What Can I Expect If I Have A Silent Heart Attack
Everyones experience is a bit different based on how much their heart attack hurt their heart, but most people can get back to doing regular things little by little and have active lives.
Some people can get abnormal heart rhythms or heart failure, which can be serious. People who wait too long to get help for a heart attack run the risk of severe damage to their hearts and may not survive if they dont get help soon enough.
Treatment For A Heart Attack
The goal of treatment for a heart attack is to relieve pain, preserve the heart muscle function, and prevent death.
Treatment in the emergency department may include:
- Intravenous therapy, such as nitroglycerin and morphine
- Continuous monitoring of the heart and vital signs
- Oxygen therapy to improve oxygenation to the damaged heart muscle
- Pain medicine to decrease pain. This, in turn, decreases the workload of the heart. The oxygen demand of the heart decreases.
- Cardiac medicine such as beta-blockers to promote blood flow to the heart, improve the blood supply, prevent arrhythmias, and decrease heart rate and blood pressure
- Fibrinolytic therapy. This is the intravenous infusion of a medicine that dissolves the blood clot, restoring blood flow.
- Antithrombin or antiplatelet therapy with aspirin or clopidogrel. This is used to prevent further blood clotting.
- Antihyperlipidemics. These medicines lower lipids in the blood, particularly low density lipid cholesterol. Statins are a group of antihyperlipidemic medicines. They include simvastatin, atorvastatin, and pravastatin. Bile acid sequestrantscolesevelam, cholestyramine, and colestipoland nicotinic acid are two other types of medicines that may be used to lower cholesterol levels.
You may need other procedures to restore blood flow to the heart. Those procedures are described below.
Can Women Reduce Their Risk Of Having A Heart Attack
As a woman, your hormones might give you some protection from CHD in your pre-menopause years. Post menopause, your risk rises and continues to rise as you get older. As you get older it is increasingly important to be aware of the risk factors that can affect your risk of developing CHD. The more risk factors you have, the higher your risk. Risk factors include:
- being overweight
- not doing enough physical activity.
Identifying and managing risk factors early on could help lower your risk of a heart attack in the future.
- Get tips and advice on healthy living.
We recommend that all women over the age of 40 visit their local GP or nurse for a health check to check their cardiovascular risk. If you’re aged 4074 and living in England, you can ask for an NHS health check. Similar schemes are also available in other parts of the UK.Your doctor should invite you to review your risk every five years, but you can also just make an appointment yourself to check your blood pressure and cholesterol. This check might help to highlight anything that could put you at increased risk of having a heart attack.
If you have a family history of heart or circulatory disease make sure you tell your doctor or nurse. You’re considered to have a family history of heart or circulatory disease if:
Don’t Miss: What Should My Target Heart Rate Be
Why Sudden Cardiac Arrests No Longer Peak In The Morning
New research, published in the journal Heart Rhythm, discovers that due to recent cultural shifts in our work schedules and daily stressors, sudden cardiac arrests no longer tend to occur in the mornings.
Until now, the consensus has been that a range of cardiovascular events, such as angina, heart attacks, and stroke, tend to happen mostly in the early hours of the morning.
A possible explanation for this phenomenon is that in the morning, the sudden pressures of daily activities put a strain on peoples cardiovascular system.
Just waking up, in fact, releases the activity of certain hormones, such as cortisol, that raise blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels, as well as narrow blood vessels and prompt our hearts to pump harder.
However, given the new pressures of modern life such as instant communication, the prevalence of smartphones, apps, and the online medium in general the timing of our daily stressors may have changed.
So, do these changes have a bearing on certain cardiovascular events and the time of day in which they occur? New research suggests so.
Scientists from the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, CA led by Dr. Sumeet Chugh, a professor of medicine set out to investigate when the peak times for sudden cardiac arrests during the day are.
A heart attack, on the other hand, occurs when blood flow to the heart is partially blocked, which does not usually cause the heart to stop beating.
