Management Of Acute Heart Failure In The Emergency Department
The treatment for acute heart failure has not changed meaningfully in the last four decades. Medications such as loop diuretics and vasodilators still are used as the primary treatment for acute heart failure. However, one new addition to the management of heart failure is the use of noninvasive ventilation in cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Studies have shown that early use in these patients can prevent the need for endotracheal intubation.21,36
Initial treatment of acute heart failure is most influenced by the blood pressure. About 50% or more of patients who arrive at the emergency department with acute heart failure have an elevated blood pressure, about 40% have a normal blood pressure, and only 5% have a low blood pressure.21,37,38 For intial treatment decisions, the three primary blood pressure divisions are: hypertensive , normotensive , and hypotensive .21,39 It is important to stress that these cutoff points are intended as guidelines and are not absolute thresholds.21
How Does Diastolic Heart Failure Affect My Body
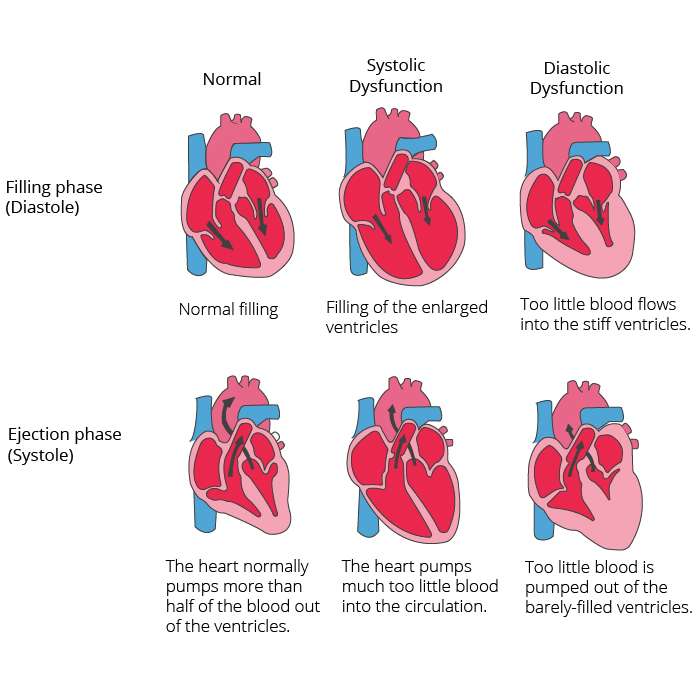
When the left side of your heart stiffens, your heart:
- Cant relax properly between beats.
- Doesnt fill up with as much blood as it should.
- Pumps out less blood to the rest of your body than a healthy heart would.
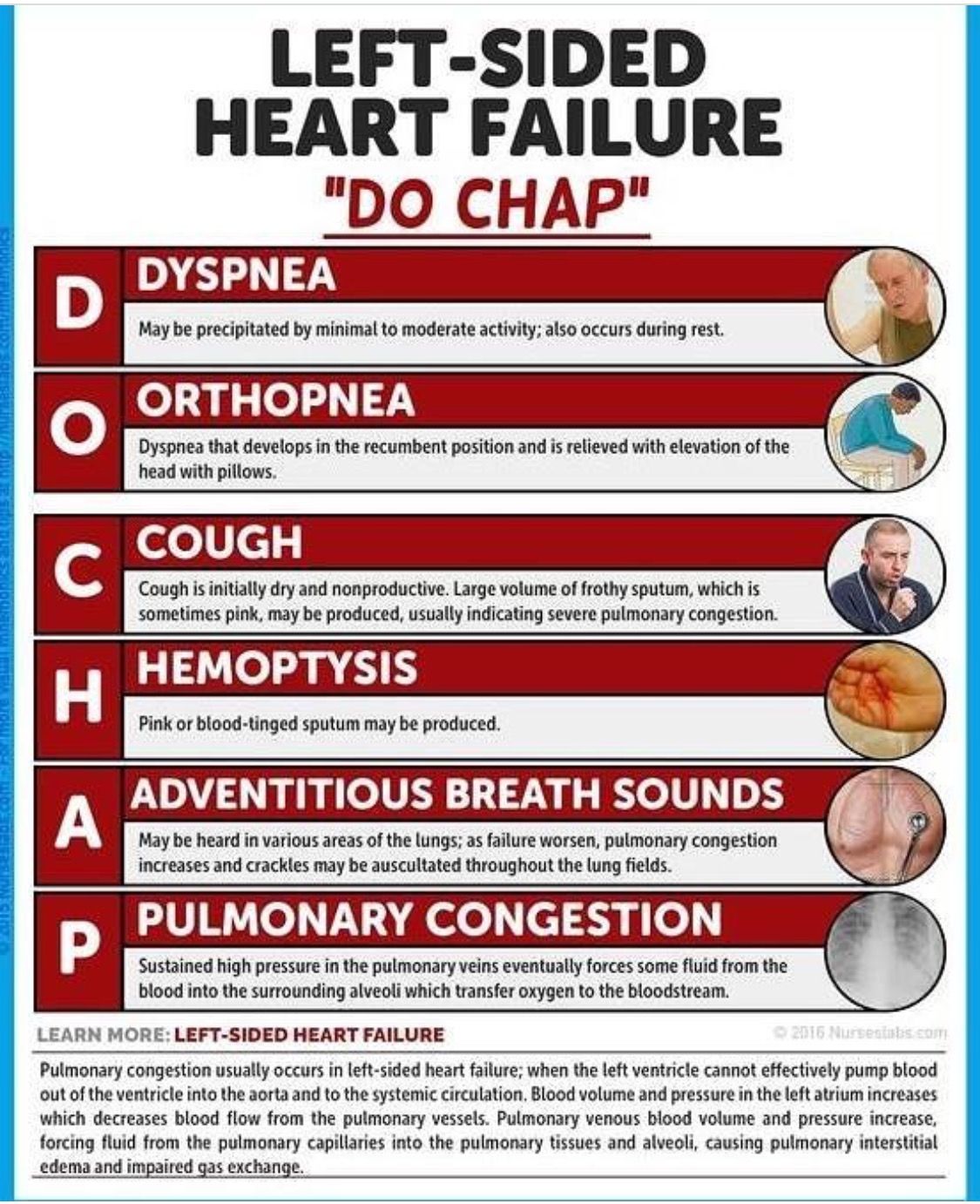
As a result, you experience symptoms of heart failure. You might feel short of breath or fatigued . Your breathing may get worse at night when you try to lay flat. You may also notice swelling in your belly or legs . These symptoms might get worse over time.
Palliative And Hospice Care
