Evidence Linking Alcohol And Heart Disease
Until recently it was thought that light-to-moderate drinking had cardio-protective benefits that reduce coronary heart disease mortality. However, the chief medical officer acknowledges in the current UK guidance that the cardio-protective benefits of alcohol are no longer thought to be as great as previously believed and that these benefits are thought to apply only to women over the age of 55 and are less likely to apply to men . We must therefore question whether alcohol has the same cardio-protective effects in people with HF. This could be important as people with a diagnosis of HF are required to make significant lifestyle changes to manage their symptoms.
Requirements such as fluid restriction may encourage people with HF to abstain from alcohol completely they may think this is an important way of improving their mortality. However, the Framingham Heart Study found that the risk of developing HF was 59% lower in men who consumed 8-14 alcoholic drinks a week compared with those who did not drink alcohol this finding was supported by Bryson et al .
Djoussé and Gaziano also found similar statistical evidence that people who drank moderate amounts of alcohol had a lower risk of developing HF. Their study also included people who had previously had a myocardial infarction given that ischaemia is one of the most common causes of HF in the UK, this is of great importance.
Alcohol May Be More Risky To The Heart Than Previously Thought
Madrid, Spain 22 May 2022: Levels of alcohol consumption currently considered safe by some countries are linked with development of heart failure, according to research presented at Heart Failure 2022, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology .1
This study adds to the body of evidence that a more cautious approach to alcohol consumption is needed, said study author Dr. Bethany Wong of St. Vincent’s University Hospital, Dublin, Ireland. To minimise the risk of alcohol causing harm to the heart, if you dont drink, dont start. If you do drink, limit your weekly consumption to less than one bottle of wine or less than three-and-a-half 500 ml cans of 4.5% beer.
According to the World Health Organization, the European Union is the heaviest-drinking region in the world.2 While it is well recognised that long-term heavy alcohol use can cause a type of heart failure called alcoholic cardiomyopathy,3 evidence from Asian populations suggests that lower amounts may also be detrimental.4,5As there are genetic and environmental differences between Asian and European populations this study investigated if there was a similar relationship between alcohol and cardiac changes in Europeans at risk of heart failure or with pre-heart failure, said Dr. Wong. The mainstay of treatment for this group is management of risk factors such as alcohol, so knowledge about safe levels is crucial.
ENDS
Heavy Alcohol Consumption And Risk Of Hf
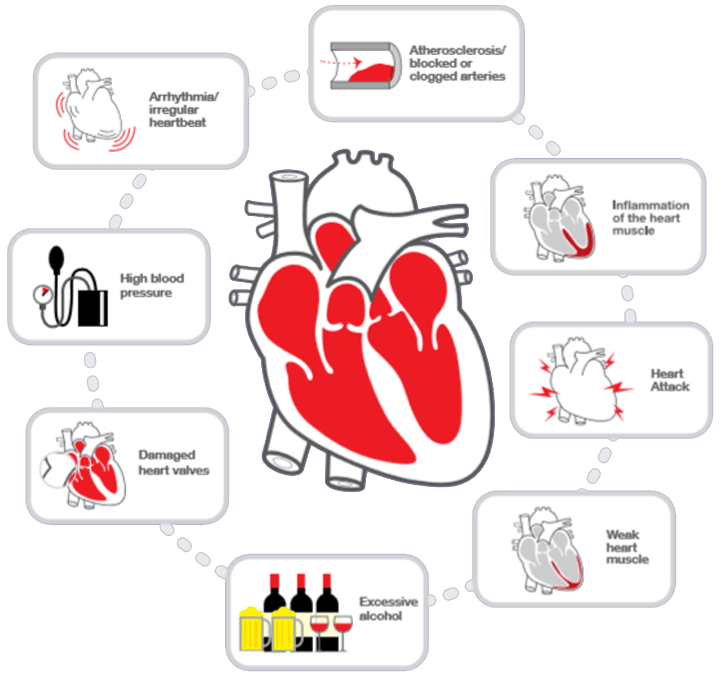
Heavy alcohol consumption is associated with alcoholic cardiomyopathy . Alcoholic cardiomyopathy is characterized by left ventricular dilation, increased left ventricular mass, and reduced or normal left ventricular wall thickness among patients with a long-term history of heavy alcohol consumption . Limited data are available on the amount and duration of consumption required to produce symptomatic alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Most studies have reported that alcoholic patients with symptomatic HF had 10 years or more of exposure to heavy drinking . Previous reports suggest that even among alcoholic patients, alcohol abstinence leads to improved survival in patients with alcoholic cardiomyopathy .
Pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying alcoholic cardiomyopathy are poorly understood. Excessive alcohol consumption has been associated with left ventricular myocyte loss in some animal models but not in all studies . In addition, heavy drinking may cause myocyte dysfunction and elevated levels of norepinephrine . Increasing doses of ethanol have been associated with a negative inotropic effect on myocytes in animal experiments . In humans, acute ethanol ingestion may also lead to depressed myocardial contractility .
Also Check: How To Bring Heart Rate Down
Drinking Patterns And Other Modifiers Of The Association Between Alcohol Consumption And Hf
Recent data suggest that drinking patterns play an important role in the association between alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease . Specifically, whereas binge drinking has deleterious health effects, light-to-moderate alcohol consumption spread over several days of the week appears to yield most of the beneficial health effects. In other words, for a given volume of alcohol within moderate-drinking range, it would be better to distribute this volume evenly throughout the week than to consume an equal volume within 2 to 3 days. This hypothesis is supported by transient effects of ethanol on fibrinolytic parameters. To our knowledge, no study has examined the effects of drinking patterns on the risk of HF.
Quantity Of Alcohol Intake In Cardiac Disease
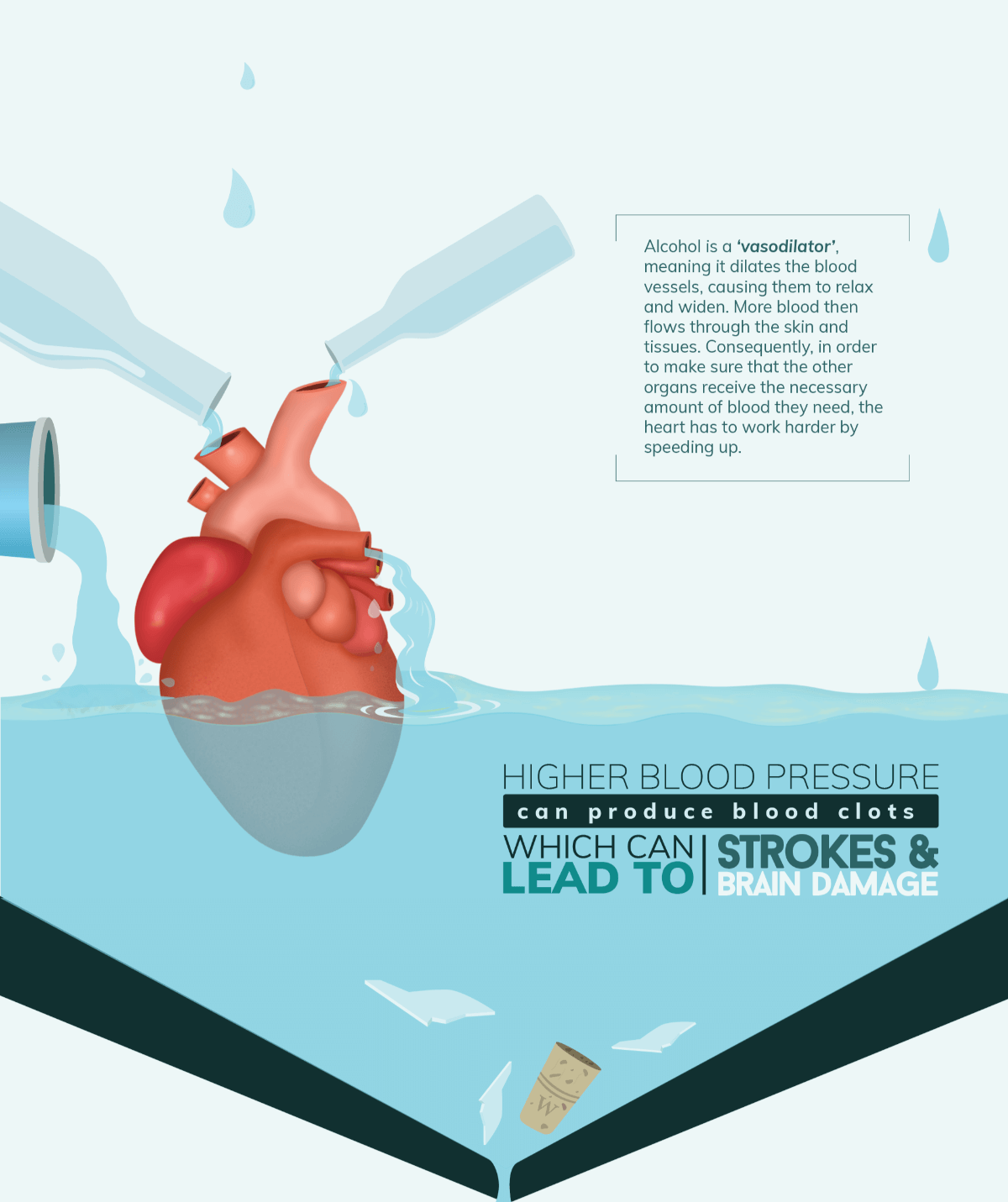
Excessive intake of alcohol may result in increased systemic blood pressure in a dose-response relationship, and this may contribute to chronic myocardial dysfunction. Patients who consume more than two drinks per day have a 1.5- to 2-fold increase in hypertension compared with persons who do not drink alcohol, and this effect is most prominent when the daily intake of alcohol exceeds five drinks. Because hypertension may directly contribute to left ventricular dysfunction, this may be a confounding comorbidity in persons who abuse alcohol, and it should be differentiated from pure forms of alcoholic cardiomyopathy.
In 1989, Urbano-Marquez et al reported on 48 men with alcohol abuse with a mean daily intake of 243 g of alcohol and showed an inverse relationship between total lifetime intake and ejection fraction and fractional shortening and a direct relationship between total lifetime intake and LV mass. In persons who consumed 70 g of ethanol per day for 20 years, 36% had an abnormal ejection fraction. Age and nutritional status appeared to play little or no role.
