What Is Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is an accumulation of extra fluid in your lungs that can be life-threatening. This comes from pressure going up and blood collecting on the left side of your heart, usually because of heart failure. In addition to difficulty breathing, cardiac edema can lead to organ damage from a lack of enough oxygen.
Cardiac edema vs. pulmonary edema
Both of these mean you have too much fluid in your lungs, which makes it hard for you to breathe. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is a type of pulmonary edema with a heart problem as its cause. An injury to your lungs causes the non-cardiogenic type of pulmonary edema.
Cardiac edema vs. renal edema
These are both names for excess fluid in your organs. With cardiac edema, theres too much fluid in your lungs. With renal edema, theres too much fluid in your kidneys. Heart failure can cause both of these. Also, your kidneys cant get enough fluid out of your blood and into your pee.
Pulmonary Edema Vs Pleural Effusion
Sometimes pulmonary edema is confused with pleural effusion, another condition that involves fluid buildup in the lungs. However, pleural effusion specifically causes a buildup of fluids in the pleural tissues. These cover the outside of each of your lungs as well as the inside of the chest wall.
Pleural effusion can be caused by CHF, poor nutrition, and pneumonia. Its also sometimes cancerous .
With pleural effusion, you may experience:
- breathing difficulties
- shortness of breath
- chest pain and discomfort
A chest x-ray can help diagnose pleural effusion. Your doctor may take a biopsy from pleural tissues if cancer is suspected. Depending on the cause, pleural effusion may be treated with a combination of fluid removal techniques and surgery.
Why Does Pulmonary Edema Cause Pink Frothy Sputum
Acute pulmonary edema occurs when the pulmonary lymphatics fail to remove transupdated fluid . The edema develops as fluid moves from the intravascular compartment into the interstitial space and from there, in severe cases, into the alveoli and eventually forms overt and copious pink frothy sputum.
Recommended Reading: Which Of The Following Is Considered A Symptom Of A Heart Attack
Dilatation Of Azygos Vein
Dilation of the azygos vein is a sign of increased right atrial pressure and is usually seen when there is also an increase in the width of the vascular pedicle.The diameter of the azygos vein varies according to the positioning.In the standing position a diameter > 7 mm is most likely abnormal and a diameter > 10 mm is definitely abnormal.In a supine patient > 15 mm is abnormal. An increase of 3 mm in comparison to previous films is suggestive of fluid overload. The difference of the azygos diameter on an inspiration film compared to an expiration film is only 1mm. This means that the diameter of the azygos is a valuable tool whether or not there is good inspiration.
What Can I Expect If I Have Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
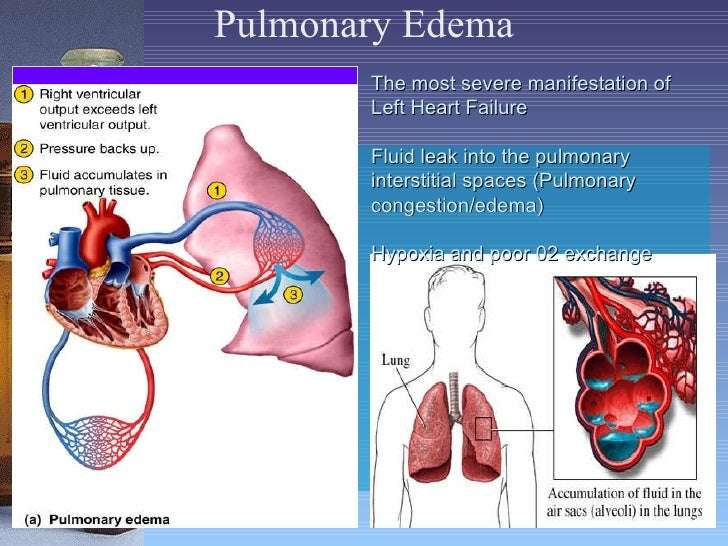
Pulmonary edema is life-threatening, but your prognosis depends on what caused it. One year after discharge from a hospital, about 50% survive cardiac edema.