Someone living with a serious condition like heart failure can access palliative care at any stage of their condition. Palliative care is intended to support overall wellness and quality of life and can happen alongside other treatments.
With very severe heart failure, people may choose to access hospice care to receive supportive care at the end of life.
Don’t Miss: Echelon Heart Rate Monitor
Chf Icd 10 Codes And Guidelines
Most of the heart failure codes include in chapter 9 of ICD-10 CM manual, diseases of circulatory system, code range I00-I99.
- Combination code If patient has any type of heart failure and hypertension, it should be combined and coded as I11.0 eventhough physician has not linked both. It should not be coded combined if the medical record states the conditions are unrelated.
- Heart failure should be coded additionally when coding I11.0
- Do not code I11.9 when coding I11.0 .
- When coding biventricular heart failure it is necessary to code the type of left heart failure also according to the code also note with I50.82
Go by Failure, Heart to find correct codes for heart failure in ICD-10 CM manual index.
Look at the below scenarios to clearly understand the coding concepts of CHF.
CHF ICD 10 Code Example 1
Elizabeth is a 65 year old female who comes to emergency department for shortness of breath and leg edema from past 2 days. She came to visit doctor as the symptoms are getting worse. She has hypertension and takes Lisinopril for the same. She does not have chest pain or palpitation. She is not a smoker. Her family history includes heart disease for her mother and brother. Vitals showed temperature 97.3 F, heart rate 72 bpm, respiratory rate 25, BP 150/96 mmHg. Physical exam showed pitting edema on both the extremities, shortness of breath and dry skin. Physician ordered for blood tests, EKG and chest X-ray. This case was diagnosed as acute diastolic heart failure.
