How Does Blood Flow Through Your Lungs
Once blood travels through the pulmonic valve, it enters your lungs. This is called the pulmonary circulation. From your pulmonic valve, blood travels to the pulmonary arteries and eventually to tiny capillary vessels in the lungs.
Here, oxygen travels from the tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, passes from the blood into the air sacs. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. Once the blood is oxygenated, it travels back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Exchange Of Gases Nutrients And Waste Between Blood And Tissue Occurs In The Capillaries
Capillaries are tiny vessels that branch out from arterioles to form networks around body cells. In the lungs, capillaries absorb oxygen from inhaled air into the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide for exhalation. Elsewhere in the body, oxygen and other nutrients diffuse from blood in the capillaries to the tissues they supply. The capillaries absorb carbon dioxide and other waste products from the tissues and then flow the deoxygenated blood into the veins.
Which Blood Vessels Carry Blood Away From The Heart
Explanation:
The ARTERIES are major blood vessels connected to your heart.
1. The pulmonary artery carries blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs to pick up a fresh supply of oxygen.
2. The aorta is the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood from the left side of the heart to the body.3. The coronary arteries are the other important arteries attached to the heart. They carry oxygen-rich blood from the aorta to the heart muscle, which must have its own blood supply to function.
The VEINS also are major blood vessels connected to your heart.
1. The pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left side of the heart so it can be pumped to the body.
2. The superior and inferior vena cavae are large veins that carry oxygen-poor blood from the body back to the heart.
You May Like: Reflux Palpitations
What Are Blood Vessels
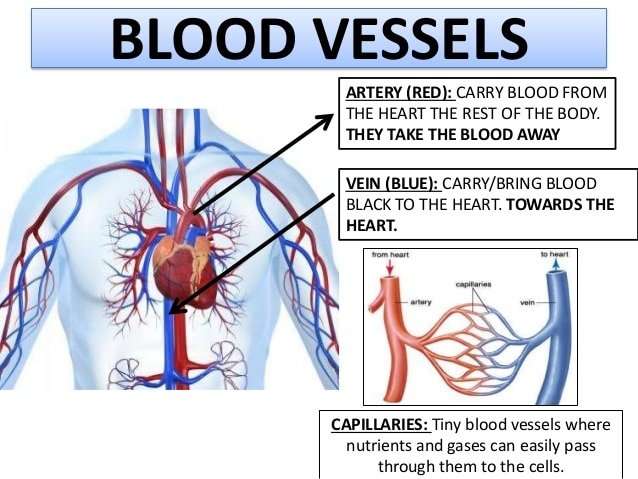
Blood vessels are channels that carry blood throughout your body. They form a closed loop, like a circuit, that begins and ends at your heart. Together, the heart vessels and blood vessels form your circulatory system. Your body contains about 60,000 miles of blood vessels.
There are three types of blood vessels:
- Arteries carry blood away from your heart.
- Veins carry blood back toward your heart.
- Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, connect arteries and veins.
Which Blood Vessels Carry Deoxygenated Blood Away From The Heart
pulmonary arteries
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues. The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart. They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
Also Know, what vessels carry deoxygenated blood to the right atrium? Great VesselsThe superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava bring deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium. The pulmonary trunk exits from the right ventricle and carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
One may also ask, which of the following blood vessels carries deoxygenated blood?
The heart
| Carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart. | |
| Pulmonary artery | Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. |
| Pulmonary vein | Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. |
| Aorta | Carries oxygenated blood from the heart around the body. |
Do veins carry blood away from the heart?
Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure
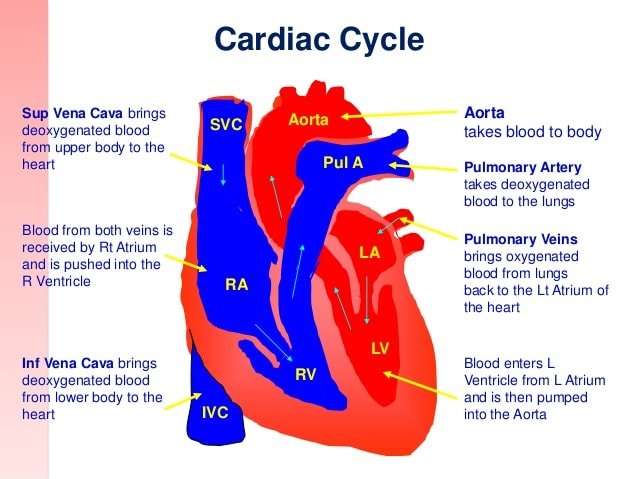
How Blood Flows Through The Body
As the heart pumps, blood is pushed through the body through the entire circulatory system. Oxygenated blood is pumped away from the heart to the rest of the body, while deoxygenated blood is pumped to the lungs where it is reoxygenated before returning to the heart.
Circulatory system: This illustration of the circulatory system shows where blood flows in the body. Red indicates oxygenated blood, while blue indicates deoxygenated blood.