Clinical Characteristics Of Ca In The Toilet
The demographics and resuscitation profiles of the 101 patients who sustained CA while in the toilet are summarized in Table . Their age ranged from 26 to 96 years . Witnesses to the collapse were present in 10 % of events, and ROSC was achieved in 41 % of patients. One patient achieved a long-term survival of > 12 months.
Also Check: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
Recommended Reading: How Long After Shoveling Snow Can You Have A Heart Attack
What Do I Do During A Heart Attack
If you or someone else is having a heart attack:
- You or someone else should call 911 immediately if you suspect a heart attack.
- Every minute matters, and emergency professionals can transport heart attack victims to the hospital much faster than if theyre taken by others. Emergency professionals can also initiate interventions and notifications that lead to quicker treatment at the hospital.
- Emergency professionals are also trained in what to do if a persons heart stops beating and will have equipment and other resources on board the ambulance to intervene on the trip to the hospital.
Be Aware Of Your Heart While Shovelling Heavy Snow
Tuesday, November 16th 2021, 1:09 pm Heart attacks have been known to occur while shovelling heavy amounts of snow here are signs to watch for and how to do it as safely as possible.
Shovelling the white stuff can not only hurt your back, but it can also be hard on your heart.
Heart attacks during shovelling usually occur when people rush to clear a heavy amount of snow.
Health officials say blood vessels are tighter in the cold weather, making it harder for blood to pass through them. Combine that with the stress of physical activity, and it can mean disaster for some unsuspecting shovellers.
Read Also: How Does A Heart Attack Occur
Preventing Heart Attacks By Understanding Cardiovascular Risks
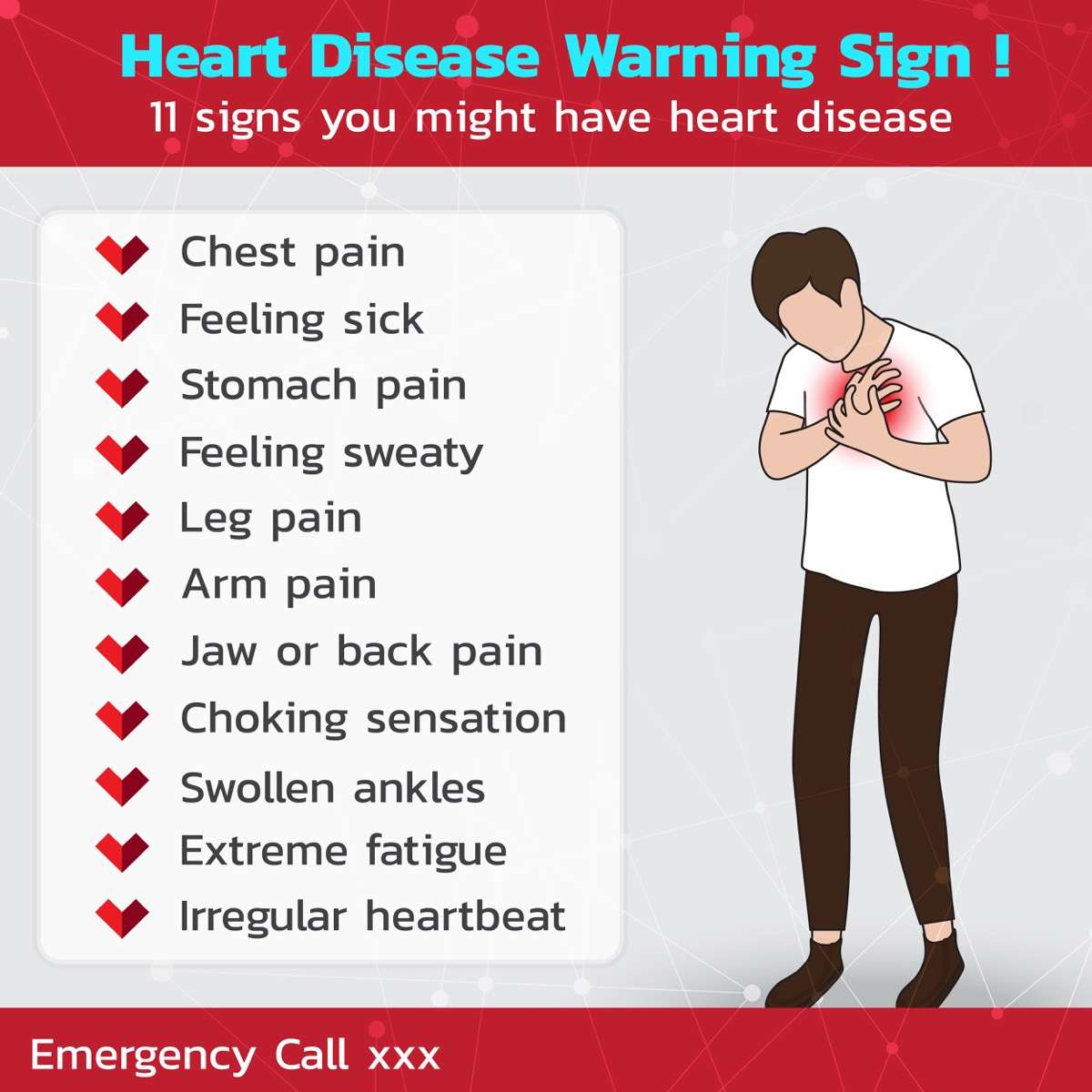
Do you know that heart attacks have beginnings that can occur days or weeks before an actual attack? It is important to recognize these beginnings, with the help of an EHAC doctor, to help prevent the actual attack and its potential health consequences. People often mistake the early warning signs of a heart attack, such as chest pain, for heartburn or pulled a muscle. The unfortunate outcome is that many people wait too long before getting help.
