospital worried theyre experiencing heart attack symptoms, they have to take tests and wait up to six hours for the results? If urgency is the key to care, that doesnt seem quite right.
The American Heart Association announced in Circulation that the US Food and Drug Administration approved a new blood test that quickly measures the amount of troponin T in your system. This protein is released when the heart muscle is damaged. The more the heart is damaged, the larger the amount of troponin T. This new test can potentially rule out a heart attack in less than an hour.
Recommended Reading: When Are Heart Palpitations Serious
How Long Does A Heart Attack Last
Initial heart attack symptoms, including chest pain and shortness of breath, may come and go. Symptoms often last around 10 minutes or longer.
A study published in Critical Pathways in Cardiology found that symptoms lasting less than five minutes are unlikely to indicate a heart attack, while symptoms lasting longer than five minutes should be taken seriously as signs of a myocardial infarction .
However, this finding comes from only one study. So if you have symptoms lasting longer than a few minutes, you need to call 911.
Chest Pain Pressure Squeezing And Fullness
Picture someone having a heart attack, and chances are you imagine them gasping for air and clutching their chest before falling unconscious. While you may experience chest pain during a heart attack, it may not be as dramatic. In some cases, it may not even be described as pain. Instead, it may feel more like pressure or squeezing in the chest.
Chest pain or chest discomfort is caused by an insufficient supply of oxygen-rich blood to your heart. During a heart attack, you may feel this pain in the center of the chest. It can last for a few minutes and disappear, or it may recur after a short break.
This symptom is a warning sign of blocked or narrowed arteries. Dont hesitate to report this to your doctor, even if this and other symptoms are not intense.
You May Like: Is Blood Pressure Related To Heart Rate
Chest Pain: How A Doctor Decides It Could Be A Heart Attack
Posted October 26, 2015
Patients with chest pain come to my clinic with a nervous expression and a million-dollar question, “Doctor, is it my heart?”
Such concern is valid. But understanding how medical providers think about chest pain may allay some fear.
If you come to a clinic with chest pain, your provider will have questions about the major factors for heart disease. I will ask if you:
- smoke
- have diabetes
- assess your age and gender
- check to see if you have a family history of heart disease.
Heart With Muscle Damage And A Blocked Artery
A less common cause of heart attack is a severe spasm of a coronary artery. The spasm cuts off blood flow through the artery. Spasms can occur in coronary arteries that aren’t affected by atherosclerosis.
Heart attacks can be associated with or lead to severe health problems, such as heart failure and life-threatening arrhythmias.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats. Ventricular fibrillation is a life-threatening arrhythmia that can cause death if not treated right away.
You May Like: Which Of The Following Statements Is False Regarding Coronary Heart Disease And Smoking
Can You Recognize A Heart Attack Or Stroke
What To Do When Every Moment Counts
How would you react to a medical emergency? When it comes to life-threatening conditions like heart attack or stroke, every minute counts. Get to know the signs and symptoms of these health threats. If you think you or someone else might be having a heart attack or stroke, get medical help right away. Acting fast could save your life or someone elses.
Heart disease and stroke are 2 of the top killers among both women and men in the U.S. Nationwide, someone dies from a heart attack about every 90 seconds, and stroke kills someone about every 4 minutes, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Quick medical help could prevent many of these deaths. Fast action can also limit permanent damage to the body.
Heart attack and stroke are caused by interruptions to the normal flow of blood to the heart or brain2 organs that are essential to life. Without access to oxygen-rich blood and nutrients, heart or brain cells begin to malfunction and die. This cell death can set off a series of harmful effects throughout the body. The changes ultimately lead to the familiar symptoms of a heart or brain emergency.
You might know the most common symptoms of heart attack: sustained, crushing chest pain and difficulty breathing. A heart attack might also cause cold sweats, a racing heart, pain down the left arm, jaw stiffness, or shoulder pain.
Chest Pain: Its Not Always A Matter Of The Heart
There are plenty of other potential suspects when it comes to chest pain.
Mild or severe discomfort in the middle or left side of the chest that feels like fullness, pressure or squeezing could be a potential sign of a cardiovascular event.Most people experience chest pain at some point, but how do you know if it is a heart attack or simply heartburn or anxiety?
Understanding the differences between cardiovascular events and other causes of chest pain can save you a trip to the emergency room. It is also important because the discomfort could be caused by other urgent conditions, as well as less serious issues that may point to a chronic medical problem.
When it comes to cardiovascular causes of chest pain, UAB Medicinecardiologist Gregory Chapman, M.D., says the usual suspects include coronary artery blockages, high blood pressure, and heart valve or rhythm disorders. But there are plenty of other potential suspects. Chapman included a chapter on chest pain diagnosis in his book A Strong and Steady Pulse: Cardiac Stories, which is scheduled for publication in 2021.
Take symptoms seriously
In the United States, nearly 6 percent of emergency room patients report chest pain. More than half of those cases involve non-cardiac chest pain, or NCCP, that is caused by heartburn, anxiety or other issues. A staggering 80 percent of patients who complain of chest pain during primary care visits are simply experiencing NCCP.
Gregory Chapman, M.D.Mimicking a heart attack
You May Like: How To Take Heart Rate Manually