Heart failure, a common cause of cardiogenic pulmonary edema, is a chronic disease that can get better with treatment. Out of every three people whove been in the hospital because of heart failure, one person lives five or more years after their stay.
Don’t Miss: What Heart Rate Should I Exercise At
How Can I Reduce My Risk
Since cardiogenic pulmonary edema happens when you already have a problem with your heart, the best way to reduce your risk is by keeping your heart strong and healthy.
Ways to do that include:
- Eating foods that are low in saturated fats and trans fats.
- Exercising every day.
- Limiting how much alcohol you drink.
How Do You Sleep With Fluid In Your Lungs
Sleeping Position When sleeping, you should lie on your side while placing a pillow between your legs. Your back should be straight, and you should also place a pillow under your head so that it is a little elevated. If this does not work, you can bend your knees slightly and place the pillow under your knees.
Recommended Reading: Can Lisinopril Cause Heart Palpitations
Are There Any Complications
If pulmonary oedema continues, it can cause increased pressure in the right side of the heart and eventually cause the right ventricle to fail. Failure of the right ventricle can cause fluid swelling of the legs , fluid swelling of the tummy , called ascites, and congestion and swelling of the liver.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Effective treatment of comorbidities and risk factor reduction can decrease the chance of developing heart failure. Patient education should be focused on ensuring compliance with prescribed evidence-based treatments.
- Hypertension – effective treatment of systolic and diastolic hypertension can reduce the risk of heart failure by approximately 50%
- Diabetes – is directly associated with the development of heart failure, independent of other associated clinical conditions
- Alcohol – heavy alcohol use is associated with heart failure
- Metabolic syndromes – important to keep up treatment based on evidence-based guidelines to decrease the risk of heart failure
- Patient education regarding dietary salt restriction and fluid restriction is imperative
Recommended Reading: How To Slow Your Heart Rate When Nervous
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The treatment of heart failure and acute decompensated heart failure is challenging despite the use of maximal evidence-based therapy based on the stage of heart failure. Given the limited effect that current treatment strategies have on the progression of heart failure, it is important to identify ways to maximize patient outcomes and quality of care by the interprofessional team.
Patients at potential risk for heart failure based on comorbidities or other identified risk factors should receive appropriate evidence-based preventative counseling and treatments. When appropriate, the primary care providers who may be the most involved in the management of the patients’ risk factors should consult other specialists, including cardiologists, endocrinologists, pharmacists, cardiology nurses, and nutritionists, to ensure that they are providing the best advice and treatment for their patients. Nurses monitor patients, provide education, and collaborate with the physicians and the rest of the team to improve outcomes. Pharmacists review medications, inform patients and their families about side effects and monitor compliance.
Given the propensity of heart failure patients to require re-current admissions, often because of non-heart failure related conditions, the collaboration between inpatient and outpatient services can be of benefit in the continuity of care and helping promote improved outcomes.
Why Pulmonary Edema Is A Problem
Pulmonary edema is a serious medical condition that happens when excess fluid begins to fill the lungs’ air sacs . When the alveoli are filled with fluid, they cannot adequately add oxygen to, or remove carbon dioxide from, the blood. So pulmonary edema produces significant breathing difficulties, and may often become a life-threatening problem.
You May Like: Average Exercise Heart Rate
Other Symptoms Of Heart Failure To Know
While edema may be the most obvious external heart failure symptom, there are some other common symptoms that you should know about. This is especially true if youre a heart attack survivor or otherwise at high risk for heart failure.
Other heart failure symptoms include:
- shortness of breath, especially when lying down or during exertion
Treating edema usually means treating the underlying cause of the swelling. In the case of heart failure, that could involve the use of medications like:
- diuretics to reduce fluid levels in the body
- medications like ACE inhibitors and ARBs or ARNI to help the blood vessels relax, so circulation is a little easier
- beta blockers and ivabradine to reduce the burden on the heart
- mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
In very serious cases, implantable pumps or defibrillators are needed to help the heart muscle keep up with the bodys demand for blood. And in the most severe cases of heart failure, a heart transplant may be necessary.