At The Hospitals of Providence, we have an EHAC program delivered by a team of cardiologists, nurses and staff who are dedicated to helping men and women recognize the early warning signs of a heart attack. We provide care and treatment options for these signs and help prevent the emergency from happening.
Who Is Most At Risk For A Heart Attack
Several key factors affect your risk of having a heart attack. Unfortunately, some of these risk factors aren’t things you can control.
- Age and sex.
- If you have certain health conditions or diseases.
Age and sex
Your risk of heart attack increases as you get older, and your sex also influences when your risk of a heart attack starts to increase:
- Men: The risk of heart attack increases greatly at age 45.
- Women: The risk of heart attack increases greatly at age 50 or after menopause.
Family history
If you have a parent or sibling with a history of heart disease or heart attack especially at a younger age your risk is even greater. That risk increases with the following:
- Your father or a brother who was diagnosed with heart disease at age 55 or younger.
- Your mother or a sister who was diagnosed with heart disease at age 65 or younger.
Lifestyle
The lifestyle choices you make can also affect your risk of having a heart attack. The following lifestyle factors increase your risk of heart attack:
- Lack of physical activity.
- Eating disorders .
Also Check: Increased Resting Heart Rate
How Heart Attack Symptoms May Differ For People With Diabetes
Research has shown that people with diabetes are more likely to have silent heart attacks compared to people who dont have diabetes. In other words, if you have diabetes, you may not experience the typical symptoms associated with a heart attack, especially chest pain.
Many studies have been done to better understand why people with diabetes are less likely to experience chest pain and other heart attack symptoms. One explanation is that the development of neuropathy a type of nerve damage thats a common complication of diabetes may interfere with the ability to feel chest pain caused by a heart attack.
According to research , approximately 55 percent of people with diabetes have coronary artery disease. Having impaired blood flow in the coronary arteries is a major risk factor for a heart attack.