What Is The Main Term For Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure Congestive heart failure is a chronic progressive condition that affects the pumping power of your heart muscle. While often referred to simply as heart failure, CHF specifically refers to the stage in which fluid builds up within the heart and causes it to pump inefficiently.
Read Also: Does Blood Pressure Change With Heart Attack
Diagnostic Approach To Diastolic Heart Failure
The diagnosis of diastolic heart failure requires three conditions to be simultaneously satisfied : presence of signs and symptoms of heart failure presence of normal or only slightly reduced LV ejection fraction and presence of increased diastolic pressure or impaired filling caused by delayed isovolumic relaxation or elevated stiffness. Patients with shortness of breath on exertion, rales, or gallop sound but with near normal systolic function receive usually the diagnosis of congestive heart failure with diastolic dysfunction . More recently a close association of sleep-disorded breathing with diastolic heart failure has been reported but a causal relationship remains to be established . However, attempts to identify diastolic abnormalities have been compromised by the complexity of the factors involved in LV relaxation and filling. Myocardial relaxation, LV suction, viscoelastic properties of the myocardium, ventricular compliance, atrial contraction, left and right ventricular interaction, pericardial restraint as well as heart rate interact and determine directly or indirectly diastolic performance.
Chf Exacerbation Icd 11 Code
The CHF Exacerbation ICD 11 code is BD10.
Unfortunately, ICD 11 coding system also has not provided a separate code of exacerbated conditions of heart failure. According to different sources, there may be an exception in future updates of ICD-11 but currently, BD10 with extension codes should be used to show if the condition is chronic/acute or any other extension that is needed to describe the severity.
Read Also: Weak Voice And Heart Problems
Read Also: How To Regulate Heart Rate
Coding Tip: Hypertension With Heart Involvement In Icd
Kim Boy, RHIT, CDIP, CCS, CCS-P
This Coding Tip was updated on 12/10/2018
The word with is sequenced immediately following the main term in the Alphabetic Index and not in alphabetical order.
The classification presumes a causal relationship between hypertension and heart involvement and between hypertension and kidney involvement, as the two conditions are linked by the term with in the Alphabetic Index. Even in the absence of provider documentation explicitly linking them, these conditions should be coded as related.
Hypertension with heart conditions classified to I50.-or I51.4-I51.9. are assigned a code from category I11, Hypertensive heart disease. If the provider specifies a different cause then they would be coded separately and not linked. This would be the same if the physician gives another etiology for the CKD. It is an assumed link when NO other cause has been documented.
Figure 3 General Outline For Treatment Of Acute Heart Failure
Patients who are hypertensive should be treated with the goal of vasodilation instead of concentrating on fluid removal. The symptoms of patients with hypertension are most likely related to volume re-distribution, as opposed to volume overload.21,40,41 Examples of medications used for initial vasodilation are nitroglycerin , nitroprusside, nesiritide, hydralazine, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers.21
Read Also: Target Heart Rate When Working Out
Classes And Stages Of Heart Failure
If you receive a heart failure diagnosis, your doctor may use a classification system to tell you what stage of heart failure you have. This can help guide your treatment.
The is a symptom-based scale. It places heart failure in one of four categories:
- Class 1. You dont experience any symptoms at any time.
- Class 2. You can perform daily activities with ease but feel fatigued or short of breath when you exert yourself.
- Class 3. You have difficulty completing daily activities.
- Class 4. You have heart failure symptoms like shortness of breath even when youre at rest.
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association classification is a stage-based system. Its used to identify your risk for or level of heart failure. The letters A to D convey the stage that youre in:
- Stage A: At risk of heart failure. You have one or more risk factors for heart failure, but you arent experiencing any symptoms.
- Stage B: Pre-heart failure. Your test results show signs of heart disease, but you dont have symptoms of heart failure.
- Stage C: Symptomatic heart failure. You have heart disease, and youre experiencing symptoms of heart failure.