Treating the edema itself may include:
- compression stockings to help increase the pressure in your lower legs, which may help push blood up to the heart
- exercise to get the leg muscles affected by edema working harder and pumping blood back to the heart
- elevating your legs or other swollen part of the body above the heart to help keep blood returning to the central circulation.
What Does Congestive Heart Failure Do To Your Body
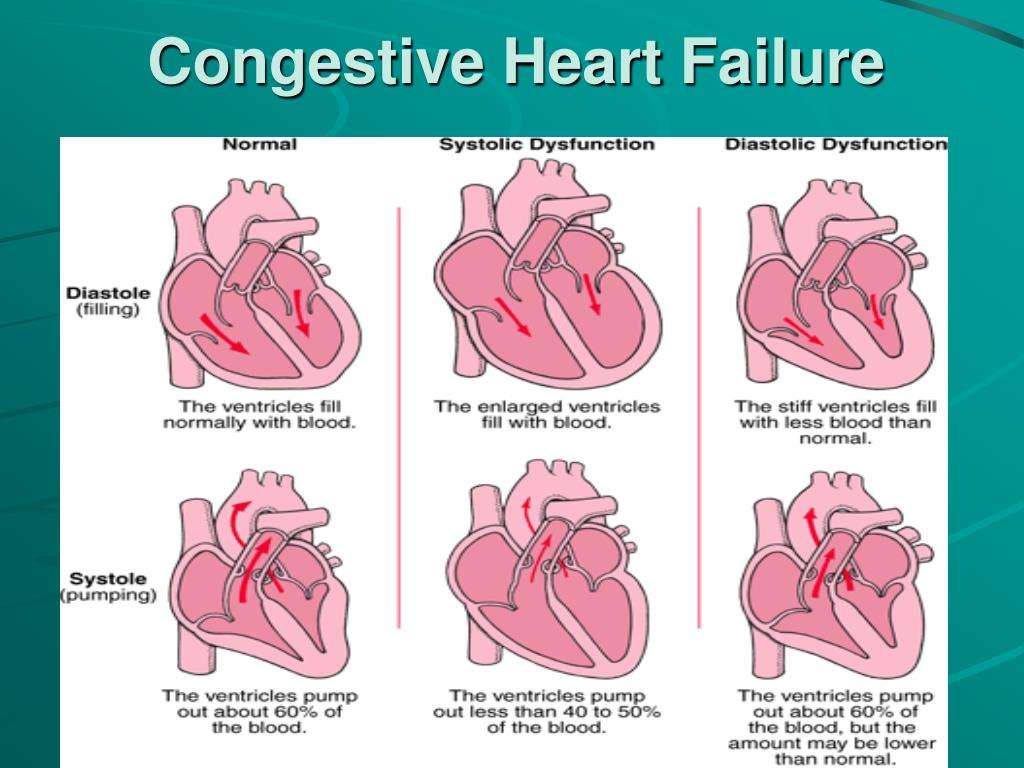
Congestive heart failure can cause:
- Shortness of breath: This happens when fluid collects in your lungs. It’s also called pulmonary edema. It may be worse when you’re lying down or when you’re active. If you’re having a hard time breathing, call your doctor or 911 right away.
- Coughing: Like shortness of breath, this is usually caused by extra fluid in your lungs.
- Tiredness: With heart failure, your body doesn’t pump out enough blood to keep your cells healthy. That can make you tired. You might find it hard to do everyday things like climb stairs.
- Swelling : This happens when there’s too much fluid in your tissues. Your legs and ankles are the most likely places to swell. But other areas of your body, like your arms or belly, can also swell.
- Weight gain: This is caused by extra fluid that doesn’t get flushed from your body the way it should.