Because of this risk, its important that people with diabetes keep their blood sugar levels under control, get frequent blood tests to check cholesterol levels, and work closely with a doctor to ensure their diabetes is managed well.
From Indigestion To A Pulled Muscle Survivors Share Very Different Experiences
by Jennifer Wolff, AARP, December 12, 2019| 0
En español | More than 1 million Americans will suffer from a heart attack this year, and about 150,000 of them will die from it, according to the American Heart Association. Thing is, more than half of the people who have a heart attack dont recognize its symptoms. People have this idea of the Hollywood heart attack, which is a man squeezing his chest, the feeling of the balloon about to burst, says clinical cardiologist Malissa Wood, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. So when people dont have that classic symptom that theyve seen or heard about, they think, Well, this must be something else.’
Wood admits that the medical literature describing telltale symptoms can contradict itself, and says the combination of misinformation and downright denial complicates matters. Basically if you feel something in your back, chest, jaw or tooth that you havent felt before, get it checked out, she says. The way to know is if you experience something you havent felt before. For those whove had heart problems previously, the advice often still applies. The one uniform thing people say is the symptom that they had was very different from what they had felt previously. And its not always pain. Sometimes its just a little discomfort, or an ache.
Here, five heart attack survivors share their very different experiences and what they wish theyd realized sooner.
Also Check: What Is Diastolic Heart Failure
Cardiac Arrest Vs Heart Attack
Sometimes there is confusion between the terms cardiac arrest and heart attack. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, is damage to the heart muscle that occurs due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, depriving the heart muscle of the oxygen it needs to function properly.
Cardiac arrest means that the heart stops beating and death is imminent. A heart attack, if severe, can lead to cardiac arrest, and this is what occurs when a heart attack is fatal. However, other conditions, such as serious arrhythmias or shock, can also cause cardiac arrest.
Recovering After A Heart Attack
It is natural to feel worried, scared, frustrated or isolated as you begin your recovery at home. If you can, try to have someone with you at home for the first few days or weeks, depending on how you feel. Or, arrange to stay with friends or family for a few days.
When you first get home, try to take things easy and get plenty of rest. Avoid any activities that make you feel out of breath. Its ok to have a few visitors or take a walk round your house or garden, but avoid playing sports or doing housework such as hoovering.
About 10 days after a heart attack, most people will be ready to start doing some gentle physical activity. The key is to start slowly and gradually build up the amount you can do. How quickly you are able to do this will depend on the condition of your heart and on how active you were before your heart attack.
Just like the physical aspects of recovery, recovering from the emotional impact of a heart attack can take time. There may be lots of thoughts and questions going through your mind, and you may wonder what the future is going to be like.
It is normal to feel anxious and stressed, and you may also feel frustrated, vulnerable or scared. If you have previously been fit and healthy, you may find it particularly difficult to be dependent on other people. It is also common to feel afraid that it might happen again.
Try not to bottle up how you are feeling. Ask for help or advice if you need to.