Other studies and reviews have also quoted quantities similar to those mentioned above, and the type of beverage consumed appeared to be irrelevant.
Read Also: How Long Does Heart Bypass Surgery Take
Alcohol And The Heart
Drinking alcohol comes with risks to health, and not drinking alcohol is a healthy choice. If you drink alcohol its important to keep within recommended guidelines whether you drink every day, once or twice a week or just occasionally.
Heavy or binge drinking episodes increase risk of heart disease even in people who dont usually drink much.
Scientific research, reported in our ‘Alcohol and the heart’ – Evidence Paper, suggests that there may be some benefits of alcohol for reducing heart disease for some people. However, this is not true for everyone, even when consumption is low or moderate. Our ‘Alcohol and the heart’ – Position Statement concludes that the relationship between alcohol and cardiovascular disease is complex, and for most people there will be little, or no, overall benefit.
Alcohol can have a range of harmful health effects. As there is no safe drinking threshold for many of the impacts, there is no potential ‘window of benefit’ where benefits can be gained without risk of harm. Alcohol shouldn’t be thought of as a safe or effective treatment for heart disease.
Alcohol is also high in calories, so, if you are trying to lose weight, reducing your alcohol intake, eating a heart healthy diet and regular physical activity could help you reach your goal.
Be Alert To Changing Symptoms
Having heart failure requires an active watch by both the client and his/her caregivers in order to catch early indications of any change in symptoms. If anyone notices something new, or a sudden worsening of a current symptom, it is important that steps be taken immediately. Here is a sample of what to watch for:
- Sudden weight gain three or more pounds in one day, five or more pounds in one week, or other amounts the physician designates.
- Increased shortness of breath while at rest, not related to exercise or exertion.
- Increased swelling of the lower limbs .
- Swelling or pain in the abdomen.
- Increased trouble sleeping .
- New or increased frequency, dry hacking cough.
- New or increased loss of appetite.