- Stage D: Advanced heart failure. You have advanced heart failure that affects your daily life and requires specialized treatments.
Doctors often use these two classification systems together to determine the best treatment or prevention plan for you.
Transition From Diastolic Dysfunction To Heart Failure
Abnormalities in diastolic function may be manifested as impaired relaxation, which may or may not deteriorate LV filling during exertion but not at rest . This mildest form of diastolic dysfunction occurring typically at the initial stage of LV hypertrophy and can remain asymptomatic for several years . Diastolic abnormalities may lead to elevated filling pressure during exercise with the progression of the disease . When the disease goes on, diastolic dysfunction occurs, which may lead to elevated filling pressure at rest, left atrial enlargement, and, ultimately, atrial fibrillation, reduced exercise tolerance with signs of congestive heart failure .
Pathophysiology of diastolic heart failure. Abnormal relaxation and increased stiffness are associated with diastolic filling abnormalities and normal exercise tolerance in the early phase of diastolic dysfunction. When the disease progresses, pulmonary pressures increase abnormally during exercise with reduced exercise tolerance. When filling pressures increases further, left atrial pressure and size increase and exercise tolerance falls with clinical signs of congestive heart failure .
Also Check: Is It Normal For Heart Rate To Increase After Eating
Example Of Hypertension And Heart Involvement:
- Patient is discharged with final diagnosis of exacerbated CHF, and a secondary diagnosis of hypertension. For this patient, CHF and hypertension would be coded as code I11.0, Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure since the causal relationship is assumed due to the word with following the main term in the Alphabetic Index under hypertension. Since the heart disease falls within the code range of I50.- or I51.4-I51.9 the link would be assumed. Additional code for the type of heart failure would be assigned as a secondary diagnosis, I50.9. This was verified at the AHIMA Coding Community meeting in Baltimore, MD on October 15, 2016 by Nelly Leon-Chisen.
- Patient is discharged with final diagnosis of atherosclerotic heart disease with unstable angina and hypertension. For this patient, the causal relationship would not be linked because the heart disease does not fall within the code range listed for the causal effect to be assumed. CAD falls within the code range of I25.-. The code range for the assumed link is I50.- or I51.4-I51.9 only.
References
Surgery And Other Approaches
Depending on the underlying cause of the condition and the specific symptoms or complications, a doctor may recommend:
- surgery, to open blocked passages in the heart or repair heart valves, for example
- monitoring the persons fluid balance, kidney health, and other factors, to manage diabetes
- assessing blood pressure, heart rate, and other cardiac measures, to control high blood pressure
- counseling, for alcohol or drug use
- preparing a follow-up plan that includes sodium and fluid restriction
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Diastolic Chf Icd 11 Code
The Diastolic CHF ICD 11 Code is BD10. ICD 11 does not have category and subcategory but these terms are named as stem code and extensions respectively. The main stem code is the same just like the category in ICD-10 BD10 there is no code for exacerbation.
There are some extensions about types of heart failure that are divided based on code rules of ICD-11 like if there is an effect on physical activity or not and others. Currently, BD10 with an acute extension should be used to code this condition.