- A need to pee more often.
Read Also: What Should Your Heart Rate Be When Working Out
Fast Facts On Pulmonary Edema
- Pulmonary edema is a condition involving fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Sudden onset pulmonary edema is a medical emergency.
- Symptoms include shortness of breath, cough, decreased exercise tolerance or chest pain.
To raise the patients blood oxygen levels, oxygen is given either through a face mask or prongs tiny plastic tubes in the nose. A breathing tube may be placed into the trachea if a ventilator, or breathing machine, is necessary.
If tests show that the pulmonary edema is because of a problem in the circulatory system, the patient will be treated with intravenous medications to help remove fluid volume and control blood pressure.
During normal breathing, the small air sacs in the lungs alveoli fill up with air. Oxygen is taken in, and carbon dioxide is expelled. Pulmonary edema occurs when the alveoli are flooded.
When the alveoli are flooded, two problems occur:
Common causes include:
Q& a: Sequencing Pulmonary Edema And Congestive Heart Failure
Q: What advice do you have for sequencing pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure when both appear to meet the definition of principal diagnosis?
A: The ICD-9-CM guidelines state that when a patient has two or more interrelated conditions that both meet the definition of principal diagnosis, coders may sequence either condition as principal unless the circumstances of the admission, the therapy provided, or the tabular list or alphabetic index indicate otherwise.
Interrelated conditions are those in the same ICD-9-CM chapter. They also include manifestations characteristically associated with a disease process.
Applying this guideline to pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure can be tricky and is often scenario-specific. Consider the following scenarios:
A patient is admitted for pulmonary edema. The physician documents pulmonary edema secondary to end-stage renal disease . The patient also receives treatment for congestive heart failure. Code ESRD as the principal diagnosis.
A patient is admitted for pulmonary edema, congestive heart failure, ESRD, and pulmonary edemaall of which are listed as discharge diagnoses with no indication of the underlying etiology of the pulmonary edema. Query to determine the underlying cause of the pulmonary edema and the chronicity of the pulmonary edema.
A patient is admitted with a history of congestive heart failure and is taking medication. Code the congestive heart failure as a secondary diagnosis.
Read Also: Why Does Alcohol Increase Heart Rate
Pulmonary Edema Vs Pneumonia
Pneumonia is another serious condition of the lungs. Unlike edema, pneumonia is caused by either a viral, fungal, or bacterial infection. As your lungs become infected, fluid builds up in the air sacs .
While both pulmonary edema and pneumonia cause a form of buildup in the lungs, the former is primarily caused by CHF. Pneumonia, on the other hand, is caused by an infection. A weakened immune system can increase your chances of getting pneumonia from a common cold or flu.
Symptoms of pneumonia may include:
- high fever with chills
- cough with mucus that continues to worsen
- chest pain and discomfort
Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
| Heart failure |
|---|
| Acute interstitial pulmonary edema. Note enlarged heart size, apical vascular redistribution , and small bilateral pleural effusions . |
| Cardiology |
Acute decompensated heart failure is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, an abnormal heart rhythm, infection, or thyroid disease.
Treatment consists of reducing the fluid level with diuretics and improving heart function with nitrates, or levosimendan other treatments such as aquapheresis ultra-filtration may also be required.
Recommended Reading: How Do Beta Blockers Prevent Heart Attacks
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
Congestive heart failure doesn’t mean your heart has stopped. It means it’s not pumping blood the way it should. When that happens, blood and fluid can back up in your body and make it harder for your kidneys to flush out sodium and water. That can make you hold on to too much fluid, which causes swelling.
There’s no cure. But your doctor may give you medication to do things like lower your blood pressure, relax your blood vessels, make your heart beat stronger, or ease swelling. And diet and lifestyle changes — like not smoking — can help, too.
Treatment Of Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema is a serious condition that requires quick treatment. Oxygen is always the first line of treatment for this condition. Your healthcare team may prop you up and deliver 100 percent oxygen through an oxygen mask, nasal cannula, or positive pressure mask.