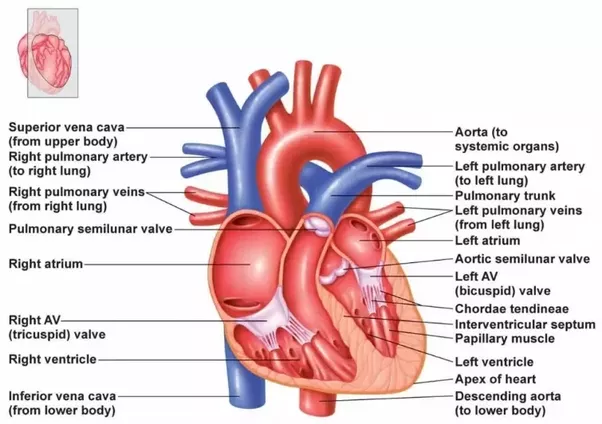
Introduction To The Major Blood Vessels Of The Heart:
The major blood vessels of the heart are the larger arteres and veins that attach to the atria and ventricles and transport blood to and from the
Blood is delivered to the right atrium from the systemic circulatory system by two veins:
- The superior vena cava transports oxygen-depleted blood from the upper extremities, head, and neck.
Learning about the cardiovascular system? You may like this cardiovascular system revision guide complete with diagrams, quizzes and free worksheets.
Don’t Miss: Low Blood Pressure Heart Failure Elderly
The Blood Supply To The Heart
Like any other muscle, the heart muscle needs a good blood supply. The coronary arteries take blood to the heart muscle. These are the first arteries to branch off the large artery which takes blood to the body from the left ventricle.
- The right coronary artery mainly supplies the muscle of the right ventricle.
- The left coronary artery quickly splits into two and supplies the rest of the heart muscle.
- The main coronary arteries divide into many smaller branches to supply all the heart muscle.
Read Also: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Function Of The Pericardium
The pericardium is important because it protects the heart from trauma, shock, stress, and even infections from the nearby lungs. It supports the heart and anchors it to the medastinum so it doesnt move within the body. The pericardium lubricates the heart and prevents it from becoming too large if blood volume is overloaded .
Despite these functions, the pericardium is still vulnerable to problems of its own. Pericarditis is the term for inflammation in the pericardium, typically due to infection. Pericarditis is often a severe disease because it can constrict and apply pressure on the heart and work against its normal function. Pericarditis comes in many types depending on which tissue layer is infected.
You May Like: How Long Can Someone Live With Heart Failure
What Causes Vascular Disease
Causes of vascular disease include:
-
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of vascular disease. It is unknown exactly how atherosclerosis starts or what causes it. Atherosclerosis is a slow, progressive, vascular disease that may start as early as childhood. However, the disease has the potential to progress rapidly. It is generally characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits along the innermost layer of the arteries. If the disease process progresses, plaque may form. This thickening narrows the arteries and can decrease blood flow or completely block the flow of blood to organs and other body tissues and structures.
-
Blood clots. A blood vessel may be blocked by an embolus or a thrombus .
-
Inflammation. In general, inflammation of blood vessels is referred to as vasculitis, which includes a range of disorders. Inflammation may lead to narrowing and blockage of blood vessels.
-
Trauma or injury. Trauma or injury involving the blood vessels may lead to inflammation or infection, which can damage the blood vessels and lead to narrowing and blockage.
-
Genetic. Certain conditions of the vascular system are inherited.
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Veins Carry Blood Back Toward The Heart
After the capillaries release oxygen and other substances from blood into body tissues, they feed the blood back toward the veins. First the blood enters microscopic vein branches called venules. The venules conduct the blood into the veins, which transport it back to the heart through the venae cavae. Vein walls are thinner and less elastic than artery walls. The pressure pushing blood through them is not as great. In fact, there are valves within the lumen of veins to prevent the backflow of blood.
Read Also: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Flutters
There Are Three Main Types Of Blood Vessels
Arteries
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues.The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart.
- They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
- They branch several times, becoming smaller and smaller as they carry blood further from the heart.
Capillaries
- Capillaries are small, thin blood vessels that connect the arteries and the veins.
- Their thin walls allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and waste products to pass to and from the tissue cells.
Veins
- These are blood vessels that take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Veins become larger and larger as they get closer to the heart.
- The superior vena cava is the large vein that brings blood from the head and arms to the heart, and the inferior vena cava brings blood from the abdomen and legs into the heart.
This vast system of blood vessels – arteries, veins, and capillaries – is over 60,000 miles long. That’s long enough to go around the world more than twice!
Blood flows continuously through your body’s blood vessels. Your heart is the pump that makes it all possible.
Adding Oxygen To Blood
Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood enters the hearts right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs.
The pulmonary artery then carries the oxygen-poor blood from your heart to the lungs. Your lungs add oxygen to your blood. The oxygen-rich blood returns to your heart through the pulmonary veins. Visit our How the Lungs Work Health Topic to learn more about what happens to the blood in the lungs.