Don’t Miss: Best Hospitals For Heart Surgery
Catch The Signs Early
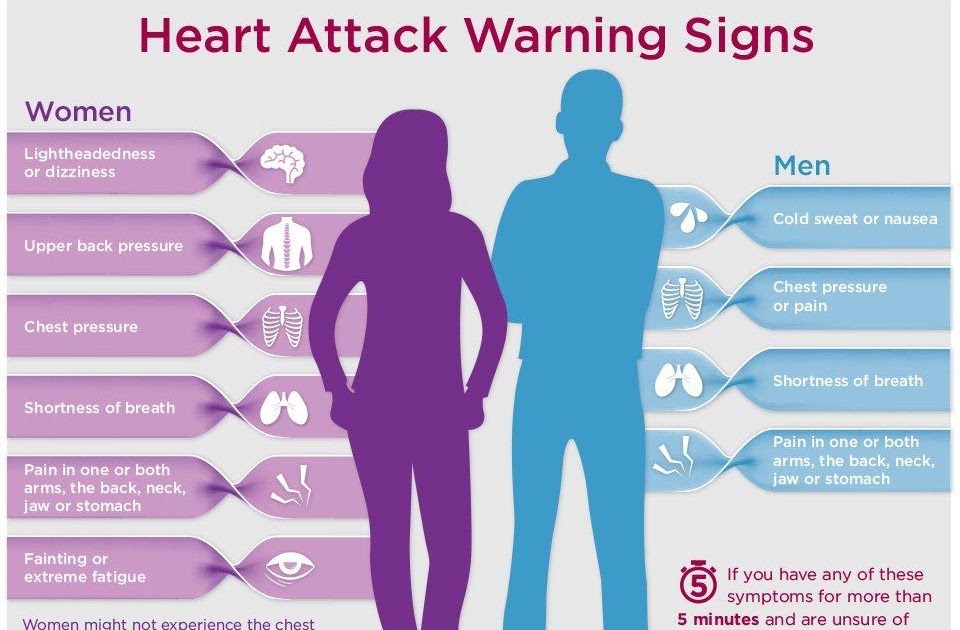
Dont wait to get help if you experience any of these heart attack warning signs. Some heart attacks are sudden and intense. But most start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort. Pay attention to your body and call 911 if you experience:
- Chest discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes or it may go away and then return. It can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain.
- Discomfort in other areas of the upper body. Symptoms can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
- Shortness of breath. This can occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Other signs. Other possible signs include breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea or lightheadedness.
Download the common heart attack warning signs infographic |
Heart Disease Among Men And Women
The prevalence and incidence of diagnosed ischemic heart disease and heart failure are consistently higher among men than women . The difference by sex is more pronounced for the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction. On average, men are about 2 times more likely than women to have a first acute myocardial infarction. In addition, the gap between men and women in the overall number of acute myocardial infarction occurrences is steadily increasing over time. There were close to 80,000 more occurrences among men than women in 2000/01, compared to just over 200,000 occurrences in 2012/13.
Figure 1: Age-standardized prevalence of ischemic heart disease and heart failure , and acute myocardial infarction occurrence , by sex, Canada,* from 2000/01 to 2012/13
Age-standardized to the 2011 Canadian population. *Data from Yukon were not available. Notes: The 95% confidence interval shows an estimated range of values which is likely to include the true value 19 times out of 20. : Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2016.
| 1.5 | 3.1 |
Figure 3: Age-standardized all-cause mortality rates among those with diagnosed ischemic heart disease and heart failure , and those who had an acute myocardial infarction , by sex, Canada,* from 2000/01 to 2012/13
| 26.3 |
Heart pain image via shutterstock
Recommended Reading: How To Get Your Heart Rate Up
What Happens After A Heart Attack
After a heart attack, it is likely you will stay in hospital for around 3-5 days so your condition can be stabilised and monitored.Some people develop other conditions linked to their heart attack, including:
- Increased blood sugar levels, which can be treated with insulin
- Arrythmias, a change to your hearts usual rhythm, which can be treated with a pacemaker if they are severe enough to be dangerous
- Chest pain or angina, which is caused by insufficient blood supply to your heart muscle
- Heart failure, when the damage to your heart muscle is so significant that it cannot pump enough blood to supply your body fully
- High blood pressure, which can be treated with medication and diet
For most people, after a couple of days, your heart will settle down. The immediate risk of another heart attack lessens, and intensive monitoring can be stopped. Your doctor will advise when it is safe for you to return home from hospital.
It is normal to feel tired, overwhelmed and anxious after a heart attack. You may find that you dont remember a lot of what the doctors and nurses told you, especially during the first few days. Dont be afraid to ask questions of staff. It can help to talk to your family about what has been happening too.Before you leave hospital, your doctor will talk to you about any medications you may need to take, as well as give you information about support services available in your local area, such as cardiac rehabilitation.