Your doctor will also diagnose the cause of pulmonary edema and prescribe the appropriate treatment for the underlying cause.
Depending on your condition and the cause of your pulmonary edema, your doctor may also give:
- Preload reducers. These help decrease pressures from the fluid going into your heart and lungs. Diuretics also help reduce this pressure by making you urinate, which eliminates fluid.
- Afterload reducers. These medications dilate your blood vessels and take pressure off your heart.
- Heart medications. These will control your pulse, reduce high blood pressure, and relieve pressure in arteries and veins.
- Morphine. This narcotic is used to relieve anxiety and shortness of breath. But fewer doctors today use morphine due to the risks.
In severe cases, people with pulmonary edema may need intensive or critical care.
In other cases of pulmonary edema, you may need treatment to help you breathe. A machine will deliver oxygen under pressure to help get more air into your lungs. Sometimes this can be done with a mask or cannula, also called Continuous Positive Airway Pressure .
Your doctor may need to insert an endotracheal tube, or breathing tube, down your throat and use mechanical ventilation.
Recommended Reading: Which Of The Following Is Not A Symptom Of A Heart Attack
Cardiac Disorders Manifesting As Cpe
Atrial outflow obstruction
This can be due to mitral stenosis or, in rare cases, atrial myxoma, thrombosis of a prosthetic valve, or a congenital membrane in the left atrium . Mitral stenosis is usually a result of rheumatic fever, after which it may gradually cause pulmonary edema. Other causes of CPE often accompany mitral stenosis in acute CPE an example is decreased LV filling because of tachycardia in arrhythmia or fever.
LV systolic dysfunction
Systolic dysfunction, a common cause of CPE, is defined as decreased myocardial contractility that reduces cardiac output. The fall in cardiac output stimulates sympathetic activity and blood volume expansion by activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which causes deterioration by decreasing LV filling time and increasing capillary hydrostatic pressure.
Chronic LV failure is usually the result of congestive heart failure or cardiomyopathy. Causes of acute exacerbations include the following:
-
Acute myocardial infarction or ischemia
-
Patient noncompliance with dietary restrictions
-
Patient noncompliance with medications
-
Severe anemia
-
Myocardial toxins
-
Chronic valvular disease, aortic stenosis, aortic regurgitation, and mitral regurgitation
LV diastolic dysfunction
Ischemia and infarction may cause LV diastolic dysfunction in addition to systolic dysfunction. With a similar mechanism, myocardial contusion induces systolic or diastolic dysfunction.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- Whats the cause of my cardiac edema?
- Can you treat whats causing my cardiac edema?
- What changes do I need to make to how I live?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
When your healthcare provider diagnoses and treats your cardiogenic pulmonary edema early, its better than if you wait to get care. This is why its good to keep going to your regular checkups with your provider. They can keep an eye on any cardiac issues you have that may lead to cardiac edema. Taking the medicines they give you can prevent heart problems you have from getting worse.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can A Heart Attack Last
Pulmonary Edema Or Pneumonia
Pulmonary edema can overlap with pneumonia, but it is a different condition. Pneumonia is an infection that often occurs as a complication of a respiratory infection, such as the flu.
It can be difficult to distinguish between the two. If the individual or a family member can provide a detailed medical history, this will make it easier for a physician to make the correct diagnosis and provide the right treatment.
The patient will undergo a physical exam first. The doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to the lungs for crackles and rapid breathing, and the heart for abnormal rhythms.
Blood tests will be carried out to determine blood oxygen levels the doctor will often order other blood tests, including:
- electrolyte levels
- liver function
- blood counts and blood markers of heart failure
An ultrasound of the heart, an echocardiogram, and an electrocardiogram can help determine the condition of the heart.
A chest X-ray may be used to see whether there is any fluid in or around the lungs and to check the size of the heart. A CT scan of the chest may also be ordered.