Diseases Of The Circulatory Systemtype 2 Excludes
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Code First
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Applicable To
- end stage heart failure, if applicable
- combined systolic and diastolic heart failure
- Acute diastolic heart failure
- heart I50.9ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.9
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
Applicable To
- Cardiac, heart or myocardial failure NOS
- Congestive heart disease
Recommended Reading: Potassium And Heart Failure
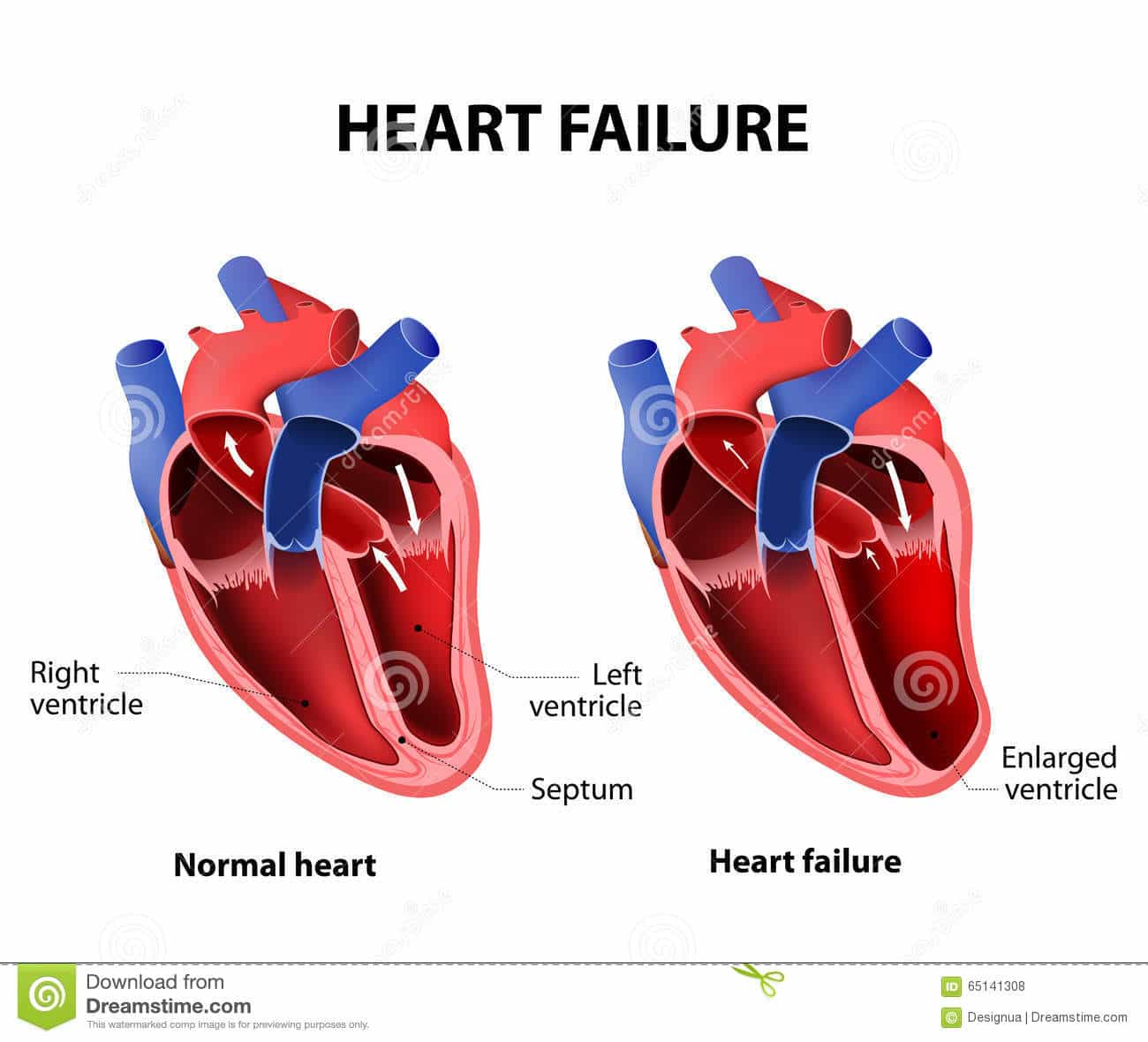
Myocytes And Myocardial Remodeling
In the failing heart, increased myocardial volume is characterized by larger myocytes approaching the end of their life cycle. As more myocytes drop out, an increased load is placed on the remaining myocardium, and this unfavorable environment is transmitted to the progenitor cells responsible for replacing lost myocytes.
Progenitor cells become progressively less effective as the underlying pathologic process worsens and myocardial failure accelerates. These featuresnamely, the increased myocardial volume and mass, along with a net loss of myocytesare the hallmark of myocardial remodeling. This remodeling process leads to early adaptive mechanisms, such as augmentation of stroke volume and decreased wall stress and, later, to maladaptive mechanisms such as increased myocardial oxygen demand, myocardial ischemia, impaired contractility, and arrhythmogenesis.