The oxygen-rich blood from the lungs then enters the left atrium and is pumped to the left ventricle. The left ventricle generates the high pressure needed to pump the blood to your whole body through your blood vessels.
When blood leaves the heart to go to the rest of the body, it travels through a large artery called the aorta. A balloon-like bulge, called an aortic aneurysm, can sometimes occur in the aorta.
Read Also: Can Tylenol Raise Blood Pressure
What Are The Different Types Of Arteries
There are three types of arteries. Each type is composed of three coats: outer, middle, and inner.
- Elastic arteries are also called conducting arteries or conduit arteries. They have a thick middle layer so they can stretch in response to each pulse of the heart.
- Muscular arteries are medium-sized. They draw blood from elastic arteries and branch into resistance vessels. These vessels include small arteries and arterioles.
- Arterioles are the smallest division of arteries that transport blood away from the heart. They direct blood into the capillary networks.
There are four types of veins:
- Deep veins are located within muscle tissue. They have a corresponding artery nearby.
- Superficial veins are closer to the skins surface. They dont have corresponding arteries.
- Pulmonary veins transport blood thats been filled with oxygen by the lungs to the heart. Each lung has two sets of pulmonary veins, a right and left one.
- Systemic veins are located throughout the body from the legs up to the neck, including the arms and trunk. They transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore an artery.
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to explore a vein.
Outside View Of The Back Of The Heart
Coronary veins -take oxygen-poor blood that has already been used by muscles of the heart and returns it to the right atrium.
Circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium and the side and back of the left ventricle.
Left coronary artery divides into two branches .
Left anterior descending artery supplies blood to the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum.
Pulmonary veins -bring oxygen-rich blood back to the heart from the lungs.
Right coronary artery supplies blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum.
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Where Are The Heart And Blood Vessels Found
The heart is a fist-sized organ which lies within the chest behind the breastbone . The heart sits on the main muscle of breathing , which is found beneath the lungs. The heart is considered to have two ‘sides’ – the right side and the left side.
The heart has four chambers – an atrium and a ventricle on each side. The atria are both supplied by large blood vessels that bring blood to the heart . Atria have special valves that open into the ventricles. The ventricles also have valves but, in this case, they open into blood vessels. The walls of the heart chambers are made mainly of special heart muscle. The different sections of the heart have to squeeze in the correct order for the heart to pump blood efficiently with each heartbeat.
Structure Of The Heart
The heart has four chambers . There is a wall between the two atria and another wall between the two ventricles. Arteries and veins go into and out of the heart. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood to the heart. The flow of blood through the vessels and chambers of the heart is controlled by valves.
You May Like: How Does Atropine Increase Heart Rate
Which Blood Vessel Takes Oxygen Rich Blood From The Lungs And Brings It Back To The Heart
pulmonary arterypulmonary veins
. Keeping this in consideration, which blood vessel takes blood from the lungs to the heart?
pulmonary artery: A blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen and then returns to the heart. pulmonary vein: One of four veins that carry oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart.
Furthermore, what part of the heart receives oxygen rich blood from the lungs? The right ventricle pumps the oxygen–poor blood to the lungs through the pulmonary valve. The left atrium receives oxygen–rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle through the mitral valve. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen–rich blood through the aortic valve out to the rest of the body.
Likewise, people ask, which blood vessel sends oxygen rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body?
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues. The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart. They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
How many vessels return oxygenated blood to the heart?
The oxygenated blood from the lungs now returns to the left atrium via four tubes that are known as pulmonary veins . The pulmonary veins empty into the back portion of the LA.
Blood Vessels Leading Into And Out Of The Heart
There are four main blood vessels that take blood into and out of the heart.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart .
The main artery is the aorta.
The main vein is the vena cava.
Don’t Miss: Esophageal Palpitations
What Is Vascular Disease
A vascular disease is a condition that affects the arteries and veins. Most often, vascular disease affects blood flow, either by blocking or weakening blood vessels, or by damaging the valves that are found in veins. Organs and other body structures may be damaged by vascular disease as a result of decreased or completely blocked blood flow.
Improving Health With Current Research
Learn about the following ways the NHLBI continues to translate current research and science into improved health for people who have heart conditions. Research on this topic is part of the NHLBIs broader commitment to advancing heart and vascular disease scientific discovery.
Learn about some of the pioneering research contributions we have made over the years that have improved clinical care.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Weak Heart Valves
What Are The Coronary Arteries
Like all organs, your heart is made of tissue that requires a supply of oxygen and nutrients. Although its chambers are full of blood, the heart receives no nourishment from this blood. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries, called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta near the point where the aorta and the left ventricle meet:
- Right coronary artery supplies the right atrium and right ventricle with blood. It branches into the posterior descending artery, which supplies the bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum with blood.
- Left main coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, as well as the side and back of the left ventricle. The left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood.
These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
When the coronary arteries narrow to the point that blood flow to the heart muscle is limited , a network of tiny blood vessels in the heart that aren’t usually open may enlarge and become active. This allows blood to flow around the blocked artery to the heart muscle, protecting the heart tissue from injury.