- New or increased fatigue or feeling tired all the time.
Recommended Reading: End Stage Heart Failure How Long To Live
Abuse Associated With Increased Risks
Among 14,727,591 residents in the database, 268,084 were coded with an alcohol abuse diagnosis. The researchers analysis found that alcohol abuse was associated with an increased risk of heart attack, AF and congestive heart failure of at least a similar magnitude to well-established risk factors for each disease.
Specifically, those California residents with alcohol abuse had more than three times the risk of AF, much higher than the majority of well-established risk factors. For heart attack and congestive heart failure, the risk from alcohol abuse was similar to multiple well-established risk factors such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
Further, individuals without the conventional risk factors for cardiovascular disease exhibited a disproportionately enhanced risk for all three conditions.
Extrapolating data to the estimated prevalence of each disease, the complete eradication of alcohol abuse could result in more than 73,000 fewer cases of atrial fibrillation, 34,000 fewer heart attacks and 91,000 fewer congestive heart failure patients in the United States.
Other contributors to the JACC study were lead author Isaac Whitman, MD, Gregory Nah, MA, and Eric Vittinghoff, PhD, of UCSF Vratika Agarwal, MD, Staten Island University Hospital Jonathan Dukes, MD, Cardiology Associates Medical Group and former UCSF cardiology clinical fellow and Thomas Dewland, MD, Oregon Health & Science University and former UCSF resident and cardiology electrophysiology fellow.
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
Recommended Reading: Can This 10 Second Trick Prevent Your Heart Attack
Alcohol And Heart Palpitations
Palpitations occur when the heart skips a beat in its regular rhythm or adds an extra beat. People affected by these abnormalities can experience a racing heartbeat. Additional possible symptoms include a fluttering or pounding sensation located in the chest, throat, or neck.
In a study conducted with 223 patients with cardiac arrhythmia, 133 reported irregular palpitations when drinking or intermittent/paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and 90 had SVT without any atrial fibrillation.
Most of the time, palpitations are harmless and disappear on their own in a short amount of time. However, they can also indicate the presence of a severe irregularity called atrial fibrillation .
Afib is the Worlds Most Common Form of an Irregular Pulse. In Addition to Palpitations, Symptoms of this Condition Include:
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
In severe cases, atrial fibrillation can also lead to a life-threatening stroke or pulmonary embolism.
People who consume just one to three standard servings of hard liquor or wine per day can develop atrial fibrillation accompanied by palpitations and additional symptoms. However, moderate beer consumption does not appear to trigger increased Afib risks. When consumed in excessive amounts, all types of alcohol can contribute to the development of the condition. This pattern of consumption can take the form of binge-drinking or ongoing heavy intake.
How Much Alcohol Is Too Much
Whether or not moderate drinking is good for your heart is open to debate. However, for most people, it doesnt appear to be harmful to the heart but the key word is moderate.
Moderate drinking is defined as an average of one drink per day for women and one or two for men. A drink might be less than you think: 12 ounces of beer, 4 ounces of wine or 1.5 ounces of 80-proof spirits.
Some people should avoid even that much and not drink at all if they have certain heart rhythm abnormalities or have heart failure.
Read Also: How To Check Heart Rate On Apple Watch
Is This Condition Only A Chronic Problem
While the long-term effects of alcoholic cardiomyopathy tend to get the most attention, theres also the potential for acute problems. An example of this is a condition sometimes known as holiday heart syndrome.
Drinking a large quantity of alcohol in a short period can also have toxic effects on your heart muscle. This can cause a disruption in your heart rhythm called fibrillation. This is when the chambers of your heart try to beat so quickly that they only twitch or quiver. When chambers of your heart do this, they dont pump effectively. This happens in one of two ways:
- Atrial fibrillation. The upper chambers of your heart are the left atrium and right atrium . When they fibrillate, not all the blood inside them gets pumped to the next chamber of your heart. When blood pools in those chambers, a clot can form. If that clot leaves your heart and travels to your brain, it can get stuck there and cause a stroke.