As heart failure advances, there is a relative decline in the counterregulatory effects of endogenous vasodilators, including nitric oxide , prostaglandins , bradykinin , atrial natriuretic peptide , and B-type natriuretic peptide . This decline occurs simultaneously with the increase in vasoconstrictor substances from the RAAS and the adrenergic system, which fosters further increases in vasoconstriction and thus preload and afterload. This results in cellular proliferation, adverse myocardial remodeling, and antinatriuresis, with total body fluid excess and worsening of heart failure symptoms.
Diagnosis Of Diastolic And Systolic Heart Failure
Diagnosis of heart failure is ultimately a clinical one, but objective evidence can be obtained via echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. While systolic heart failure has a measurable value that characterizes impaired left ventribular systolic function an ejection fraction < 35-40% there is no correspoinding ejection fraction value or criteria to diagnose diastolic heart failure. To make matters more interesting, diastolic heart failure usually accompanies systolic heart failure, so a depressed ejection fraction cannot exclude diastolic heart failure.
The gold standard for diagnosing diastolic heart failure is cardiac catheterization, which shows increased ventricular diastolic pressure with preserved systolic function and normal ventricular volumes.6 If during cardiac catheterization micromanometer catheters are placed in the left ventricle, impaired LV diastolic relation can be assessed by determining the peak negative change in intracavitary presssure and the time constant of LV relaxation .
Cardiac catheterization continues to be an invasive procedure that is not without risk. That is why echocardiography is a more attractive approach to assist in the diagnosis of systolic heart failure while simultaneously being able to evaluate blood flow across the valves and ventricular and valvular functions.
Don’t Miss: How To Take Your Heart Rate
Acute Systolic Chf Icd 10
If the patients condition is acute, the second code under this subcategory should be used for reimbursement purposes. If the medical note states that the patients condition has been worsening or there is an emergency condition of chronic failure but does not document it as acute, do not presume it as an acute condition.
A query to the medical doctor would work here best asking about the exact condition. The ICD 10 code for acute systolic CHF is I50.21.
Diagnosis Of Diastolic Heart Failure
The diagnosis of diastolic heart failure requires three conditions to be simultaneously satisfied : 1), Presence of signs and symptoms of heart failure 2), Presence of normal or only slightly reduced LV ejection fraction a 3) Presence of increased diastolic pressure or impaired filling caused by delayed iso-volumic relaxation or elevated stiffness.
Patients with shortness of breath on exertion, pulmonary rales, or gallop sound but with near normal systolic function are usually diagnosed with DHF .
Also Check: Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Recovery Elderly
Management Of Diastolic Heart Failure
Diastolic dysfunction may be present for several years before any symptoms occur and may represent the first phase of diastolic heart failure . Thus, it is important to detect diastolic dysfunction early and to start treatment before irreversible structural alterations and systolic dysfunction have occurred. However, no single drug presently exists with pure lusitropic properties, which selectively enhance myocardial relaxation without negative effects on LV contractility or pump function. Therefore, an ideal treatment strategy for patients with diastolic dysfunction has not been devised, and medical therapy of diastolic dysfunction is often empirical and lacks clear-cut pathophysiologic concepts. Nevertheless, four treatment goals have been advocated for the therapy of diastolic dysfunction:
Reduction of central blood volume
Improvement of LV relaxation
Regression of LV hypertrophy
Maintenance of atrial contraction and control of heart rate
NO donors have been shown to exert a relaxant effect on the myocardium which is associated with a decrease in LV end-diastolic pressure . In patients with severe LV hypertrophy an increased susceptibility to NO donors has been documented which may be beneficial for the prevention of diastolic dysfunction.
Fransoo Et Al And Fransoo Et Al
- In The 2013 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. and The 2019 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. residents were considered to have CHF if they met one of the following conditions:
- one or more inpatient hospitalizations in one year with a diagnosis for CHF: ICD-9-CM code 428 or ICD-10-CA code I50 OR
- two or more physician visits in one year with a diagnosis for CHF .
Only Manitoba residents aged 40 and older were included.For more information, please see:
Don’t Miss: What Is My Target Heart Rate
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