- Ventricular fibrillation. As mentioned above, the lower chambers of your heart pump the hardest. If they aren’t pumping enough blood, it can cause you to pass out, or it may even stop your heart . While this problem is less common with acute alcoholic cardiomyopathy, it’s still extremely dangerous.
How Should I Change My Diet If I Have This Condition
Completely abstaining from alcohol is the key recommendation if you have alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Your healthcare provider will likely recommend that you also focus on improving your diet in ways that help your heart. This usually involves limiting your sodium and cholesterol intake and ensuring you are getting a diet that provides all essential nutrients. Thats because vitamin and mineral deficiencies are more common in individuals who are chronic heavy drinkers. Consider a heart-healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet or the DASH diet.
Also Check: What Does Heart Failure Feel Like
Congestive Heart Failure Drugs
There are several medications that can be used to treat CHF, including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and more.
ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors open up narrowed blood vessels to improve blood flow. Vasodilators are another option if you cant tolerate ACE inhibitors.
You may be prescribed one of the following:
voluntary recall of 5 lots of the drug Accupril due to the presence of nitrosamine. Nitrosamine, a known carcinogen with the potential to cause cancer, was found to exist in the drug at levels greater than the Acceptable Daily Intake as determined by the FDA. This recall is specific only to a handful of lot numbers and does not affect all Accupril tablets made by Pfizer. If you take Accupril tablets, talk with your pharmacist or doctor and they will help you determine if your medication has been impacted by the recall.
ACE inhibitors shouldnt be taken with the following medications without consulting a doctor, because they may cause an adverse reaction:
- Potassium-sparing diuretics and potassium supplements. These diuretics can cause potassium buildup in the blood, which may lead to abnormal heart rhythms. Examples include: riamterene , eplerenone , and spironolactone .
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs .NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, can cause sodium and water retention. This may reduce the ACE inhibitors effect on your blood pressure.
Beta-blockers
This may be achieved with:
Diuretics
Your doctor may recommend:
Alcohol Abstention And Pharmacologic Therapies
The mainstay of therapy for alcoholic cardiomyopathy is to treat the underlying cause, ie, to have the patient exercise complete and perpetual abstinence from all alcohol consumption. The efficacy of abstinence has been shown in persons with early disease and in individuals with more advanced disease .
Medical therapy for AC is identical to conventional therapy for other forms of heart failure. This includes treatment with an ACE inhibitor and with digoxin dysfunction), as well as the symptomatic use of diuretics. Newer therapies, such as beta blockers in stable patients without decompensated heart failure, are also used. In one study, investigators evaluated the clinical characteristics and outcomes of 94 consecutive patients with AC. Multiple logistic regression analysis identified the lack of beta-blocker therapy as an independent predictor of death or heart transplantation in these patients.
Electrolyte abnormalities, including hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypophosphatemia, should be corrected promptly because of the risk of arrhythmia and sudden death.
Although anticoagulation may be of benefit to patients with profound LV dysfunction and atrial fibrillation, the risks must be weighed heavily in this patient population.
A summary of the treatment for AC is as follows:
-
Abstention from alcohol
-
Vasodilators – ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers , nitrates, hydralazine
Contributor Information and Disclosures
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Coronary Heart Disease
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
To diagnose this condition, healthcare providers will typically use several of the following methods.
Physical exam
This involves a doctor examining you for visible symptoms such as swelling in your legs or bulging neck veins. They will also use a stethoscope to listen to your heart and lung sounds. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy commonly causes a crackling sound in the lungs and heart murmurs .
Imaging tests
To diagnose changes in the shape of your heart, doctors need to see the shape of your heart in the first place. They can do that using the following tests:
- Echocardiogram. This test uses a device held against the skin of your chest that produces ultra-high-frequency sound waves. Those waves help create a picture of your heart .
- Electrocardiography . This test uses sensors attached to the skin of your chest to detect the electrical activity of your heart and show it as a wave on a paper printout or computer display. That lets providers see if this condition is affecting your hearts electrical activity.
- Chest X-ray. An X-ray can often show heart enlargement.
- Cardiac computed tomography scan. This imaging test uses computer processing to assemble X-ray images into a 3-D picture of the heart.
- Heart magnetic resonance imaging . This test generates images using computer processing and an extremely powerful magnet.
